Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Peripheral smear description | Peripheral smear images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Flow cytometry images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Balakrishna J. Reactive lymphadenopathy. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphnodesreactivegeneral.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Lymph node enlargement due to proliferation of some or all compartments or cellular components of lymph nodes, reflecting antigenic stimulation
- Can be acute or chronic depending on the pathogenic agents
Essential features
- Lymph node enlargement
- Acute: painful or tender; chronic: nontender
- 4 architectural patterns: follicular hyperplasia, sinus histiocytosis, interfollicular / mixed and diffuse
- Clonal B or T cell proliferations are generally not detected but reactive clonal populations may occur
- Lacks significant cytologic or architectural atypia
Terminology
- Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia
- Reactive follicular hyperplasia
- Diffuse paracortical hyperplasia
- Sinus histiocytosis
- Acute nonspecific lymphadenitis
- Chronic lymphadenitis
ICD coding
- ICD-10: R59.9 - enlarged lymph nodes, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Represents the reaction of lymphoid tissue to intrinsic or environmental antigens
- Most lymph node enlargements are reactive
- Can occur in any age group and gender
- In children, most lymphadenopathies are benign; in adults, chance of malignancy increases with age (Mayo Clin Proc 2000;75:723)
Sites
- Any lymph node group can be affected depending on the etiology and area of drainage (Clin Pediatr (Phila) 2011;50:683)
Pathophysiology
- Lymph nodes filter lymph drained from tributary regions
- Antigenic substances reaching the lymph nodes evoke an immune reaction (Semin Diagn Pathol 2018;35:4)
- Bacteria and fungi cause predominantly inflammatory reactions; viruses and drugs cause predominantly immune reactions
- Acute nonspecific lymphadenitis: acute inflammation of the lymph node due to an infectious or inflammatory etiology
- Chronic nonspecific lymphadenitis: chronic inflammation of the lymph node in response to a pathogen / antigen, known or unknown
Etiology
- Infections: virus, bacteria, fungi and protozoa
- Chemicals: environmental pollution
- Drugs: phenytoin, allopurinol, gold, penicillin, quinidine
- Altered tissue components: inflammation, tissue necrosis
- Inflammatory / autoimmune conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis
- Other antigens or allergens, including vaccines (Mayo Clin Proc 2000;75:723, Iran J Med Sci 2014;39:158, Pediatr Clin North Am 2002;49:1009)
Clinical features
- Clinical features reflect the underlying cause
- Enlarged lymph nodes (Am Fam Physician 2016;94:896)
- In acute lymphadenitis, can be painful or tender and nodes may be soft or fluctuant, with or without associated fever, weight loss, malaise, loss of appetite and redness of overlying skin
- In chronic lymphadenitis, enlarged lymph nodes are commonly painless (Mayo Clin Proc 2000;75:723)
Diagnosis
- Clinical examination
