Table of Contents
Definition / general | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Weisenberg E. Malakoplakia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lungnontumormalakoplakia.html. Accessed December 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Usually in urinary tract; very rare in lung, usually in immunocompromised patients
- Caused by macrophage dysfunction involving intracellular lysosomal mediated killing of bacteria
- In AIDS patients, usually due to Rhodococcus equi, an animal pathogen causing opportunistic infections (Chest 1999;115:889)
Case reports
- Two cases in immunocompetent patients (Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2011;54:133)
Treatment
- Antibiotics
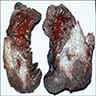
Gross description
- Nodular masses or infiltrates with cavitation
Microscopic (histologic) description
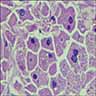
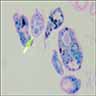
- Intraalveolar histiocytes with pink or foamy cytoplasm (von Hansemann’s histiocytes) that fill and destroy alveoli, not interstitium
- Histiocytes contain PAS+ bacteria, also Michaelis-Gutmann bodies (round / oval structures, usually intracellular, 5 - 20 microns, with laminated or targetoid appearance that stain deeply with H&E, iron and calcium stains)
- Also lymphocytes, plasma cells and neutrophils
Differential diagnosis
- Atypical mycobacteria: blue histiocytes, positive acid fast stain
- Also Whipple disease, Gaucher disease, endogenous lipid pneumonia, amiodorone toxicity