Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology / etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology images | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Wu R. Diffuse pulmonary lymphangiomatosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lungtumordiffusepulm.html. Accessed December 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Diffuse proliferation of abnormal, complex lymphatic channels (lymphangiomas) that may involve lung or other organs (Lymphat Res Biol 2011;9:191)
- Pulmonary involvement often accompanied by chylous pleural effusions
- May be progressive and fatal from respiratory failure
Terminology
- Lymphangioma if proliferation is focal
Epidemiology
- Rare condition, typically presents in children and young adults
- No sex predilection
Sites
- Localized to lung / chest or can also involve multiple organs, including bone, spleen, soft tissue, liver
Pathophysiology / etiology
- Progressive disease with recurrent effusions and respiratory failure secondary to infections and chylous accumulation
- Congenital, possibly from abnormal lymphatic development
Clinical features
- Generally presents with dyspnea, wheezing, cough and may be confused with asthma
- Occasionally with chyloptysis or hemoptysis
Diagnosis
- Clinical presentation and imaging findings may suggest diagnosis, particularly if bone involvement is noted
- Most cases diagnosed with open lung biopsy
- Transbronchial biopsy may confirm disease if vesicles seen on bronchoscopy (Clin Radiol 2005;60:921)
Laboratory
- Thoracocentesis may reveal chylous effusion (elevated triglycerides)
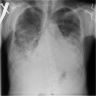
Radiology images
- Xray: nonspecific findings, including pleural effusion, diffuse pulmonary opacities, interstitial thickening
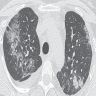
- CT: bilateral ground glass opacities, smooth thickening of interlobular septa, bronchovascular bundles, pleura; may show infiltration of the mediastinal soft tissue by cystic fluid densities
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Children have a worse prognosis than older patients; pleural and lung involvement is adverse prognostic factor (J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2004;26:136)
Case reports
- 4 year old girl with recurrent hemorrhagic pericardial effusion due to diffuse lymphangiohemangiomatosis (J Med Case Rep 2010;4:62)
- 35 year old man with diffuse pulmonary lymphangiomatosis (Basic Appl Pathol 2012;5:63)
- Diffuse pulmonary lymphatic disease presenting as interstitial lung disease in adulthood (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1548)
- Kaposiform lymphangiomatosis (Pediatr Blood Cancer 2015;62:901)
Treatment
- Supportive, including observation and medical management
- Surgical resection for localized disease; pleurocentesis, pleurodesis, pleurodectomy, ligation of thoracic duct (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2007;133:1664)
- Successful lung transplantation has been reported (Am J Transplant 2008;8:1946)
Gross description
- Subpleural and septal thickening
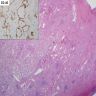
Microscopic (histologic) description
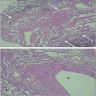
- Diffuse proliferation of complex, anastomotic lymphatic channels without significant dilatation, lined by benign appearing, flattened endothelial cells
- Prominence of lymphatic channels in visceral pleura, interlobular septa, and bronchovascular bundles with surrounding bundles of spindle cells, interspersed collagen, vessels
- Lymphatic channels may contain acellular, eosinophilic, proteinaceous material
- May show hemorrhagic kaposiform component, with compressed vascular channels, plump spindle cells, hemosiderin
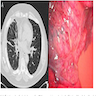
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma
- Kaposi sarcoma: HHV8 positive
- Lymphangiectasis: dilation of existing lymphatics in normal distribution
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: HMB45 positive, more smooth muscle cells
- Pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis