Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Balakrishna J. Mesothelial inclusions. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphnodesmesothelialcellinclusions.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Inclusions of benign mesothelial cells in lymph nodes
- Often missed on routine H&E sections (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:1264)
- Hyperplastic mesothelial cells in nodal tissue may derive from reactive serosal mesothelium that is dislodged into draining lymphatics (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000;124:609)
- Often associated with serosal fluid collection (pericardial, pleural, abdominal) at time of nodal biopsy (Hum Pathol 1998;29:339), including episodes of intraperitoneal hemorrhage and ascites (Pathology 2001;33:239), perhaps because effusion allows for mesothelial cell migration into lymphatics (Diagn Cytopathol 2003;29:163)
Terminology
- Benign mesothelial inclusions
- Benign metastasizing mesothelial cells
Epidemiology
- Very rare occurrence
Sites
- Mediastinal and abdominal lymph nodes
- Rare - cervical lymph nodes
Etiology
- Transportation of these cells through the lymphatics to the lymph node during injury or manipulation at the primary site of the origin
- They undergo a degeneration, and thus it becomes difficult to find them
Clinical features
- Incidental finding
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Site specific symptoms
Diagnosis
- Biopsy plus immunohistochemistry
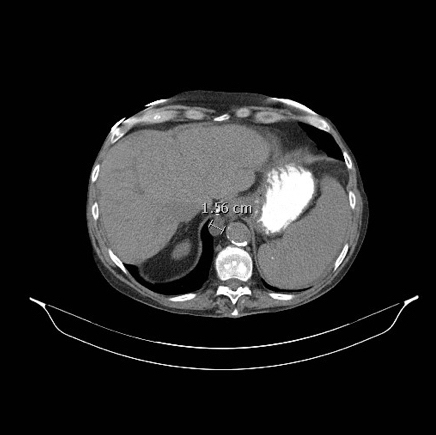
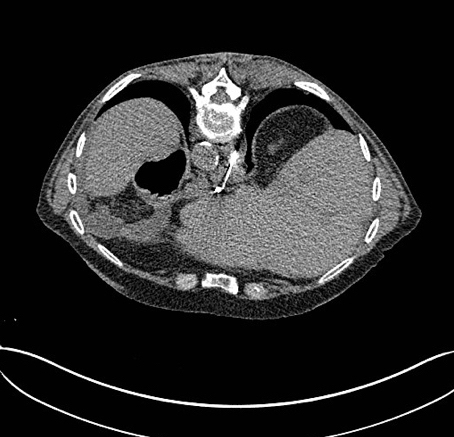
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Benign process with no significant clinical implications
Case reports
- 12 year old boy with diffuse hyperplastic mesothelial cells in multiple lymph nodes (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6:926)
- 16 year old boy with mesothelial cell inclusions mimicking adenocarcinoma (Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol 2010;31:62)
- 18 year old woman with benign metastasizing mesothelial cells (J Clin Oncol 2011;29:e546)
