Table of Contents
Definition / general | Microscopic (histologic) images | Adenocarcinoma | Breast adenocarcinoma | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Melanoma | Mesothelioma | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Papillary thyroid carcinoma | Paraganglia | Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Serous borderline tumor | Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma | Squamous cell carcinomaCite this page: DePond W. Metastases. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphnodesmetastases.html. Accessed December 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Lymph nodes are common site of metastatic disease
- Presence of metastases is important for TNM staging
- Must determine when examining lymph nodes: tumor present or not; tumor primary or metastatic; possible sites of primary; number of metastatic nodes; size of largest metastatic deposit often helpful; presence of extranodal or vascular involvement
- Nodal metastases are common with carcinoma, melanoma or germ cell tumors; rare with CNS tumors and sarcoma (except for angiosarcoma, clear cell sarcoma, epithelioid sarcoma, MFH, rhabdomyosarcoma or synovial sarcoma)
- Must also rule out lymphoma; compared to metastatic disease, lymphomas are more likely multifocal with diffuse penetration of vessel wall, minimal necrosis, no nesting, not limited to sinuses, not limited to intravascular invasion; differentiate based on special stains / immunostains (see below), touch preparations (clumping favors carcinoma), EM for epithelial features
- Rarely, there is passive transport of benign neoplastic cells to lymph nodes (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:1317)
- Carcinomas usually have cohesive tumor cells, sinus involvement, clearly defined margins with lymphoid tissue; may resemble Hodgkin lymphoma due to prominent nucleoli and mixed inflammatory infiltrate
- Tumors misinterpreted as lymphoma: nasopharyngeal carcinoma - undifferentiated (tumor cells mix with lymphocytes and tumor does not appear cohesive), melanoma (tumor cells separate from each other within clusters), breast lobular carcinoma (may appear noncohesive), seminoma (inguinal and abdominal nodes)
- Recommended stains (by Rosai) - first round: CD45 / LCA, pankeratin, S100; second round: (as necessary) CD3 (T cells), CD20 (B cell), EMA, CEA, vimentin, possibly GCDFP15 or lactalbumin (for breast), chromogranin (for neuroendocrine), PSA / PAP (for prostate)
- Note: TdT+ lymphoid precursors are present in benign pediatric lymph nodes (Am J Clin Pathol 2002;118:248) and tonsils (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:12), causing possible confusion in ALL patients
- Site of metastases:
- Upper cervical nodes: associated with upper aerodigestive tract
- Midcervical nodes: thyroid carcinoma, salivary gland, upper aerodigestive tract; also thymus or ovary
- Supraclavicular nodes: breast or lung, also stomach, pancreas, prostate, testis
- Axillary nodes: breast (women), melanoma, lung
- Inguinal nodes: external genitalia, melanoma
- Undetectable primaries with nodal metastases: nasopharynx, retrotonsillar pillars
- Posttreatment changes: foamy histiocytes, fibrosis, mucin, atypical residual tumor cells
Microscopic (histologic) images
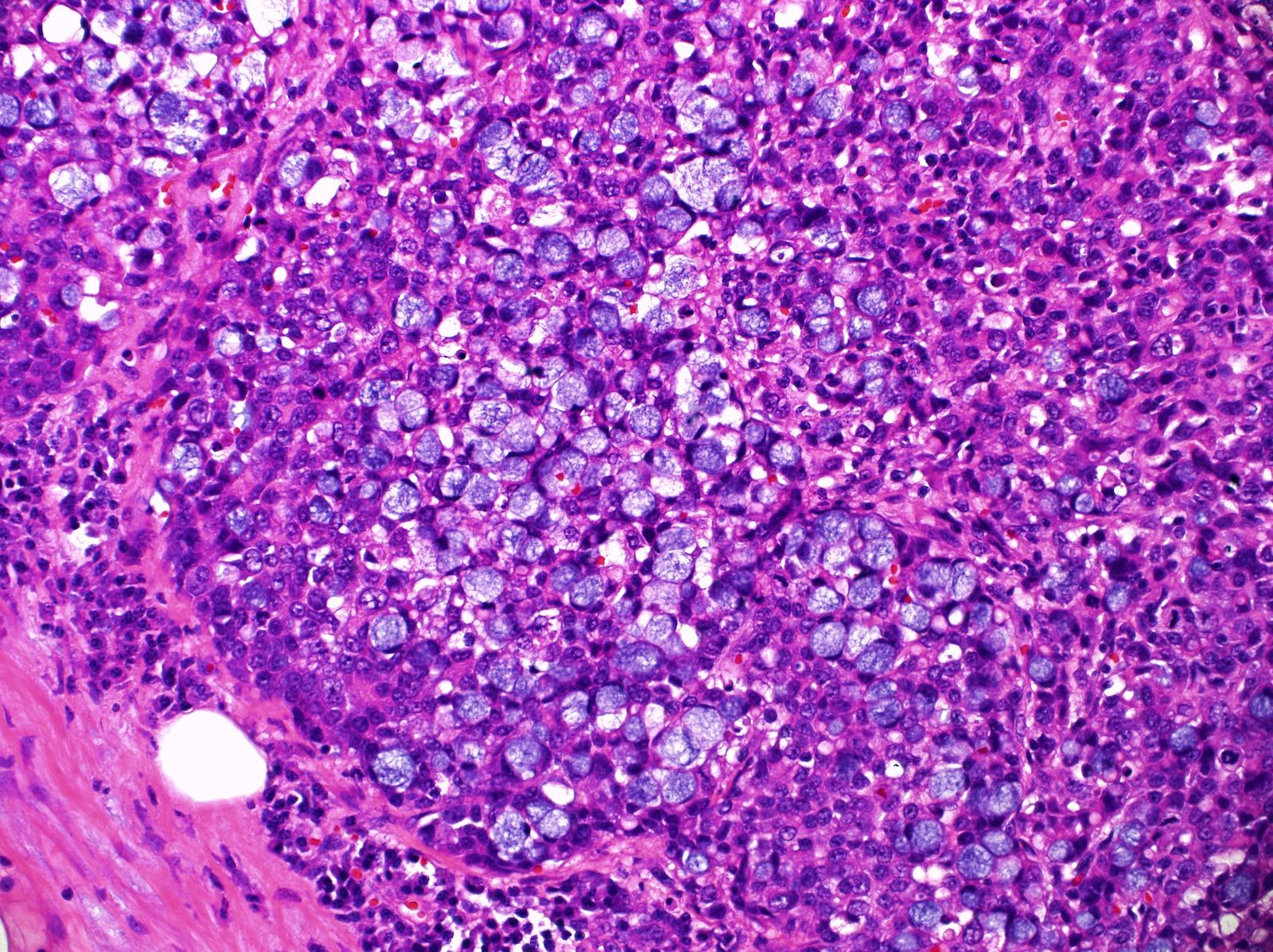
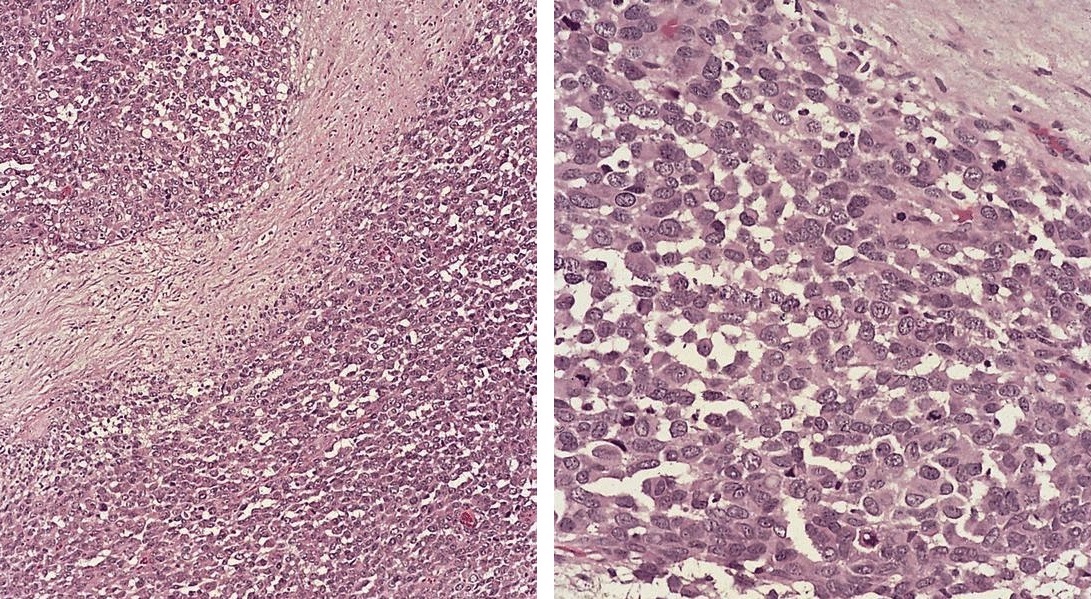
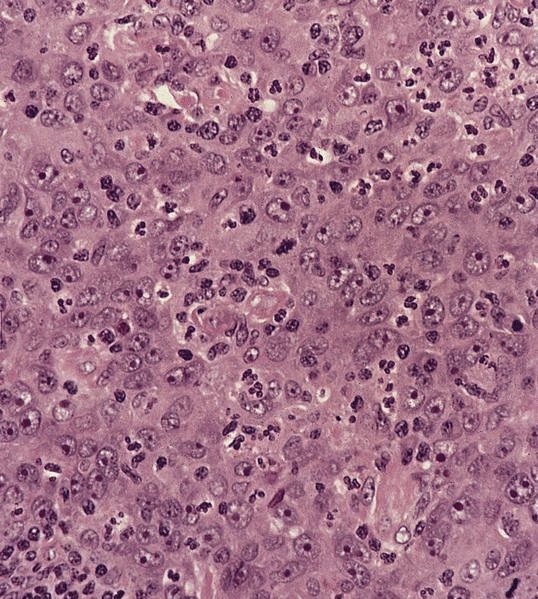
Adenocarcinoma
Definition / general
Gross images
Contributed by Dr. Mark R. Wick
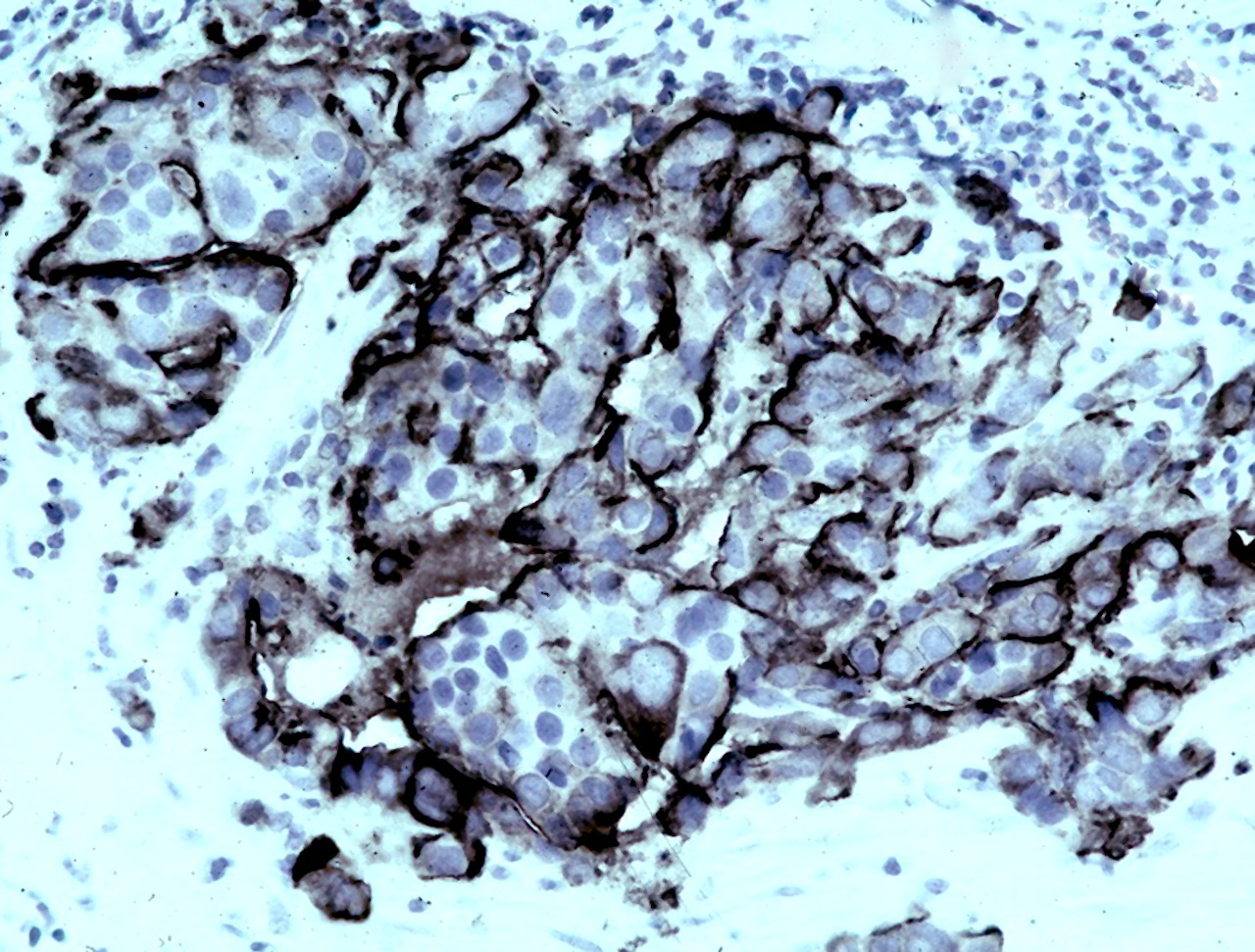
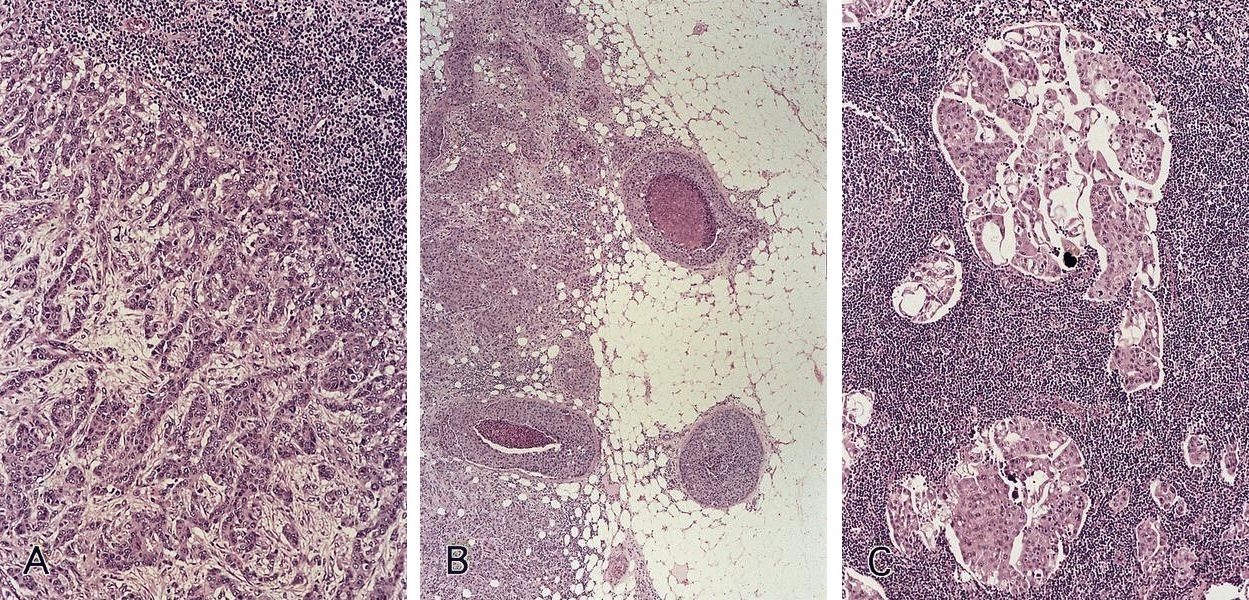
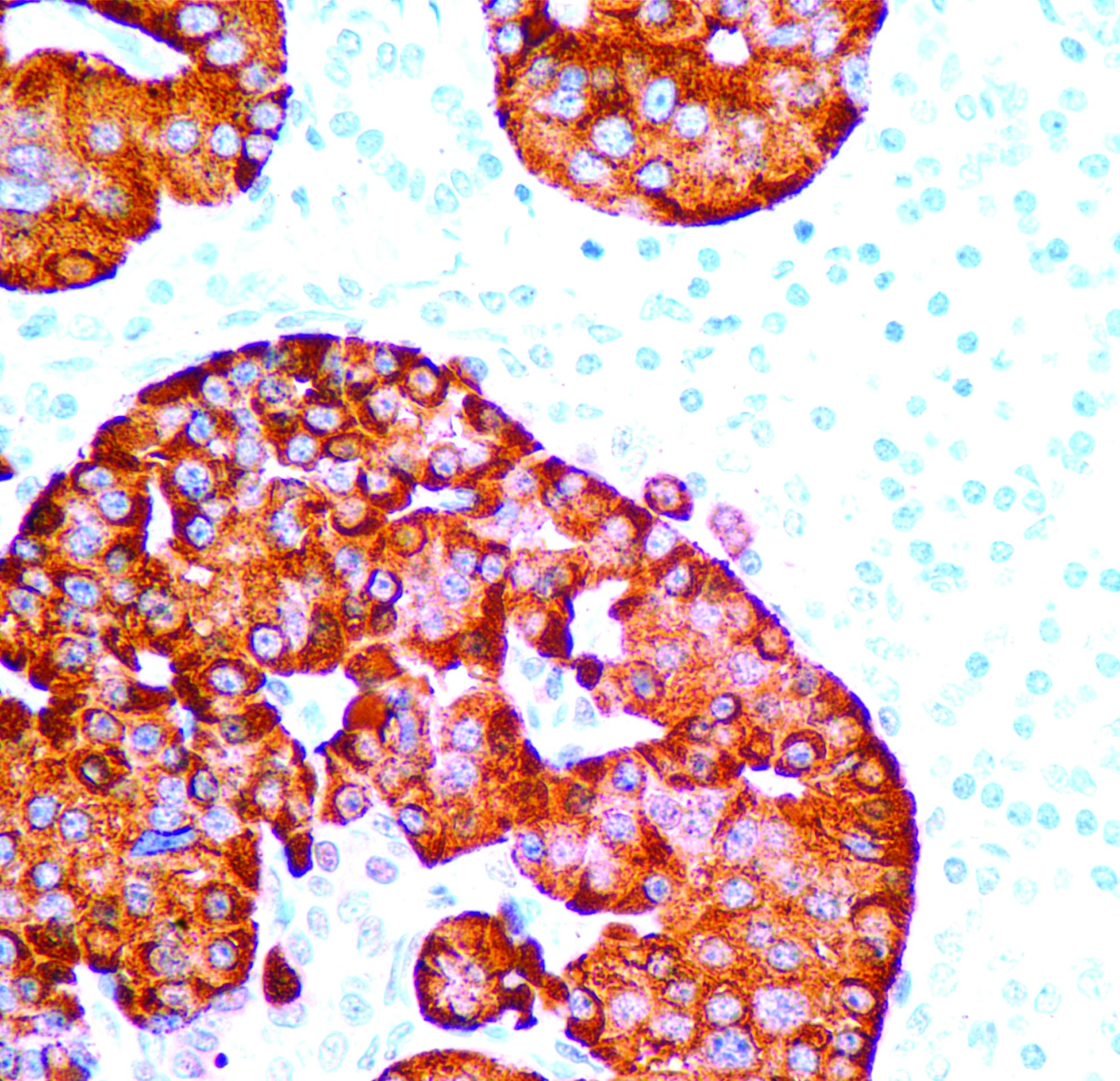
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Dr. Mark R. Wick, Marino Leon, M.D. and AFIP images
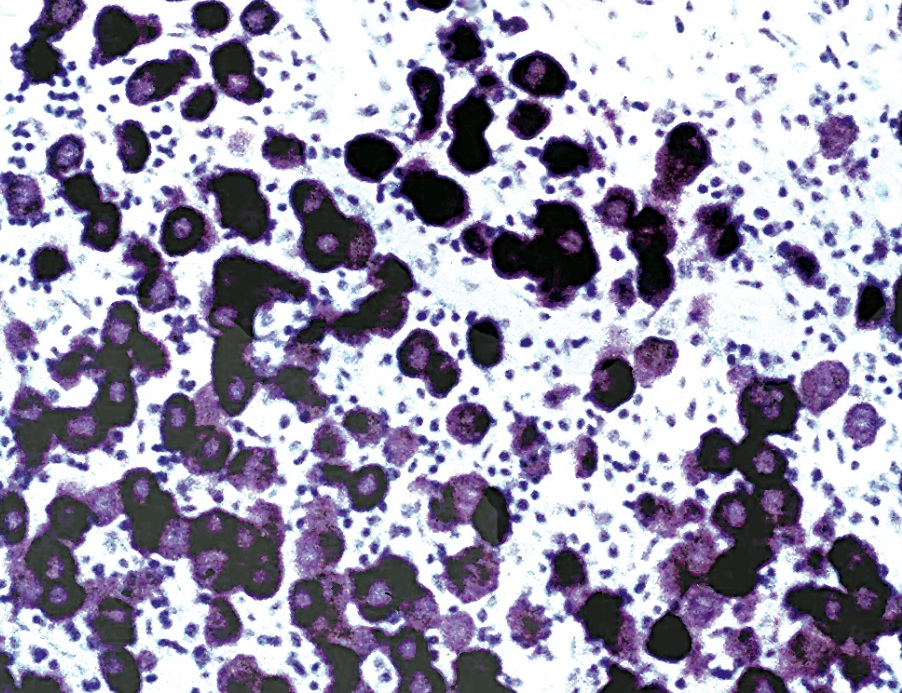
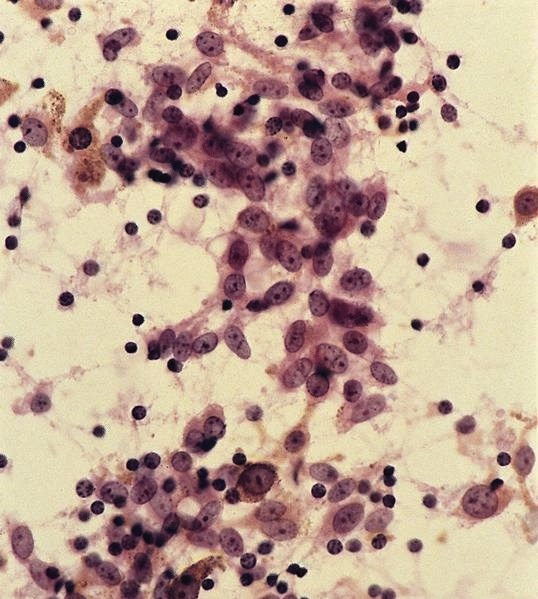
Cytology images
AFIP images
- Signet ring cells may actual be muciphages (Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:545)
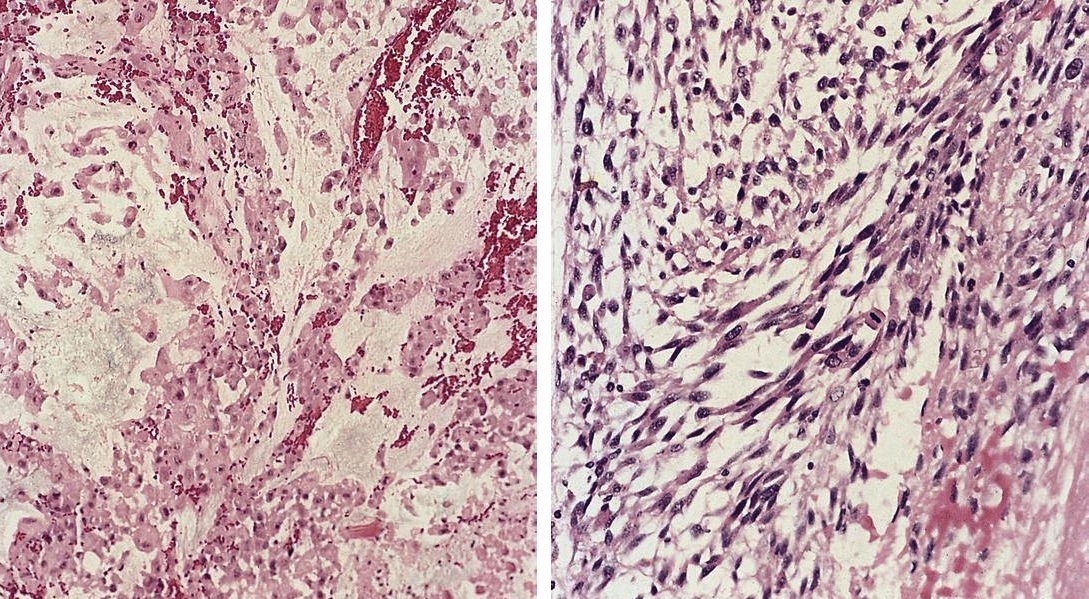
Gross images
Contributed by Dr. Mark R. Wick
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Dr. Mark R. Wick, Marino Leon, M.D. and AFIP images
Cytology images
AFIP images
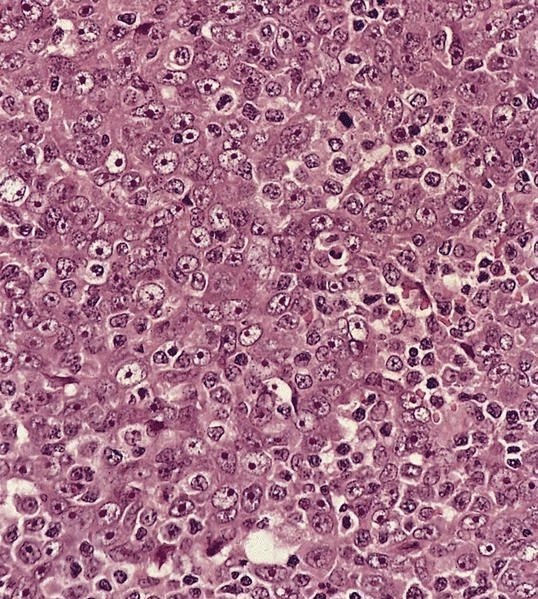
Breast adenocarcinoma
Definition / general
Microscopic (histologic) description
