Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Qiao JH. Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lungtumormpmn.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Uncommon incidental pulmonary nodules composed of interstitial nodular proliferation of small oval or spindle shaped cells arranged in a zellballen nesting pattern (J Thorac Imaging 2002;17:227)
Essential features
- Generally detected incidentally in resected lung specimens (Hum Pathol 2009;40:678)
- Occasionally detected on thin section computed tomography (Hum Pathol 2009;40:678)
- More common in patients with malignant pulmonary tumors, especially lung adenocarcinoma, than benign disease (Hum Pathol 2009;40:678)
- No significant difference in clinicopathologic factors between patients with single and multiple nodules, except for the size of each nodule (Hum Pathol 2009;40:678)
Terminology
- Pulmonary chemodectomas were first described by Korn et al. in 1960 (Am J Pathol 1960;37:641)
- In 1988, Gaffey et al. proposed to change the name of pulmonary chemodectomas to minute meningothelial-like nodules (Am J Surg Pathol 1988;12:167)
- Terminology includes
- Pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules (PMLNs)
- Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules (MPMNs)
- Pulmonary chemodectoma
- MPMN-omatosis syndrome
- Diffuse pulmonary meningotheliomatosis (DPM)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: R91.1 - solitary pulmonary nodule
Epidemiology
- F > M (10.7% versus 4.5%) (Hum Pathol 2009;40:678)
- Most frequent in the sixth decade
- Absent in fetuses, infants and children, indicating that they do not represent congenital rests
- Reported incidence is 0.3 to 9.5% at autopsy or in surgical specimens (Korean J Pathol 2012;46:87)
Sites
- Present in all lobes; incidence is not different between lobes (Hum Pathol 2009;40:678)
Pathophysiology
- Usually asymptomatic but can occasionally manifest as mild restrictive lung disease (Respiration 2013;86:145)
Etiology
- Although recognized for decades, their nature and significance remain uncertain (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:487)
Clinical features
- Patients are usually asymptomatic, as the behavior is benign (Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul) 2013;75:67)
Diagnosis
