Table of Contents
Clinical features | Pathophysiology | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Negative stainsCite this page: Weisenberg E. Histoplasma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lungnontumorhistoplasma.html. Accessed December 23rd, 2024.
Clinical features
- Deep fungal infection indigenous to Ohio and Missouri River valleys and the Caribbean basin (eMedicine)
- See also Skin - nontumor topic
- Fungi are thermally dimorphic; spore producing hyphae outside body, but yeast at body temperature
- Infection due to inhaling dust or soil particles contaminated with bird or bat droppings
- "Capsulatum" is incorrect - no capsule is present
- In immunocompetent, generally causes a self limited or latent infection, but chronic pneumonia preferentially involving lung apices associated with systemic symptoms and cough can occur; localized lung lesions, with or without lymph node involvement, are common; also localized lesions, often calcified, in adrenal, lymph nodes, liver, spleen, meninges; resembles tuberculosis with epitheliod granulomas with caseous necrosis; necrotic foci may coalesce to produce large areas of necrosis; with drug therapy or endogenous control, fibrosis and calcification occur, causing "tree bark" lesion
- In immunocompromised, disease is often virulent and widely disseminated
- If necessary, microbiologic studies, serology, or molecular studies are confirmatory
Pathophysiology
- Infection is incompletely understood, but is usually controlled by helper T cells and heat shock protein that activate macrophages to kill yeast
Gross description
- Resembles tuberculosis, may see "tree bark" appearance (due to fibrosis and calcification) or coin lesion
Microscopic (histologic) description
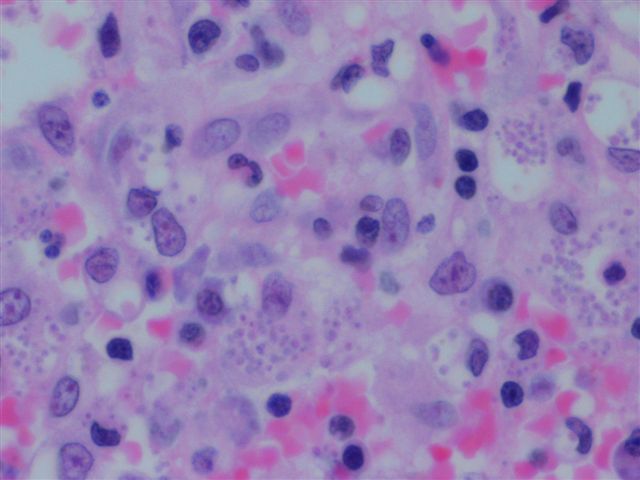
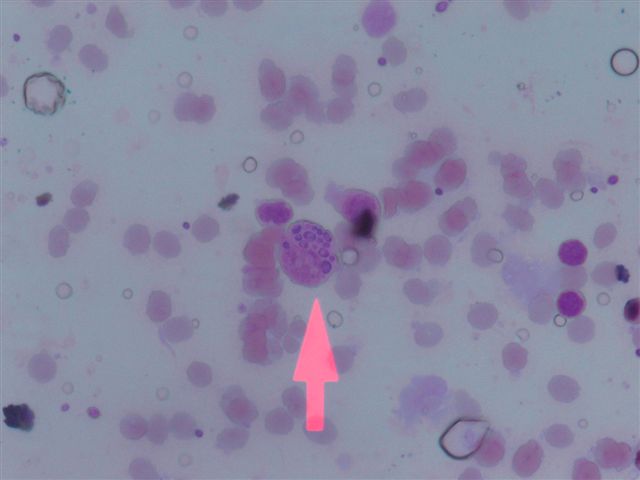
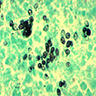
- Diagnosis based on identifying small, budding, intracellular yeast in tissue, 2 - 5 microns
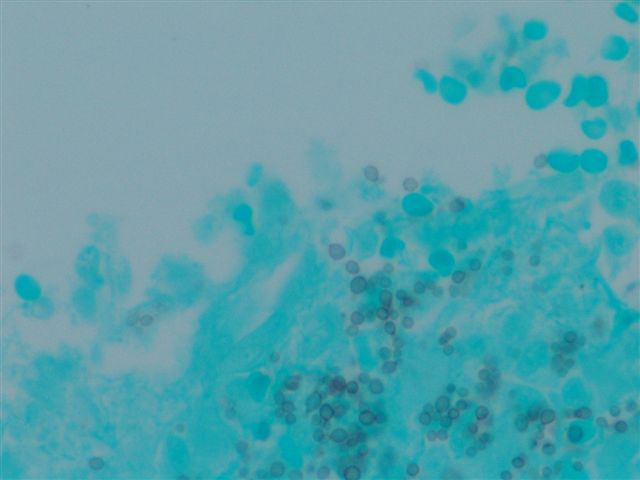
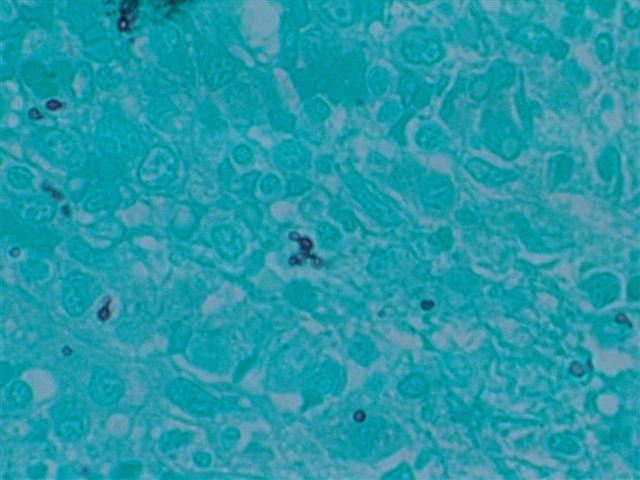
- Yeasts usually visible with H&E, but may need special stains; GMS more sensitive than PAS, but microcalcifications may create false positives
- No / minimal granulomas in immunosuppressed or neonates; yeasts fill histiocytes and are widely disseminated
Microscopic (histologic) images
Negative stains