Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Mullins CI, Musick A, Glass C. Adenocarcinoma overview. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lungtumoradenocarcinoma.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Non-small cell lung carcinoma with glandular differentiation, mucin production or pneumocyte marker expression
Essential features
- Most prevalent non-small cell lung carcinoma
- 5 main histologic patterns (acinar, papillary, micropapillary, lepidic, solid); mucinous and nonmucinous subtypes
- Positive for TTF1
Terminology
- Terminology of lung adenocarcinoma was significantly revised in the 2015 WHO classification (J Thorac Oncol 2015;10:1243)
- Discontinuation of the terms bronchioloalveolar carcinoma (BAC) and mixed subtype adenocarcinoma
- Addition of adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) as a preinvasive lesion to join atypical adenomatous hyperplasia
- Addition of minimally invasive adenocarcinoma
- Use of the term lepidic for a noninvasive component (previously classified as BAC) of an invasive adenocarcinoma
- Introduction of the term invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma for adenocarcinomas formerly classified as mucinous BAC, excluding tumors that meet criteria for AIS or minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA)
- Discontinuation of the subtypes of clear cell and signet ring adenocarcinoma
- Discontinuation of the term mucinous cystadenocarcinoma and inclusion of these under the category of colloid adenocarcinoma
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Most prevalent non-small cell lung carcinoma (PLoS One 2015;10:e0121323)
- F > M (PLoS One 2015;10:e0121323)
- Most common type of lung cancer in male nonsmokers (PLoS One 2015;10:e0121323)
- African Americans > Caucasians (PLoS One 2015;10:e0121323)
- Age 60 - 70 (PLoS One 2015;10:e0121323)
Sites
- Upper lobe > lower lobe (Lung Cancer 2018;126:139)
- Peripheral > central (Diagn Interv Imaging 2016;97:955)
- Metastasis: brain (often only site) > bone > liver > adrenal (Cancer Biol Ther 2016;17:272)
- Risk for brain metastasis increases with tumor size and lymph node stage (Radiology 2007;242:882)
Pathophysiology
- Toxic cellular exposures → genetic mutations → proliferation of endobronchial cells (PLoS Med 2016;13:e1002162, J Transl Med 2017;15:26)
- Genetic events were characterized by TCGA project, described in Molecular / cytogenetics description (Nature 2014;511:543)
Etiology
- Smoking is the greatest risk factor, including secondhand smoke (Transl Lung Cancer Res 2018;7:220)
- Radon from soil, usually in residential areas (Transl Lung Cancer Res 2018;7:220)
- Cooking oil fumes, particularly in Asia (Int J Cancer 1987;40:604, Onco Targets Ther 2016;9:2987, Transl Lung Cancer Res 2018;7:220)
- Asbestos exposure, usually occupational (ship building, construction) (Mol Clin Oncol 2017;7:135)
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Cough (productive if mucinous adenocarcinoma), hemoptysis, dyspnea, weight loss, chest pain (Chest 2012;142:1338)
- Paraneoplastic / endocrine syndromes are much less common than in small cell lung carcinoma
- Hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy with clubbing of the fingers, symmetric polyarthritis, periostitis of the long bones (World J Clin Oncol 2014;5:197)
Diagnosis
- Histological, based on morphology and staining pattern
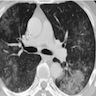
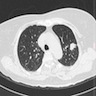
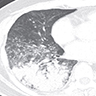
Radiology description
- Well defined borders, lobulated or spiculated, presence of air bronchograms (Diagn Interv Imaging 2016;97:955)
- Solid, dense areas have solid or acinar patterns (Diagn Interv Imaging 2016;97:955)
- Ground glass opacities are mucinous subtype or lepidic pattern (Diagn Interv Imaging 2016;97:955)
Prognostic factors
- Favorable: lepidic (J Thorac Oncol 2022;17:362)
- Unfavorable: spread through air spaces, size > 2.5 cm, visceral pleural invasion, micropapillary or solid type (Mod Pathol 2021;34:549, J Thorac Oncol 2013;8:37, Mod Pathol 2011;24:653, Sci Rep 2018;8:4743, Chest 2014;146:1619)
Case reports
- 36 year old woman at 33 weeks gestation presenting with orthopnea caused by lepidic predominant lung adenocarcinoma (Case Rep Oncol 2018;11:822)
- 38 year old man with EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma with small cell transformation (Cancer Biol Ther 2018;19:445)
- 60 year old man with fast growing lung micropapillary predominant adenocarcinoma (Respir Med Case Rep 2017;20:125)
- 60 year old woman with EGFR wild type lung adenocarcinoma complicated by ovarian metastasis (BMC Womens Health 2021;21:152)
- 63 year old man presenting with Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome caused by advanced lung adenocarcinoma (Thorac Cancer 2020;11:1334)
Treatment
- For stages I, II, IIA and IIB without invasion: surgical resection + adjuvant radiation therapy
- For stages IIB with invasion, IIIA and IIIB without invasion: surgical resection + chemoradiation
- Inoperable or metastatic: molecular dependent chemotherapy + radiation
- Reference: NCCN: NCCN Guidelines - Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer [Accessed 6 July 2022]
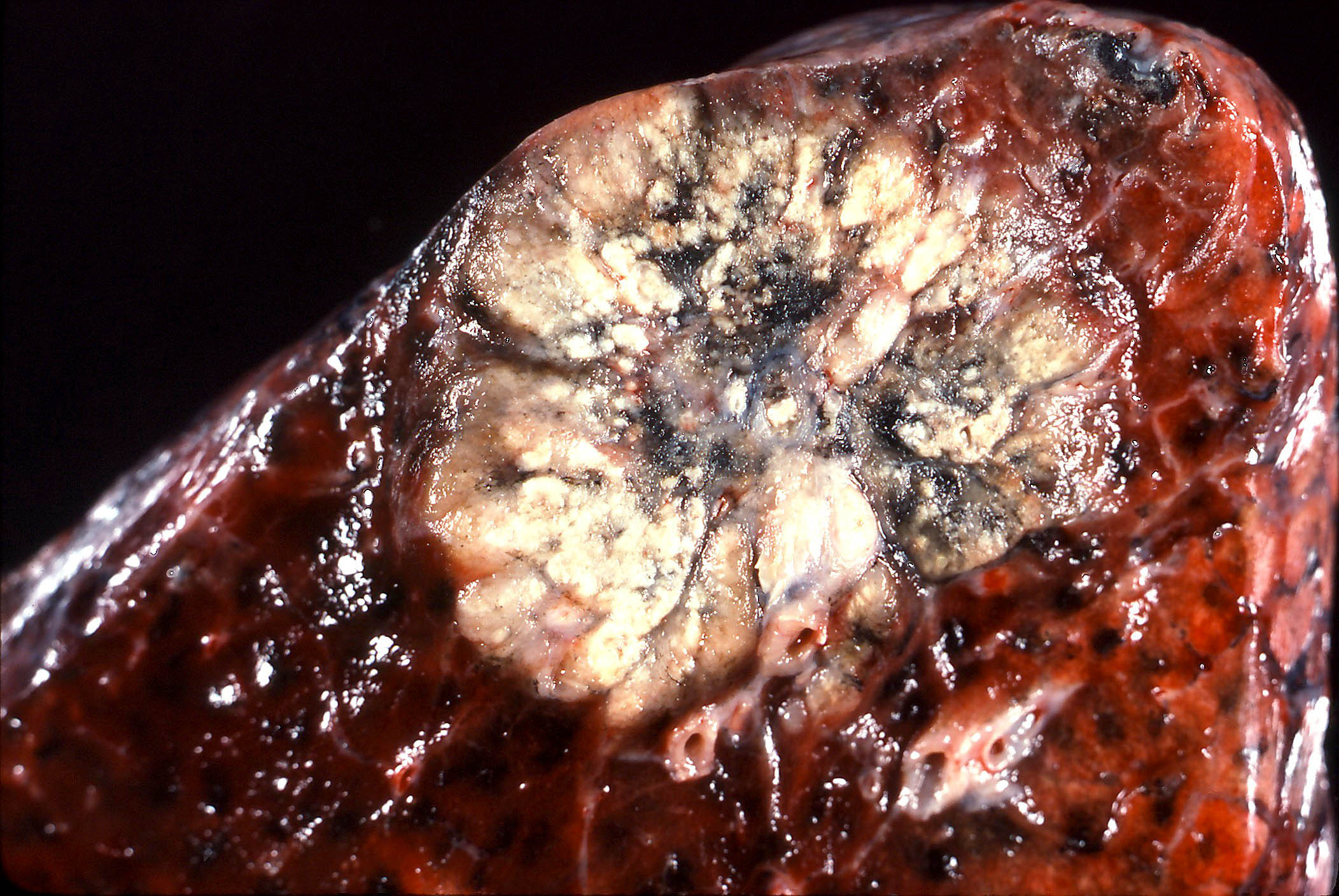
Gross description
- Adenocarcinoma (Am J Clin Pathol 2017;147:641):
- Tan-white cut surface
- May have central area of scar or necrosis
- Usually well defined but nonencapsulated
- Minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (Diagn Interv Imaging 2016;97:955):
- Focal (< 30 mm)
- Usually solitary
Gross images
Frozen section description
- Diagnosis given to surgeon: non-small cell lung carcinoma or adenocarcinoma
- 85% accurately diagnosed on frozen section (J Clin Oncol 2016;34:307)
- Sampling error is the main reason for inaccurate diagnosis (Histopathology 2015;66:922)
- High grade patterns more difficult to diagnose (Histopathology 2015;66:922)
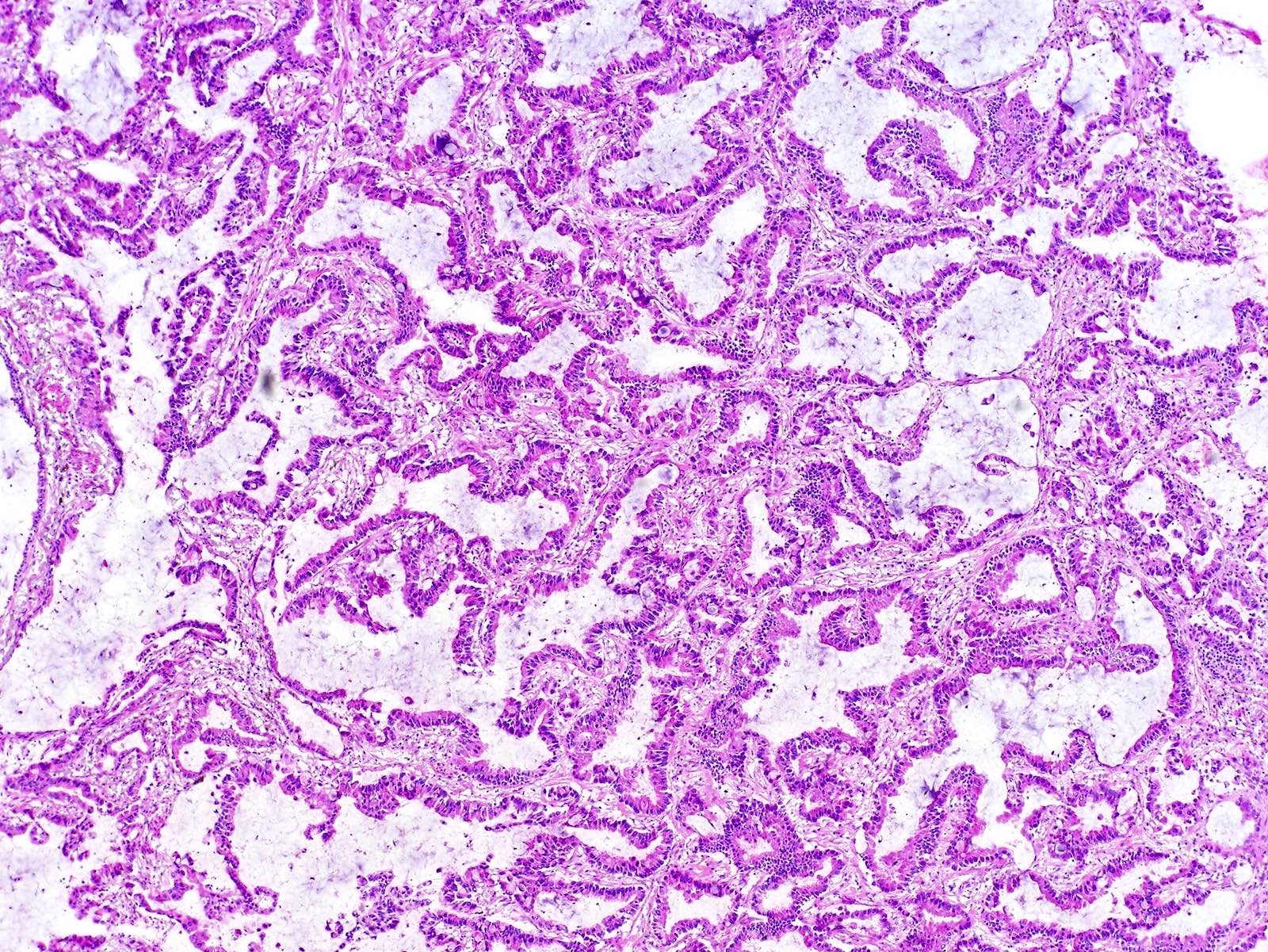
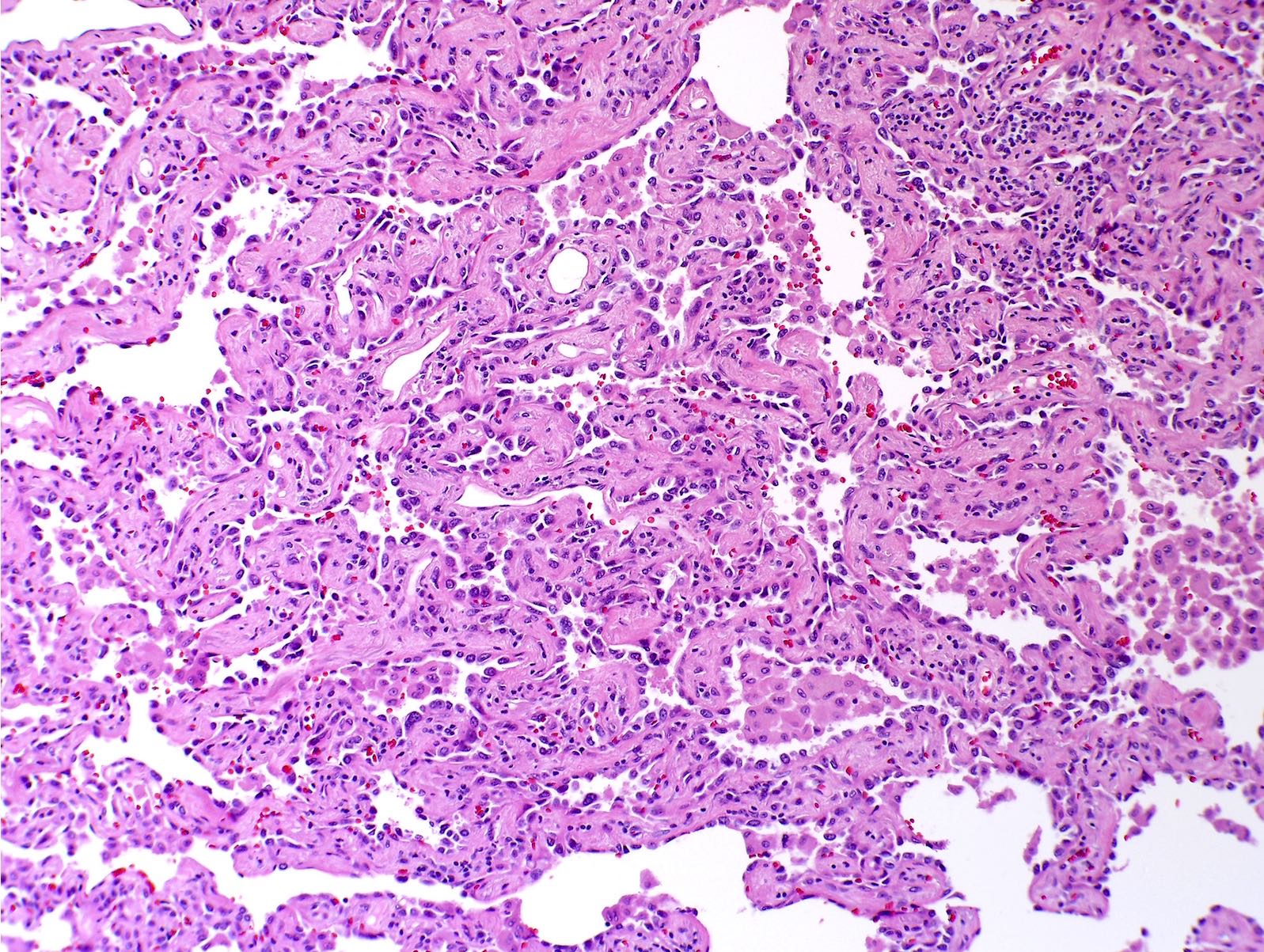
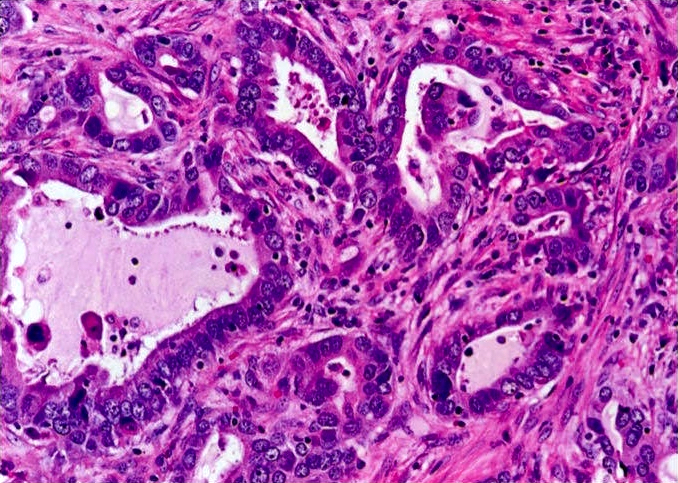
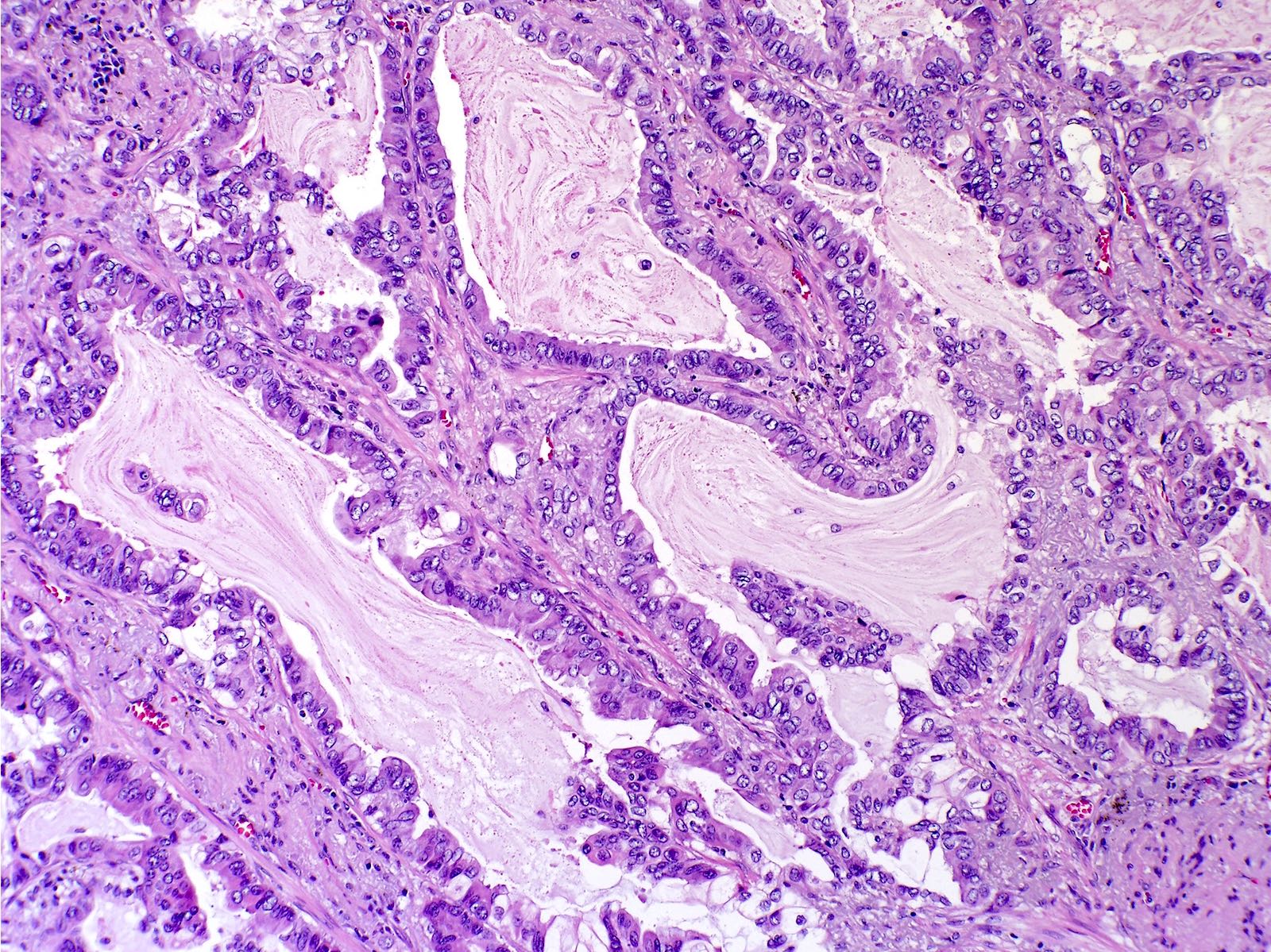
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma: invasion > 5 mm, composed of goblet or columnar cells with abundant mucin (J Thorac Oncol 2022;17:362)
- Invasive nonmucinous adenocarcinoma: invasion > 5 mm, glandular differentiation, named by predominant pattern (J Thorac Oncol 2011;6:244)
- 5 main histologic patterns:
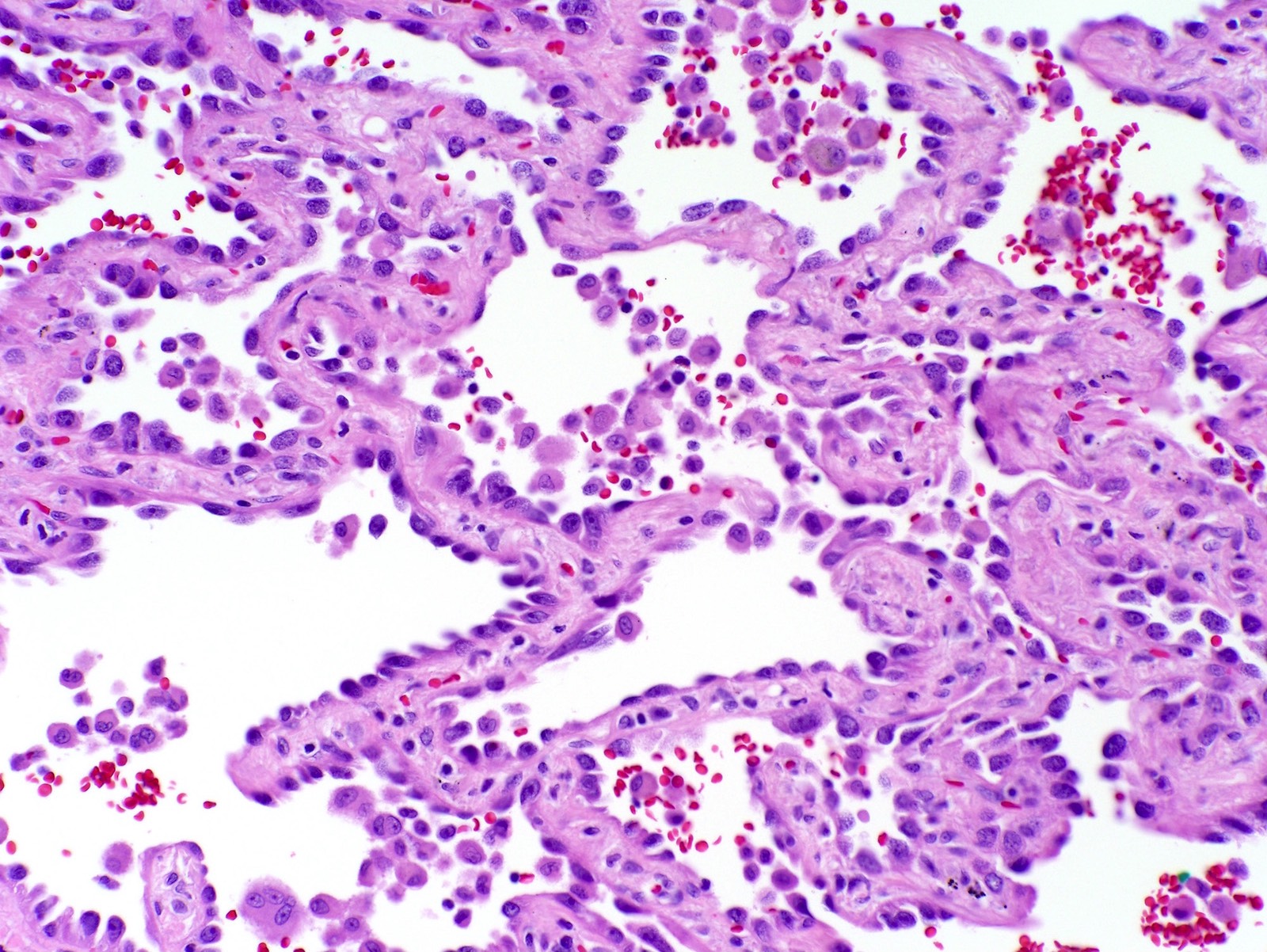