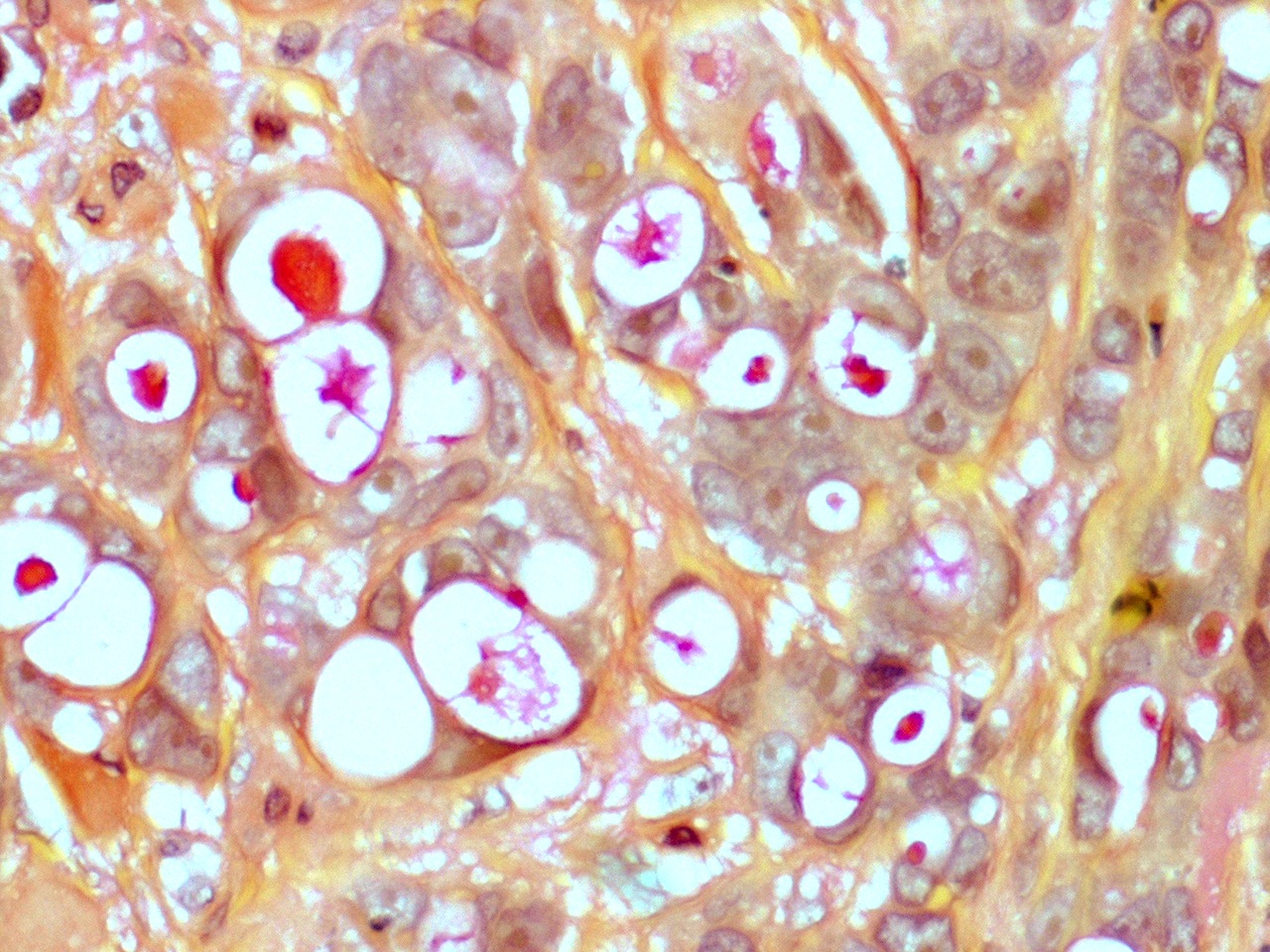
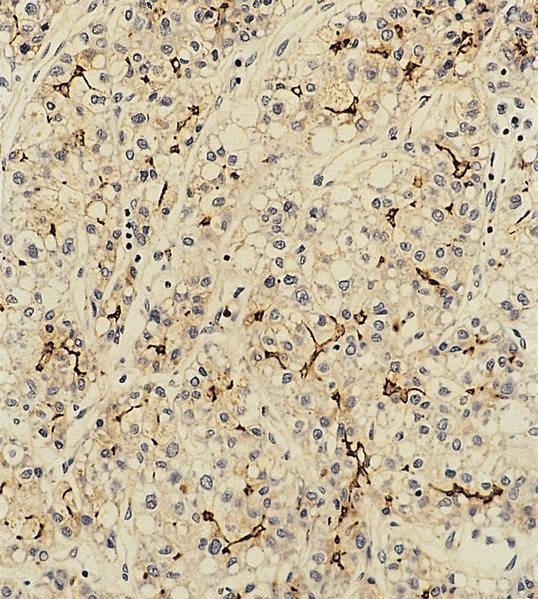
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Dr. Mark R. Wick, Case #4 and AFIP images
- Lobular carcinoma may resemble lymphoma, particularly if signet ring cells are present
Microscopic (histologic) description
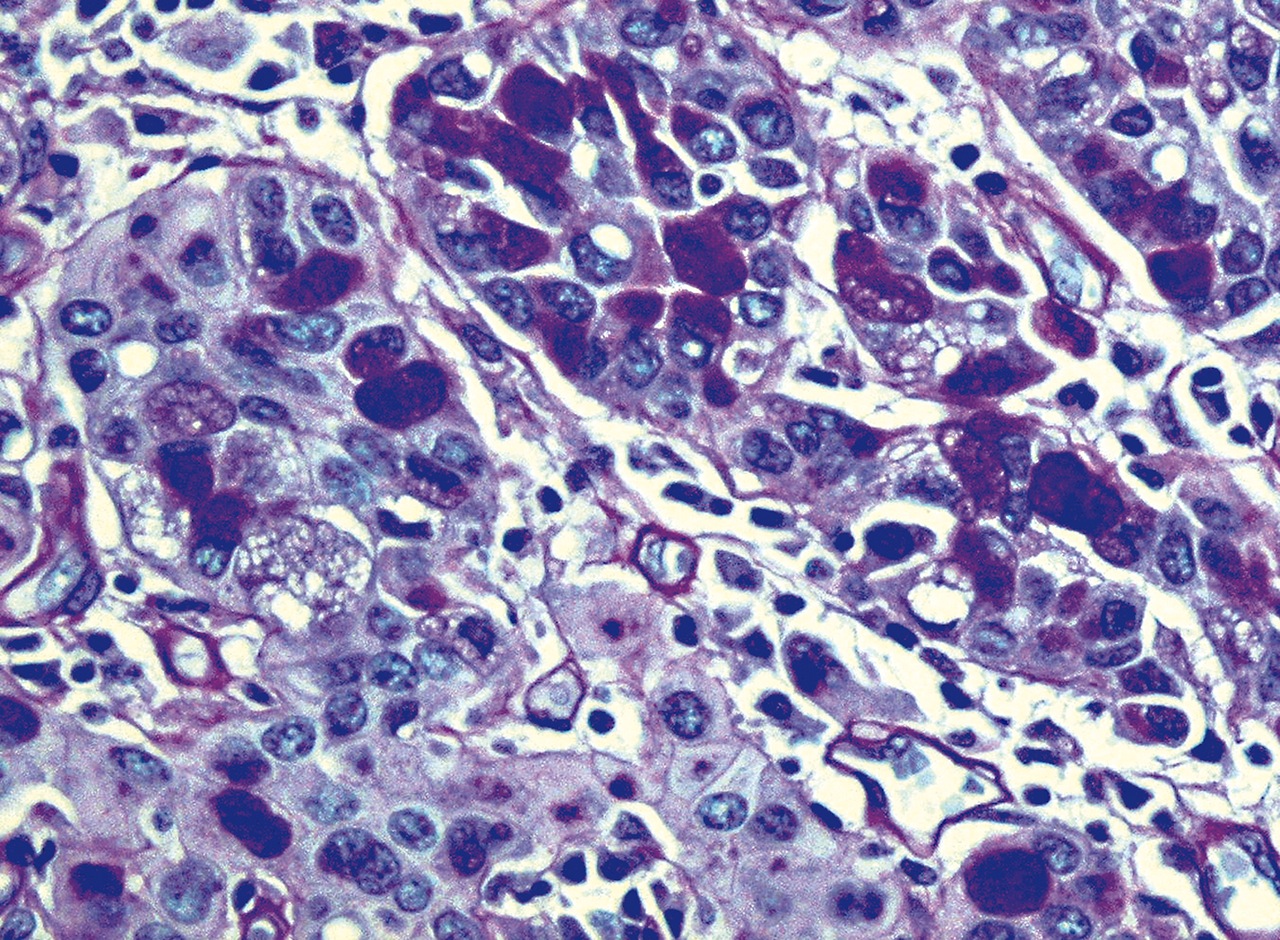
- Ductal: large apocrine-like pleomorphic cells with pink, granular cytoplasm, large nuclei and prominent nucleoli
- Often cytoplasmic mucin
- Comedo, trabecular and papillary patterns
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Dr. Mark R. Wick, Case #4 and AFIP images
Images hosted on other servers:
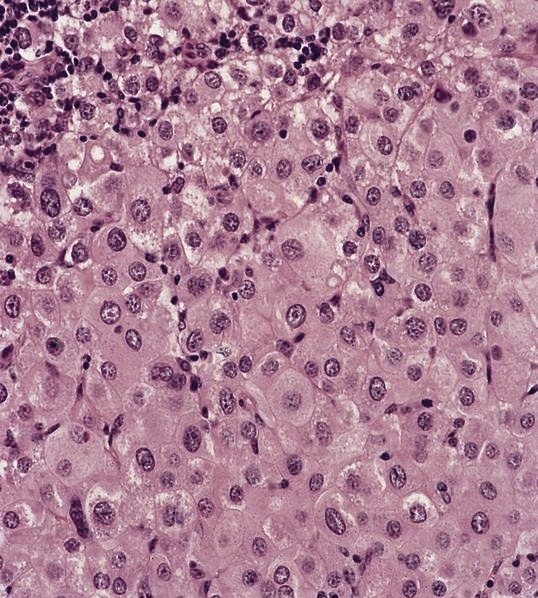
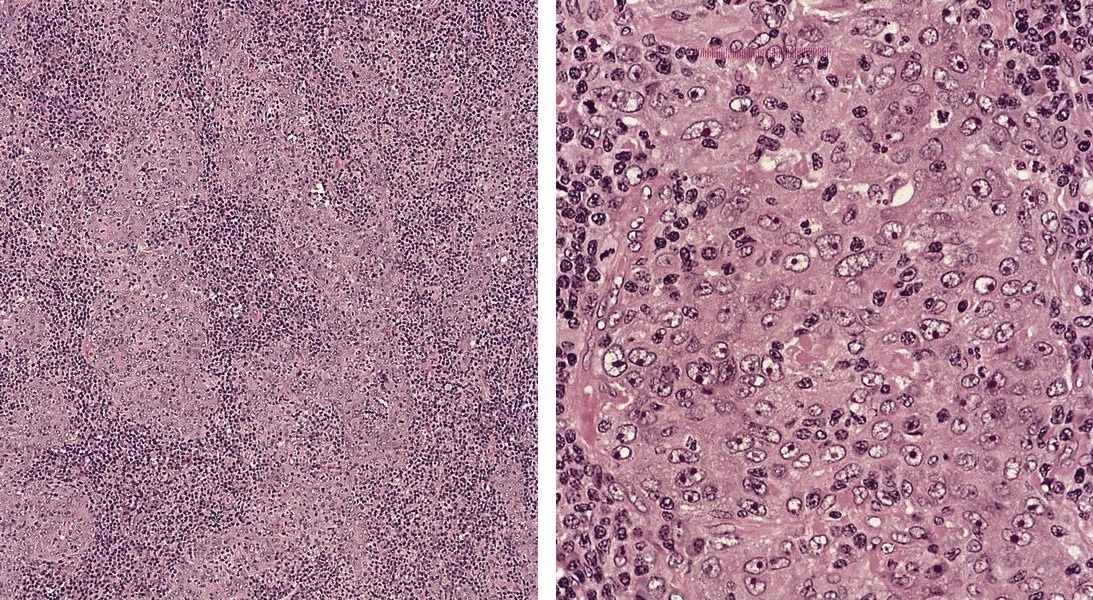
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Melanoma
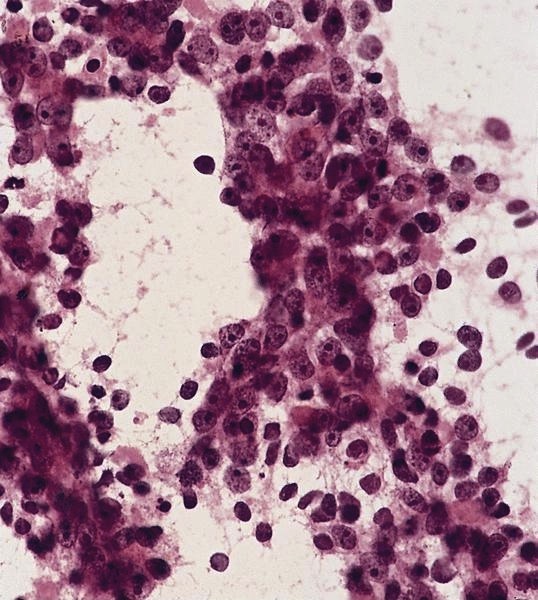
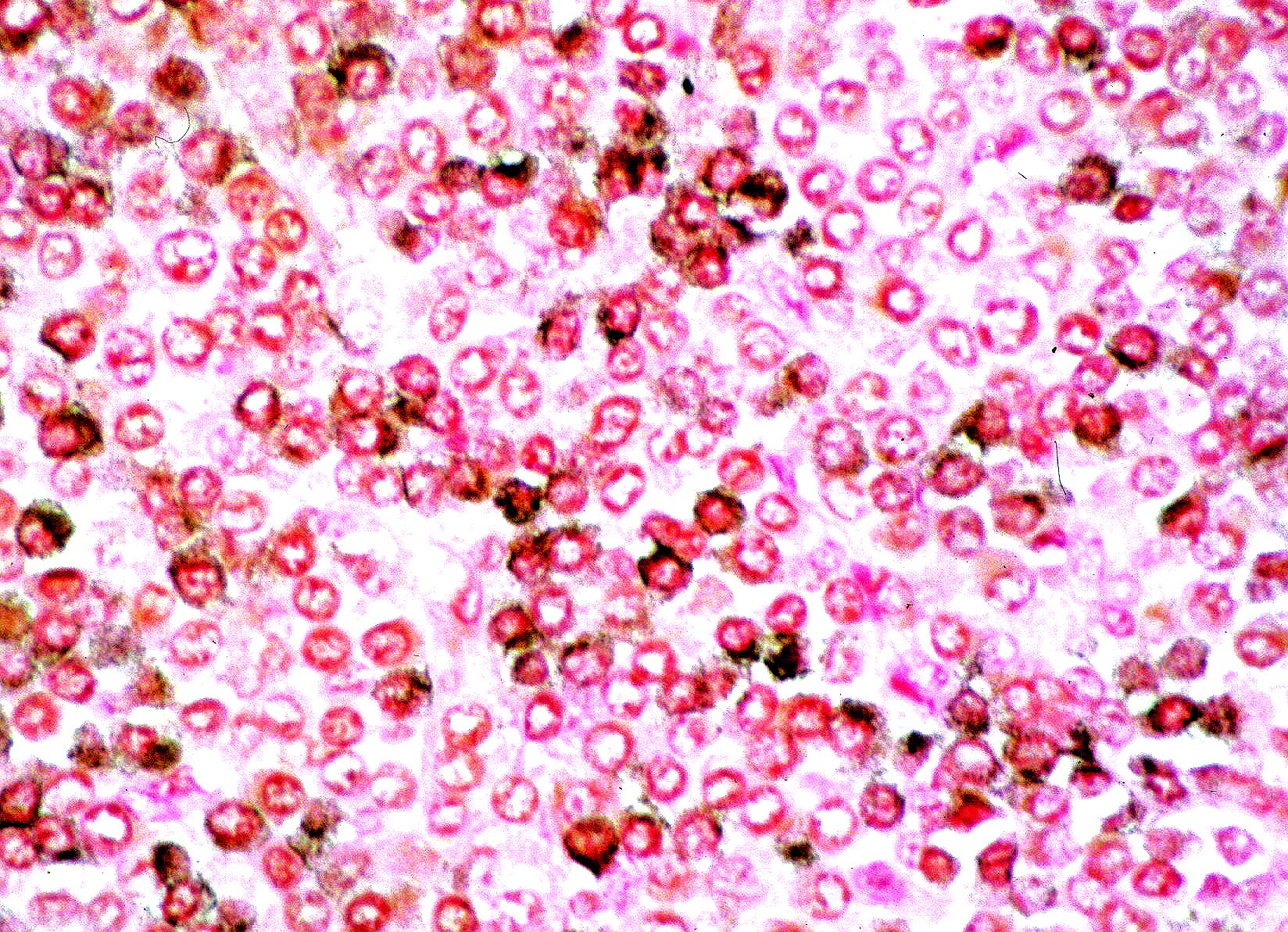
Mesothelioma
Definition / general
Microscopic (histologic) description
Cytology description
- Nodal involvement may be initial presentation (Am J Surg Pathol 1990;14:819)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- May expand sinuses