- Histopathology: biopsy is rarely performed if reactive nature is clinically obvious
- In chronic lymphadenitis, biopsy and histopathology evaluation are necessary
- Exclusion of specific causes: clinical, laboratory and imaging findings
- If suspicious, exclude lymphoid neoplasia by immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry and required genetic studies
Laboratory
- Laboratory findings depend on the etiology and nature of the process (acute versus chronic)
- Complete blood count (CBC) may show leukocytosis with neutrophilia or lymphocytosis and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) may be elevated
- Confirmatory tests for specific etiologic agents (infectious agents) may be positive
Radiology description
- Enlarged lymph node(s)
- Advanced imaging techniques may help to distinguish reactive lymph node enlargement from tumor metastases or other specific lymph node enlargements (Mol Imaging Biol 2013;15:40, Indian J Gastroenterol 2016;35:55)
Prognostic factors
- Benign, usually self limiting process with good prognosis
- Prognosis depends on the etiology and appropriate and timely management of the cause
Case reports
- 40 year old man who received dasatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia presented with a large axillary mass (Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e22791)
- 41 year old woman with a history of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and enlarged cervical lymph nodes (Clin Nucl Med 2022;47:367)
- 57 year old woman with rheumatoid arthritis and generalized lymphadenopathy (Case Rep Rheumatol 2014;2014:386328)