- 52 year old woman with mesothelial pelvic lymph node inclusions mimicking metastatic thyroid carcinoma (Gynecol Oncol 1998;68:210)
- Mesothelial cell inclusions in mediastinal lymph nodes mimicking metastatic carcinoma (Am J Clin Pathol 1990;93:741)
- Mesothelial cell inclusions within mediastinal lymph nodes (Histopathology 1994;25:483)
- Mesothelial pelvic lymph node inclusion in a patient with ovarian microinvasive borderline mucinous tumor (Int J Gynecol Cancer 2007;17:917)
- Benign hyperplastic mesothelial cells in lymph node (Int J Surg Pathol 2007;15:297)
Treatment
- Depends upon the clinical presentation / underlying cause
- In incidental findings, none necessary
Gross description
- Enlarged lymph nodes with yellowish tan to gray white, smooth to mottled surface
Microscopic (histologic) description
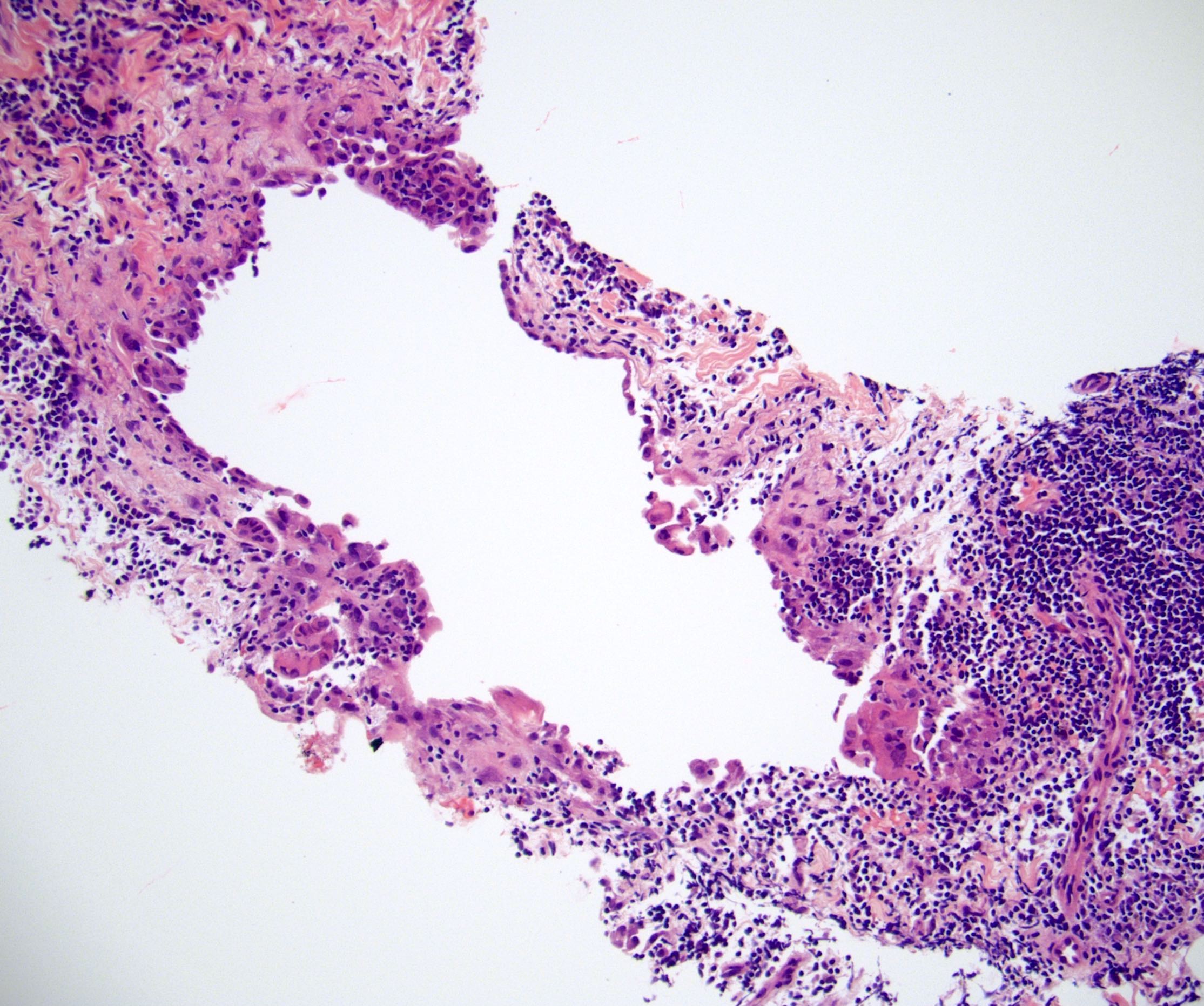
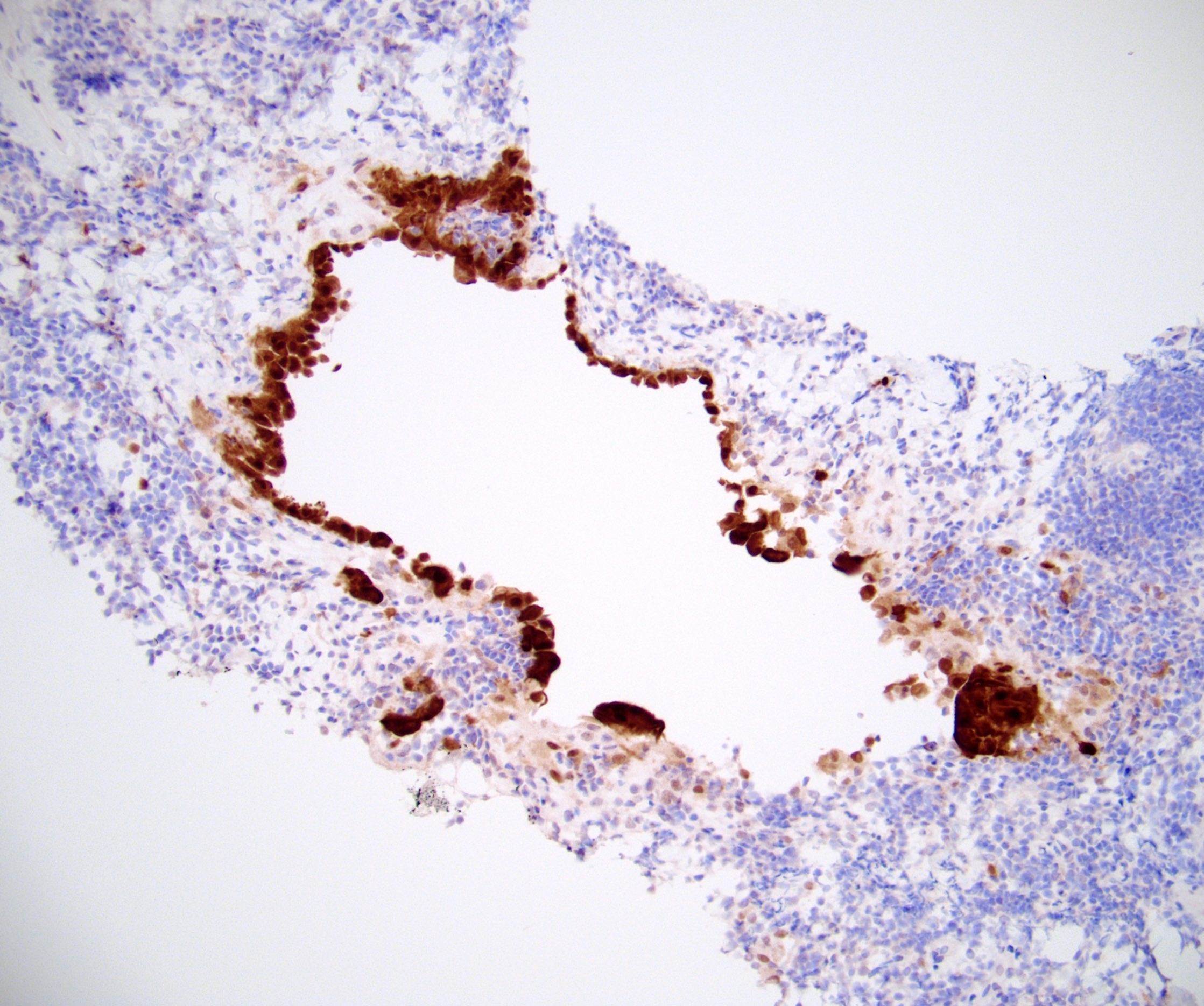
- Small clusters and singly scattered, round to polygonal cells, seen in the subcapsular and interfollicular sinuses of the nodes
