Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Balakrishna J. Adipose tissue. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphnodesadiposetissuemetaplasia.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Pathological enlargement of lymph nodes caused by abnormal accumulation of fat, due to mature, benign adipocytes within lymph node capsules
Terminology
- Lipo-lymph nodes
- Lipoplastic lymphadenopathy
Epidemiology
- Very common
Sites
- Most commonly involved sites are external iliac and obturator groups
Pathophysiology
- Accumulation of abnormal quantities of fat within lymph nodes in excess of normal aging changes
- Benign process with good prognosis
- Can cause mass effect depending on size
- May mimic lymphoma or other neoplasms
Etiology
- Unknown; postulated causes include exaggeration of normal fat deposition with aging, previous abdominal inflammatory disease, obesity
Clinical features
- Enlarged lymph nodes; may lead to formation of large masses up to 10 cm
Diagnosis
- Lymph node biopsy
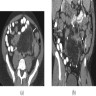
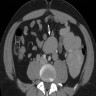
Radiology description
- Progressive enlargement and increased fatty infiltration
- CAT scan and lymphangiography findings can be misleading towards neoplastic process
Case reports
- 47 year old man with abundant macroscopic fat in intra-abdominal lymph nodes (Br J Radiol 2012;85:e91)
- 49 year old woman with lipoplastic lymphadenopathy presenting as an ovarian mass (Gynecol Oncol 1987;28:345)
- 50 year old man with generalized lipomatosis of lymph nodes (Lymphology 1979;12:262)
- Middle aged women with lipolymph nodes of mesentery (Am Surg 1985;51:596)
- Lipoplastic lymphadenopathy simulating lymphoma and pelvic lipomatosis (J Urol 1975;114:788)
- Pelvic and aortic lipolymph nodes (Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1982;61:383)
Treatment
- Excision of involved lymph node in symptomatic cases serves both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes
Clinical images
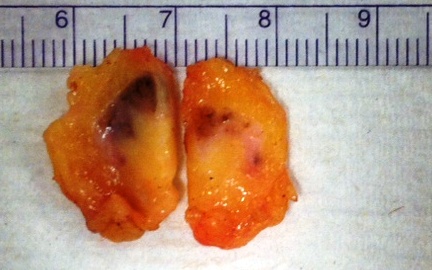
Gross description
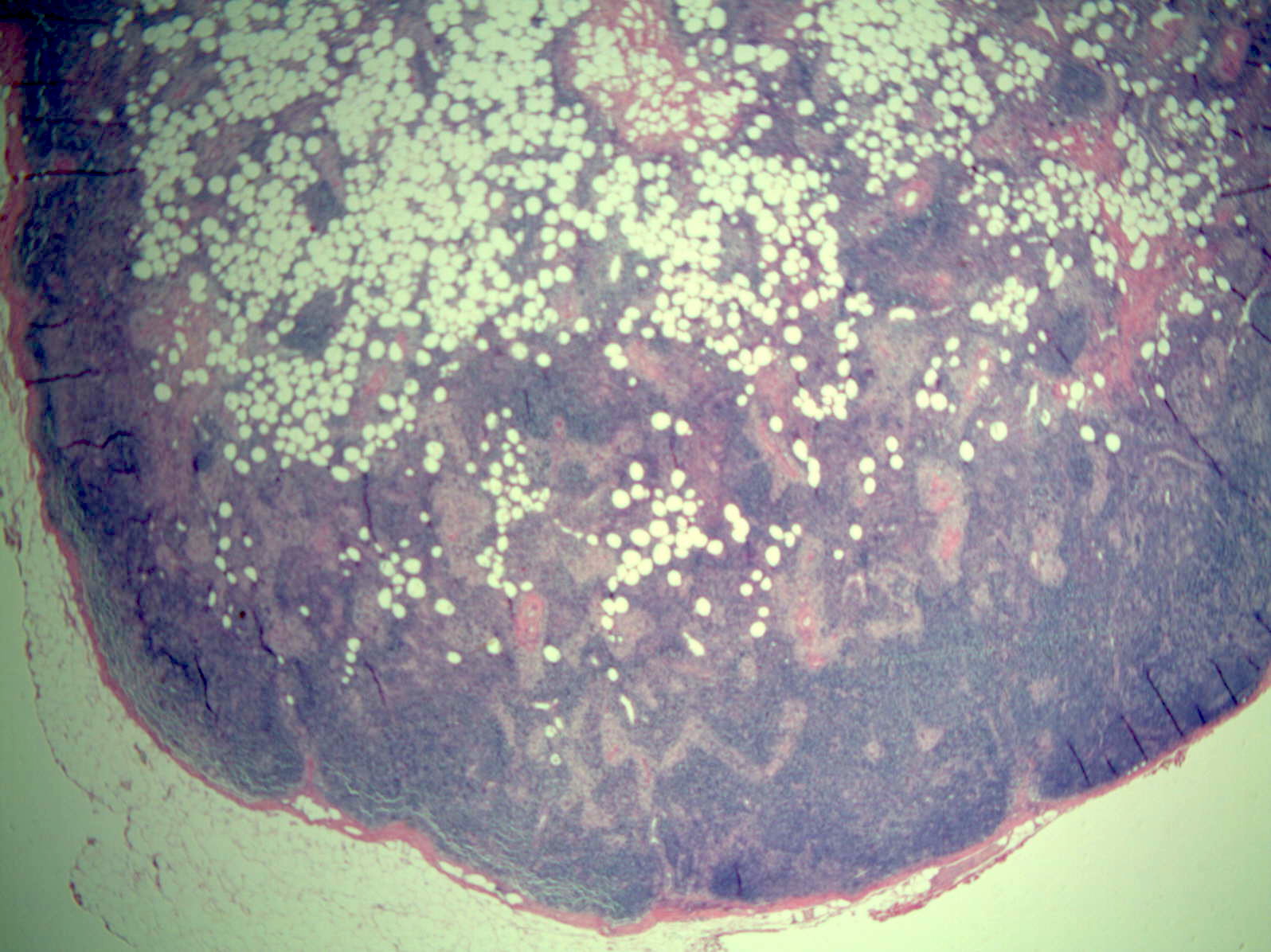
- Enlarged lymph node with soft greasy yellow areas within capsule, or entirely replaced by similar cut surfaces
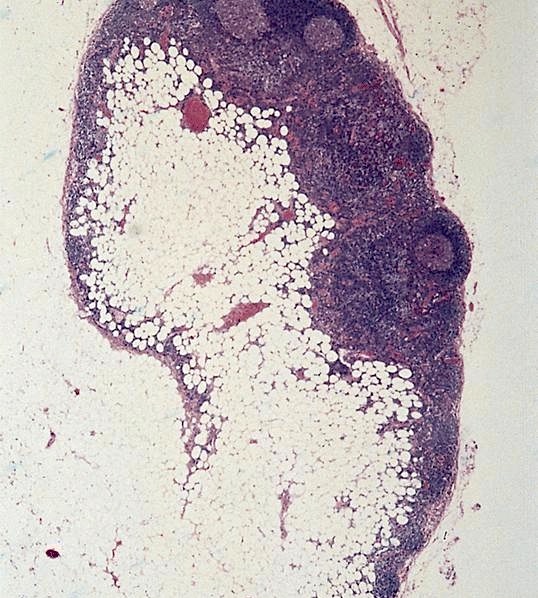
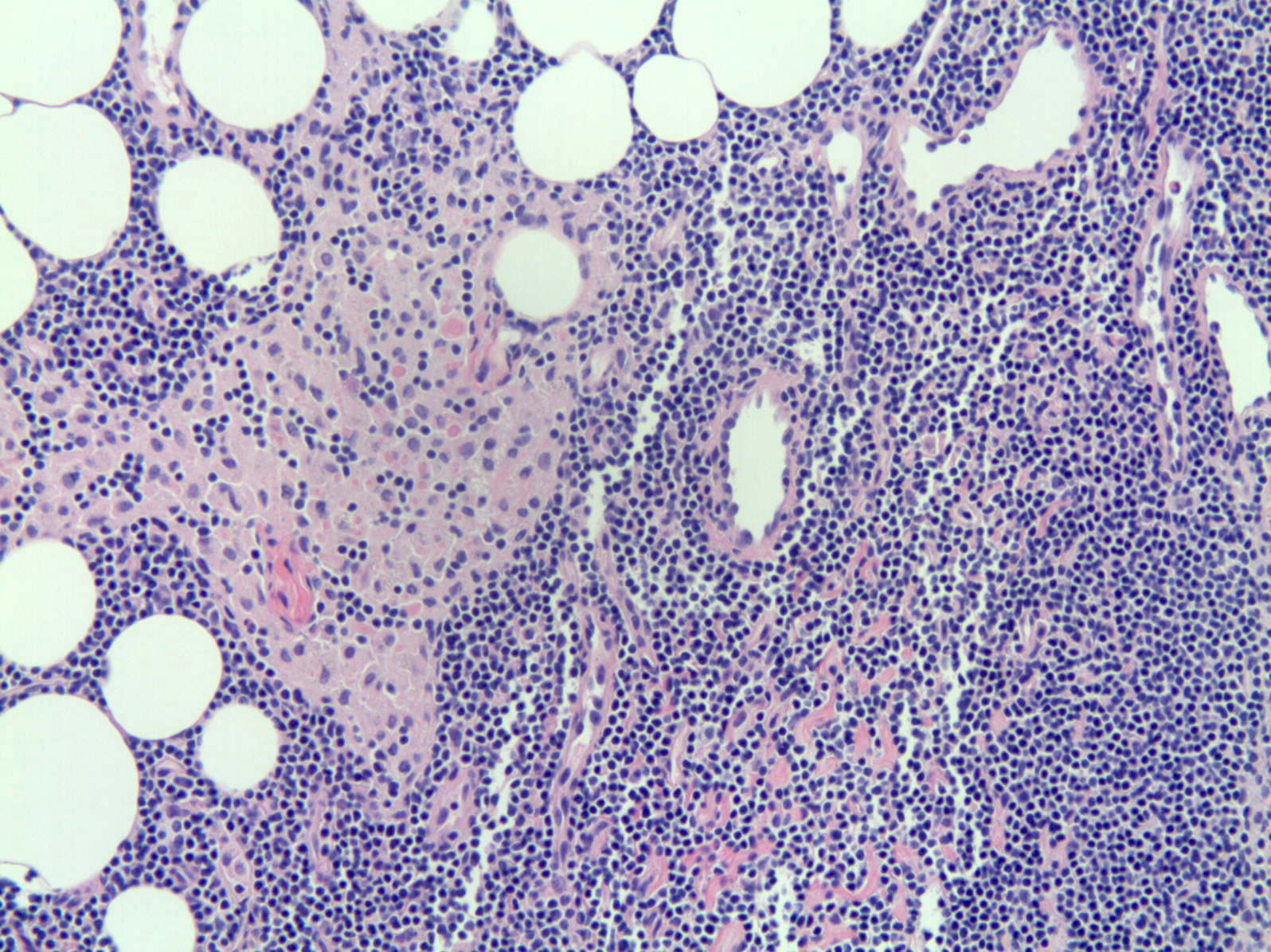
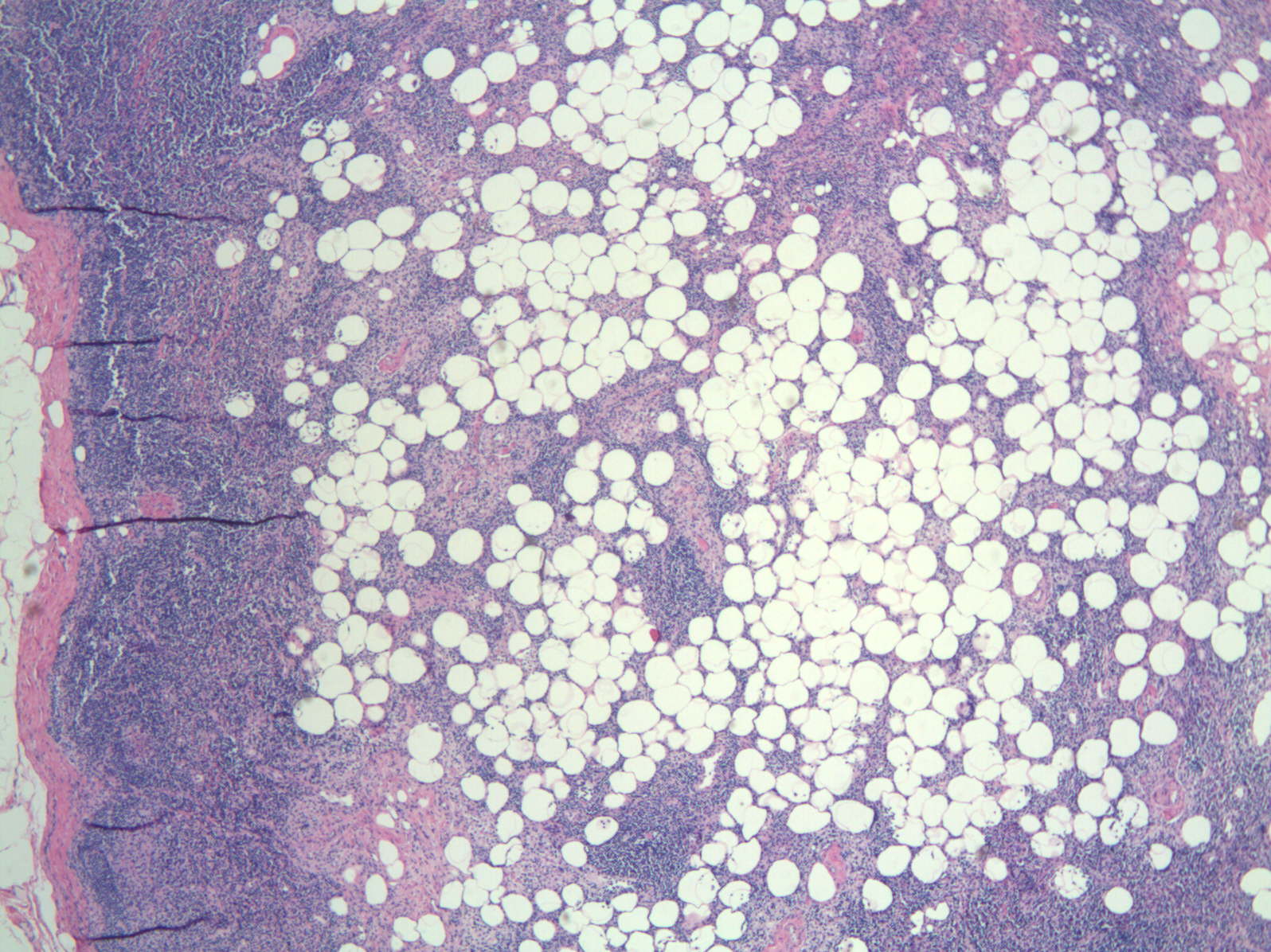
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Benign mature adipocytes populate nodes whose capsules are thinly attenuated with fine vascular trabeculae dividing fat deposits
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Intranodal angiolipoma (Int J Surg Pathol 2005;13:99)
- Other causes of lymphadenopathy: lymphoma, metastases, inflammatory / infectious causes
- Retroperitoneal or pelvic lipomatosis
Additional references