- 68 year old man with right cheek melanoma and multiple FDG avid lymph nodes in the left axilla (Clin Nucl Med 2021;46:433)
Treatment
- Treat the underlying cause
Gross description
- Enlarged, soft lymph nodes with tan, homogenous cut surfaces
- Acute lymphadenitis: suppuration may lead to necrosis and abscess formation
- Chronic lymphadenitis: thickened capsule and fibrosis may be obvious (Walker: Clinical Methods - The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations, 3rd Edition, 1990)
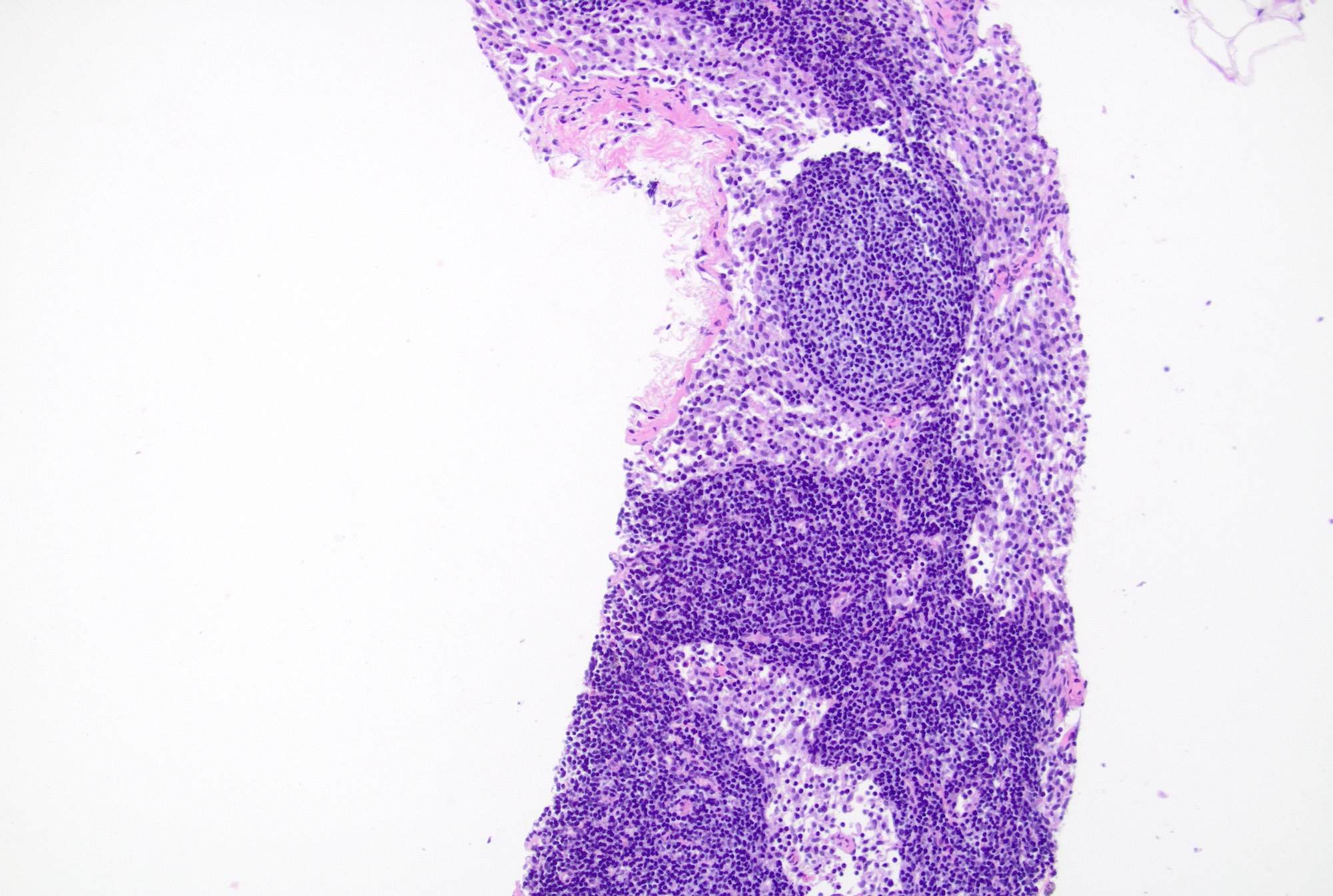
Microscopic (histologic) description
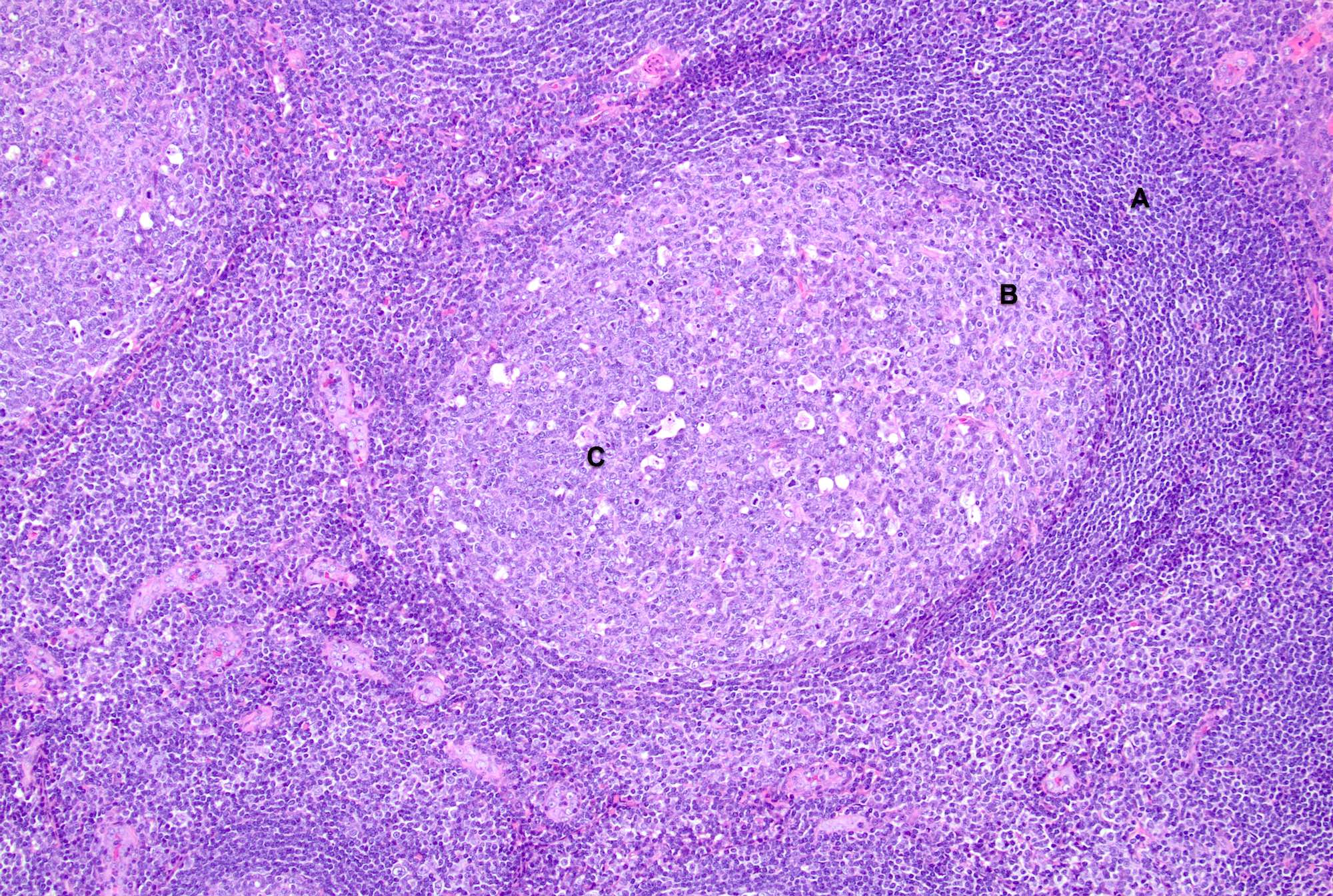
- 4 architectural patterns of reactive hyperplasia are described, depending on the etiology: follicular / nodular, sinus histiocytosis, interfollicular / mixed and diffuse
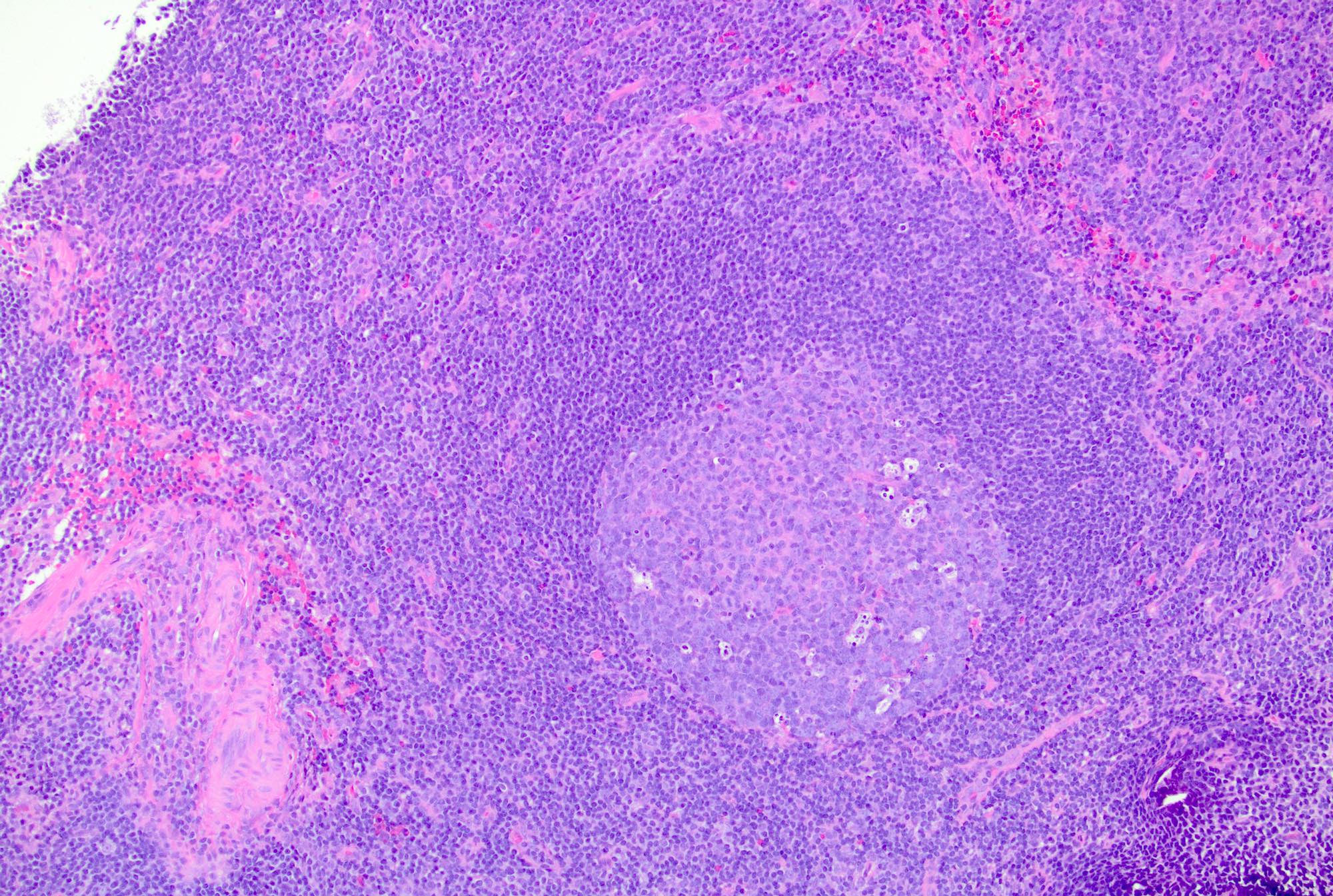
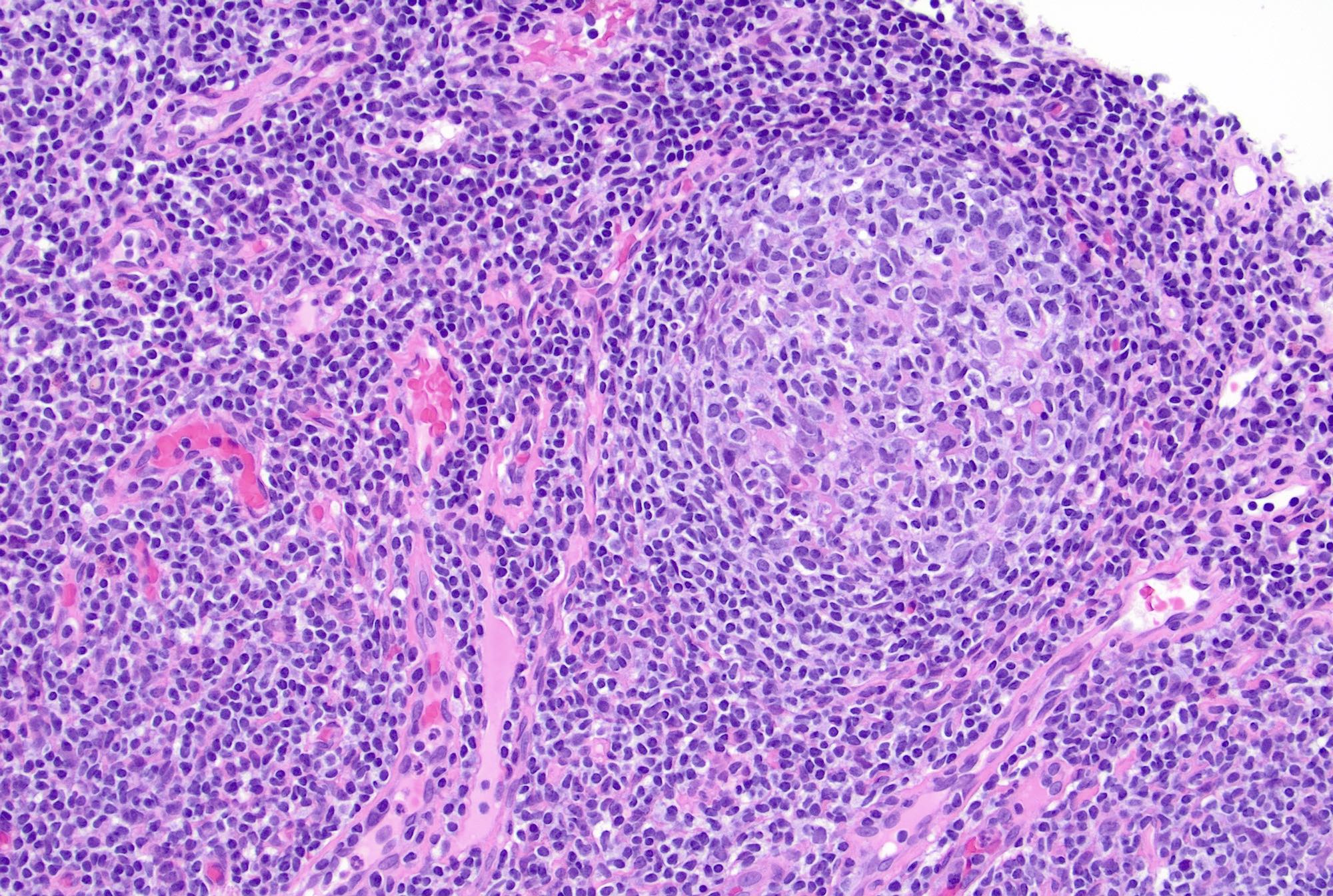
- Follicular hyperplasia (most common reactive pattern)
- Enlarged follicles, varying in size and shape, may coalesce and display different configurations
- Prominent germinal center and mantle zone
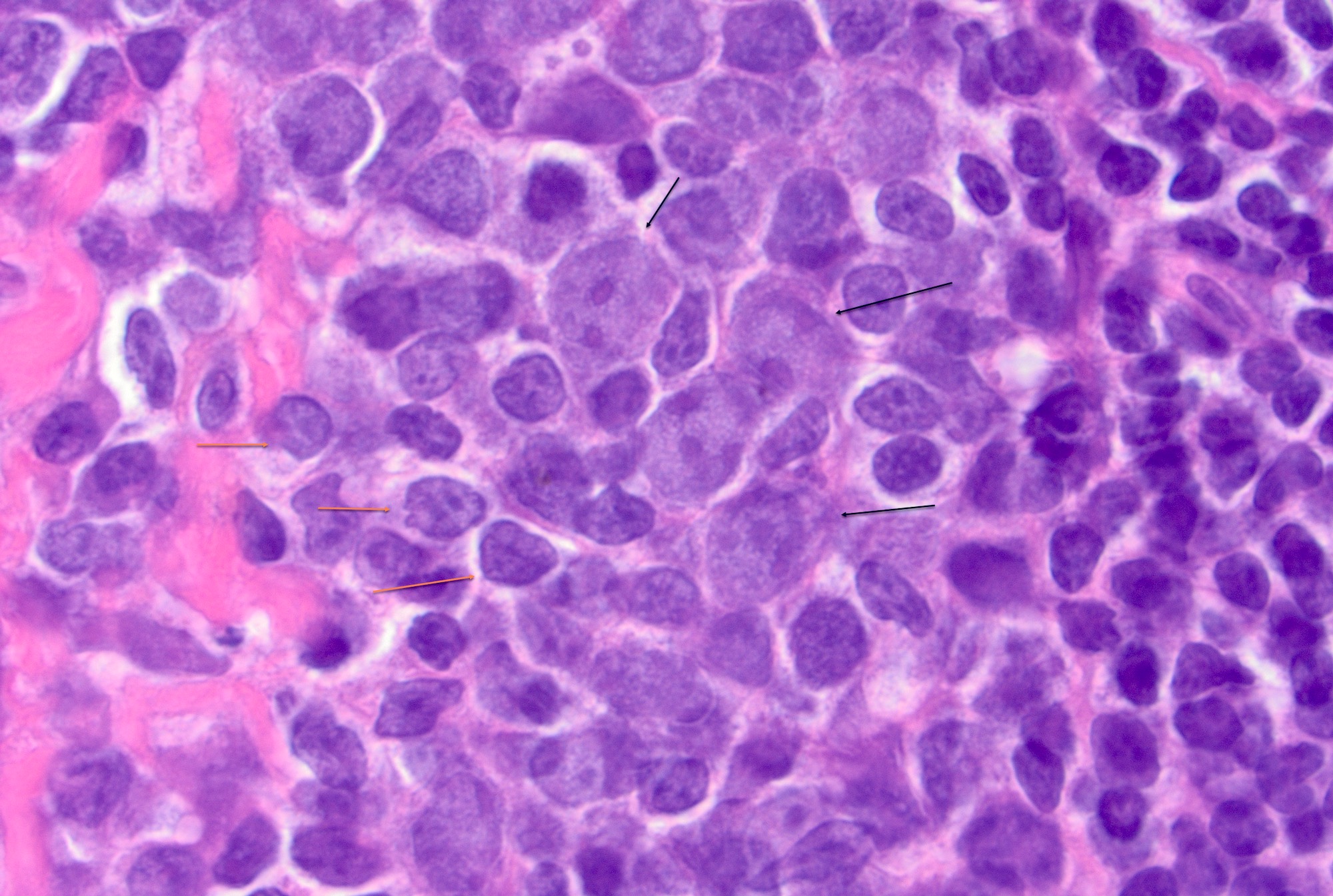
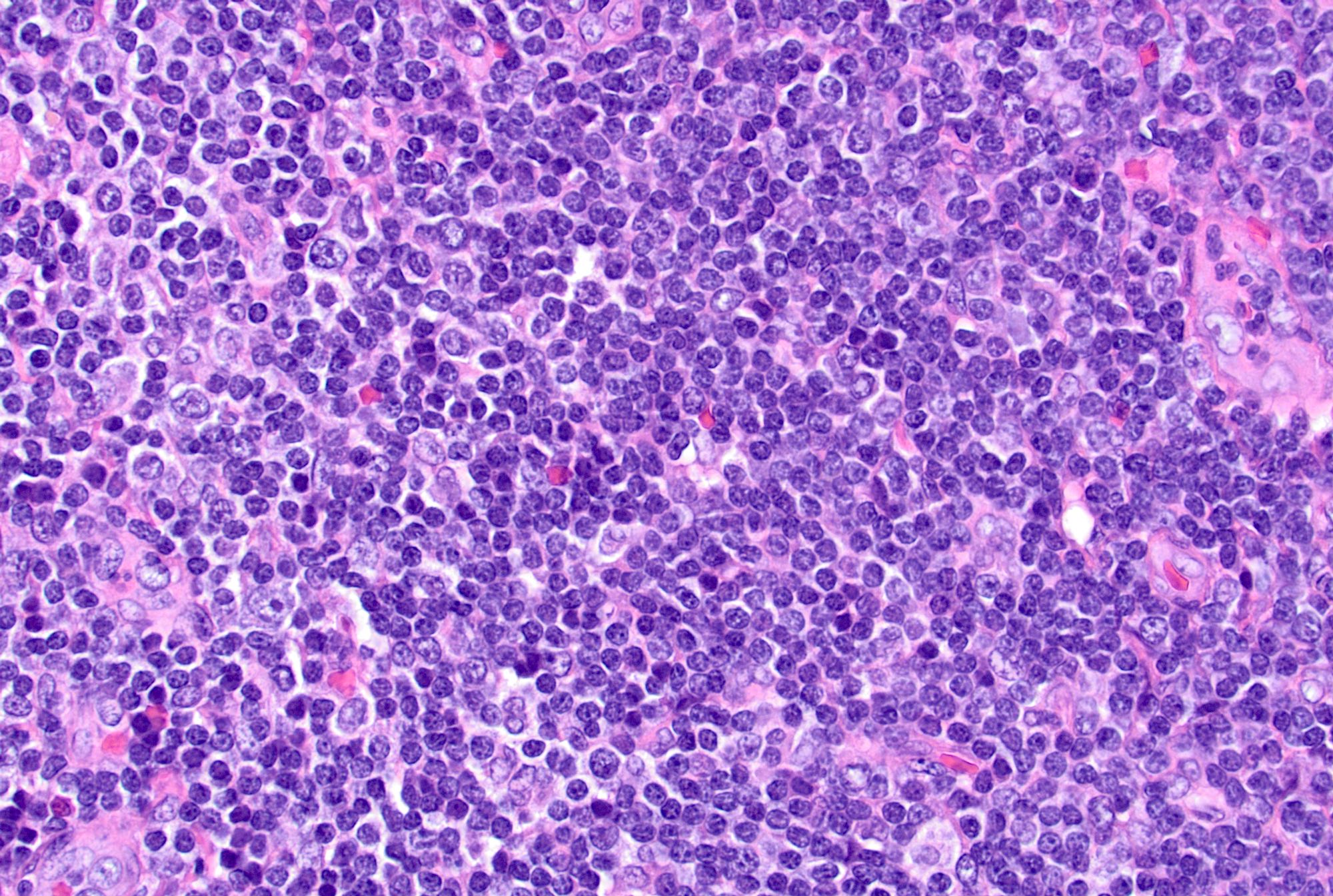
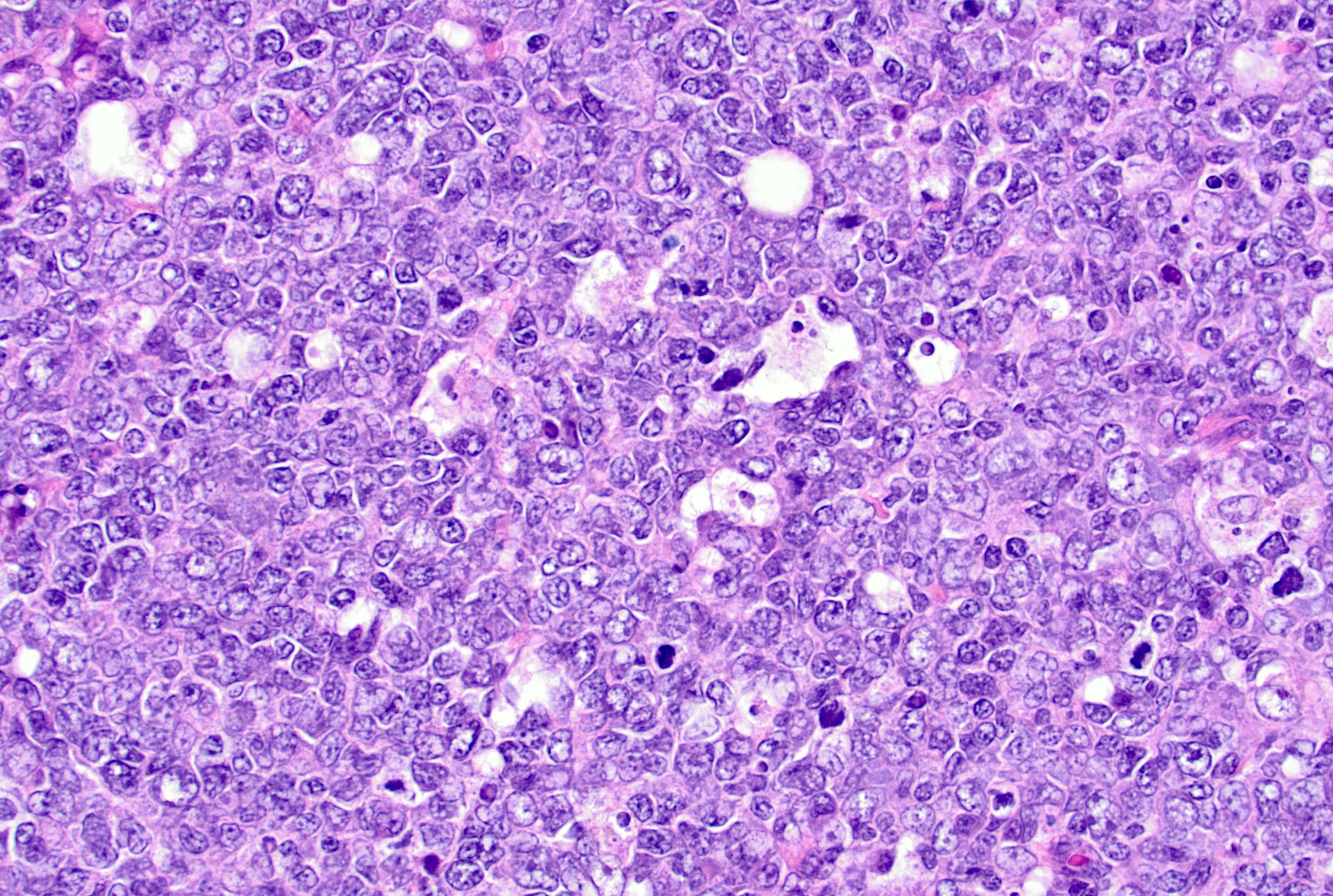
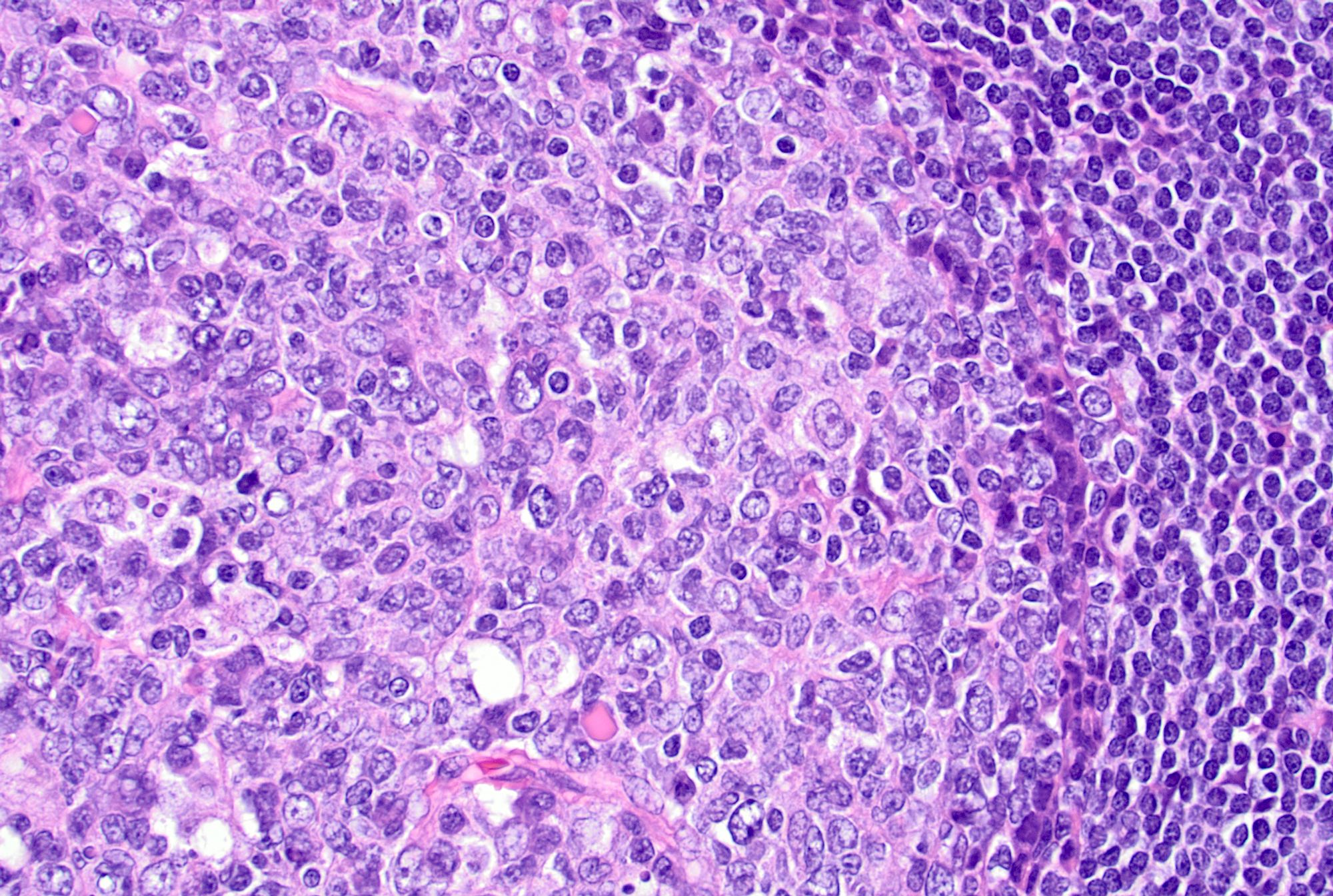
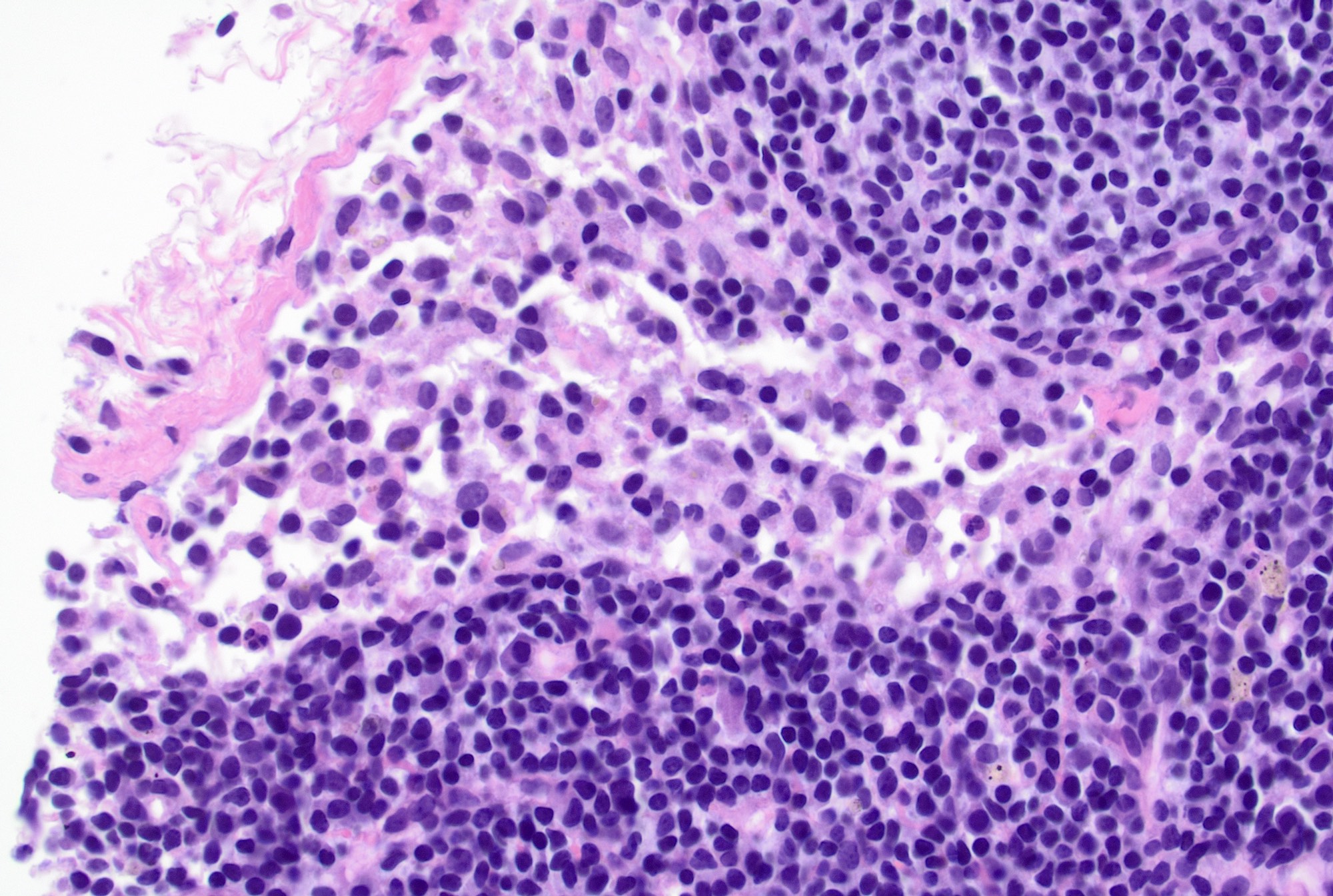
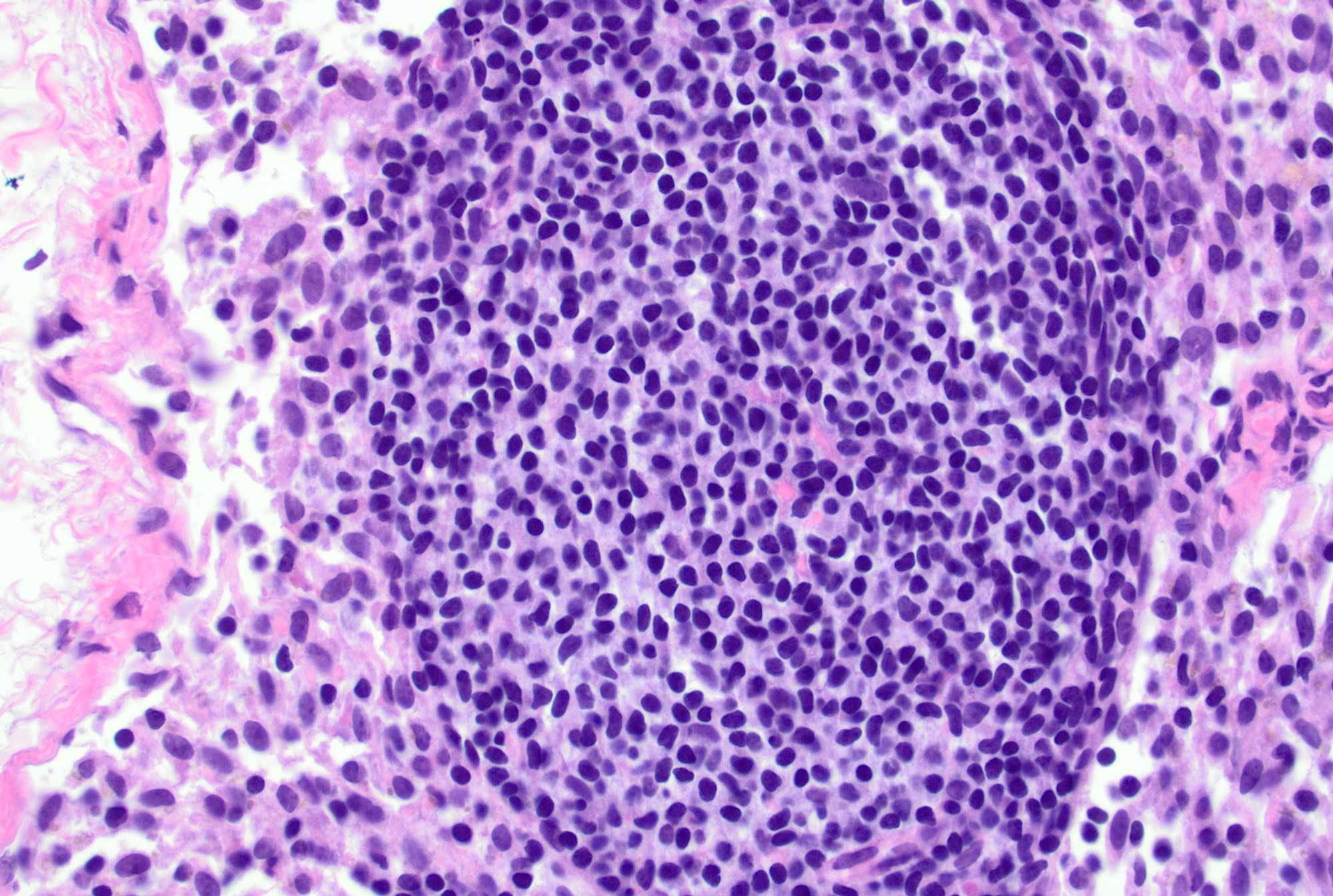
- Germinal centers show mixed small and large lymphocytes, centrocytes and centroblasts
- Centroblasts polarize to the medial pole / medullary side forming the darker zone and centrocytes accumulate at the peripheral pole / capsular side forming the lighter zone (Immunity 2016;45:471)