- Often identified as incidental findings in histopathological lung sections or in high resolution CT scans conducted for unrelated causes (Korean J Pathol 2012;46:87)
Radiology description
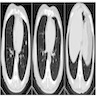
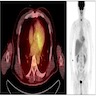
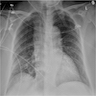
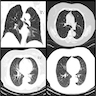
- Thin section chest CT reveals randomly distributed, well defined ground glass appearance micronodules, which may simulate metastatic disease (J Comput Assist Tomogr 2001;25:311)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Found more often in patients with malignant pulmonary tumors, especially lung adenocarcinoma (Korean J Pathol 2012;46:87)
Case reports
- 52 year old man with 1 cm nodule in the left lower lobe discovered on CT scan (Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul) 2013;75:67)
- 56 year old woman with left mastectomy for breast cancer (Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi 2002;40:499)
- 65 year old diabetic woman with breast cancer and smoking history (Korean J Pathol 2012;46:87)
- 74 year old asymptomatic woman with incidentally detected diffuse bilateral pulmonary nodules (Respirol Case Rep 2017;5:e00238)
- 75 year old woman with a history of invasive rectal adenocarcinoma (Ann Saudi Med 2013;33:400)
- Multiple incidentally detected, randomly distributed, cavitating micronodules (J Comput Assist Tomogr 2010;34:780)
Treatment
- Although curative surgical excision is sometimes needed, these usually run a benign course and conservative treatment is favored (Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul) 2013;75:67)
Gross description
- 1 - 3 mm, tan to yellow, pleural or parenchymal nodules (Am J Surg Pathol 1988;12:167)
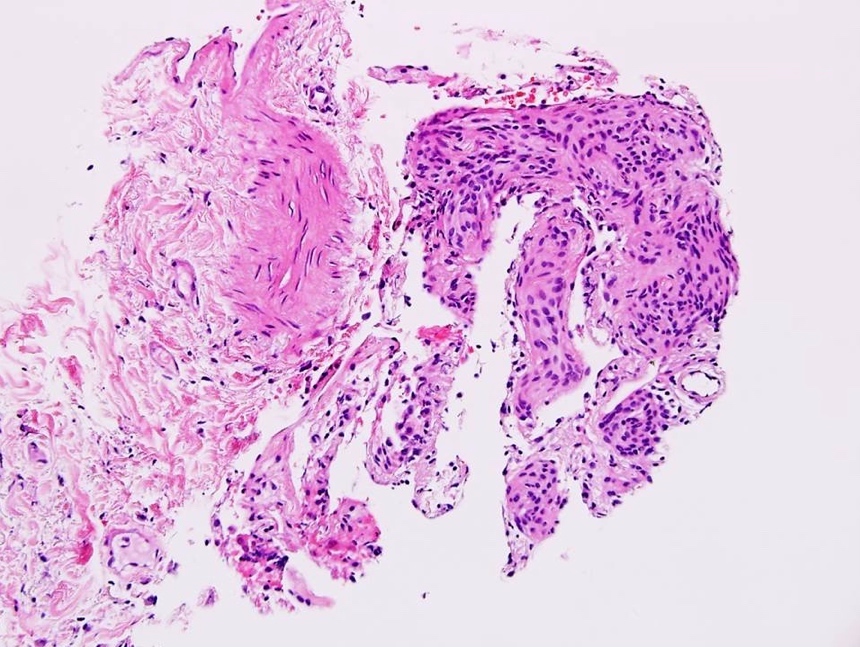
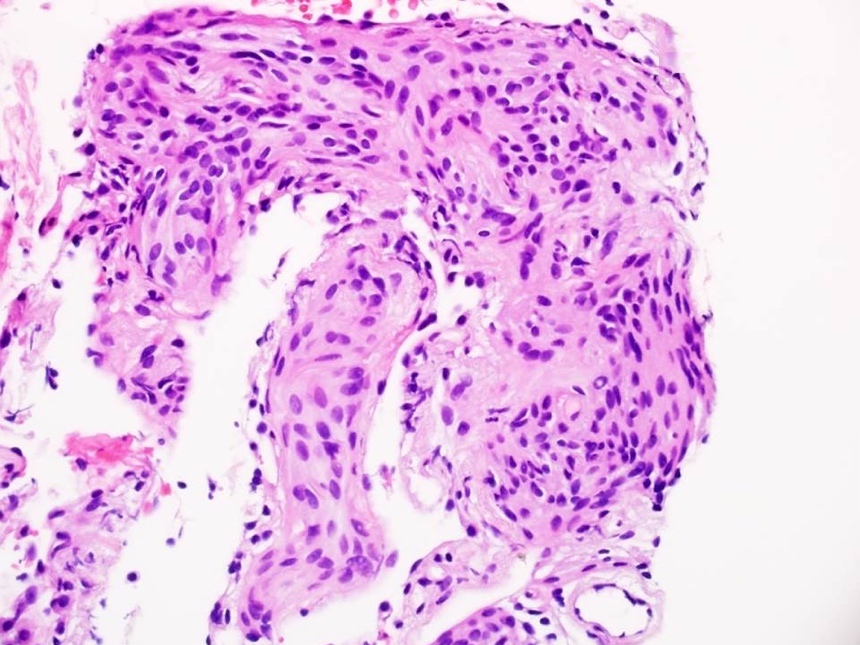
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Characteristic nests of bland spindle cells with pale eosinophilic cytoplasm expand alveolar septa
- Larger lesions connected by intervening collagen, often imparting a stellate configuration
- Smaller lesions have closely apposed nests with mildly thickened alveolar septa (Am J Surg Pathol 1988;12:167)
Microscopic (histologic) images
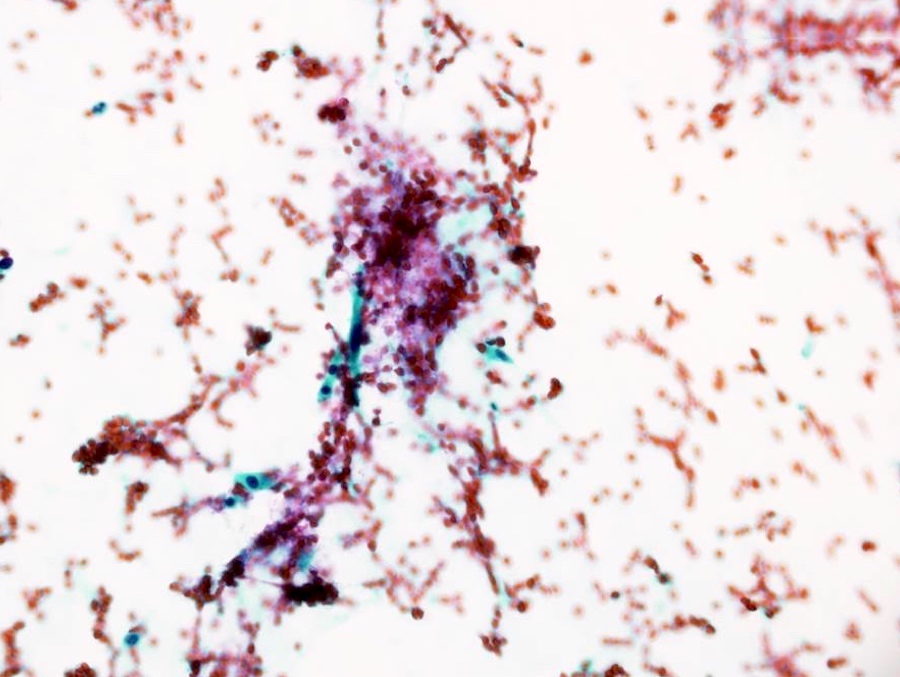
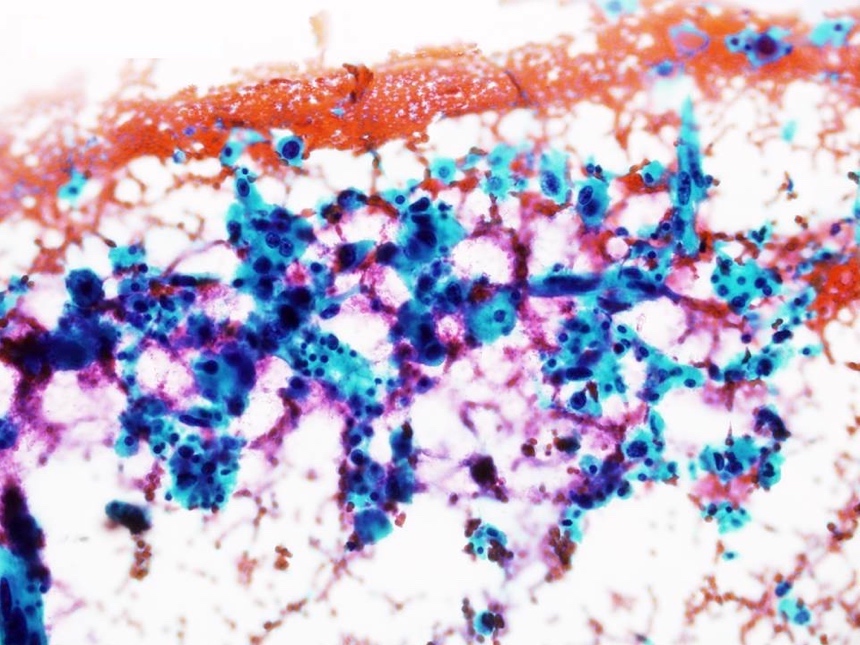
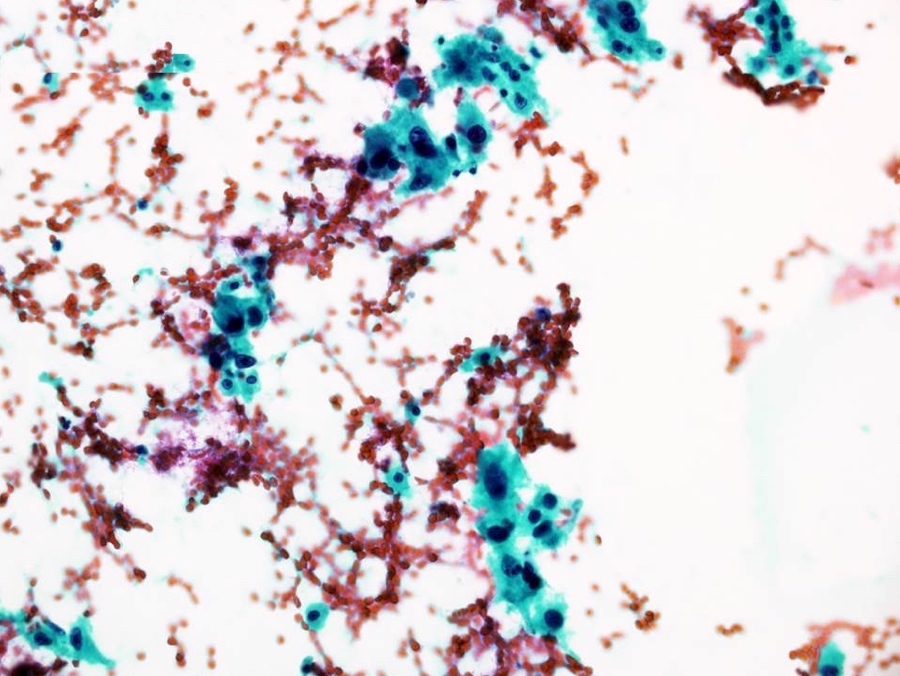
Cytology description