- Cuboidal cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and central nucleus
Cytology description
- Large dyscohesive cells with abundant pale cytoplasm, ruffled cytoplasmic borders, prominent central nucleoli (Am J Clin Pathol 1992;97:493)
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Papillary thyroid carcinoma
Paraganglia
Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor
Definition / general
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Uncommonly metastasizes to lymph nodes (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:662)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Multiple plexiform nodules within and external to node
- Nodules composed of plump fibrohistiocytic cells with multinucleated giant cells
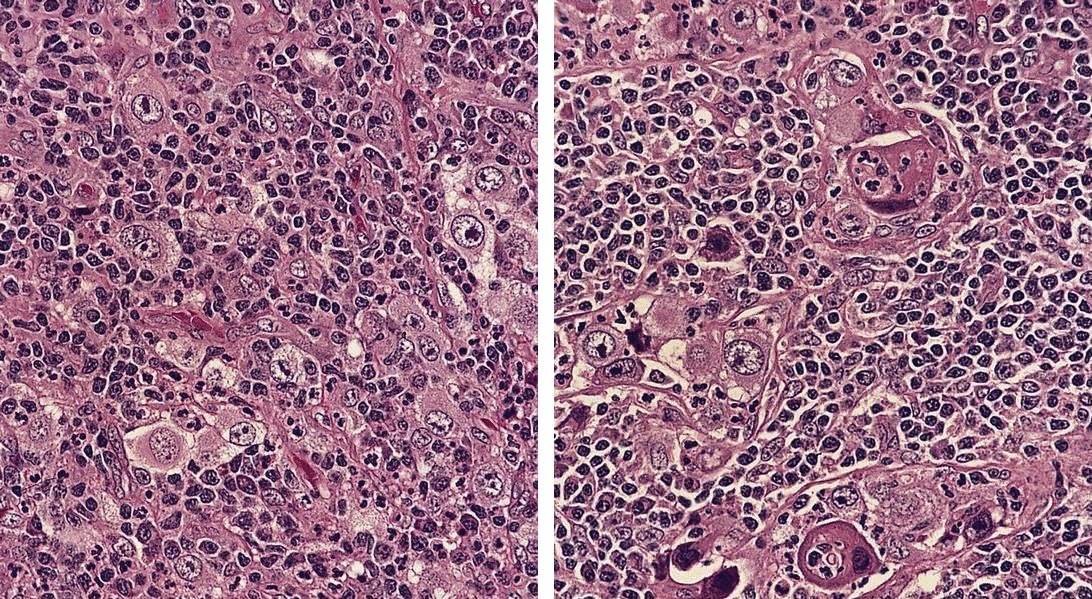
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Definition / general
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images
- Alveolar subtype may first present with nodal involvement