- Centroblasts are 3 - 4 times larger than the inactivated lymphocytes and show a narrow rim of basophilic cytoplasm and large, round to oval vesicular nuclei with 1 - 3 prominent peripheral nucleoli
- Mitotic figures are frequent
- Centrocytes are smaller lymphocytes with scant cytoplasm, cleaved nuclei, clumped chromatin and small or absent nucleoli
- Numerous tingible body macrophages are a characteristic feature of follicular hyperplasia (Semin Diagn Pathol 2018;35:4, Am J Surg Pathol 1987;11:866)
- Other cells: plasma cells, T cells and follicular dendritic cells
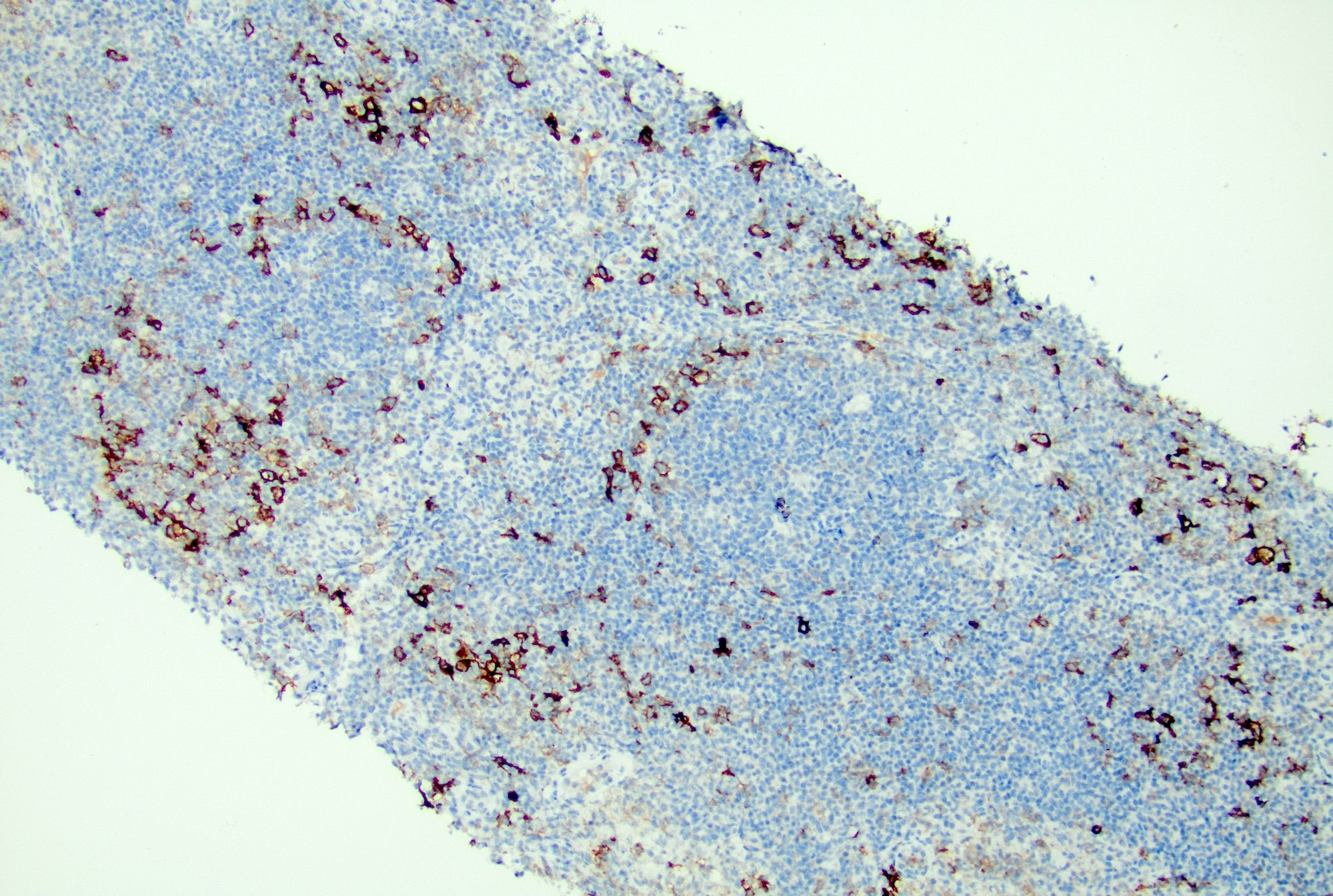
- PD-1+ T cells (T follicular helper cells) are seen predominantly at the periphery of the germinal center (Ann Diagn Pathol 2020;44:151421)
- Mantle zone: around the light zone, small lymphocytes
- Interfollicular areas may show rare transformed cells (immunoblasts), small lymphocytes, plasma cells and high endothelial venules
- Monocytoid B cell proliferation may be seen in follicular hyperplasia around cortical sinuses (Pathol Res Pract 1998;194:559)
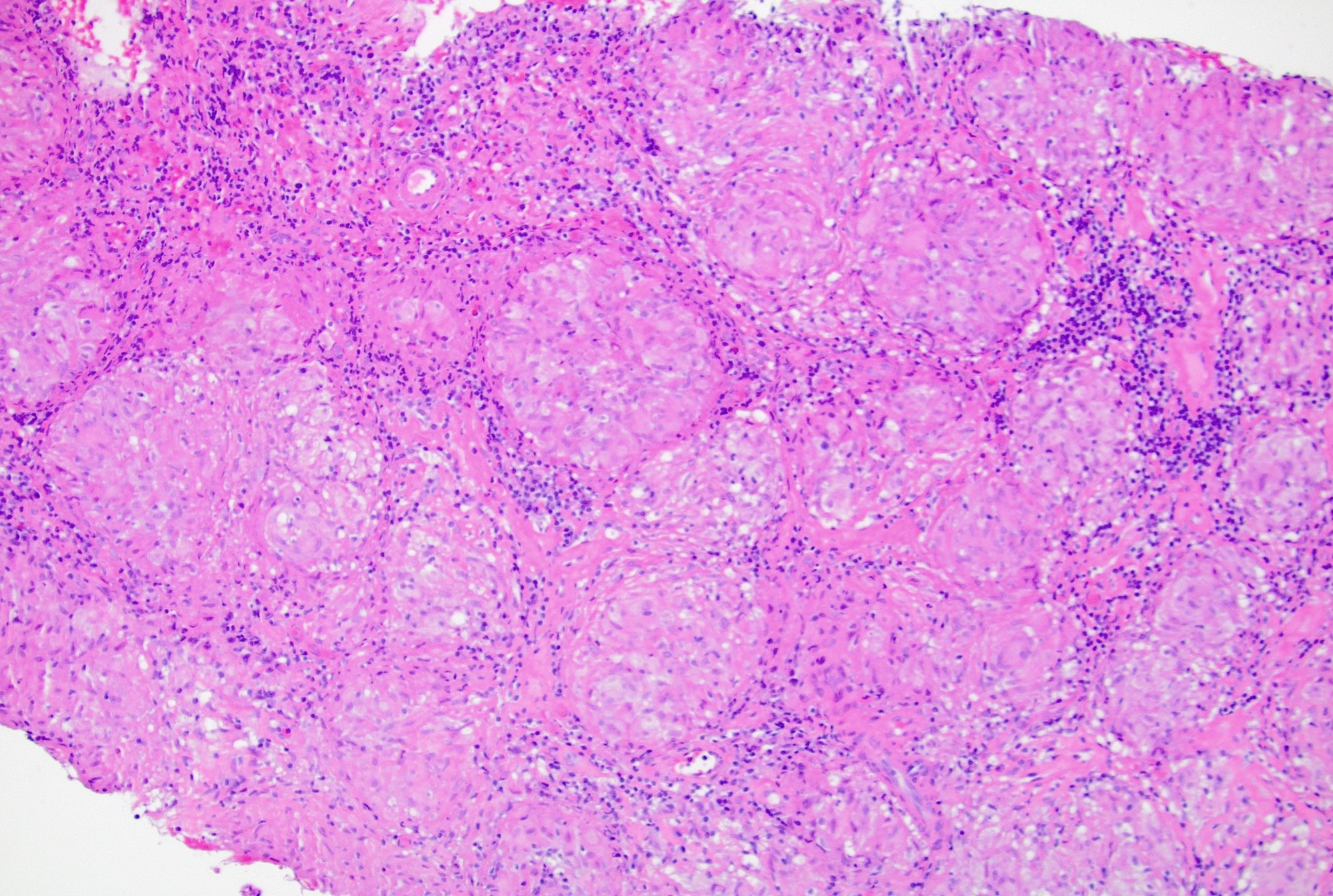
- Sinus histiocytosis
- Expansion of sinuses by histiocytes
- Common pattern in lymph nodes draining tumor (Br J Surg 1983;70:317)
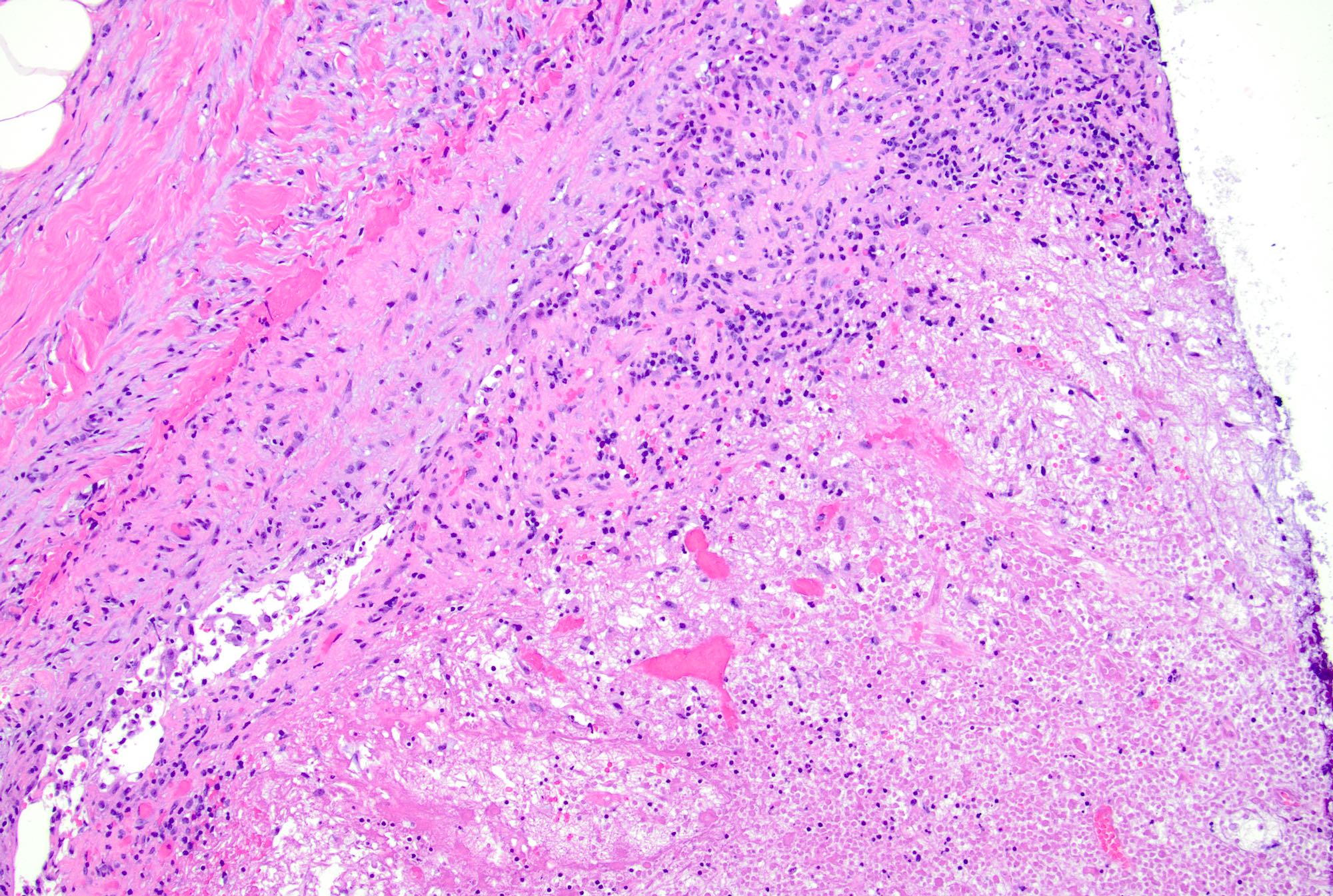
- Interfollicular / mixed patterns
- Paracortical hyperplasia: seen usually in viral infections, nodes draining tumors and autoimmune disorders (Pathol Res Pract 2001;197:237, Hum Pathol 1975;6:363, APMIS 2001;109:419)
- Mixed small lymphocytes and immunoblasts, with increased vascularity and interdigitating dendritic cells
- Granulomatous lymphadenitis: necrotizing, nonnecrotizing or suppurative granulomas depending on the etiology (Rev Infect Dis 1986;8:322)
- Diffuse
- Architecture may be effaced
- Diffuse proliferation of mixed small lymphocytes, immunoblasts and plasma cells (APMIS 2001;109:419)
- Immunoblasts may rarely mimic Hodgkin / Reed-Sternberg cells
- Follicular hyperplasia (most common reactive pattern)
- Acute lymphadenitis
- Sinus dilatation followed by accumulation of neutrophils, vascular dilatation and edema of the capsule
- Suppurative or necrotizing inflammation may be seen depending on the etiology (Semin Pediatr Surg 2006;15:99)
- Chronic lymphadenitis
- Follicular hyperplasia, prominence of postcapillary venules, increased number of immunoblasts, fibrosis, plasma cells and histiocytes
- Capsule may be inflamed or fibrotic (Semin Pediatr Surg 2006;15:99)
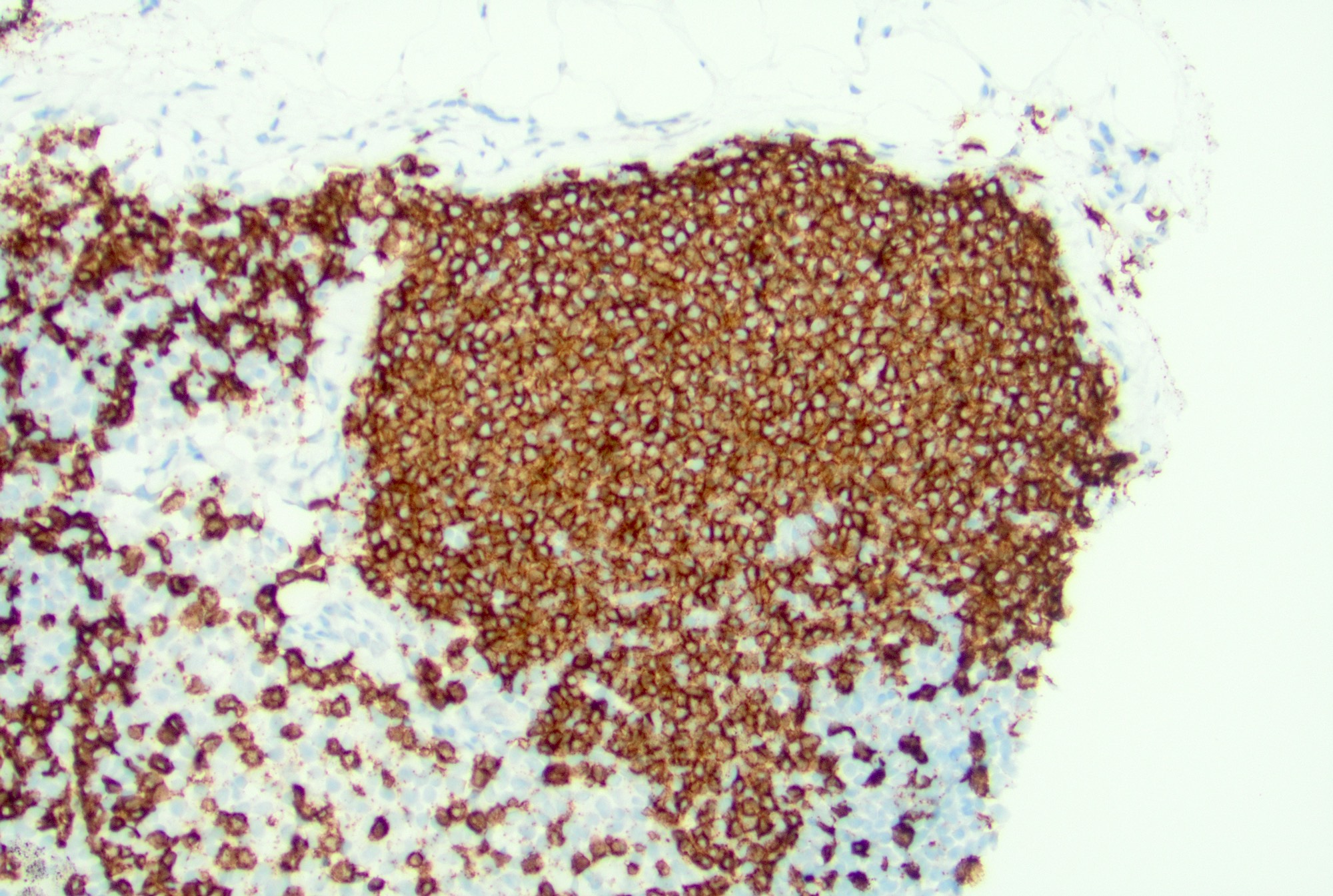
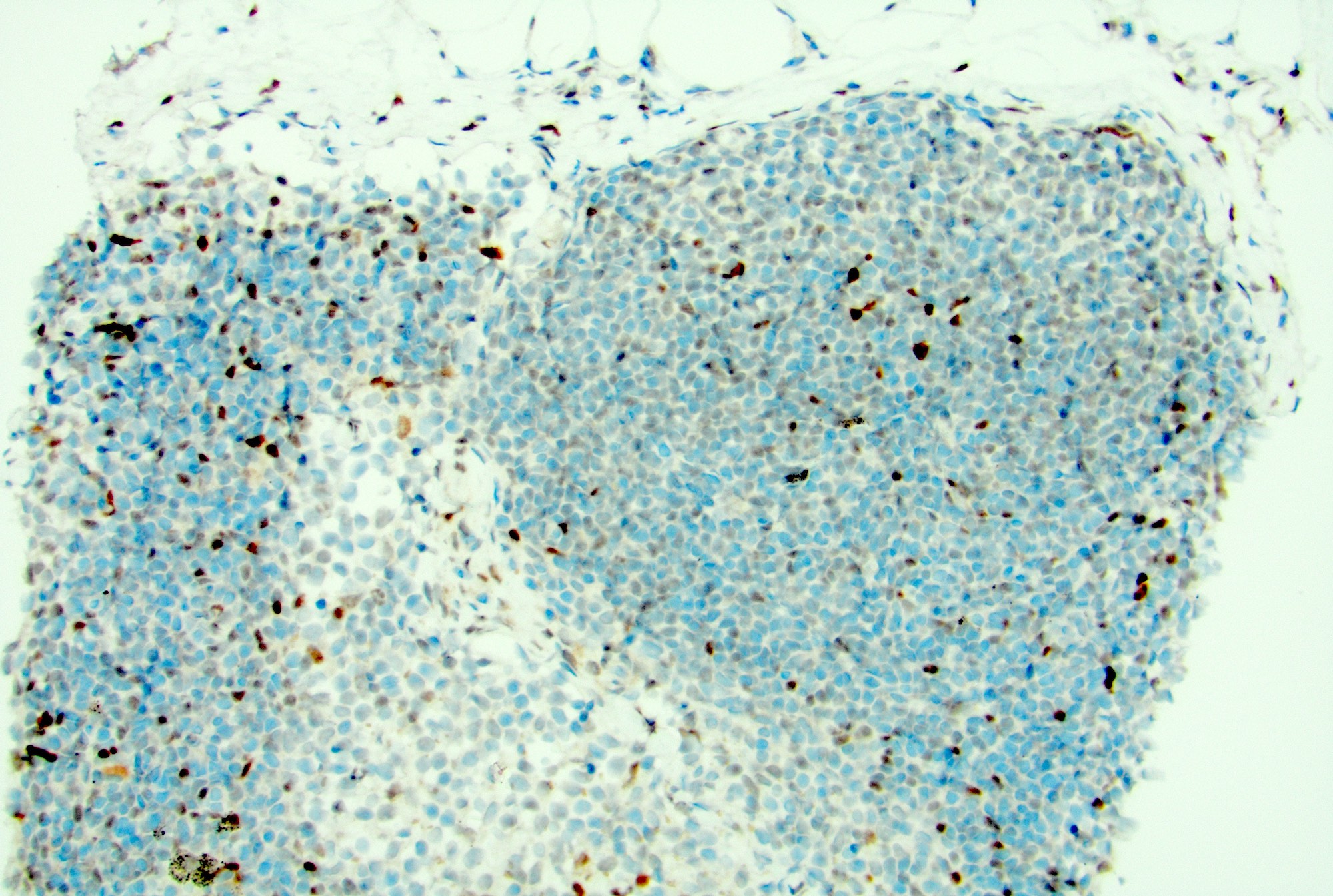
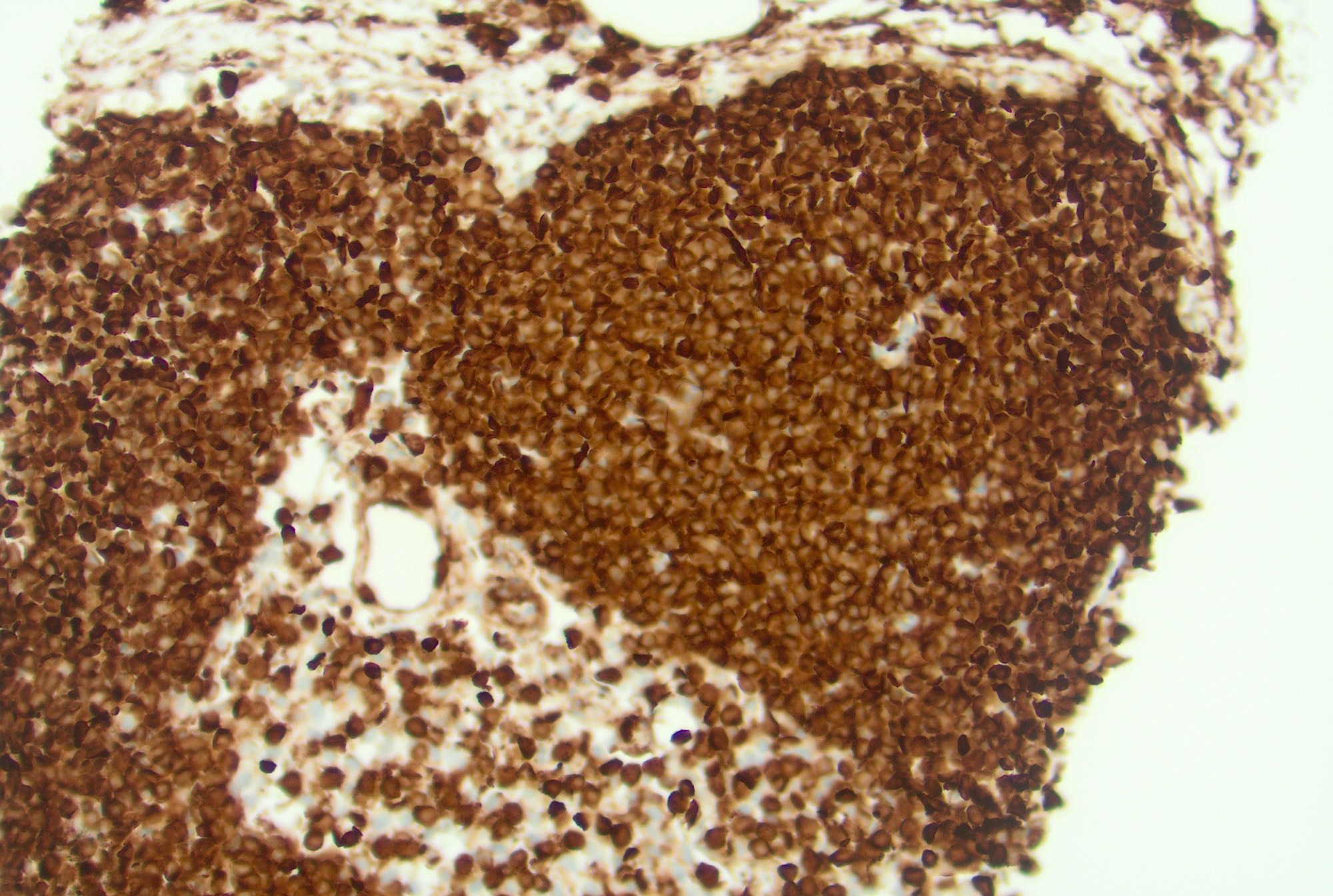
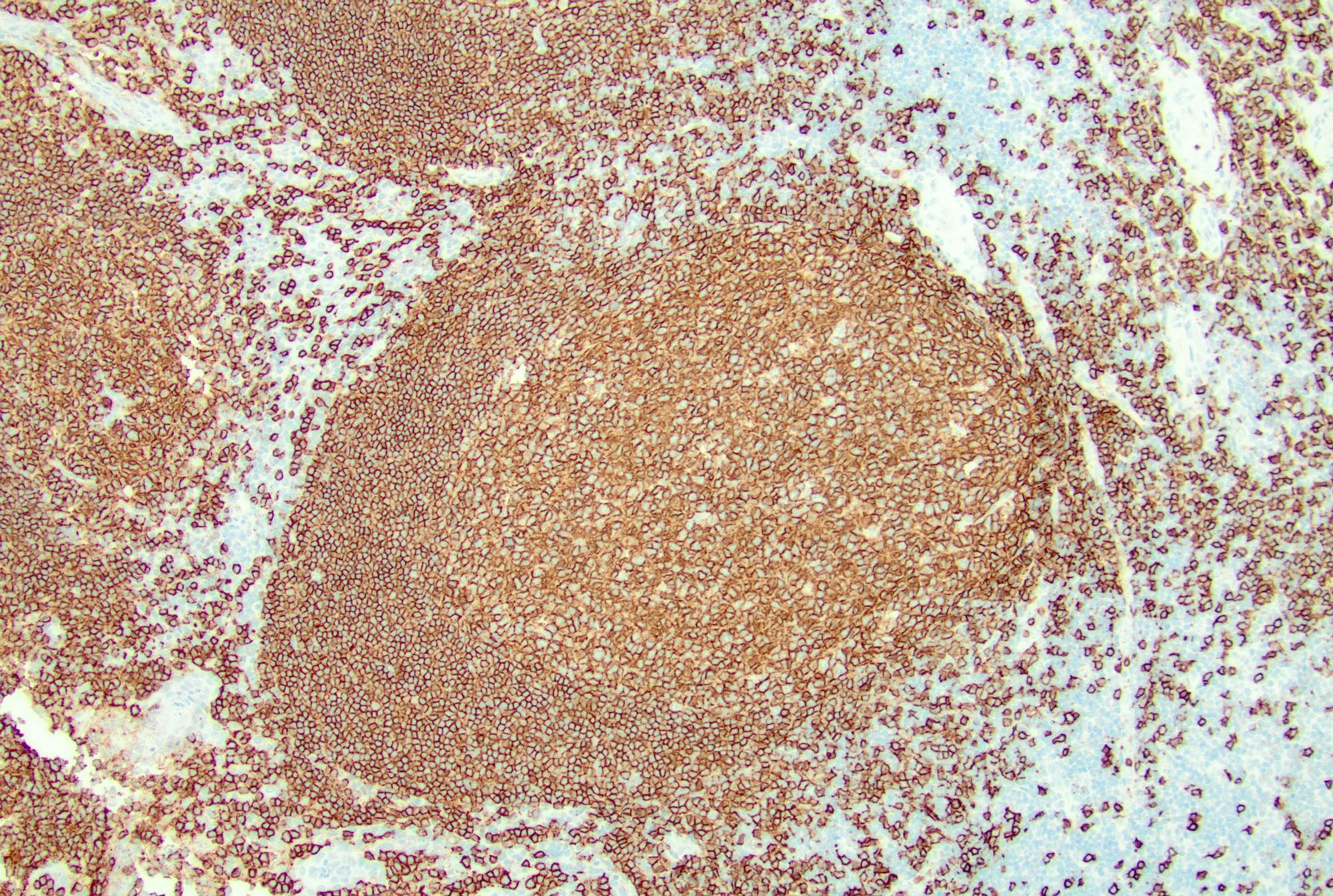
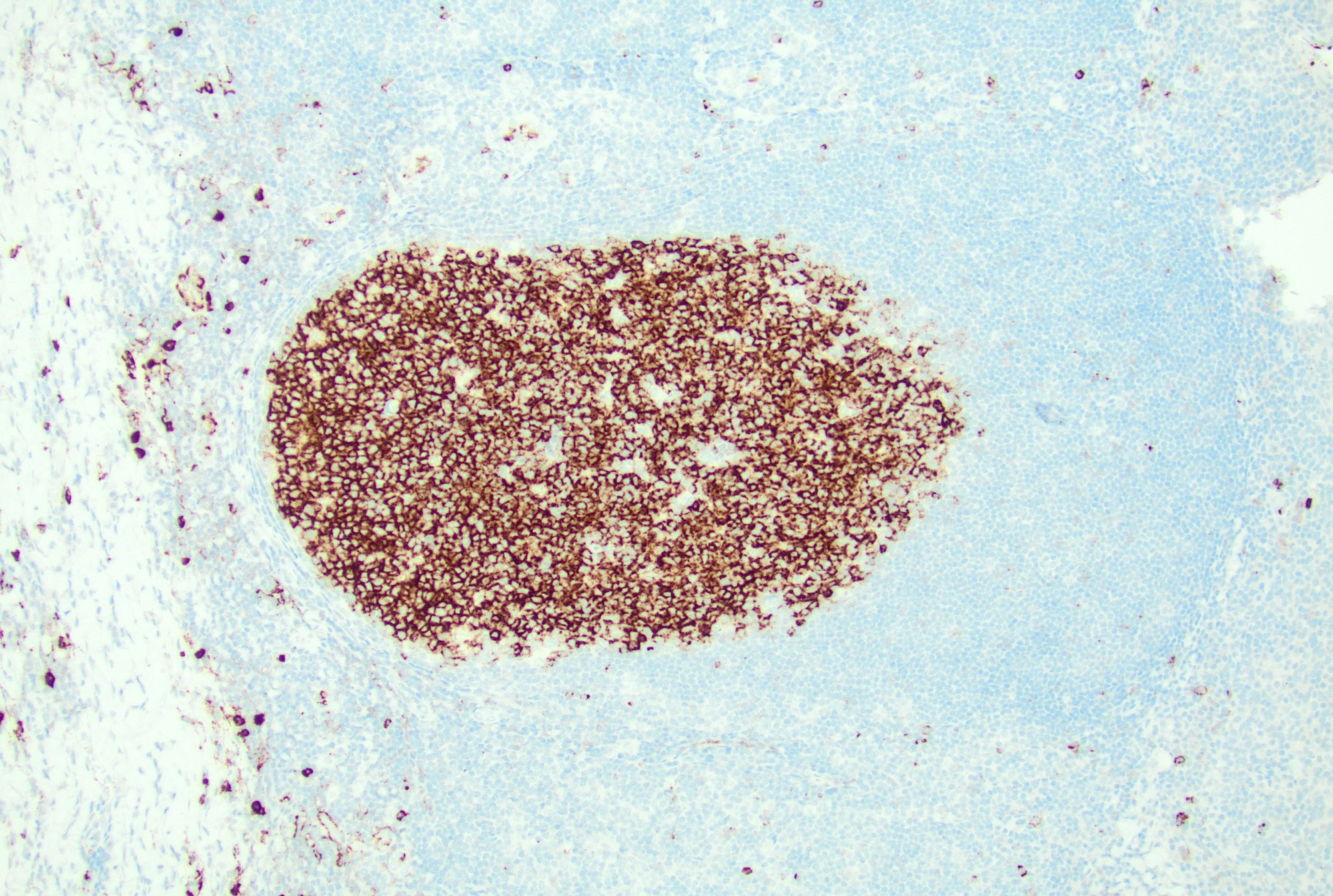
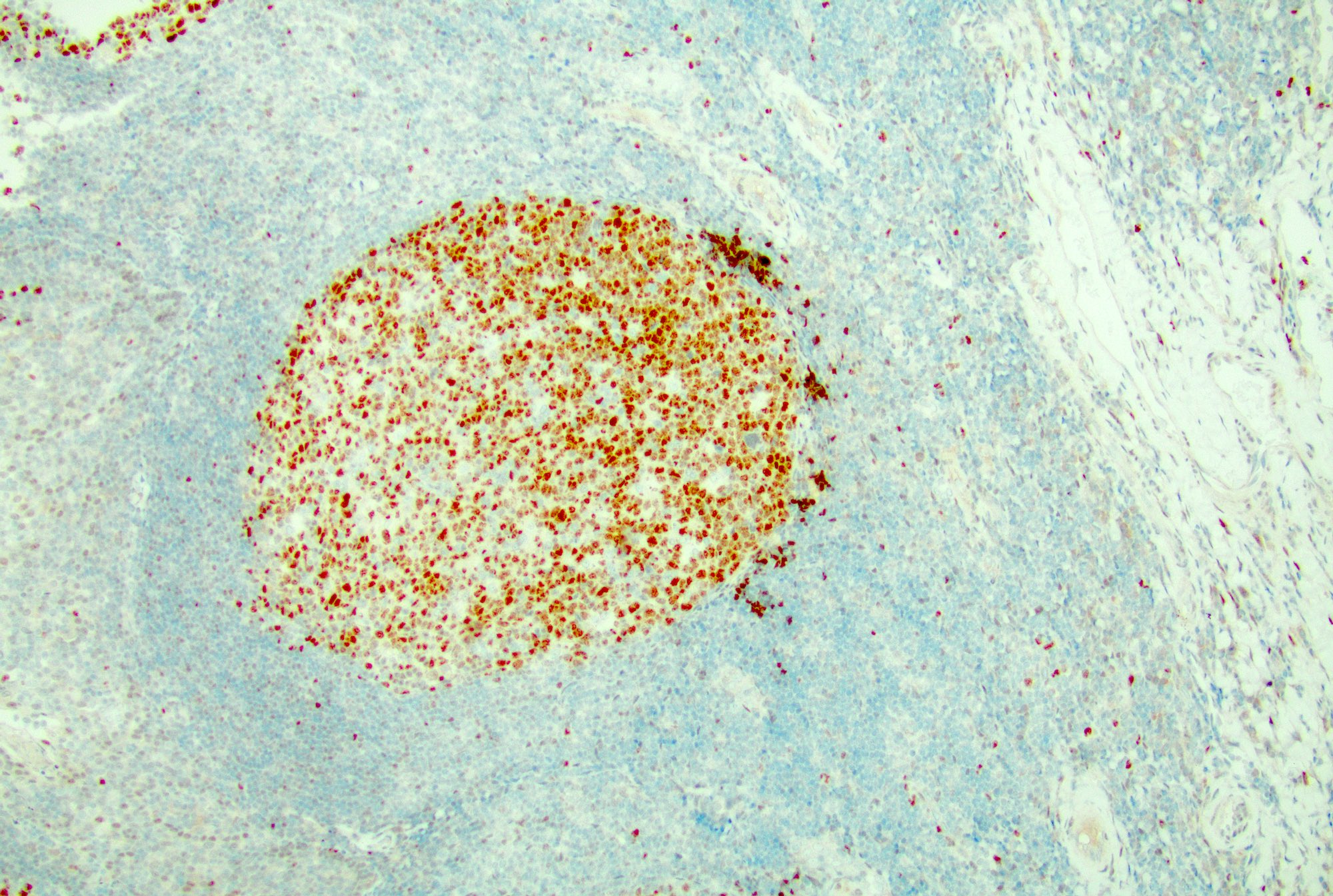
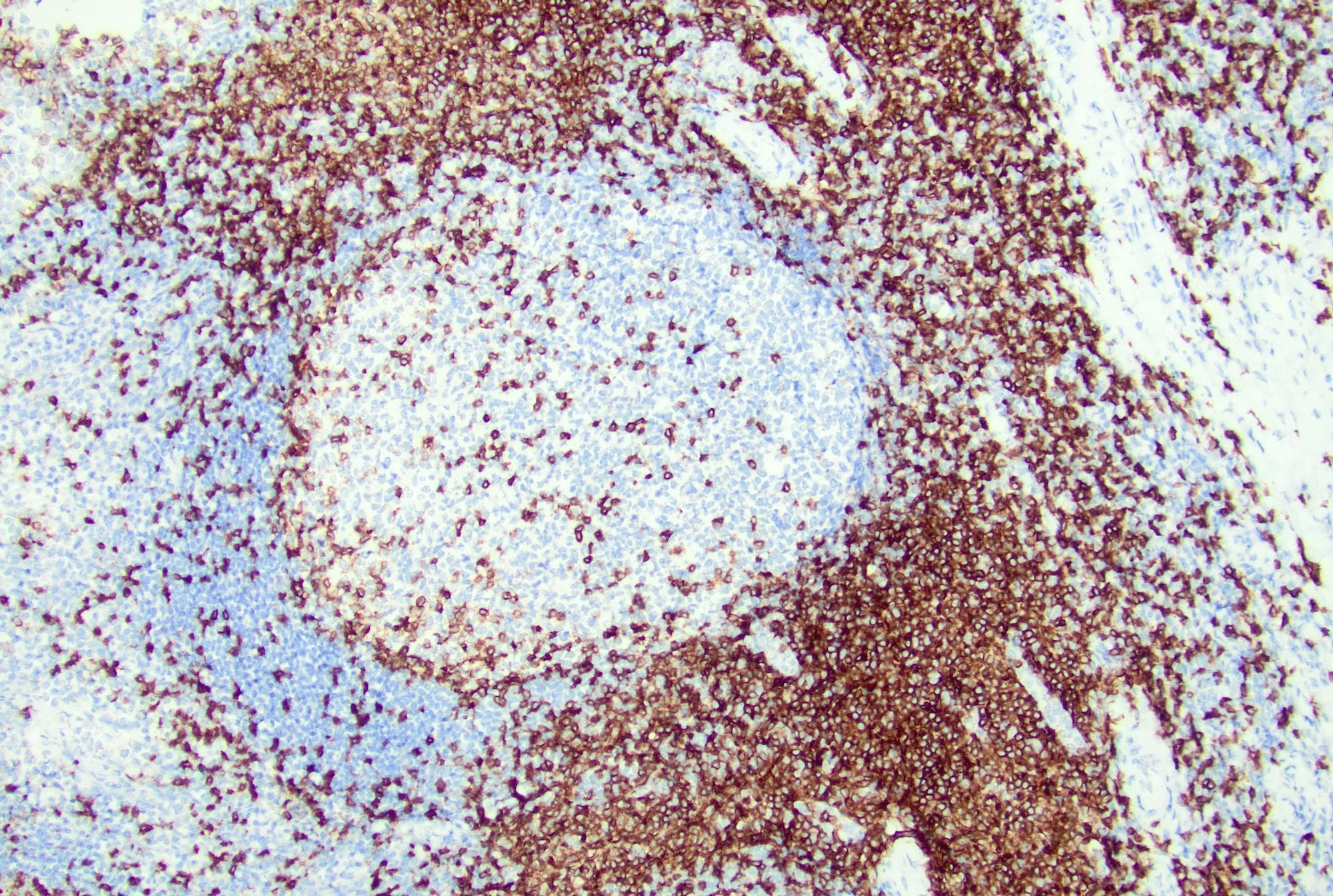
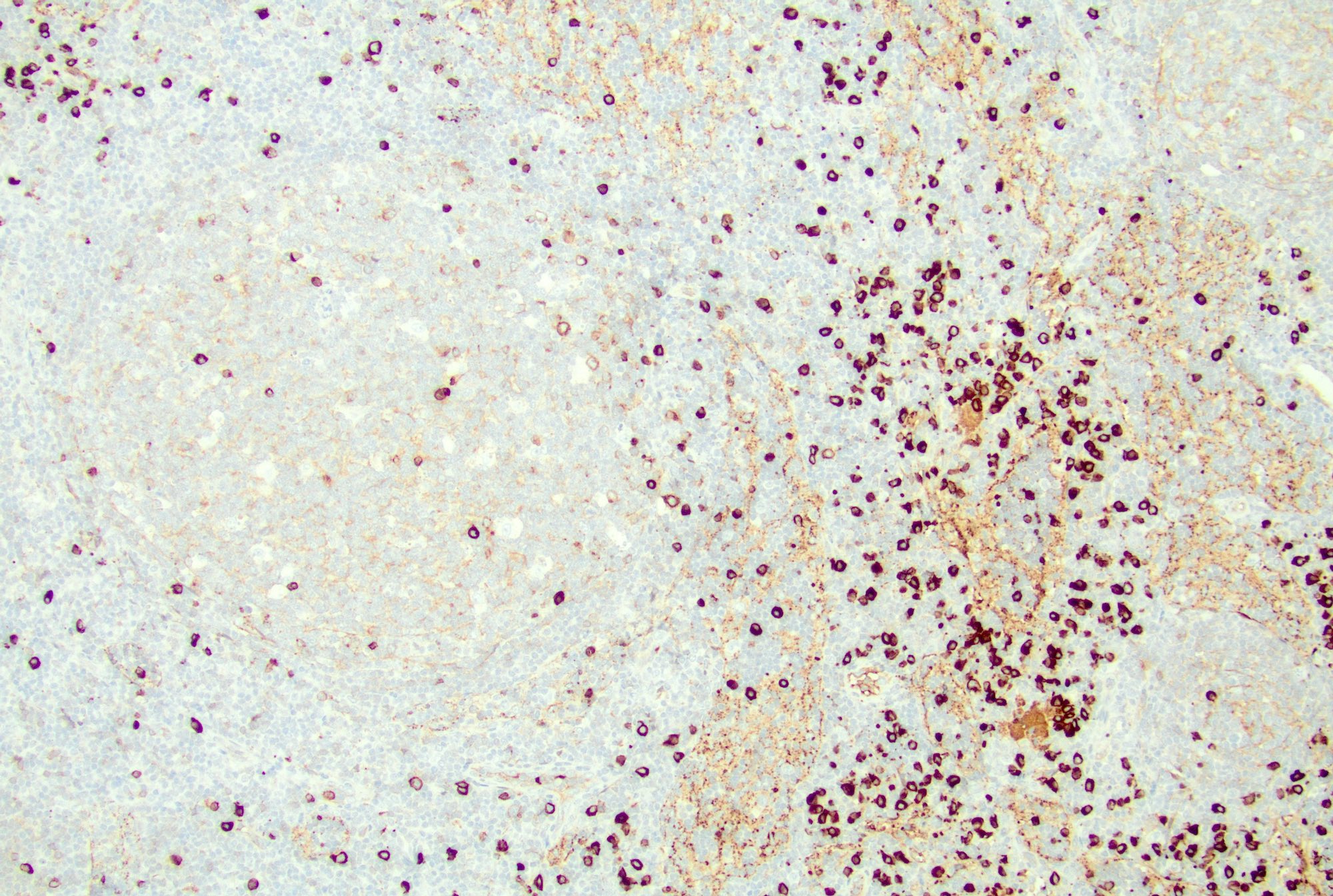
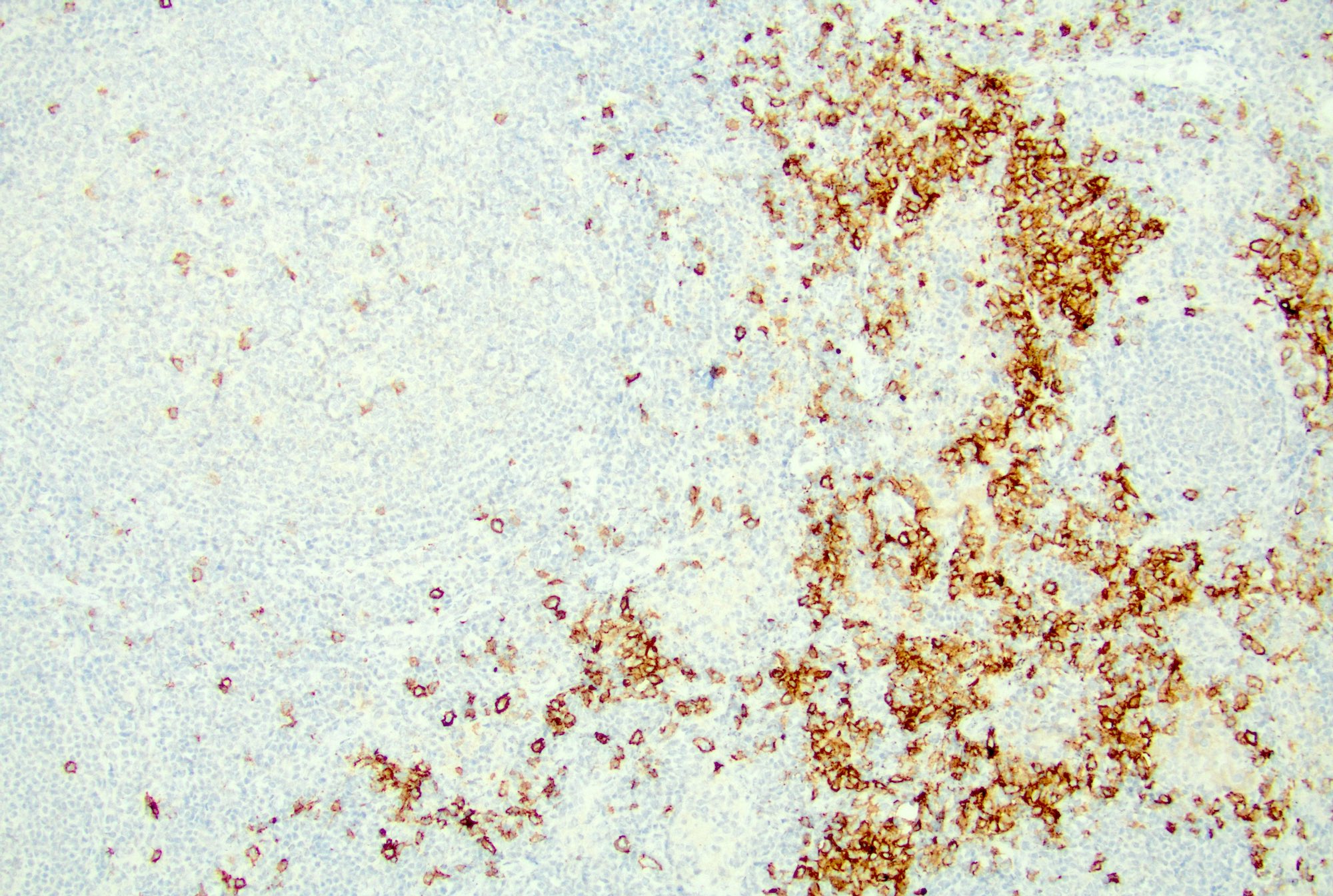
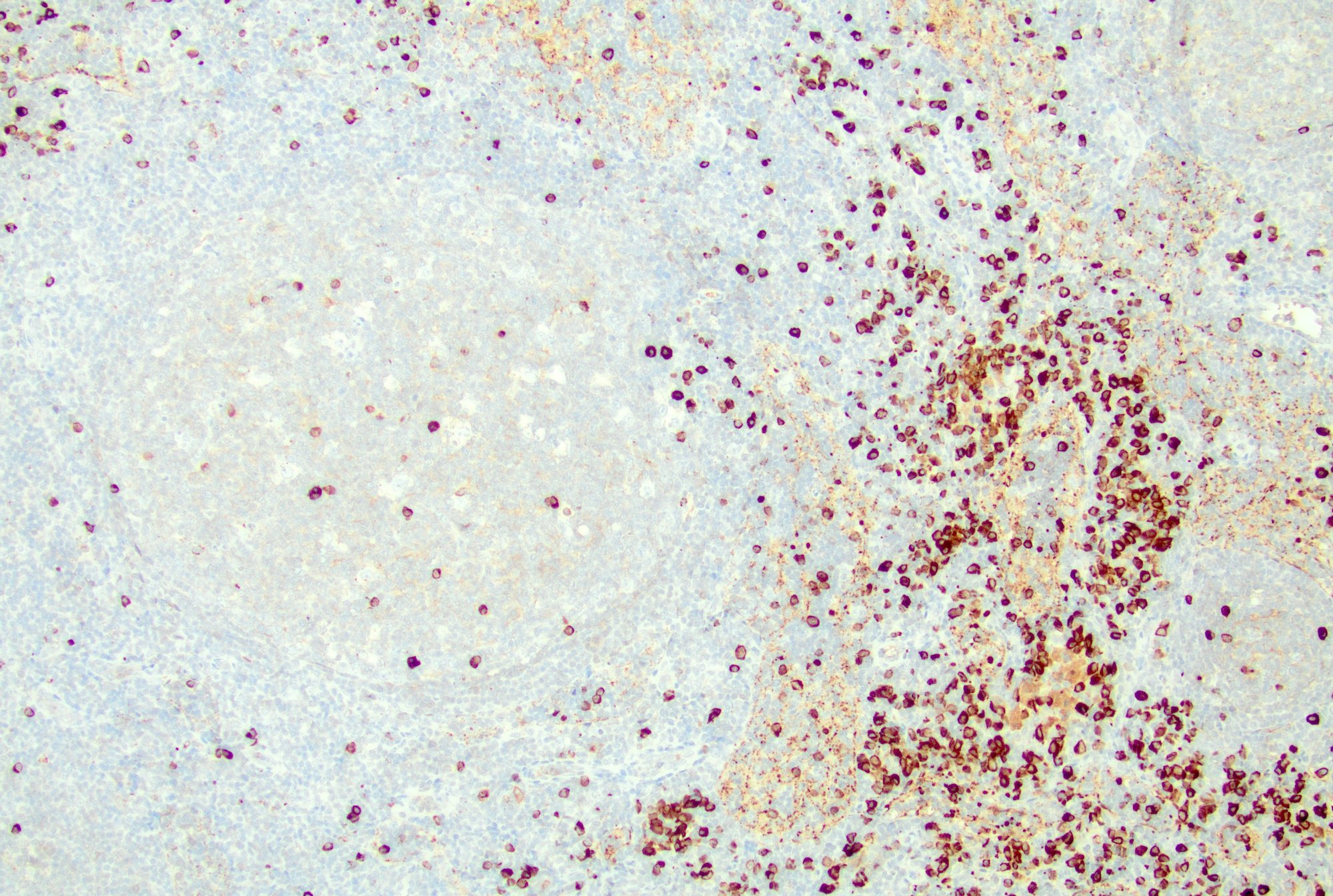
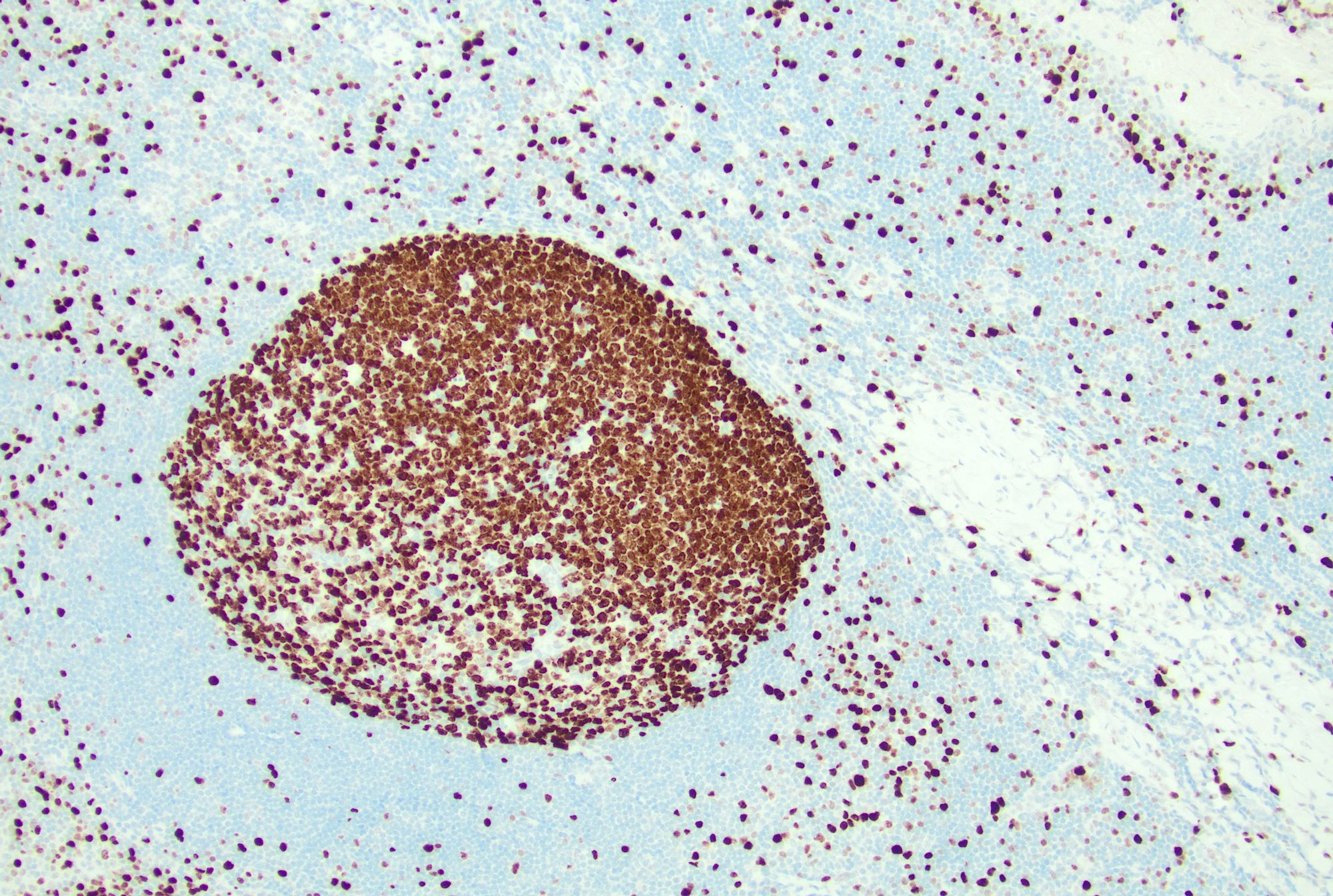
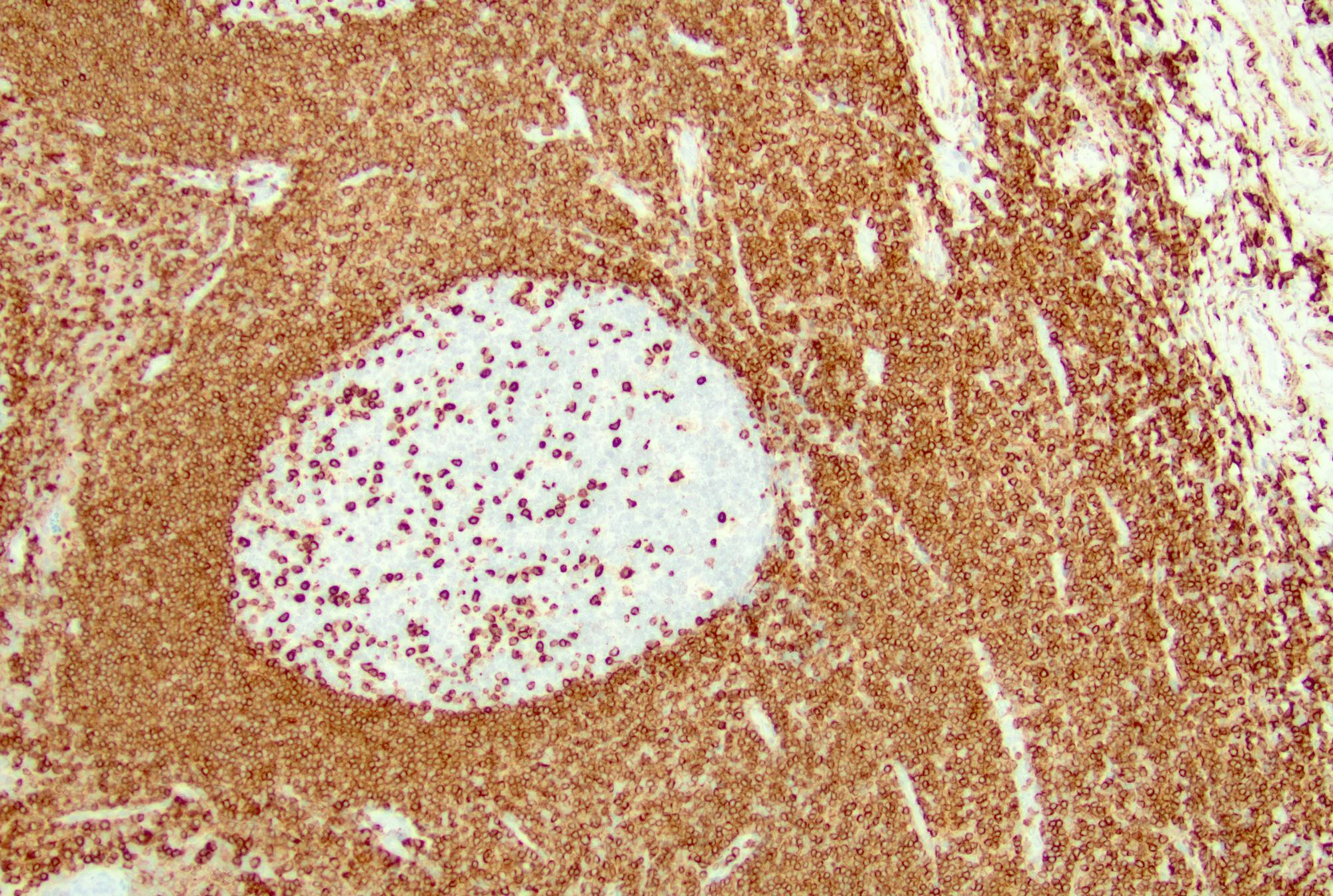
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Jayalakshmi Balakrishna, M.D.