- Single as well as clusters of bland spindle cells are present in aspirate smears
- However, marked cellular atypia is often seen with cytology diagnosis of atypical / suspicious for malignancy / positive for malignancy
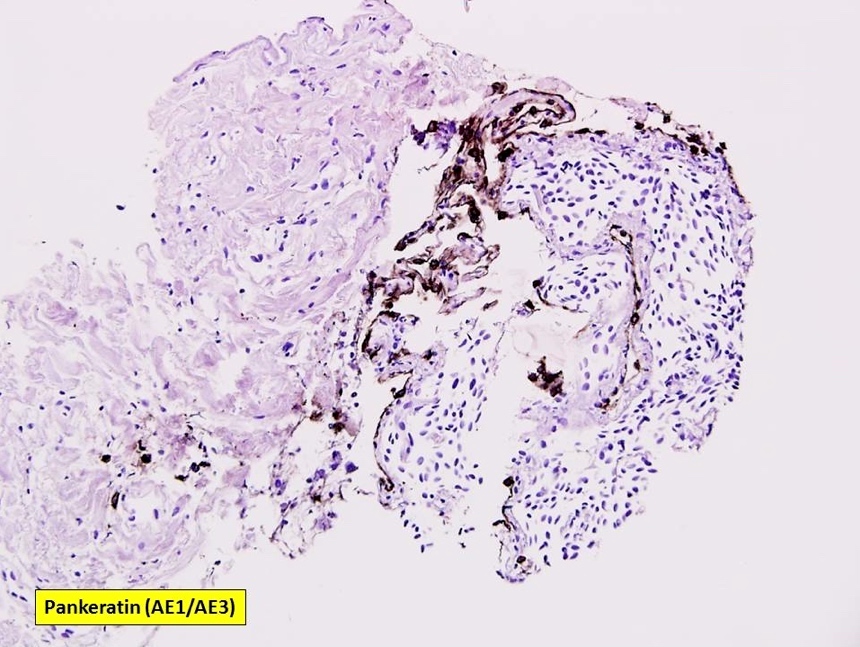
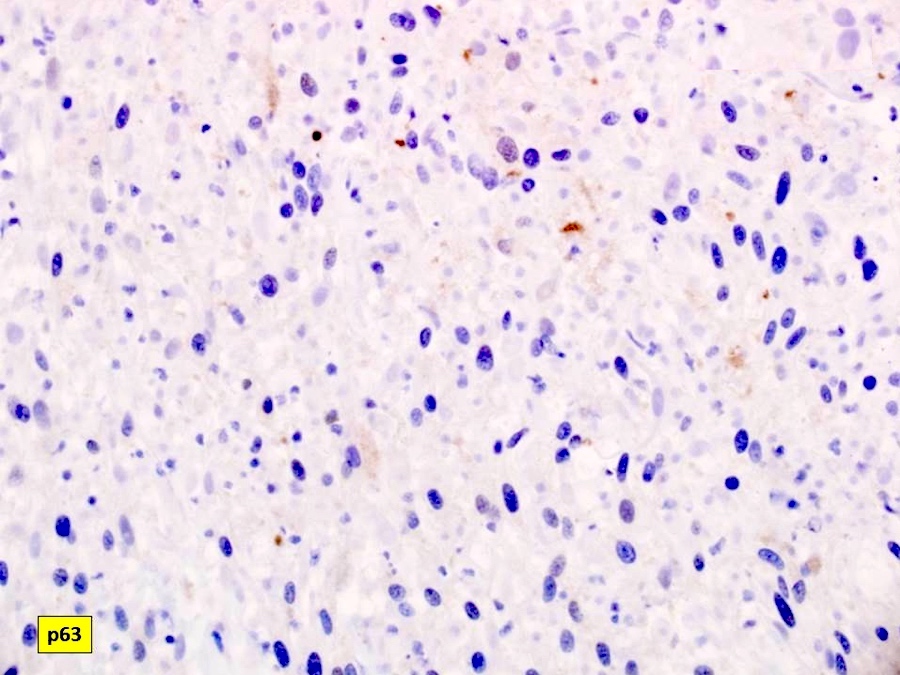
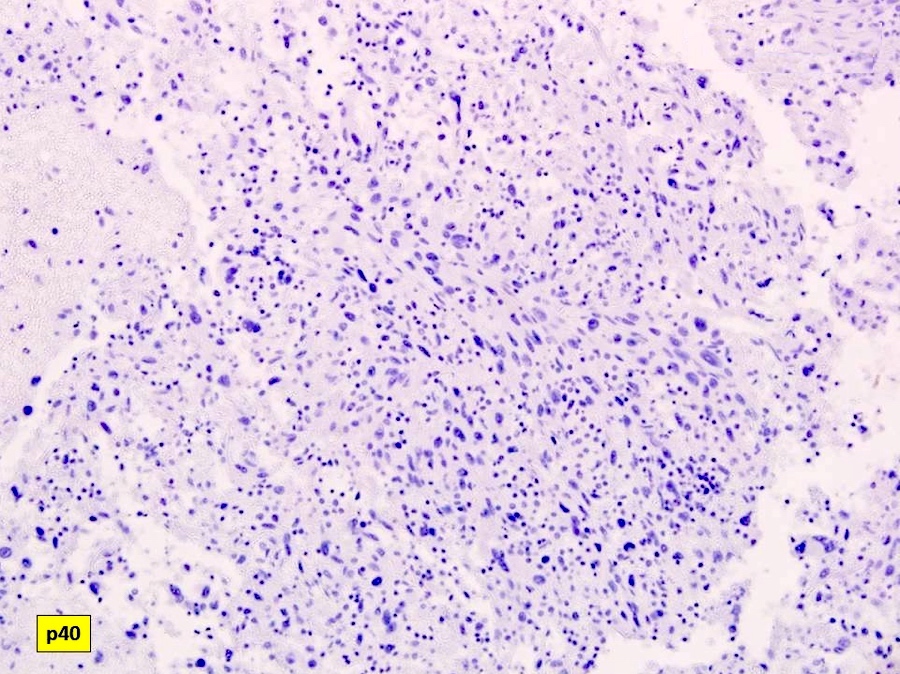
- Immunohistochemistry of cell block will rule out the possibility of carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma since the spindle cells are negative for pankeratin (AE1 / AE3), p63 and p40
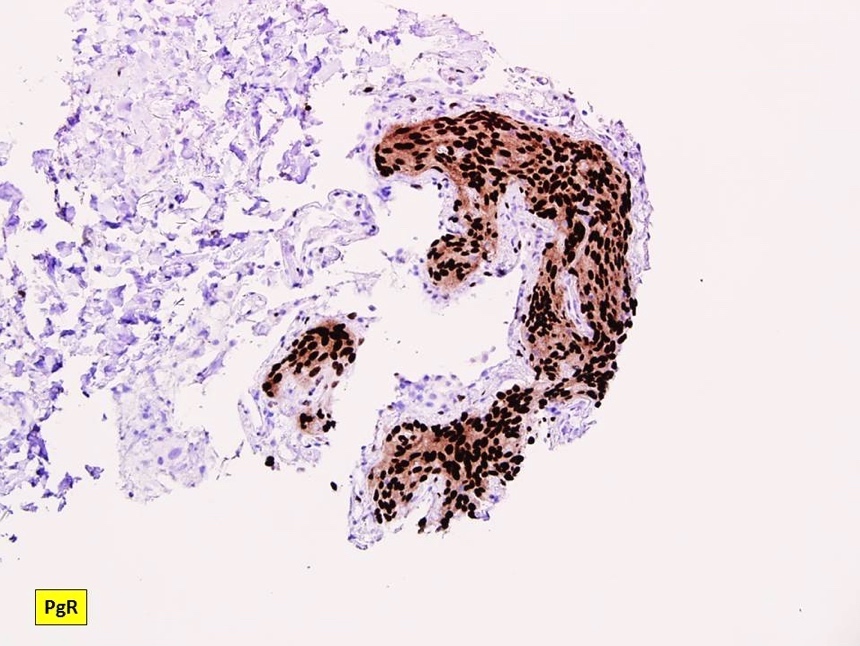
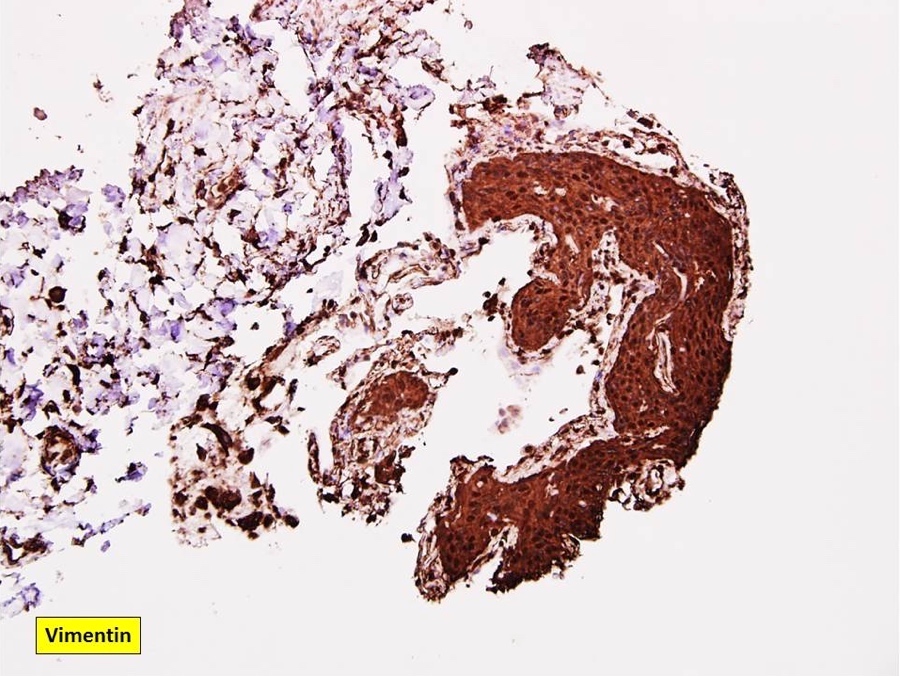
Positive stains
Negative stains
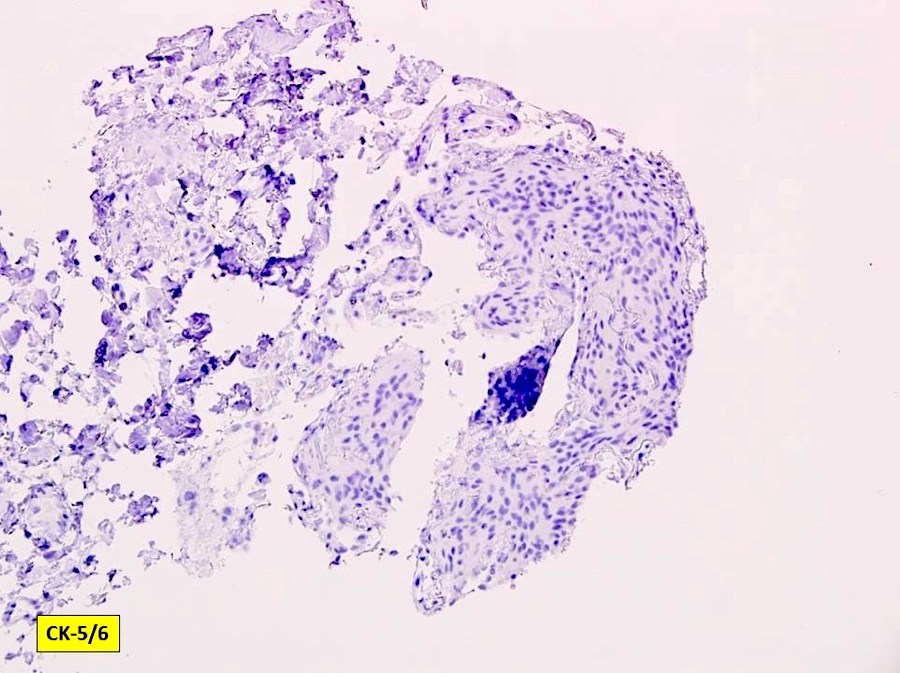
- Pankeratin (AE1 / AE3), CK5 / 6, estrogen receptor / ER, HER2 nonbreast, GCDFP-15, p63, p40, synaptophysin
Electron microscopy description
- Ultrastructural features include interdigitating cellular junctions, desmosomes and scattered intracytoplasmic filaments (Korean J Pathol 2012;46:87)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Mutational analyses were performed on microdissected tissue using 20 polymorphic microsatellite markers targeting 11 genomic regions in an effort to identify genetic similarities of MPMN and meningioma (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:207)