- These cells show a round, vesicular nucleus with small nucleolus
- The nuclear - cytoplasmic ratio is low
- No mitotic activity is detected
- There is no extranodal or parenchymal infiltration of the cells
- Tiny spaces are seen in between the cells of the clusters (mesothelial windows)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
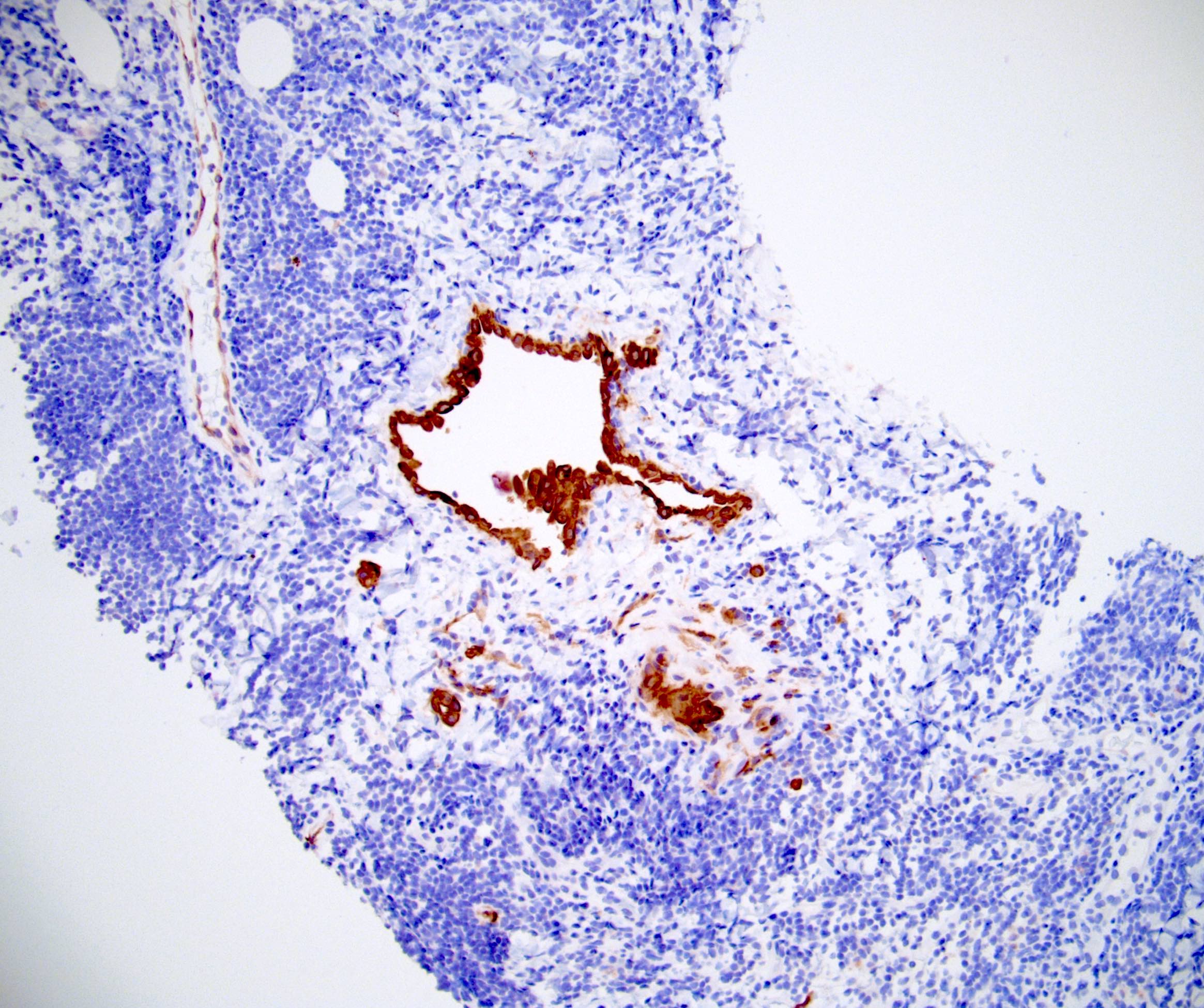
- Cytokeratin AE1 / AE3, cytokeratin 7 (CK7)
- Calretinin (nuclear and cytoplasmic), WT1, CK5 / 6, CAIX (membranous)
- EMA (weak and cytoplasmic)
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- Lymphangioma: multicystic, has smooth muscle and lymphocytes in cyst wall and lumen, keratin+
- Metastatic adenocarcinoma
- Metastatic mesothelioma
- Mucinous cystadenoma: ovarian-like stroma, mucin+, CEA+, negative for hyaluronic acid
- Müllerian inclusions: ER+; negative for calretinin, CK5 / 6; PAX8 can be positive in both
- Simple hemorrhagic cyst: keratin-
- Sinus histiocytosis