Cytology description
- Cellular smears with mixed small and large lymphocytes, tingible body macrophages and other cell types including histiocytes and follicular dendritic cells
- In acute lymphadenitis, a prominence of neutrophils may be seen
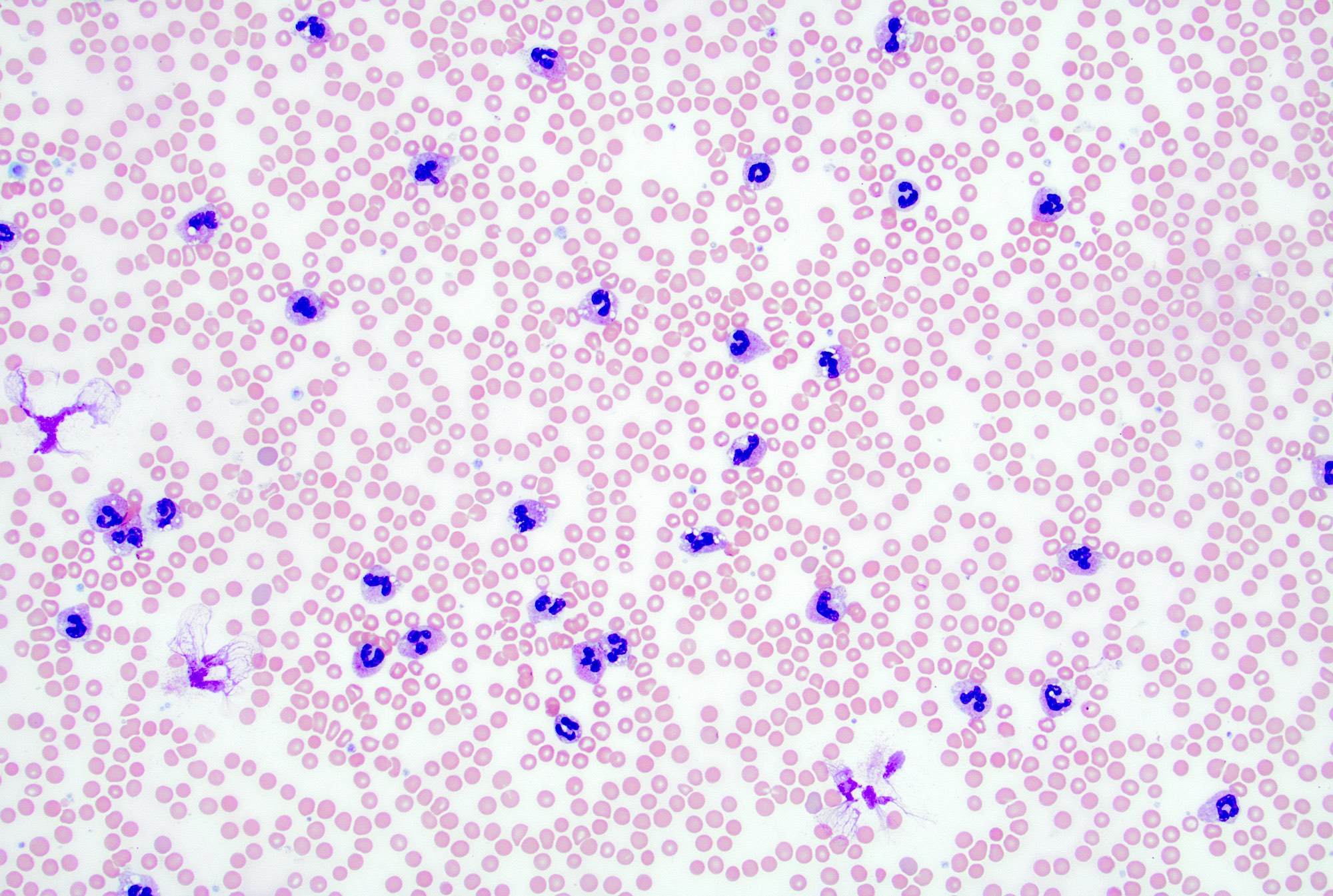
Peripheral smear description
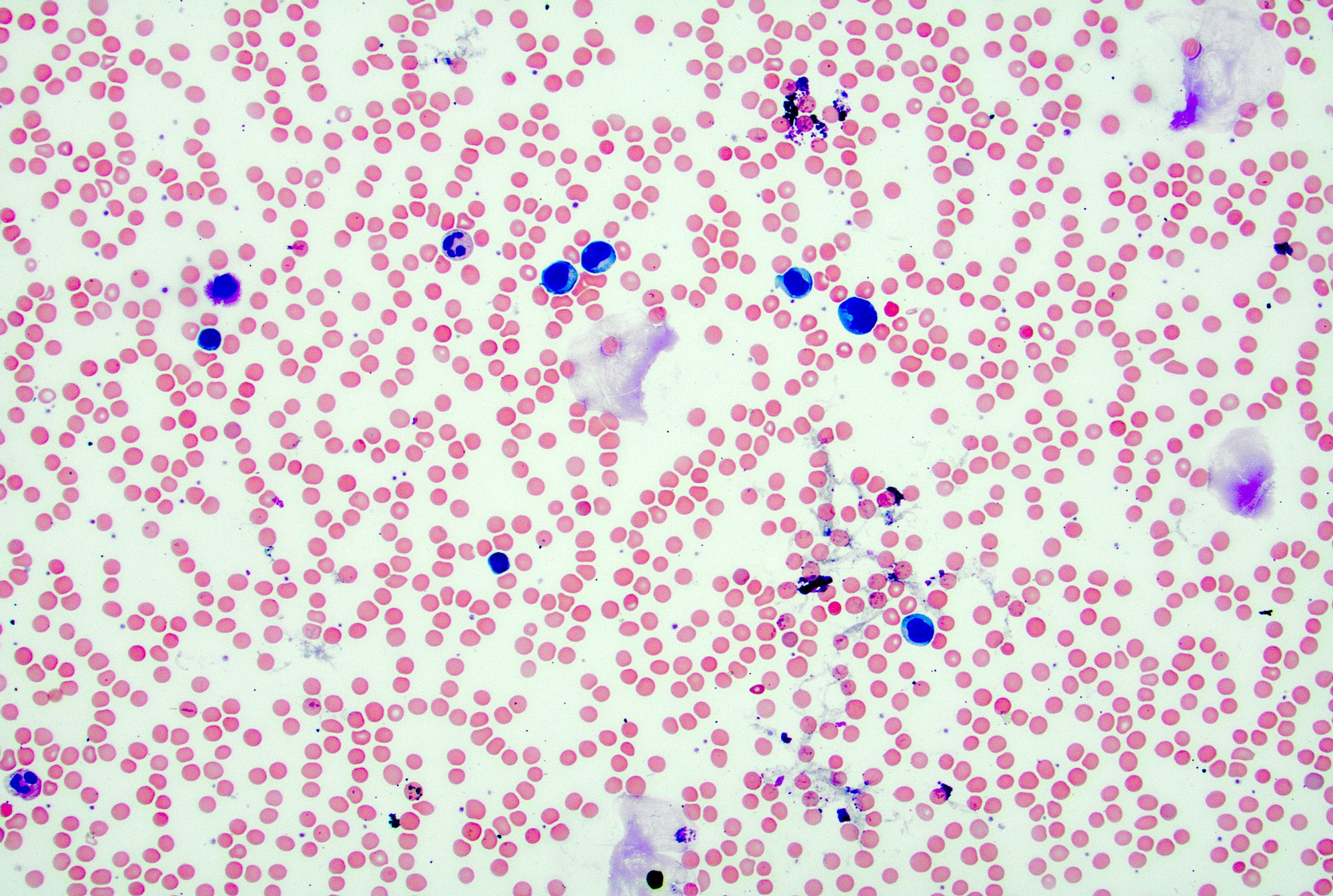
- In reactive lymphadenopathy, peripheral smears may show leukocytosis with either lymphocytosis or neutrophilia, depending on the underlying cause
Peripheral smear images
Positive stains
- Follicles: positive for pan-B cell markers, such as CD19, CD20, CD22, CD79a, PAX5
- Germinal centers: positive for germinal center markers, such as CD10 and BCL6
- Follicular dendritic cells: positive for CD21, CD23
- T cells: CD3, CD4, PD-1
- Plasma cells: CD138
- Paracortex (T cells): positive for pan-T cell markers, such as CD3, CD2, CD5 and CD7, mixed CD4 and CD8 positive T cells
- Immunoblasts: positive for CD30 (StatPearls: Histology, Lymph Nodes [Accessed 4 December 2024])
- Ki67: high proliferation rate in the germinal centers with polarization (dark zone with higher rate of proliferation and light zone with lower rate)
Negative stains
- Germinal center B cells: negative for BCL2
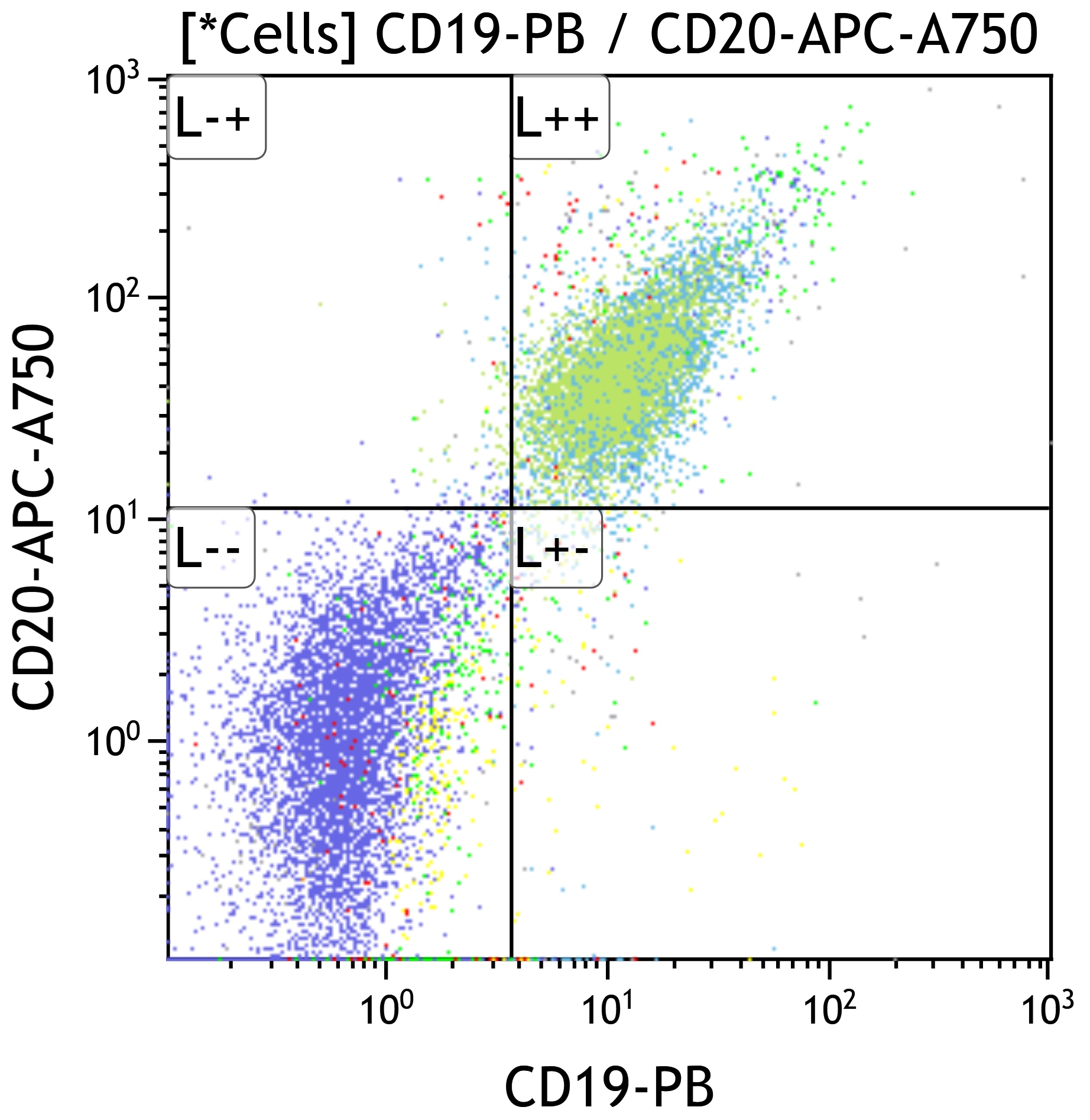
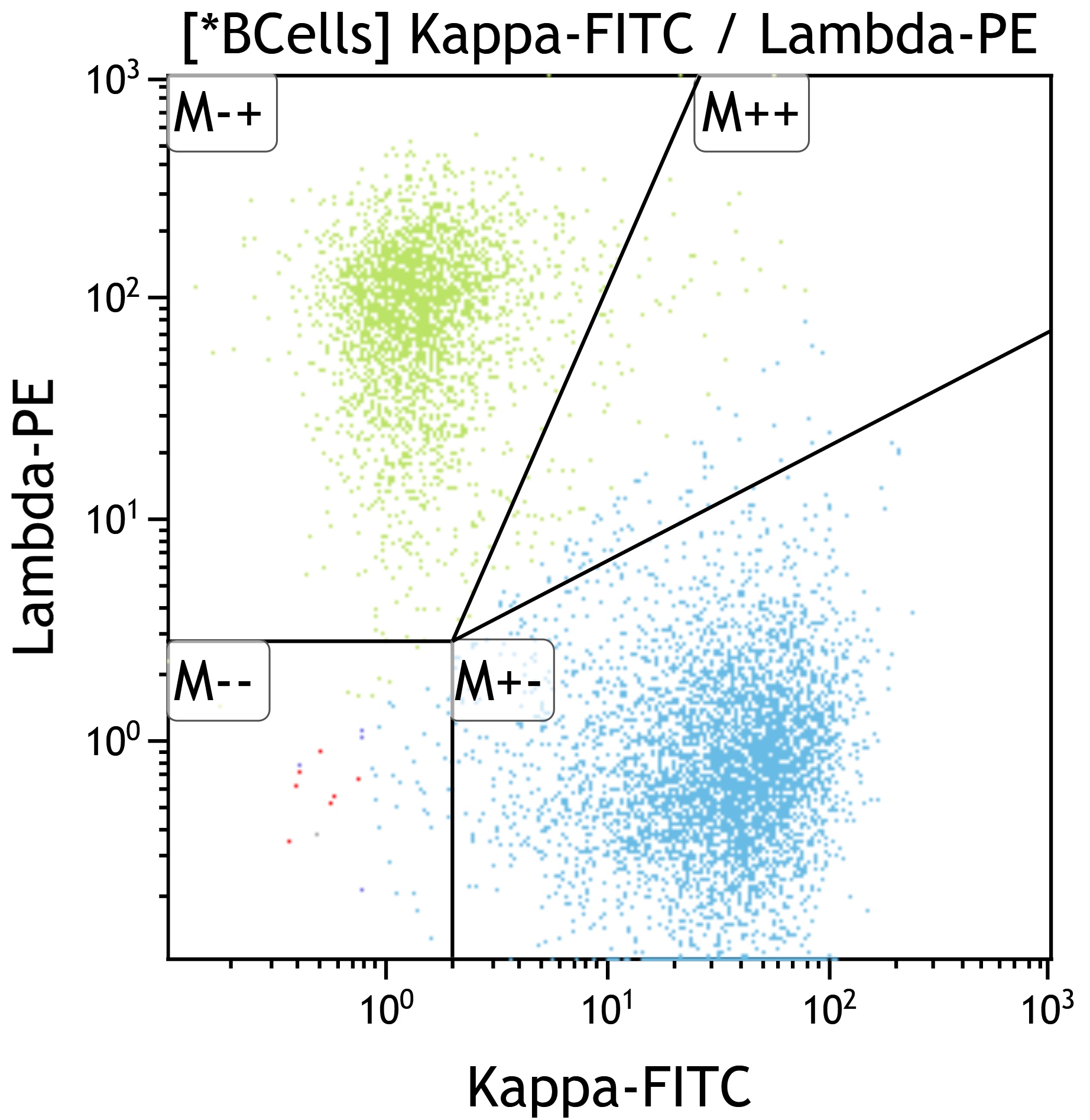
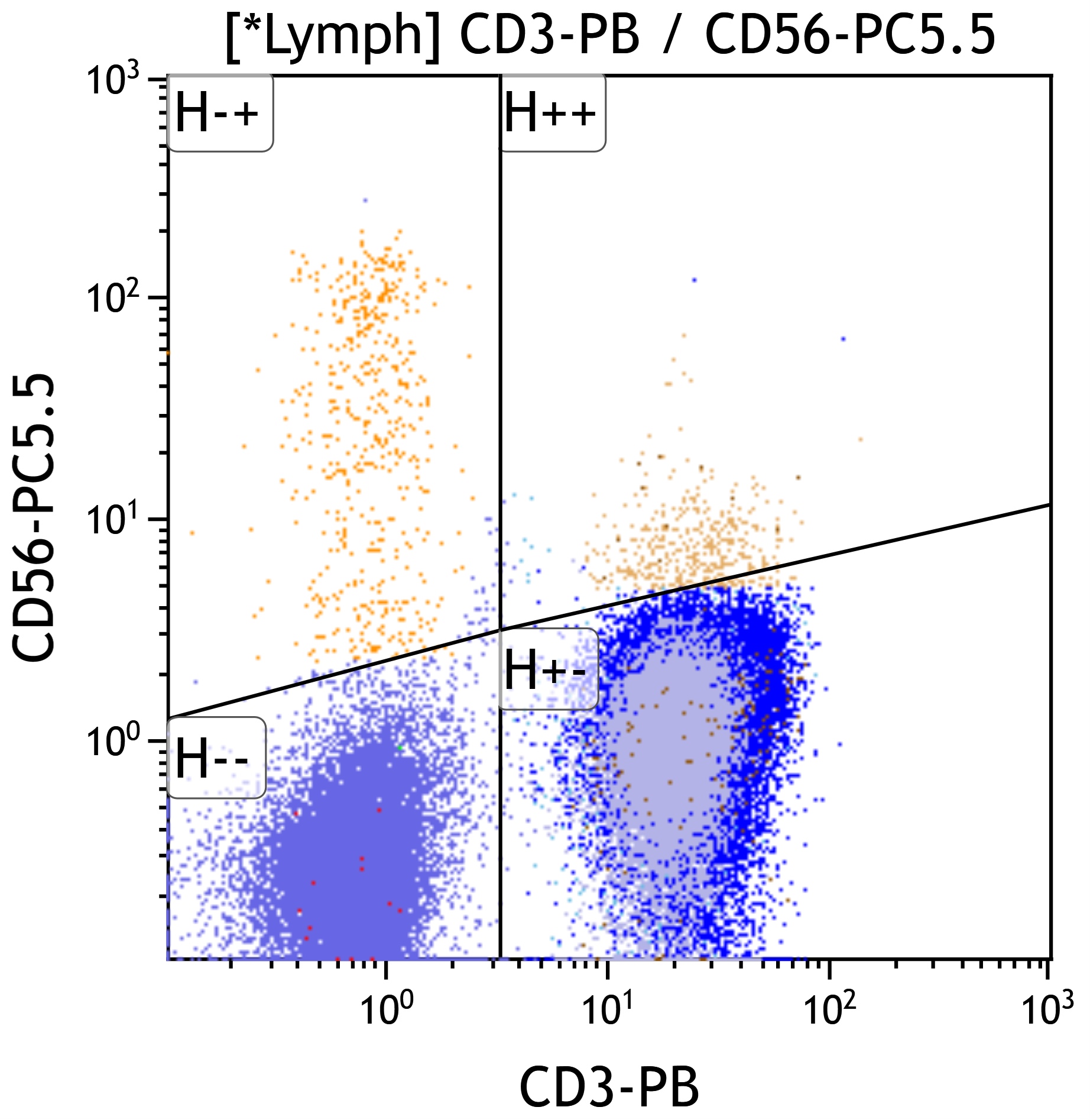
Flow cytometry description
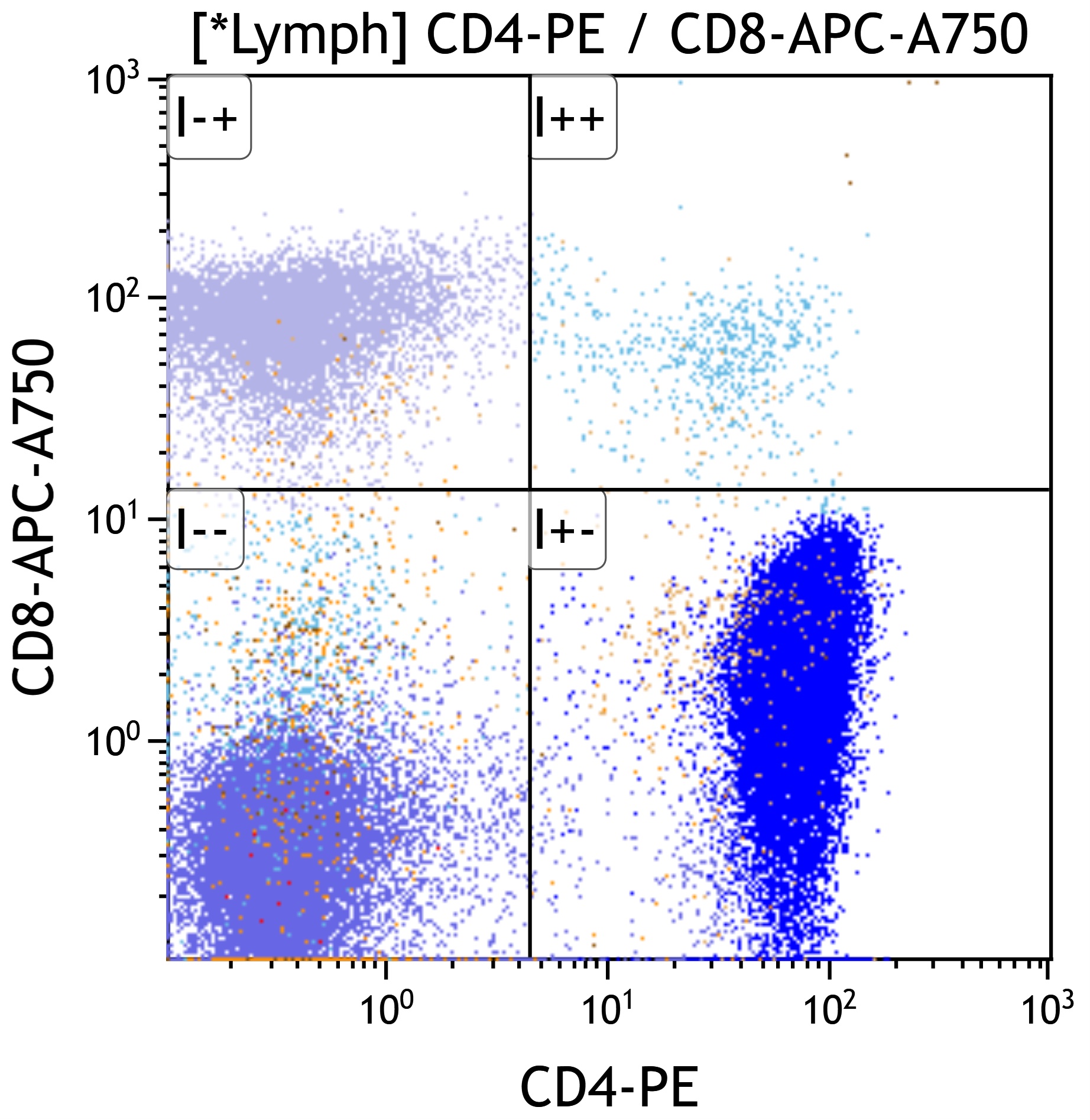
- Mixed B and T cell populations
- T cells typically show mixed CD4+ and CD8+ subsets (Cytopathology 2022;33:505, J BUON 2013;18:739)
- Usually no immunophenotypic aberrancies but rarely clonal CD10+ B cell proliferations are detected by flow cytometry (Am J Clin Pathol 2004;121:464)
- B cells polytypic based on light chain pattern (except rare cases as above)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Polyclonal pattern of B and T cell gene rearrangements
- Negative for cytogenetic or molecular abnormalities
Sample pathology report
- Lymph node, left cervical, needle core biopsy:
- Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia and no morphologic or immunophenotypic evidence of a lymphoproliferative disorder
Differential diagnosis
- Follicular hyperplasia
- Classic follicular lymphoma:
- Effaced architecture, back to back follicles, invasion of capsule or adjacent structures, no polarization of the follicle, no tingible body macrophages, no well defined mantle zones
- Positive for CD10, BCL6 and BCL2, monotypic light chain expression, monoclonal B cell gene rearrangement and presence of t(14;18)
- In situ follicular neoplasia:
- No polarization with bright expression of CD10 and BCL2 in involved germinal centers, monotypic light chain expression, monoclonal B cell gene rearrangement and presence of t(14;18)
- Classic follicular lymphoma:
- Sinus histiocytosis
- Expansion of the sinuses with tumor cells
- Melanoma:
- Positive for S100 and melanocytic markers
- Mesothelioma:
- Positive for WT1 and other mesothelial markers
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma:
- Rosai-Dorfman disease:
- Sinuses with accumulation of histiocytes with enlarged, round to oval hypochromatic nuclei and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, often containing engulfed intact inflammatory cells known as emperipolesis (Am J Surg Pathol 2021;45:35)
- Melanoma:
- Expansion of the sinuses with tumor cells
- Classic Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL):
- Architectural effacement with an inflammatory infiltrate containing large atypical cells with complex nuclear features (Hodgkin / Reed-Sternberg cells) in a mixed background of lymphocytes, histiocytes, plasma cells and eosinophils
- Generally morphologically distinct from reactive conditions but cases with partial nodal involvement, primarily interfollicular involvement or more mononuclear Hodgkin / Reed-Sternberg (HRS) forms can create diagnostic challenges
- Prolonged or atypical EBV associated lymphadenitis may develop and be observed on biopsy evaluation (Mod Pathol 2012;25:1149)
- EBV+ CHL can be distinguished based on cytologic atypia; EBER expression should be exclusive to the HRS cells
- Immunosuppression related and EBV associated lymphoproliferations:
- May show greater variation in morphology and marker expression
- Morphology may range from hyperplasias to polymorphic lymphoproliferative disorders to morphologic lymphoma
- Caution is advised in this setting, including correlation with clinical and radiographic status, type of immune suppression and whether the proliferation is viral associated (Leukemia 2022;36:1720)
- Specific causes of lymphadenitis need to be ruled out
- Acute:
- Lymphogranuloma venereum, cat scratch disease, bubonic plague, tularemia, anthrax, typhoid fever, melioidosis
- Chronic:
- Tuberculosis, leprosy, atypical mycobacteria, syphilis, fungal or parasitic infections:
- Special stains for the causative microorganisms will be positive
- Tuberculosis, leprosy, atypical mycobacteria, syphilis, fungal or parasitic infections:
- Acute:
Additional references
Board review style question #1
If a biopsy were performed, which morphologic feature would best differentiate an EBV+ classic Hodgkin lymphoma from an acute EBV lymphadenitis?
- Cytologic atypia in CD30+ cells
- Lack of detection of EBV protein EBNA2
- Paracortical expansion
- Positivity by CISH for EBV encoded RNA (EBER)
Board review style answer #1
A. Cytologic atypia in CD30+ cells. Malignant processes involving the lymph node can best be recognized by architectural distortion and cytologic atypia. Hodgkin / Reed-Sternberg cells in classic Hodgkin lymphoma will show complex nuclear features and express CD30, CD15 (often) and dim PAX5. When EBV associated, they will express EBER and EBV LMP1.
Answer B is incorrect because Hodgkin / Reed-Sternberg cells may express EBER and LMP1 but are always negative for EBNA2. EBNA2 may be expressed in EBV associated lymphadenitis but is not always present.
Answer D is incorrect because EBER can be expressed (although with different patterns) in EBV+ lymphadenitis as well as EBV+ classic Hodgkin lymphoma.
Answer C is incorrect because paracortical expansion can be seen in both reactive conditions and lymphoma. EBV+ lymphadenitis generally shows a paracortical expansion.
Comment Here
Reference: Reactive lymphadenopathy
Comment Here
Reference: Reactive lymphadenopathy
Board review style question #2
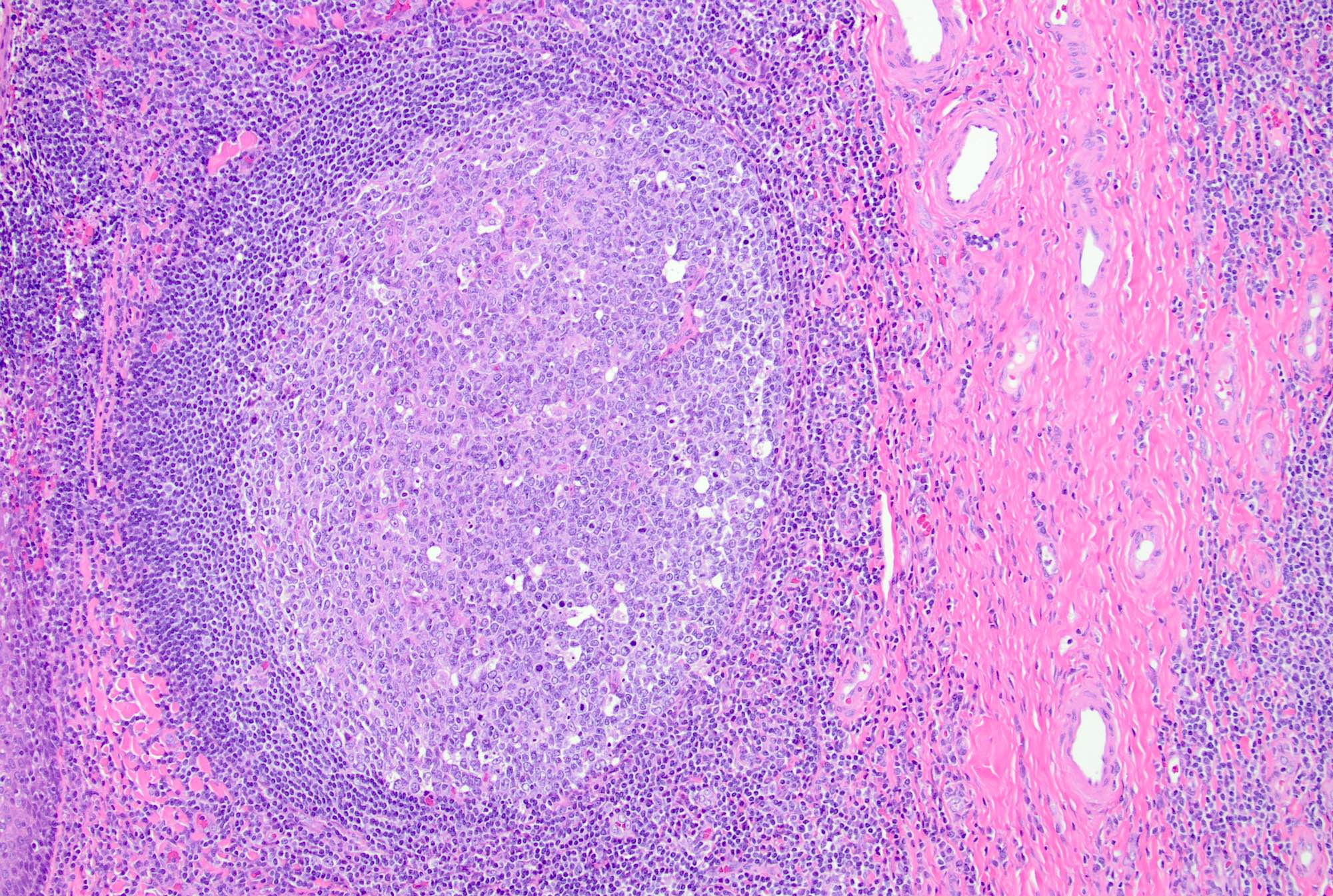
A 10 year old girl presents with bilateral cervical lymph node enlargement. Her parents state that she has had a fever and throat pain for the past few days. On examination, she is found to have multiple enlarged bilateral cervical lymph nodes. The above image shows a low power view of the cervical lymph node biopsy (H&E, 10x). What is the most likely diagnosis based on the H&E image?
- Burkitt lymphoma
- Follicular hyperplasia
- Follicular lymphoma
- Paracortical expansion
Board review style answer #2
B. Follicular hyperplasia. The presence of hyperplastic secondary follicles with prominent germinal centers, which show polarization and tingible body macrophages and mantle zone, is favorable for reactive follicular hyperplasia. Answer C is incorrect because follicular lymphoma shows effaced architecture with back to back follicles, absence of polarization and tingible body macrophages; it also lacks well defined mantle zones. Answer A is incorrect because Burkitt lymphoma is a diffuse proliferation of medium sized atypical lymphoid cells with blastoid morphology and conspicuous 1 - 3 nucleoli. Answer D is incorrect because paracortical hyperplasia is the expansion of interfollicular areas with mixed small lymphocytes, immunoblasts, vessels and interdigitating dendritic cells.
Comment Here
Reference: Reactive lymphadenopathy
Comment Here
Reference: Reactive lymphadenopathy