- Loss of heterozygosity was identified in 25% of single MPMN affecting 3 genomic loci
- No solitary MPMN had > 1 loss of heterozygosity event
- Multiple loss of heterozygosity were seen only in diffuse pulmonary meningotheliomatosis (MPMN-omatosis syndrome), where 33.3% of MPMNs showed loss of heterozygosity affecting 7 genomic loci
- Meningioma showed the highest frequency of loss of heterozygosity with major events seen at 22q (60%), 14q (42.8%) and 1p (44.4%) that were not shared by MPMN
- MPMNs are different from meningioma based on the major molecular genetic events seen in their formation and progression
- NF2 deletion similar to meningioma found in a limited series (Oncotarget 2018;9:36012)
Sample pathology report
- Left lung, mass, CT guided needle core biopsy:
- Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodule
- Negative for malignancy
- Adjacent lung parenchyma with mild interstitial fibrosis
Differential diagnosis
- Metastatic carcinoma: usually positive for pankeratin (AE1 / AE3)
- Pulmonary carcinoid tumors (or pulmonary tumorlets for lesions < 5 mm): positive for pankeratin (AE1 / AE3), synaptophysin and INSM1 (Histopathology 2018;72:1067)
- Paraganglioma: positive for neuron specific enolase, chromogranin, synaptophysin, CD57 and GFAP
- Pulmonary meningiomas: clonal neoplastic lesions, which usually present as lung masses rather than minute nodules
Additional references
Board review style question #1
An 80 year old Caucasian woman had a thyroid mass and a 1 cm pulmonary lesion. CT guided transthoracic needle biopsy was performed to rule out metastatic tumor. Microscopic examination of core needle biopsy tissue reveals the following lesion. What is your diagnosis?
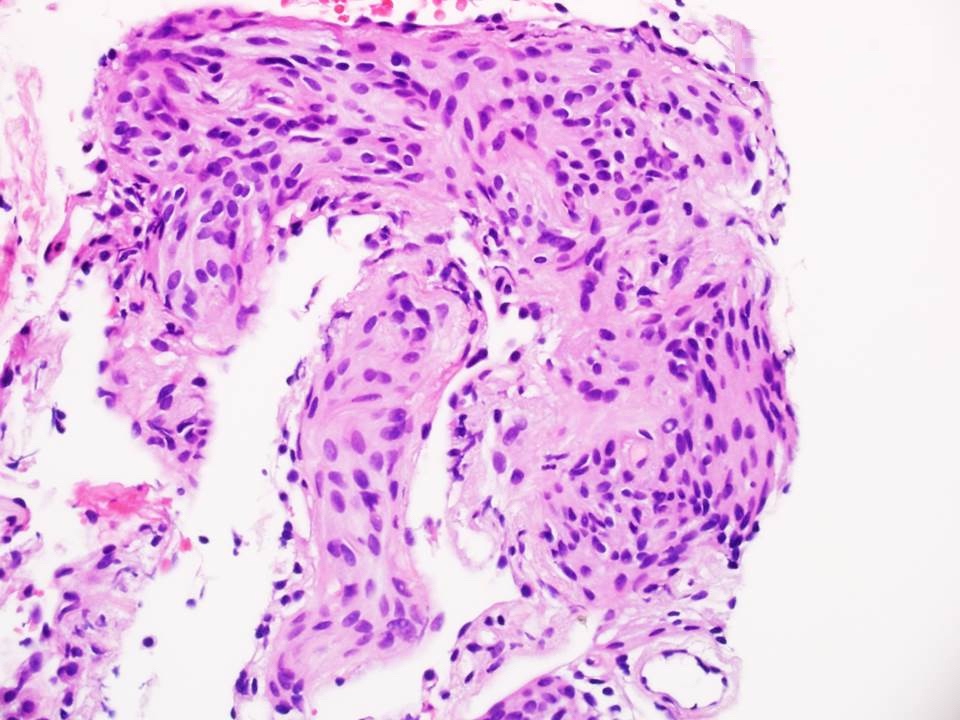

- Metastatic thyroid papillary carcinoma
- Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodule
- Pulmonary carcinoid tumor
- Pulmonary meningioma
- Pulmonary paraganglioma
Board review style answer #1
B. Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodule. Microscopic lesion is classic of pulmonary meningothelial-like nodule, with irregular and uncircumscribed interstitial nests of spindle cells, morphologically similar to meningothelial cells.
Comment Here
Reference: Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules
Comment Here
Reference: Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules
Board review style question #2
Sometimes, immunohistochemistry is necessary to work up this spindle cell lesion. Pulmonary meningothelial-like nodule is most likely positive for which of the following immunostains?
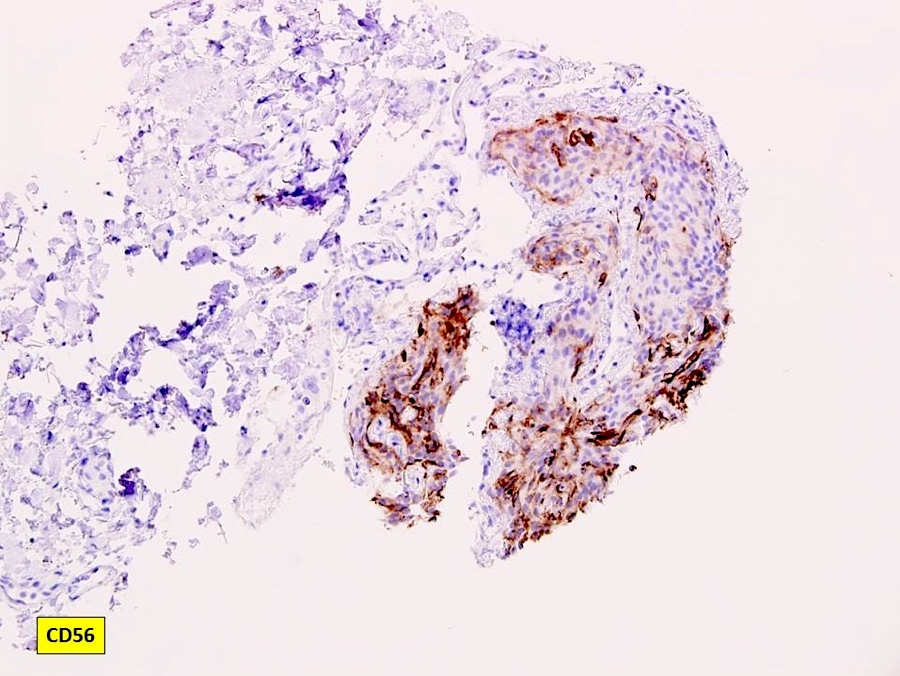
- CD56
- CK5 / 6
- ER
- Pankeratin (AE1 / AE3)
- Synaptophysin
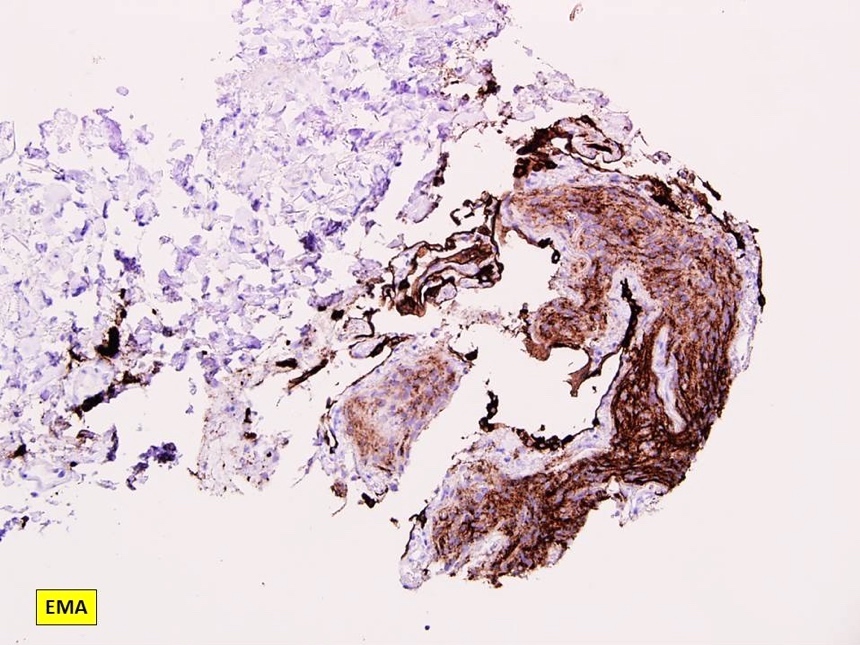
Board review style answer #2
A. CD56. Pulmonary meningothelial-like nodule is positive for CD56, EMA, progesterone receptor / PR and vimentin.
Comment Here
Reference: Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules
Comment Here
Reference: Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules