Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Keow J, Cecchini MJ. Minimally invasive. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lungtumoradenominimallyinvasive.html. Accessed March 28th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Primary lung adenocarcinoma measuring ≤ 3 cm in greatest dimension, with ≤ 0.5 cm area of either stromal invasion or nonlepidic growth pattern (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2013;137:685, J Thorac Oncol 2011;6:244)
Essential features
- Tumor with noninvasive (lepidic) and invasive components
- Total tumor size must be less than 3 cm
- Invasive or nonlepidic components must be less than 0.5 cm
- Invasive component can be of any subtype other than lepidic
- No lymphovascular invasion, tumor necrosis or pleural invasion is present
- Usually nonmucinous but can rarely occur in mucinous tumors
Terminology
- Minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA)
- Microinvasive adenocarcinoma
- Older terminology used: bronchoalveolar carcinoma; however, this is obsolete and should no longer be utilized
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8250/2 - minimally invasive adenocarcinoma, nonmucinous (international code)
- ICD-O: 8257/3 - minimally invasive adenocarcinoma, mucinous (international code)
- ICD-10: C34.9 - malignant neoplasm of unspecified part of unspecified bronchus or lung
- ICD-11: XH3QM0 - minimally invasive adenocarcinoma, nonmucinous
- ICD-11: XH2098 - minimally invasive adenocarcinoma, mucinous
Epidemiology
- F > M (Cancer 2014;120:2883)
- More common in Asian populations (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:448)
Sites
- Usually located in the peripheral lung parenchyma (Ann Thorac Surg 2000;69:893, Lung Cancer 2000;29:179)
Pathophysiology
- Hypothesized to form after a multistep progression from atypical adenomatous hyperplasia to adenocarcinoma in situ to minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (J Thorac Oncol 2008;3:340)
Etiology
- Tobacco smoking (Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2015;24:1902; Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2015;63:608)
- However, minimally invasive adenocarcinoma is not as strongly associated with smoking as other subtypes of adenocarcinoma (Int J Mol Sci 2018;19:1259)
Clinical features
- Generally asymptomatic, discovered as incidental mixed solid and ground glass lesions on CT scans (N Engl J Med 2013;368:1980)
Diagnosis
- Slow growing, ground glass opacity (see Radiology description)
- Biopsies will show adenocarcinoma with lepidic growth pattern
- Diagnosis can only be made on the resection specimen and cannot be made with limited tissue sampling (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2013;137:668, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:1027)
Radiology description
- Early lesions may present as a ground glass opacity rather than a solid nodule (J Thorac Oncol 2011;6:244)
- Foci of invasion are generally solid, surrounded by areas with a ground glass opacity (Hum Pathol 2016;51:41, Ann Oncol 2015;26:156)
Prognostic factors
- Minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (pT1mi) has a more favorable prognosis than early stage invasive adenocarcinoma (pT1a) and should be distinguished accordingly (J Clin Oncol 2012;30:1438, J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2013;146:17)
- Since tumor growth is often indolent, a 100% disease free survival may be achieved if completely resected (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:448)
Case reports
- 12 year old girl in posttreatment for a rhabdomyosarcoma developed a minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (Pediatr Blood Cancer 2016;63:344)
- 13 year old boy in posttreatment for osteosarcoma developed a minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2013;16:387)
- 64 year old woman with a resected minimally invasive adenocarcinoma and adenocarcinoma in situ (Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann 2019;27:45)
Treatment
- Surgical excision with close followup (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:448, Clin Lung Cancer 2016;17:e57)
- Adjuvant therapies are generally not indicated (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2017;154:1100, Surg Today 2015;45:1341)
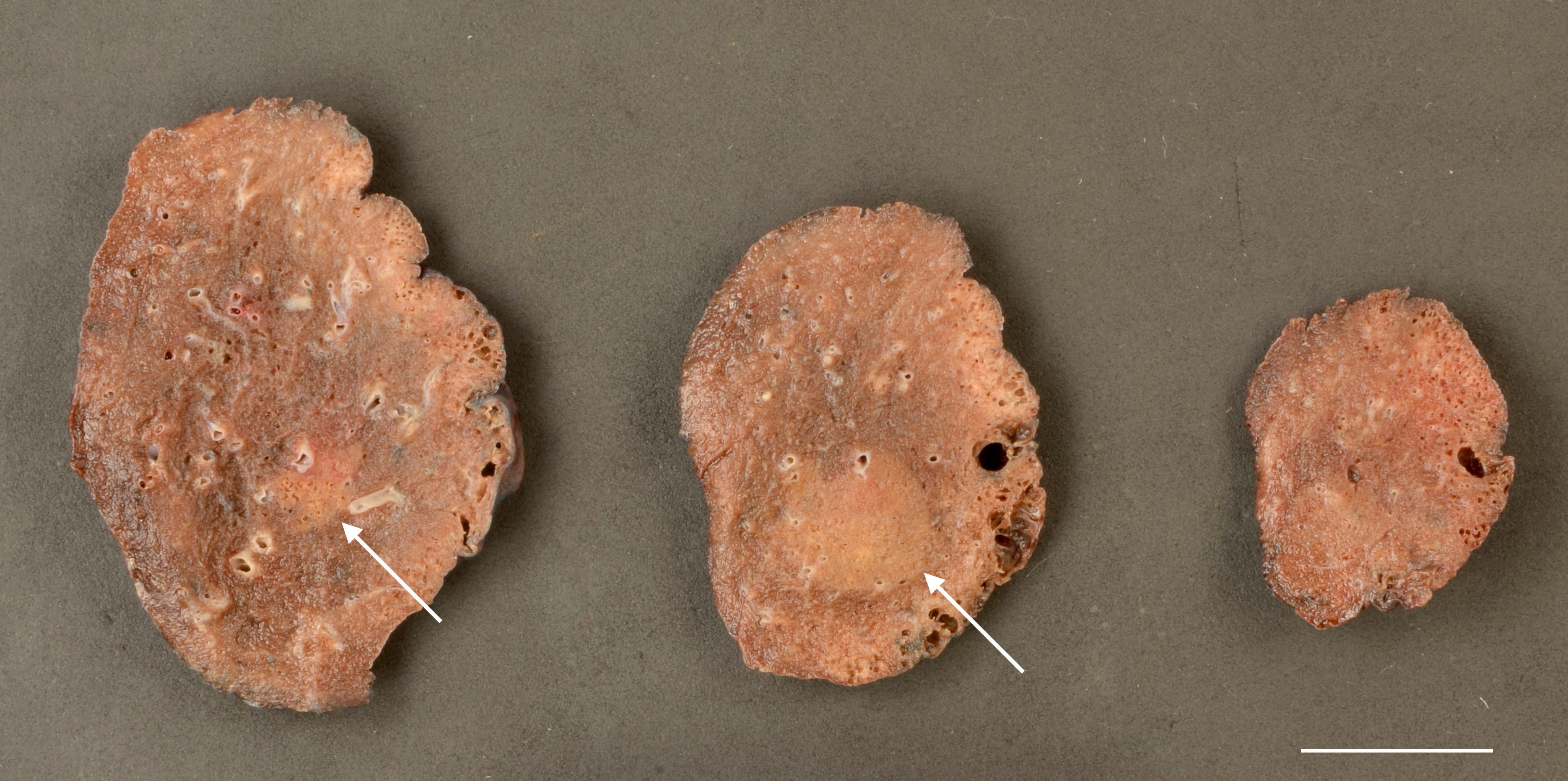
Gross description
- Peripheral, ill defined, firm, white tumor with solid areas; ill defined areas correspond to lepidic growth pattern and solid areas correspond to invasive component (Hum Pathol 2016;51:41)
- Necrosis and frank pleural invasion should be absent
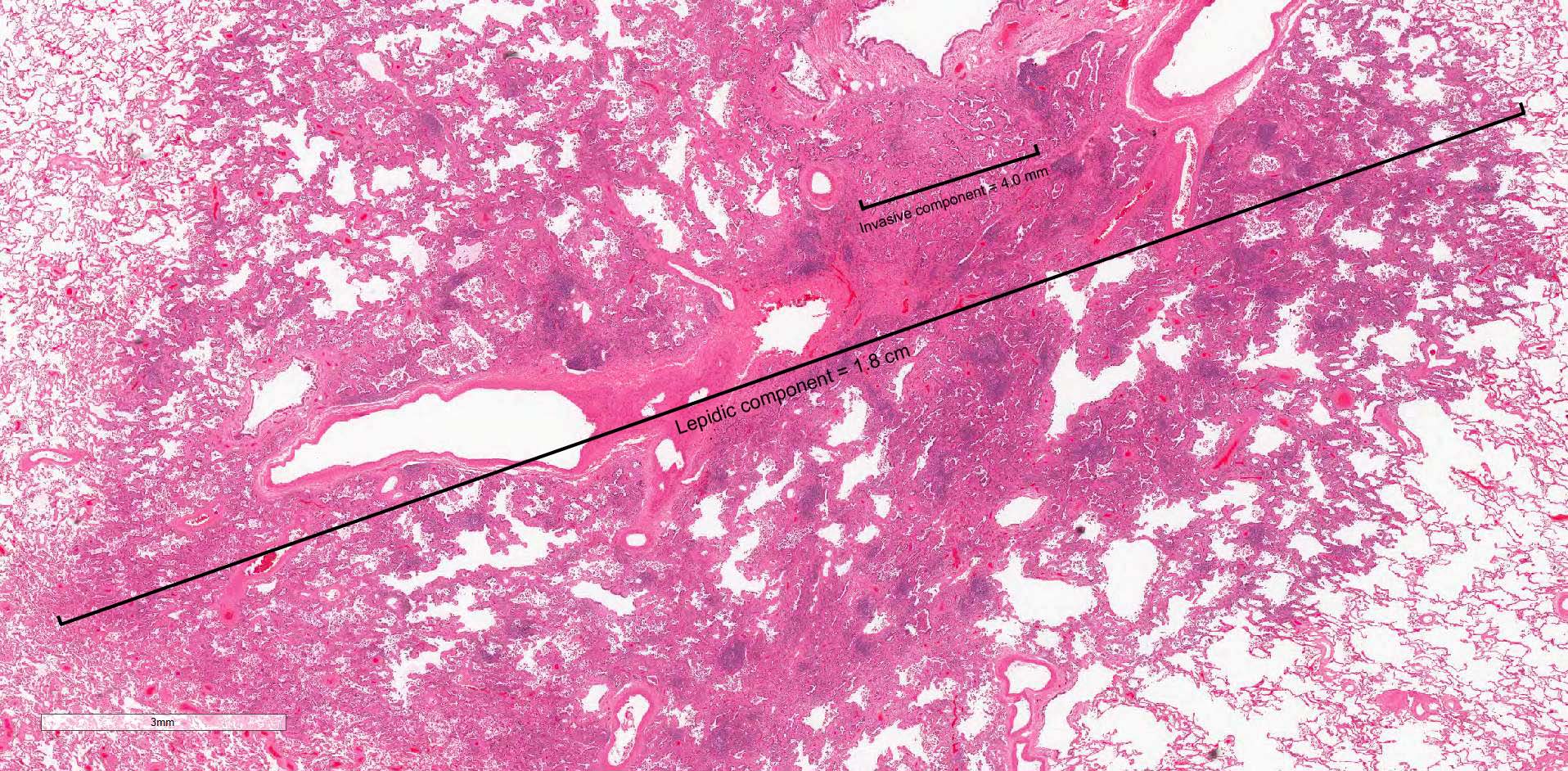
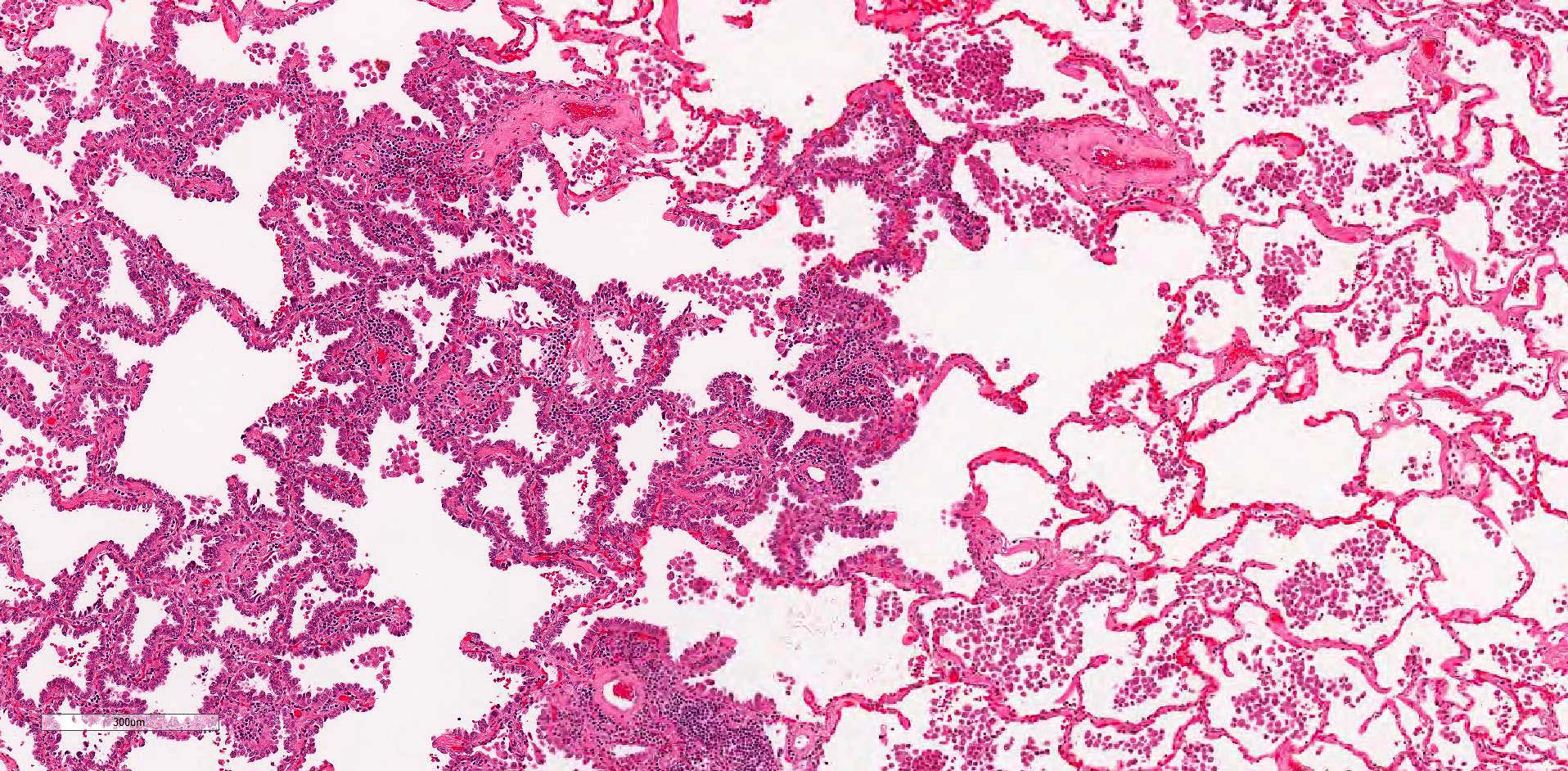
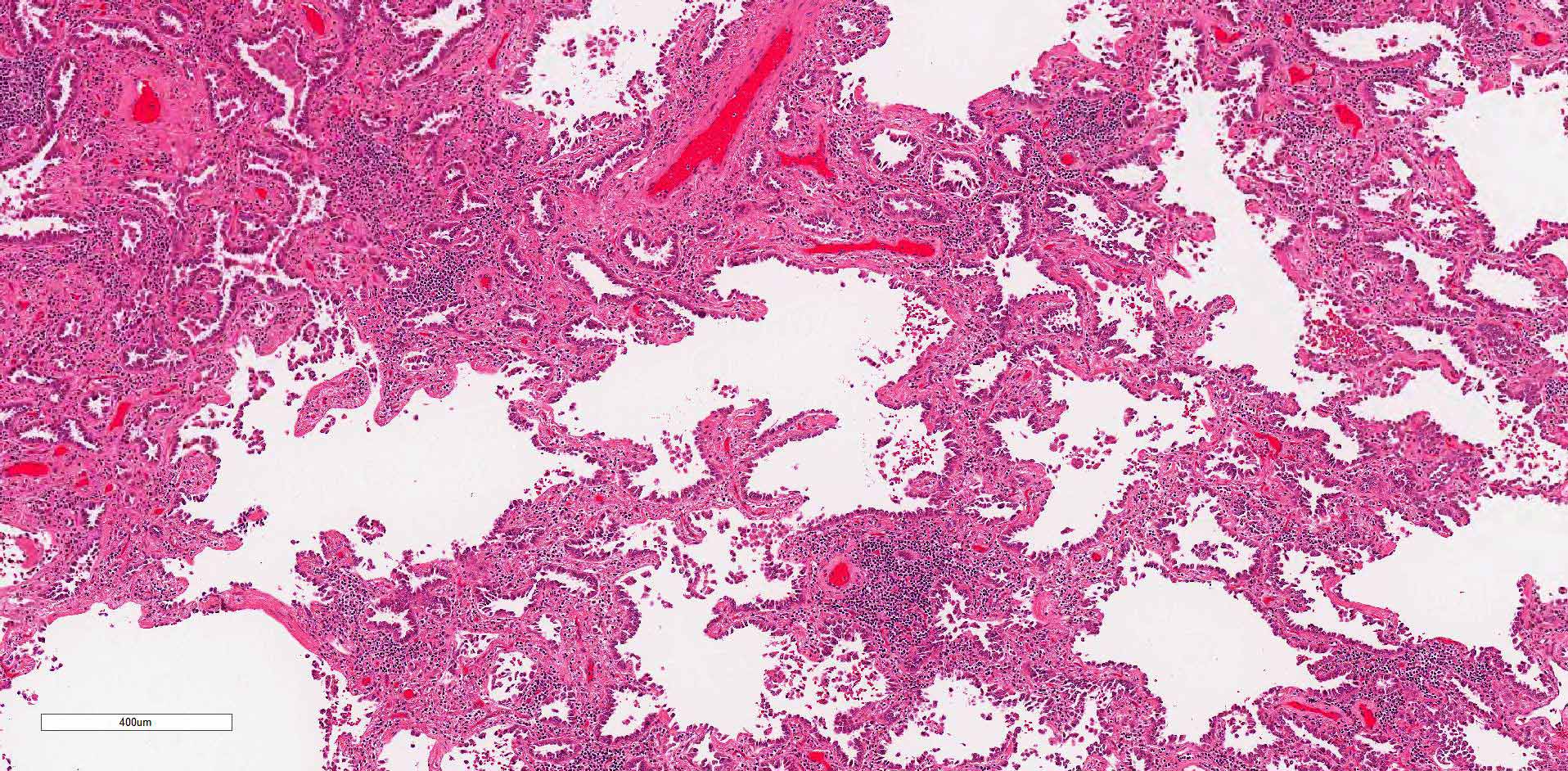
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Primary lung adenocarcinoma measuring ≤ 3 cm in greatest dimension, with ≤ 0.5 cm area of either stromal invasion or nonlepidic growth pattern (acinar, micropapillary, papillary, solid, colloid, fetal or invasive mucinous patterns)
- Foci of stromal invasion characterized by angulated glands, desmoplastic stroma and increased cytologic atypia (Cancer 1995;75:2844)
- Size of invasion should be measured as the largest focus of invasion (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:448, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2013;137:685)
- If there are multiple foci of invasion, the invasive size can be measured as a sum of the percentage of the invasive components in each section multiplied against the greatest tumor dimension (the aggregate invasive size should be ≤ 0.5 cm to render the diagnosis of a minimally invasive adenocarcinoma) (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:448, Surg Today 2019;49:828)
- Necrosis, lymphovascular invasion, pleural invasion and spread through air spaces must be absent
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- CK7
- TTF1, Napsin A
- References: J Clin Pathol 1997;50:30, Am J Clin Pathol 1994;102:764
Negative stains
Sample pathology report
- Lung, right lower lobe, lobectomy:
- Minimally invasive adenocarcinoma, pT1mi NX MX (see synoptic report)
Differential diagnosis
- Invasive adenocarcinoma, lepidic predominant pattern:
- Invasive foci must total 0.5 cm or more in aggregate
- Adenocarcinoma in situ / atypical adenomatous hyperplasia:
- No invasive component
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following tumors would be classified as a minimally invasive adenocarcinoma?
- 2 cm lepidic predominant tumor with a 0.8 cm invasive component
- 2 cm lepidic predominant tumor with a 0.4 cm invasive component
- 2 cm lepidic predominant tumor with a 0.4 cm invasive component with pleural and lymphovascular invasion
- 5 cm lepidic predominant tumor with a 0.4 cm invasive component
Board review style answer #1
B. 2 cm lepidic predominant tumor with a 0.4 cm invasive component
Comment Here
Reference: Adenocarcinoma - minimally invasive
Comment Here
Reference: Adenocarcinoma - minimally invasive