Table of Contents
Clinical features | Hantavirus | Rhodococcus | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Electron microscopy imagesCite this page: Weisenberg E. Pulmonary zoonoses. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lungnontumorpulmonaryzoonoses.html. Accessed December 25th, 2024.
Clinical features
- Zoonoses are diseases and infections naturally transmitted between people and vertebrate animals (WHO: Zoonotic Disease: Emerging Public Health Threats in the Region [Accessed 18 August 2021])
- 3 classes:
- Endemic zoonoses which are present in many places and affect many people and animals
- Epidemic zoonoses which are sporadic
- Emerging and re-emerging zoonoses which are newly appearing in a population or have existed previously but are rapidly increasing in incidence
Hantavirus
- Zoonosis transmitted by feces from infected rodents (Emerg Infect Dis 2009;15:561)
- Severe pulmonary disease, often in Southwest US; 25 - 35% mortality
- Symptoms eventually resolve in almost all survivors (Lung 2010;188;387)
- Epidemic disease occurred in Southwestern US in 1993 (Centers for Disease Control: The Detailed Story of Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) [Accessed 18 August 2021])
- Sporadic cases have occurred since then
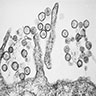
- Diagnosis confirmed by immunohistochemistry, serology, PCR, electron microscopy
- Reference: Wikipedia: Orthohantavirus [Accessed 18 August 2021]
Rhodococcus
- Zoonotic infection originally identified in lungs of foals; also cattle, swine, sheep, deer, goats, dogs, cats, other species
- Worldwide distribution in water and soil, especially near feces of herbivores
- Infection by inhalation or ingestion
- Resides primarily within lung macrophages of infected patients, also some alveolar cells (Microbes Infect 2011;13:438)
- R. equi is most common human pathogen of the Rhodococci
- Generally occurs in AIDS patients (may cause malakoplakia) (Clin Infect Dis 1999;28:1334)
- Also other immunodeficient patients; very rarely in immunocompetent
- Incidence decreasing, likely due to HAART therapy and azithromycin prophylaxis
- Rhodo since salmon pink pigment in culture
- Treated with antibiotics but mortality is 50% in AIDS patients, 20% in other immunocompromised and 10% in immunocompetent
Case reports
- 15 year old girl with congenital AIDS and cavitary lesion (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:e315)
- 68 year old man with fatal lung infection post chemotherapy for T-PLL (Emerg Infect Dis 2007;13:1942)
- 68 year old man with pneumonia post heart transplant (University of Pittsburgh: Case 146 [Accessed 18 August 2021])
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Hantavirus: interstitial pneumonitis with mononuclear infiltrate, edema, focal hyaline membranes, pleura effusions; atypical lymphocytes in pulmonary vasculature may mimic lymphoma
- Rhodococcus: epithelioid macrophages containing gram positive, partially acid fast coccobacilli that resemble mycobacteria; may produce malakoplakia