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Alveolar subtype: large packets of cells with central dehiscence, cells have moderate eosinophilic cytoplasm, with some rhabdomyoblasts present
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images
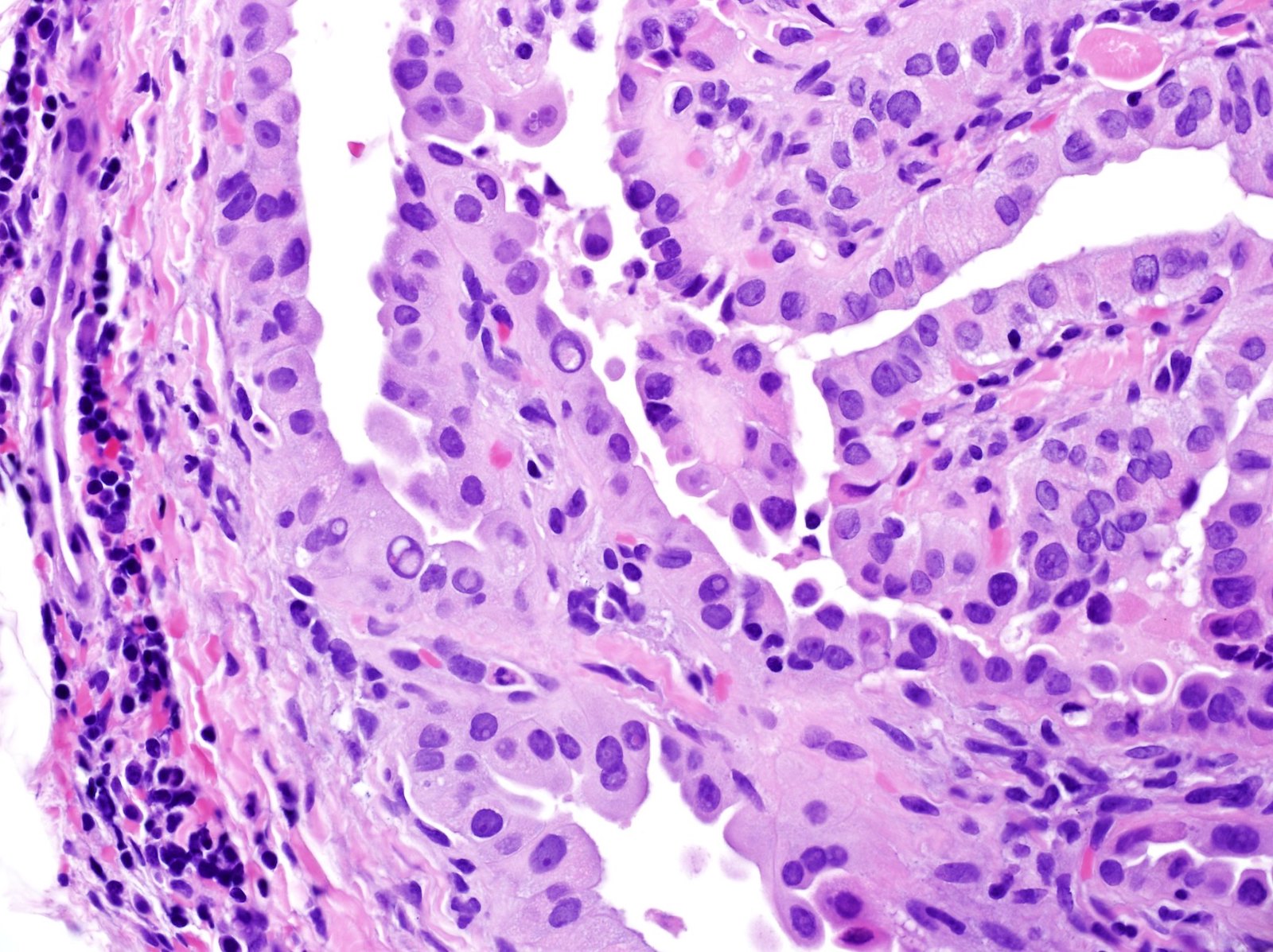
Serous borderline tumor
Case reports
- Nodal metastases may be metastatic ovarian serous borderline tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:739)
- 58 year old woman with high grade urothelial carcinoma of bladder and unknown ovary tumor 33 years prior (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:537)
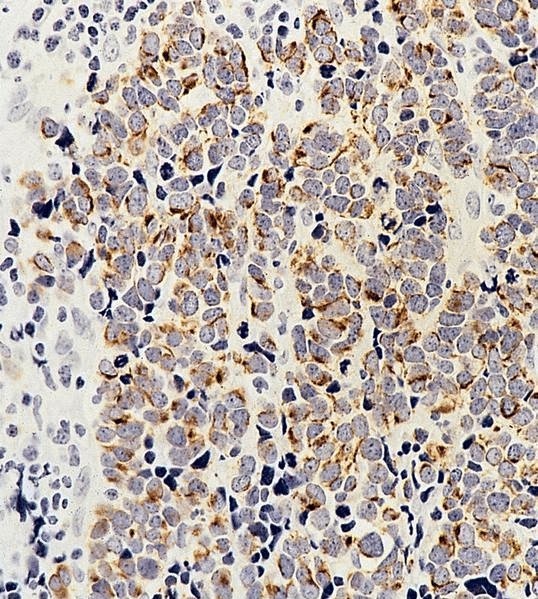
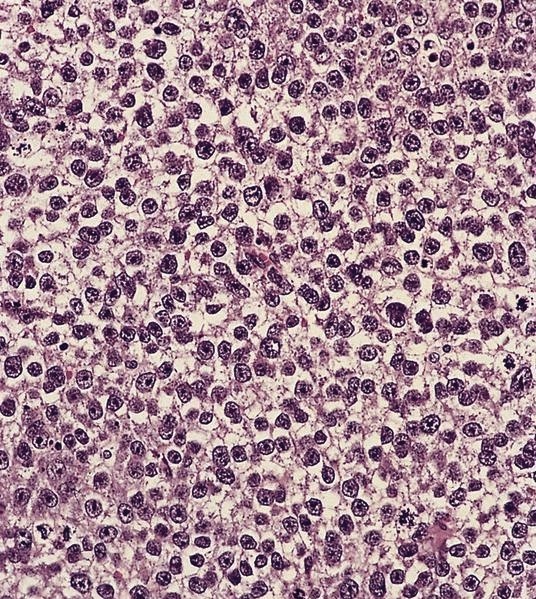
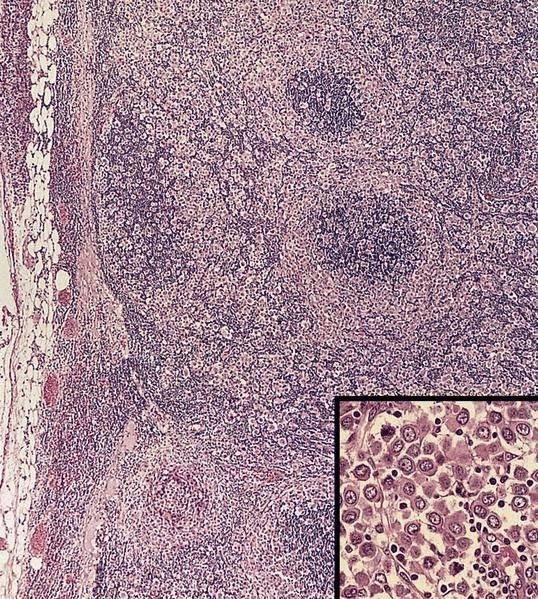
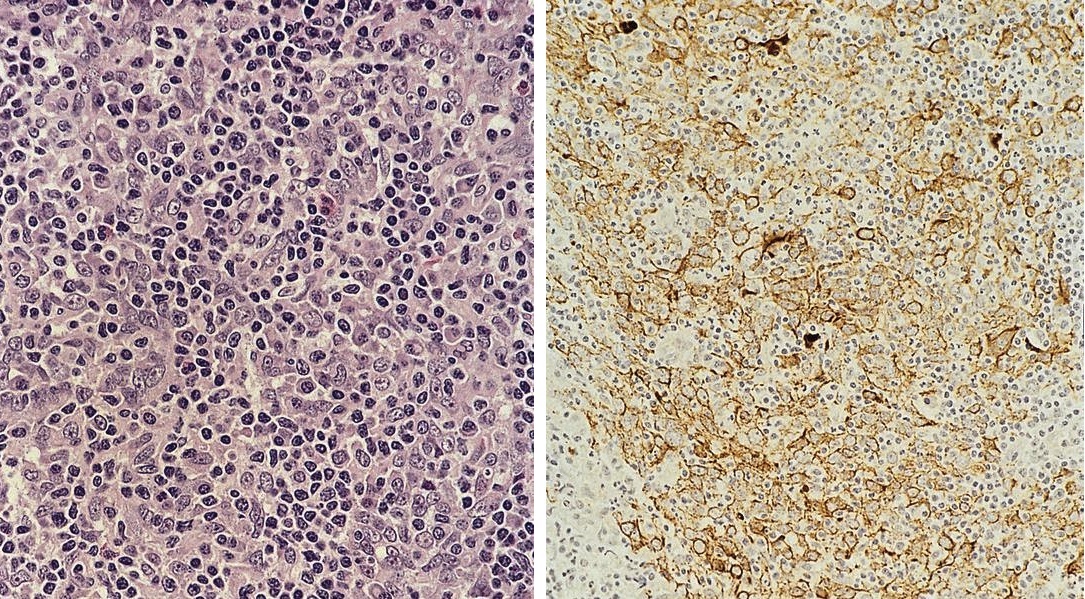
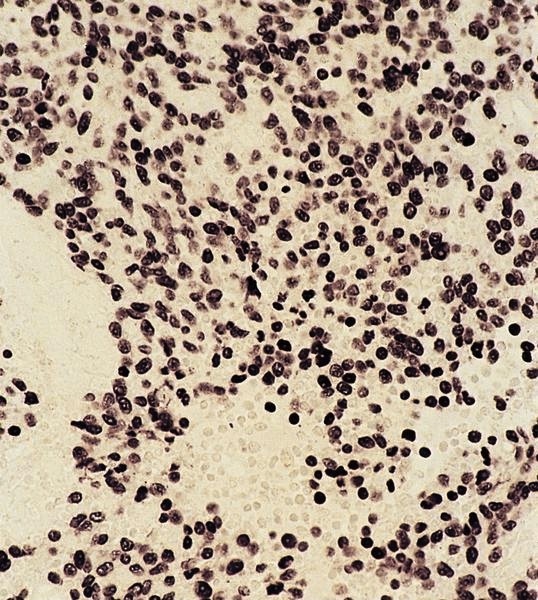
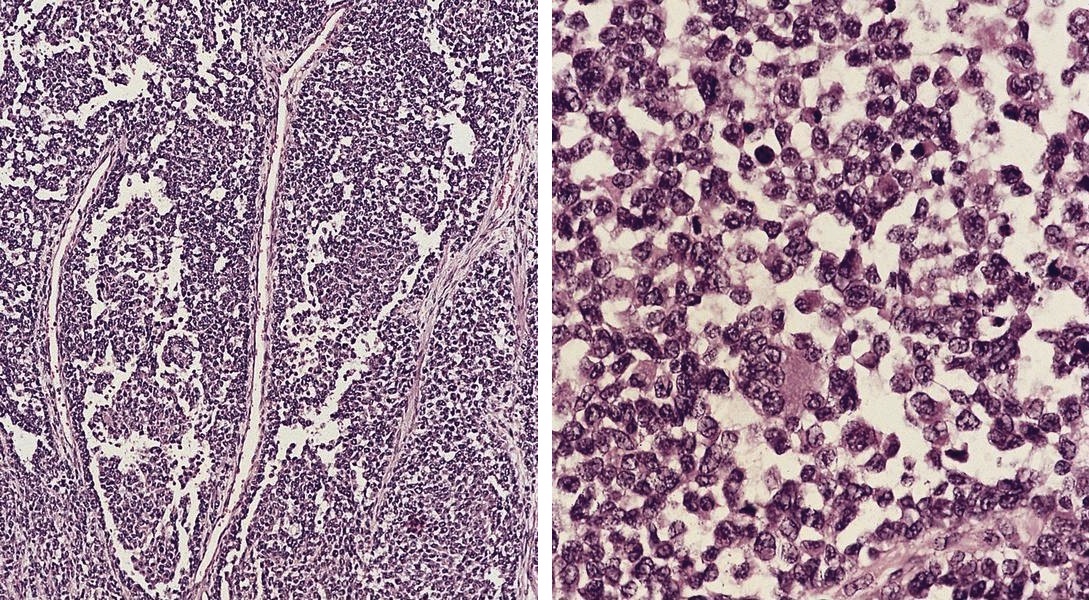
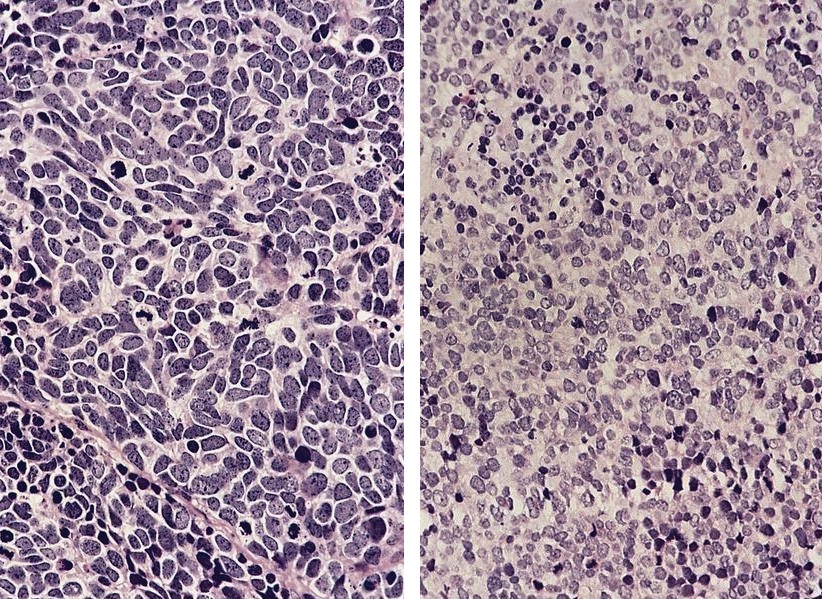
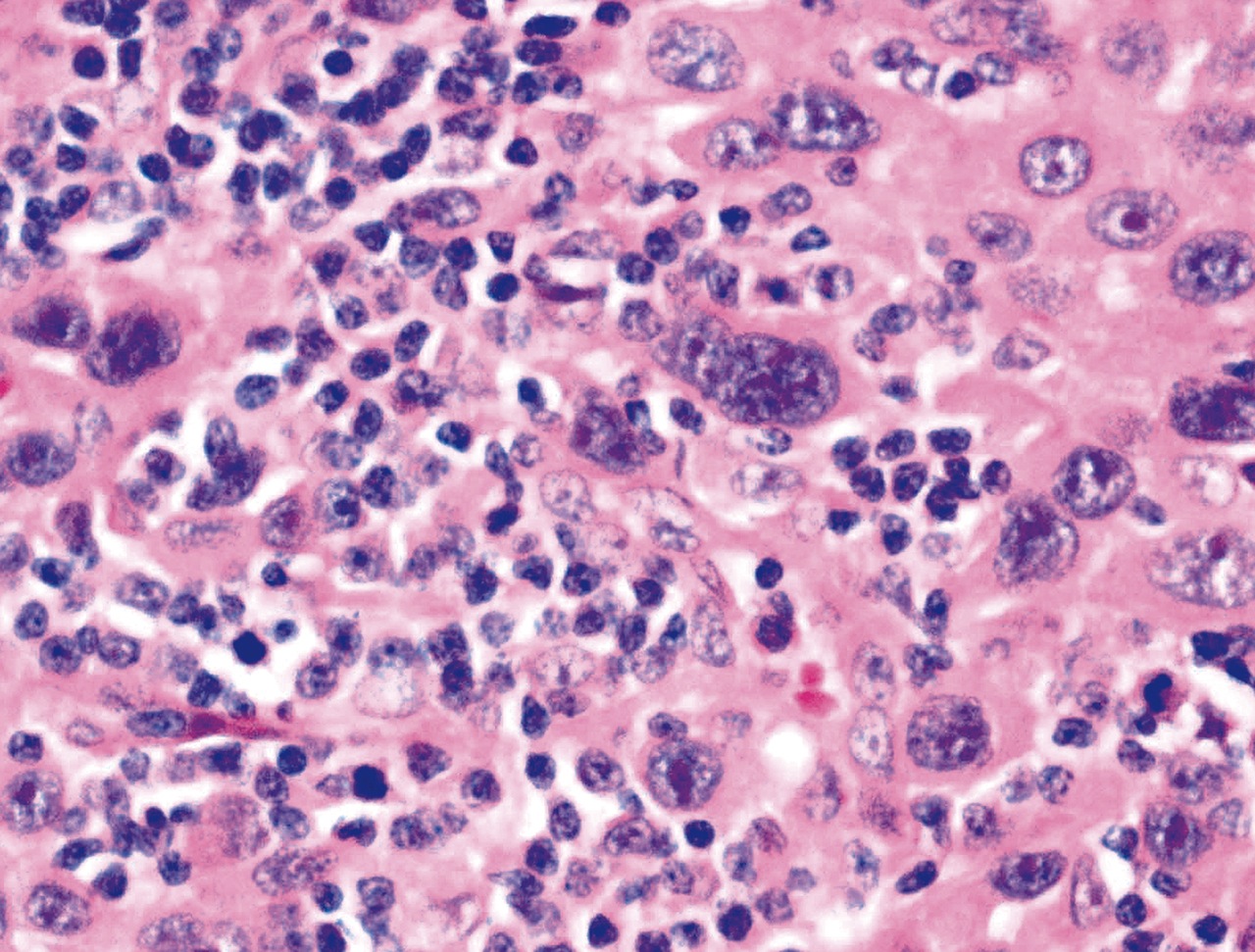
Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma
Definition / general
Microscopic (histologic) description
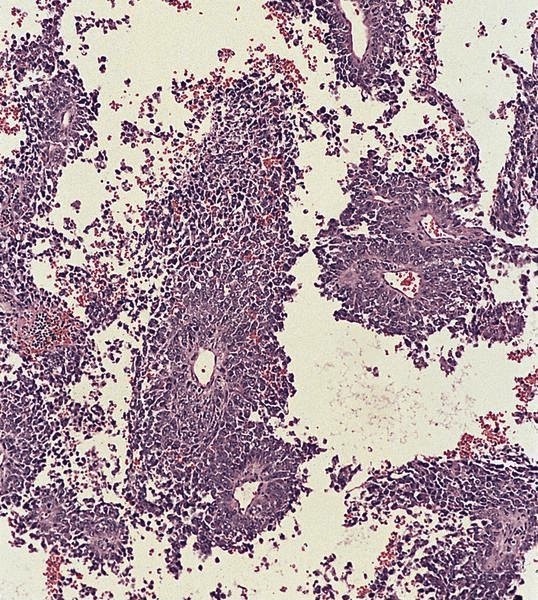