- Lepidic: type II pneumocytes and club cells proliferate to line alveolar walls; lacks architectural complexity; no lymphovascular or perineural invasion (J Thorac Dis 2017;9:2142, J Thorac Oncol 2011;6:244)
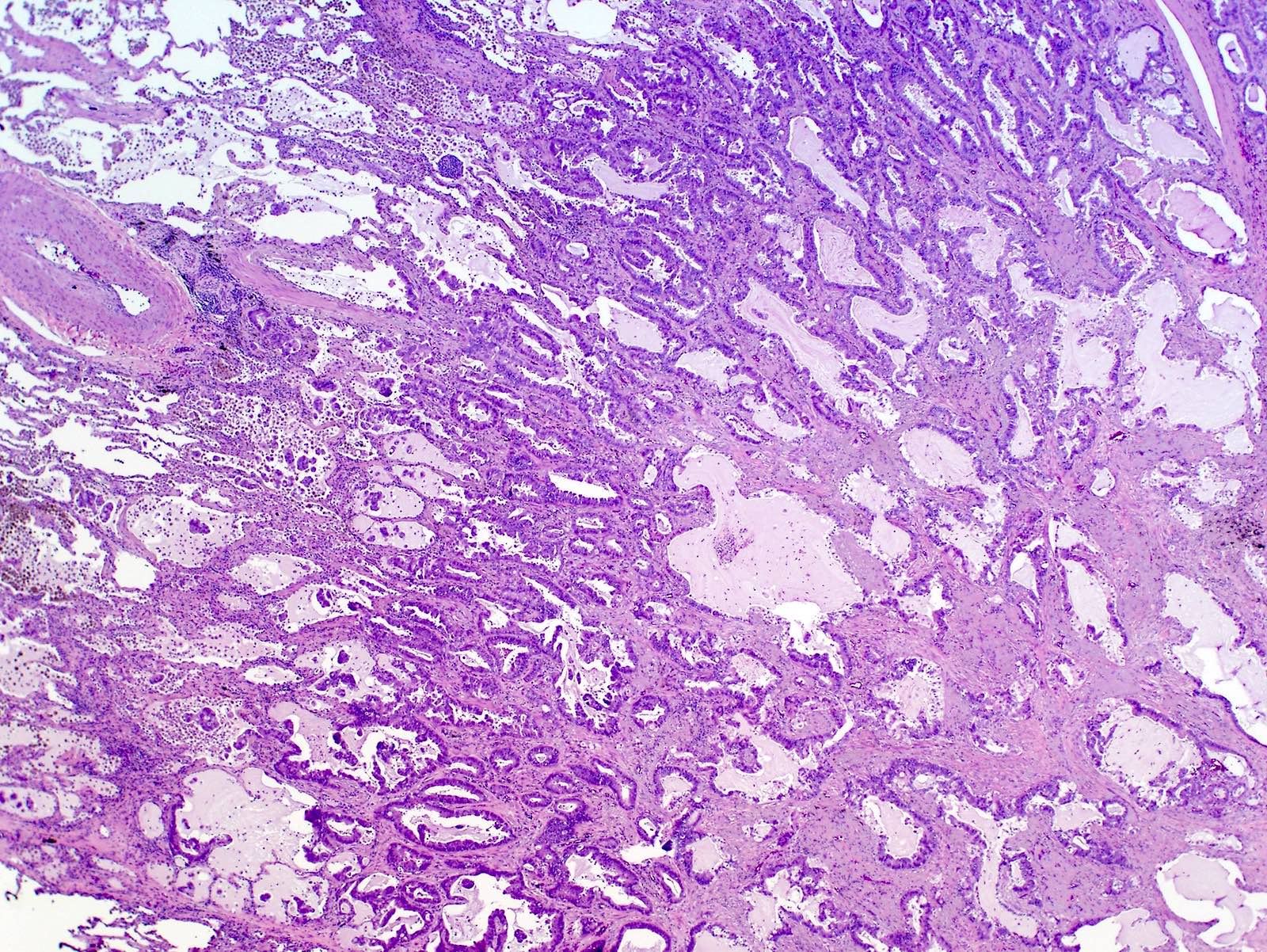
- Acinar: gland forming; round / oval glands invading the stroma (usually fibrous); includes high grade complex glandular subtypes (J Thorac Oncol 2020;15:1599, J Thorac Oncol 2011;6:244)
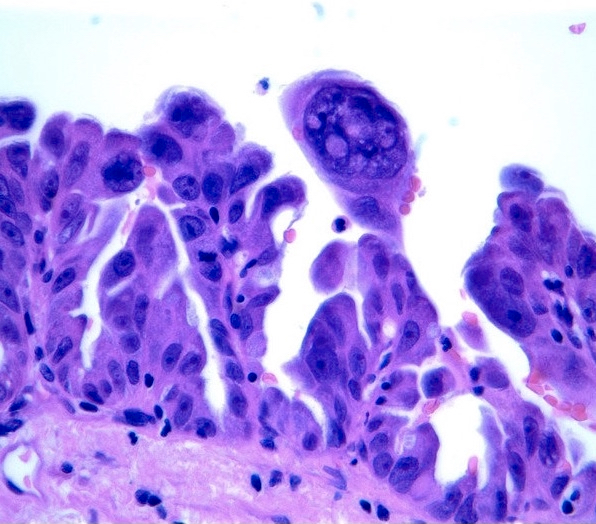
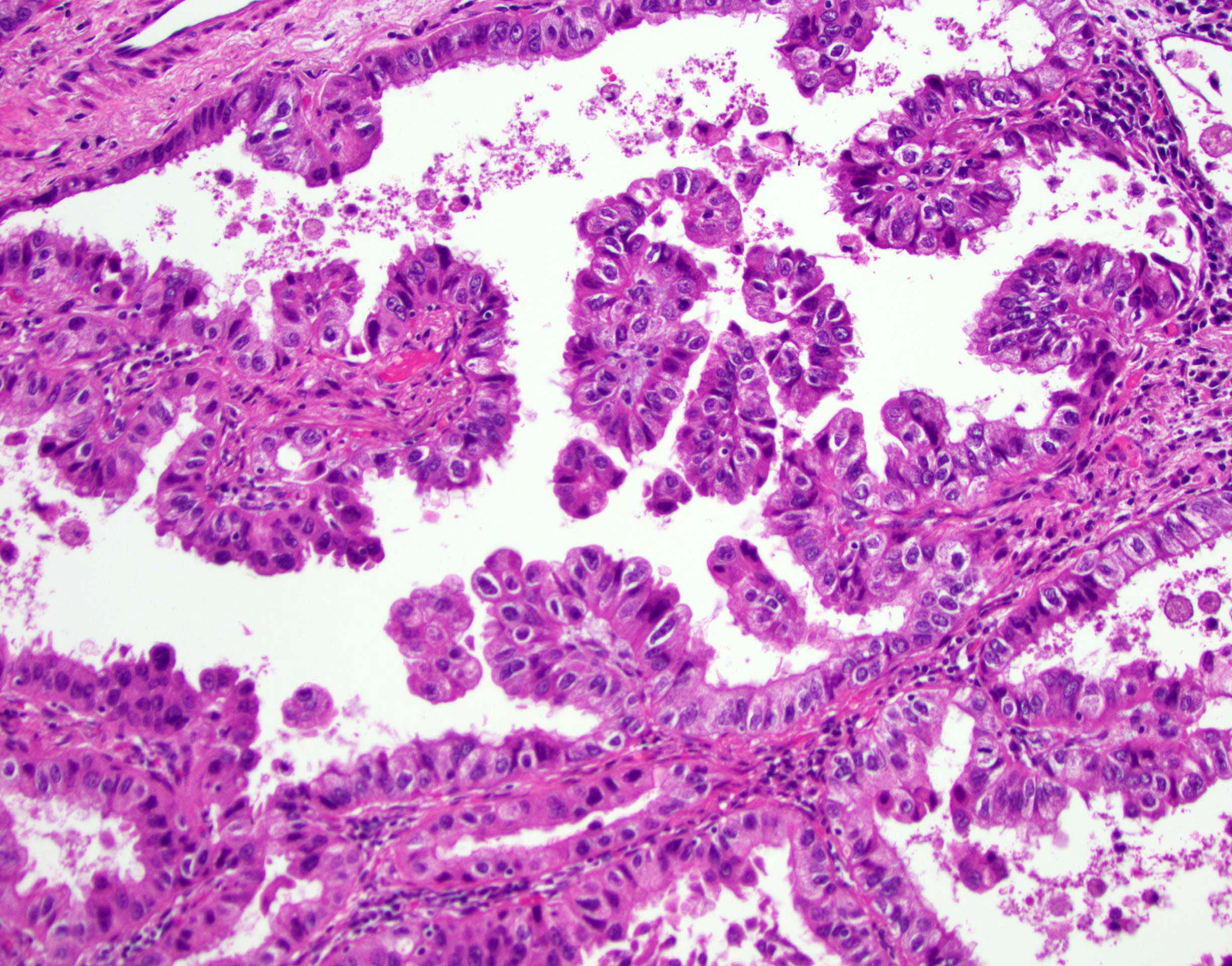
- Papillary: malignant cuboidal / columnar cells replace alveolar lining; contains fibrovascular cores (J Thorac Oncol 2011;6:244)
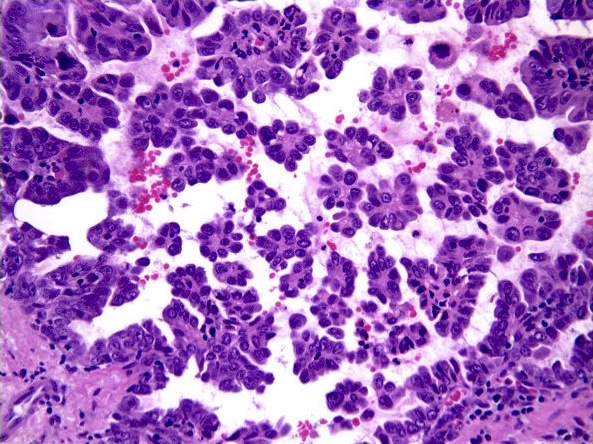
- Micropapillary: ill defined projection / tufting that lacks fibrovascular cores (J Thorac Oncol 2011;6:244)
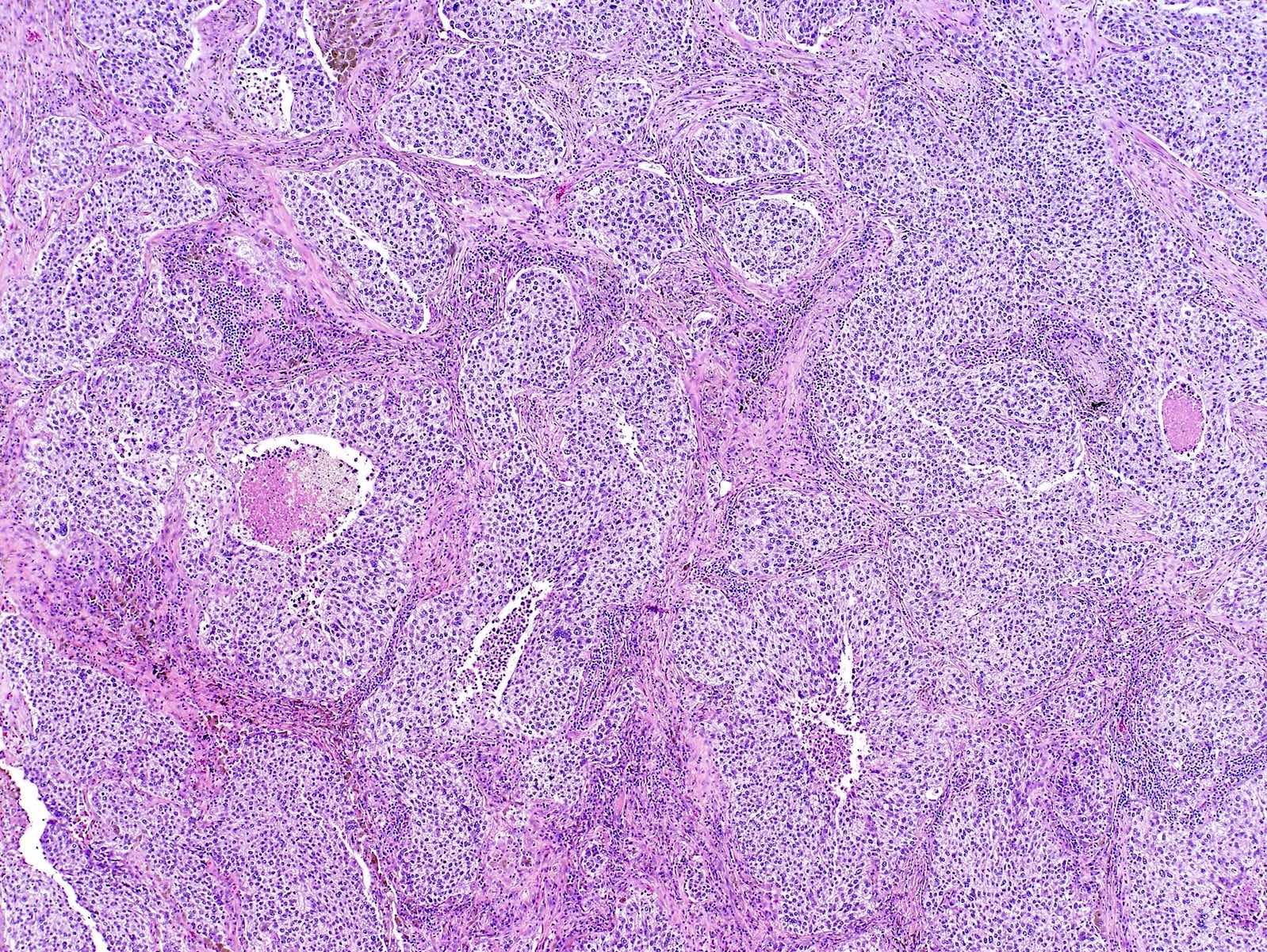
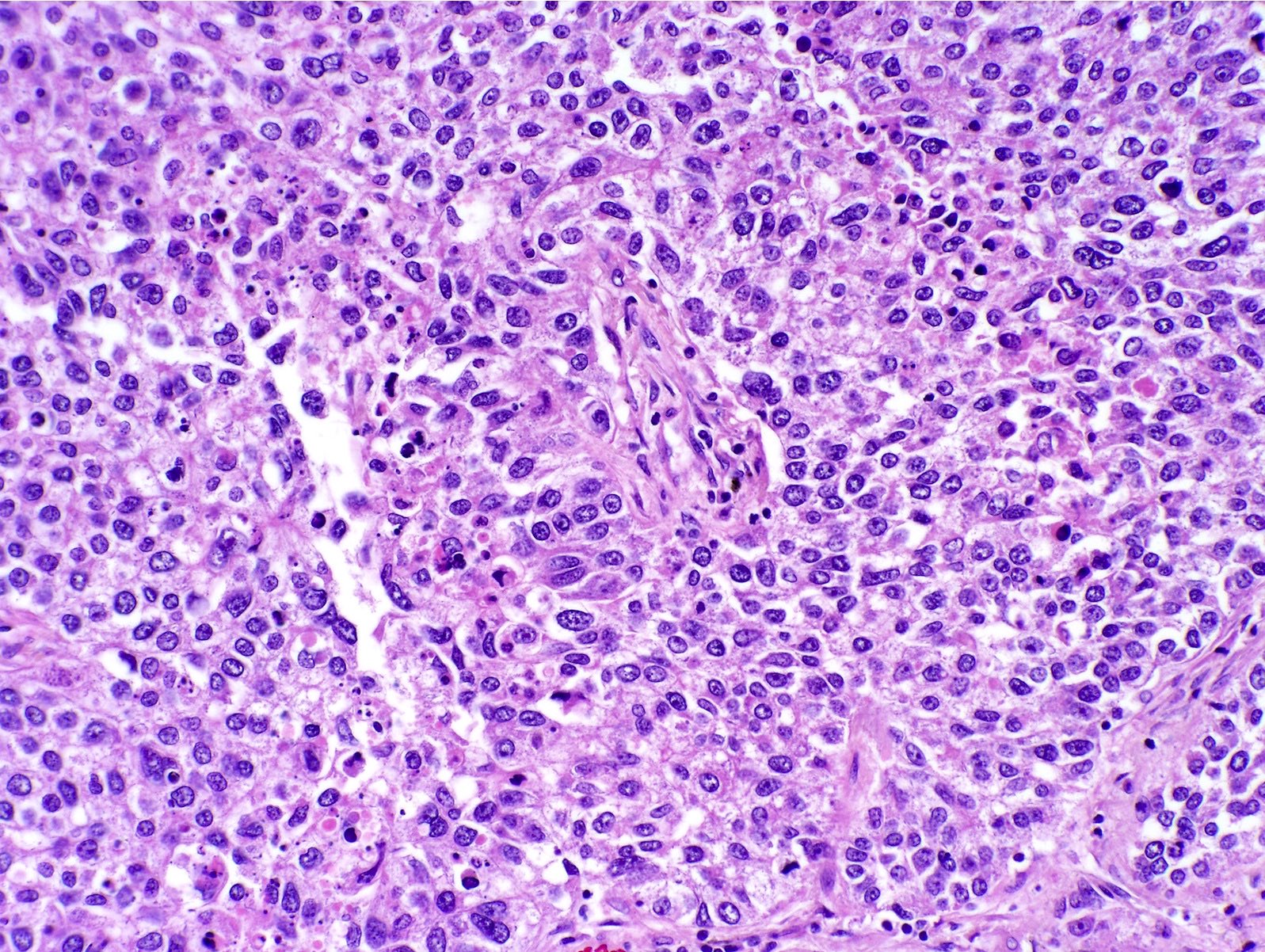
- Solid: sheets of neoplastic cells (J Thorac Oncol 2011;6:244)
- Tumor grade dependent on combination of histologic patterns (J Thorac Oncol 2022;17:362, J Thorac Oncol 2020;15:1599)
- Each pattern should be recorded in 5 - 10% increments
- Grading: (J Thorac Oncol 2022;17:362)
- Grade 1 (well differentiated): lepidic, predominant, with no or < 20% high grade pattern
- Grade 2 (moderately differentiated): acinar or papillary predominant, with no or < 20% high grade pattern
- Grade 3 (poorly differentiated): any pattern with 20% or more high grade pattern
- Less common subtypes:
- Colloid: cuboidal or columnar cells with abundant pools of extracellular mucin that distort alveolar spaces (J Thorac Oncol 2022;17:362)
- Fetal: resembles pseudoglandular fetal epithelium; can be mildly atypical and low grade or severely atypical and high grade (J Thorac Oncol 2022;17:362)
- Enteric type: resembles colorectal adenocarcinoma and has at least 1 intestinal marker (J Thorac Oncol 2022;17:362)
- Minimally invasive adenocarcinoma: focal (≤ 30 mm), predominantly lepidic pattern, ≤ 5 mm area of invasion (any subtype) (J Thorac Oncol 2022;17:362, Diagn Interv Imaging 2016;97:955)
- Spread through air spaces is more commonly associated with adenocarcinomas (versus squamous cell carcinoma) (Mod Pathol 2021;34:549)
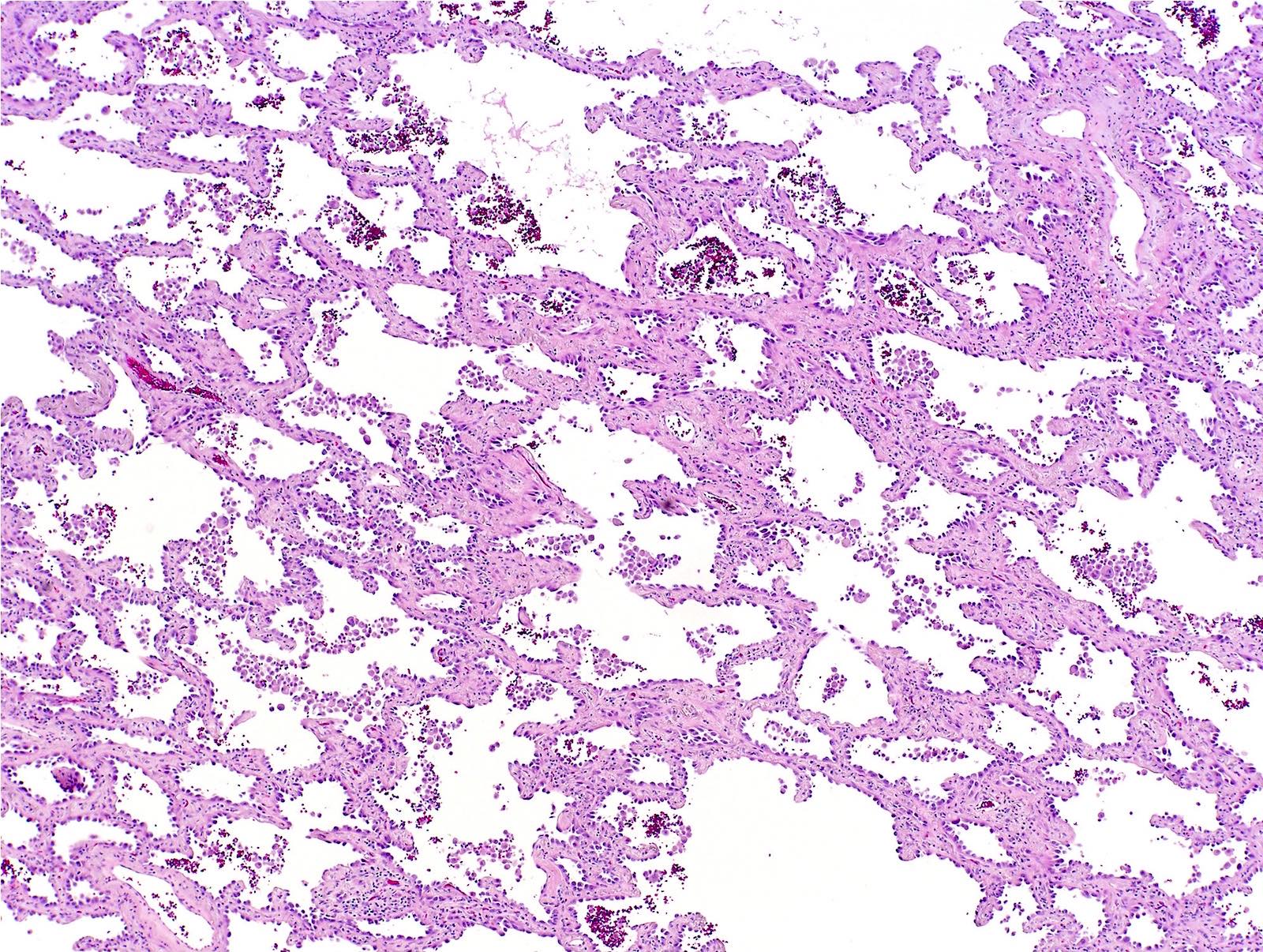
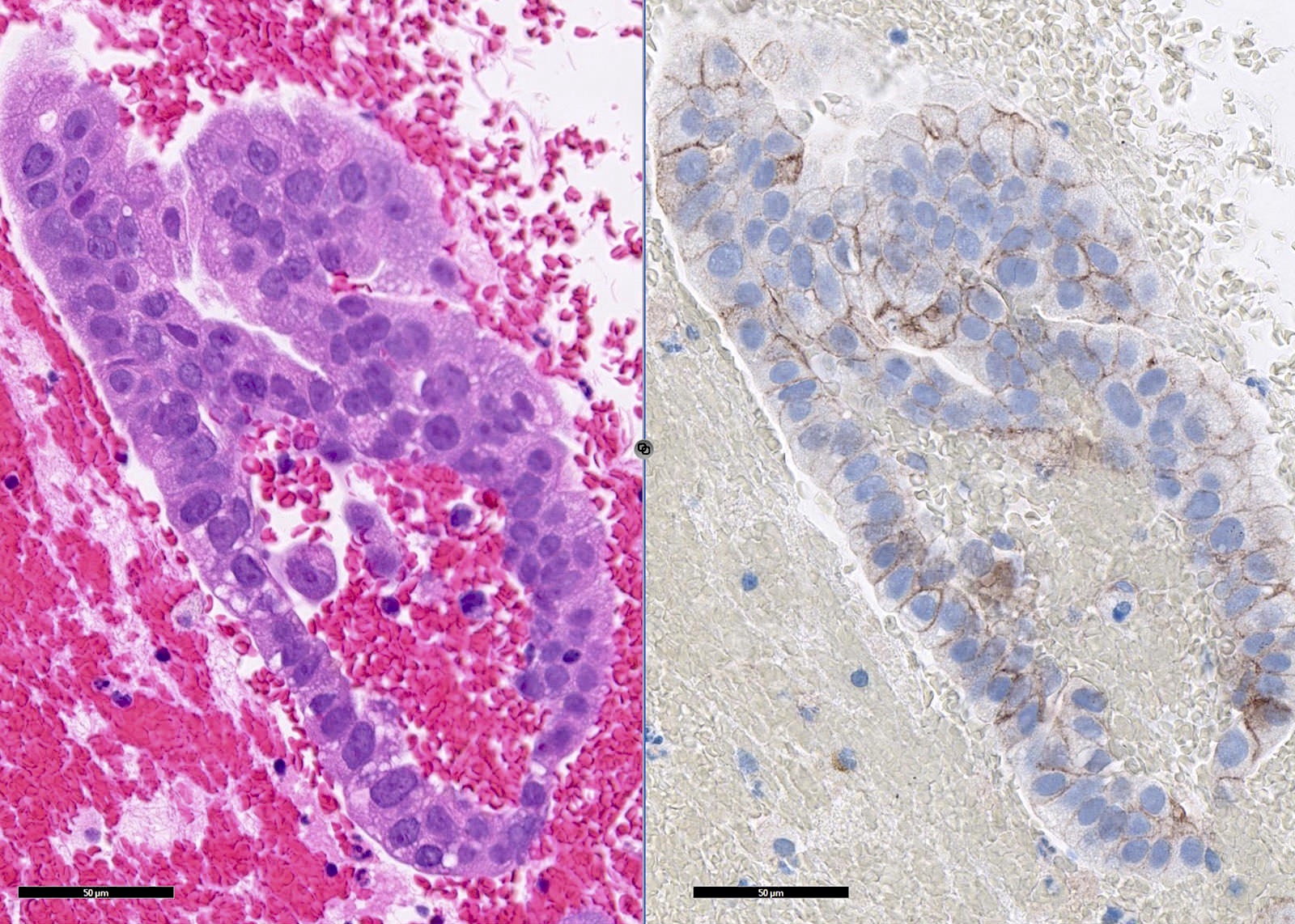
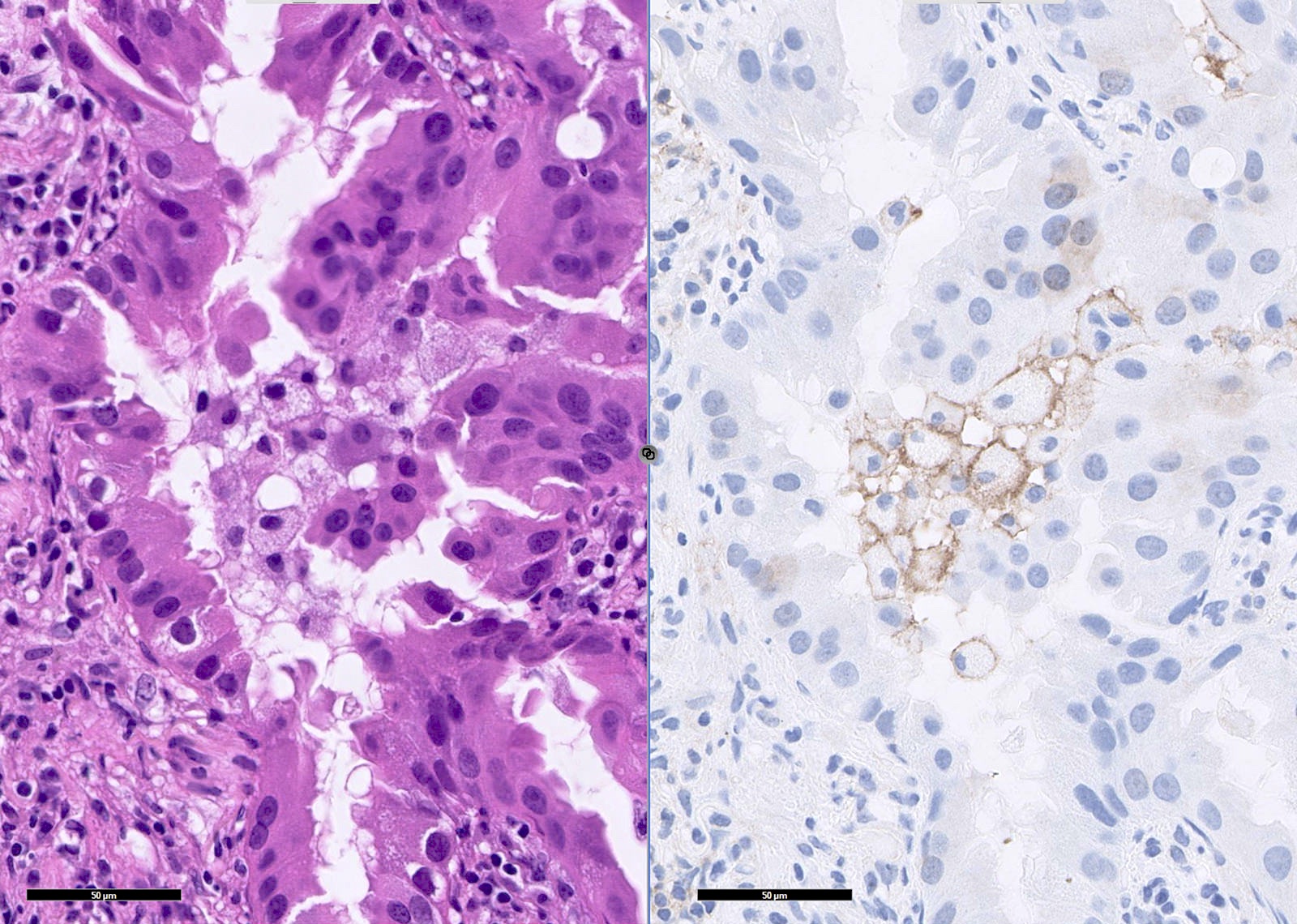
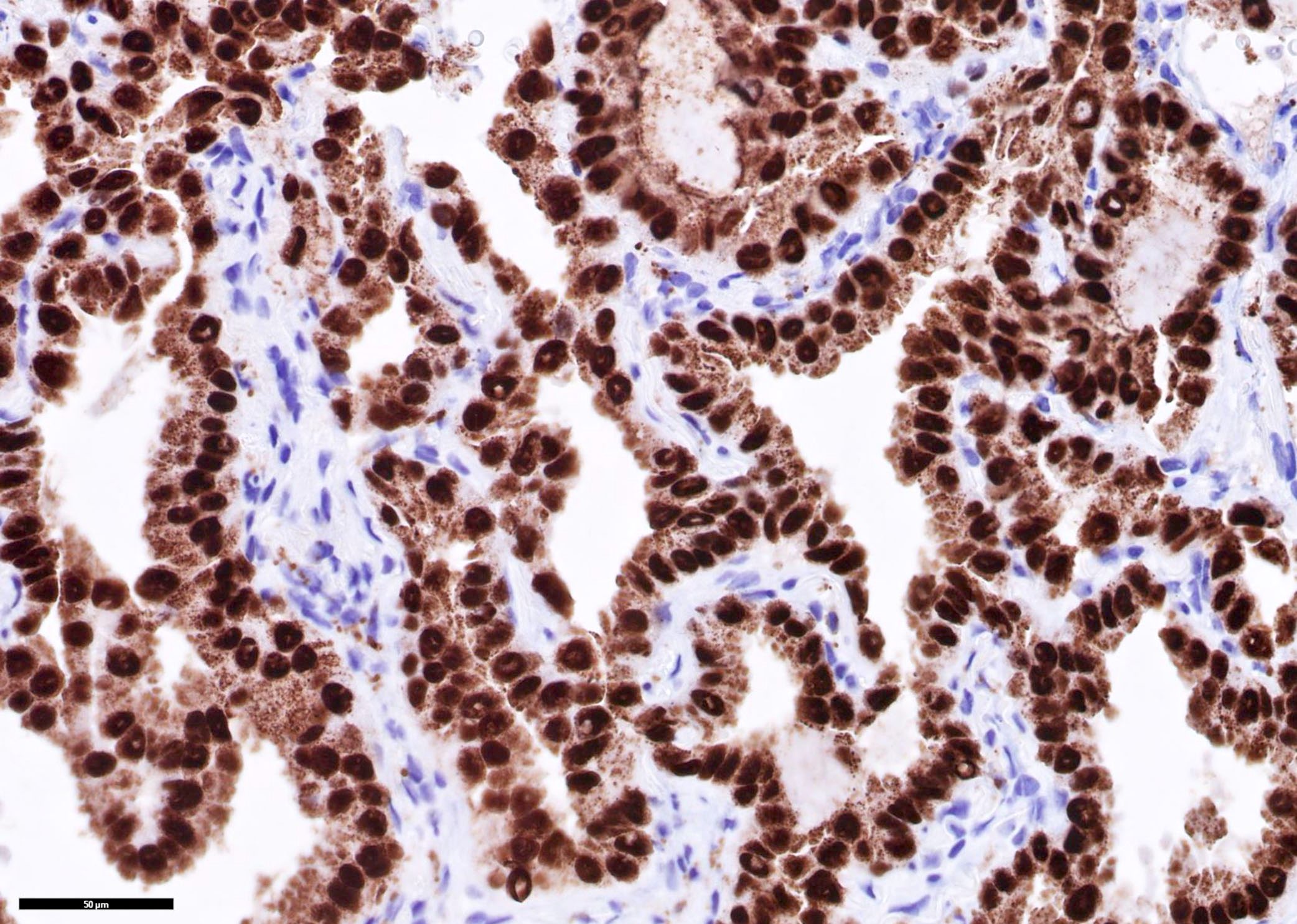
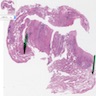
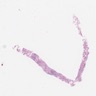
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Caroline I. Mullins, M.D., Andrey Bychkov, M.D., Ph.D., Fulvio Lonardo, M.D. and Negar Rassaei, M.D.
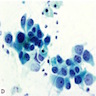
Cytology description
- 3D clusters of cohesive cells, foamy / vacuolated cytoplasm, fine chromatin, variable prominent nucleoli (J Thorac Oncol 2011;6:244)
- Usually on pleural effusions or needle washes
Positive stains
- TTF1, AE1 / AE3, CK7, beta catenin, Napsin A (Indian J Med Res 2017;146:42)
- TTF1 clone 8G7G3/1 is more specific but less sensitive compared with SPT24 and SP141 (Am J Clin Pathol 2018;150:533)
Negative stains
- p53, p40, p63, CK5/6, WT1, D2-40, calretinin, EGFR (positive in 33%) (Ann Am Thorac Soc 2015;12:429, Indian J Med Res 2017;146:42)
Electron microscopy description
- Short microvilli (Ultrastruct Pathol 2016;40:254)
- Tumor cells lack cytoplasmic cytosomes (Ultrastruct Pathol 2016;40:254)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- EGFR mutation: 10 - 15% overall, 49% in Asia, rare in mucinous subtype (Front Pharmacol 2019;10:230, Diagn Interv Imaging 2016;97:955)
- KRAS mutation: 20 - 25% overall, 76% of mucinous subtype (Diagn Interv Imaging 2016;97:955)
- ALK rearrangement: 4% (J Thorac Dis 2019;11:S3)
- ROS1 gene fusions: 1 - 2%
- BRAF mutation: 1.5 - 3.5%, V600E most common (J Thorac Dis 2019;11:S3)
- NTRK mutation: 2 - 3% (J Thorac Dis 2019;11:S3)
- RET fusion: 0.4 - 2% (J Thorac Dis 2019;11:S3)
- HER2 amplification: 13 - 22.8% (J Thorac Dis 2019;11:S3)
- MET amplification: 2 - 4% (J Thorac Dis 2017;9:2142)
- SMARCA4 loss of function: 5% (Ann Diagn Pathol 2017;26:47)
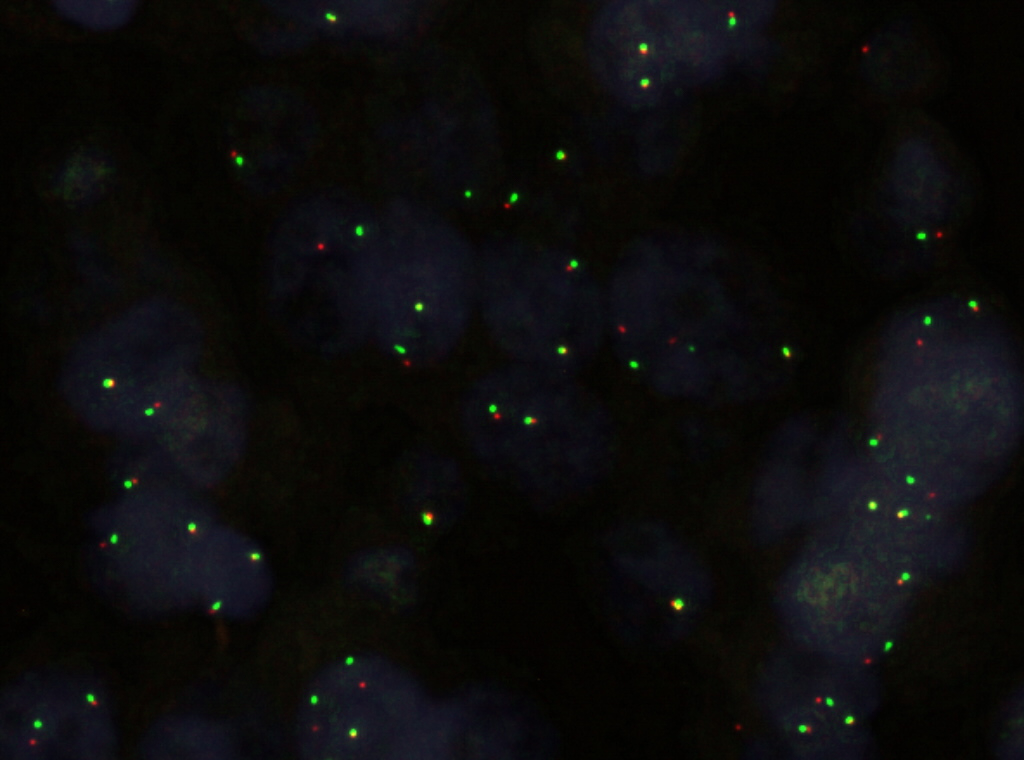
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Lung, left upper lobe, wedge resection:
- Invasive adenocarcinoma, grade 2, acinar predominant with secondary solid growth pattern (see synoptic report)
Differential diagnosis
- Squamous cell lung carcinoma:
- Small cell lung carcinoma:
- Positive for neuroendocrine markers
- Small round blue cells, usually in sheets or nests
- High grade neuroendocrine tumor:
- Increased mitotic activity (> 10/high power field), necrosis
- Positive for neuroendocrine markers and stathmin 1, nuclear chromatin is clumped / salt and pepper appearance (Ann Thorac Surg 2019;108:235)
- Metastatic adenocarcinoma:
- Negative for TTF1 (unless thyroid)
- Positive for markers from primary site
- Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia:
- ≤ 5 mm in size
- Atypical type II pneumocytes, noninvasive (Diagn Interv Imaging 2016;97:955)
- Adenocarcinoma in situ:
- ≤ 30 mm in size, atypical type II pneumocytes, purely lepidic type, noninvasive (Diagn Interv Imaging 2016;97:955)
- Bronchial adenoma / ciliated muconodular papillary tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1010, Pathol Int 2017;67:99):
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma:
- Cribriform architecture and pseudocysts
- PAS positive
- Metastatic papillary thyroid carcinoma:
- Clinical history of thyroid cancer, psammoma bodies, nuclear features of PTC (orphan Annie)
- PAX8 and thyroglobulin positive
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 59 year old man presents with cough, hemoptysis and shortness of breath. A mass in his left lung was biopsied. Which of the following statements about this disease is true?
- Exposure to benzene is an important risk factor in the development of this disease
- Masses are most frequently found in central / hilar regions of both lungs
- The growth pattern indicated in the patient's biopsy above is a poor prognostic factor
- The most common site of metastasis is the liver
- This disease has a higher incidence in men than in women
Board review style answer #1
C. The growth pattern indicated in the patient's biopsy above is a poor prognostic factor. The H&E stain demonstrates a micropapillary pattern, which is a poor prognostic factor. Lung adenocarcinoma is associated with exposure to radon (not benzene) and is typically found in the peripheral regions or upper lobes of the lung. This cancer is also more common in women than in men and most frequently metastasizes to the brain, not the liver.
Comment Here
Reference: Adenocarcinoma overview
Comment Here
Reference: Adenocarcinoma overview
Board review style question #2
A 63 year old woman presented with mass in the upper lobe of her left lung with enlargement of the mediastinal lymph nodes. Surgical biopsy shows columnar tumor cells with abundant intracytoplasmic mucin in an acinar growth pattern. The malignant cells are most likely to be positive for which of the following mutations?
- ALK rearrangement
- BRAF
- EGFR
- HER2 amplification
- KRAS
Board review style answer #2
E. KRAS is the most common mutation associated with mucinous adenocarcinoma (76%). EGFR mutations are rare in the mucinous subtype. ALK, HER2 and BRAF are uncommon mutations overall.
Comment Here
Reference: Adenocarcinoma overview
Comment Here
Reference: Adenocarcinoma overview