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Dr. Mark R. Wick and AFIP images
- May resemble lymphoma
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Minimal cytoplasm, dense chromatin with nuclear molding
- Often focal necrosis and crush artifact
- Azzopardi phenomena (dense hematoxylin staining of vessel walls)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Dr. Mark R. Wick and AFIP images
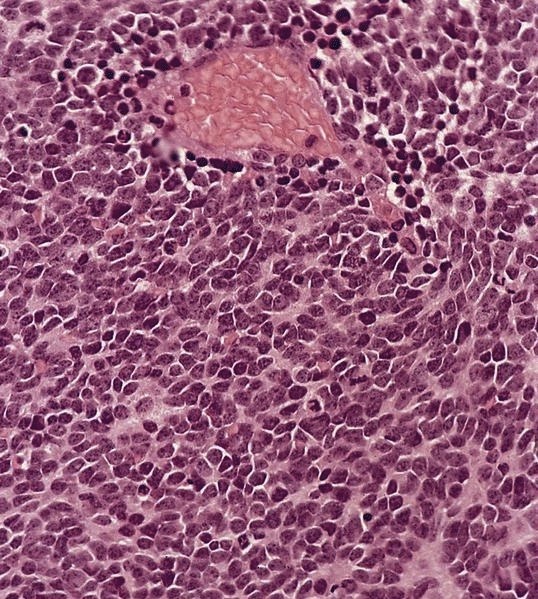
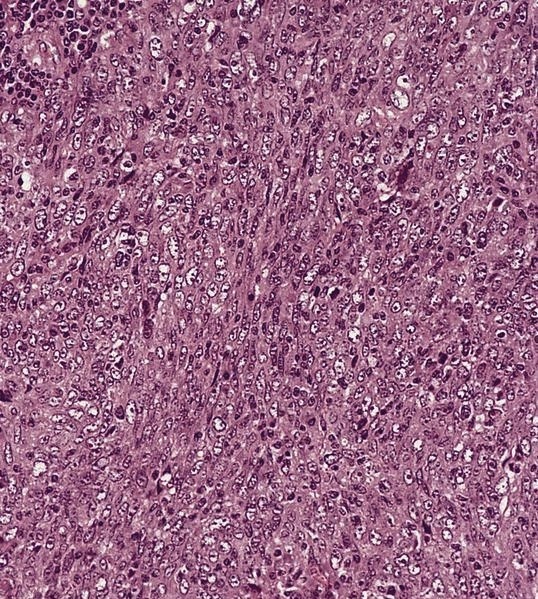
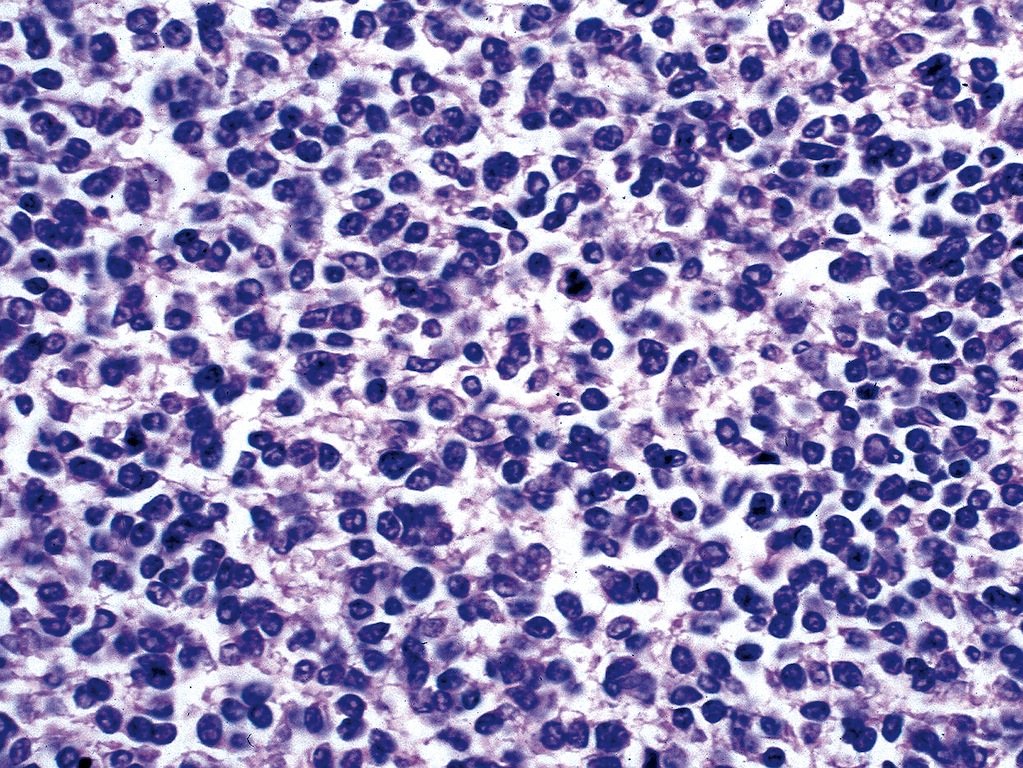
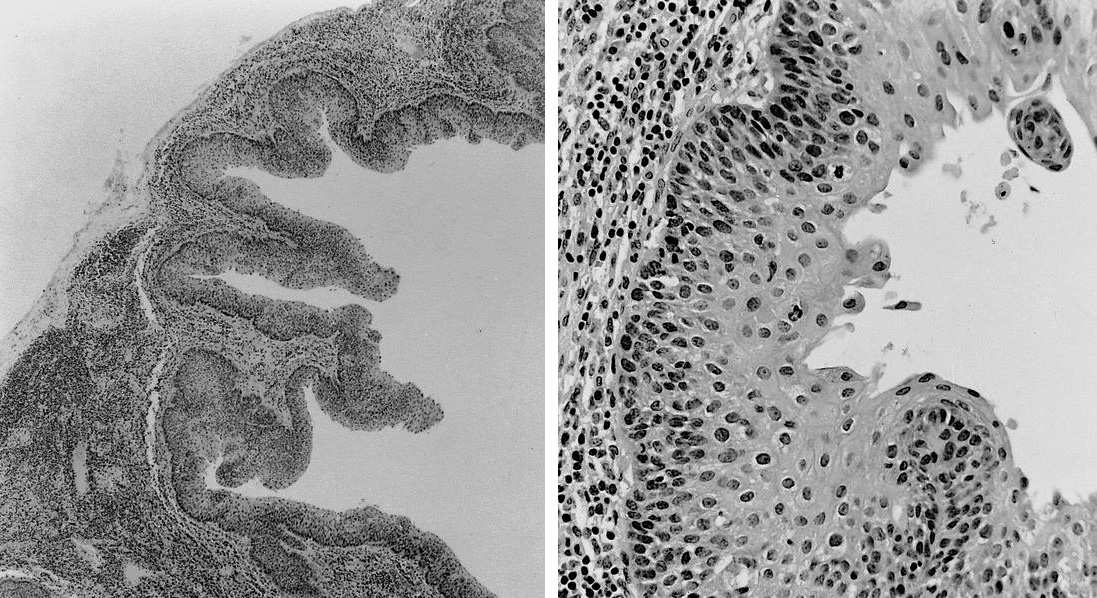
Squamous cell carcinoma
Definition / general
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Dr. Mark R. Wick and AFIP images
- Squamous cyst within cervical lymph node should be considered metastatic carcinoma until proven otherwise
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Cystic change is common, particularly from head and neck region
- Often bland looking squamous cells with only focal atypia
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Dr. Mark R. Wick and AFIP images