Cite this page: Weisenberg E. Other fungi. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lungnontumorotherfungi.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
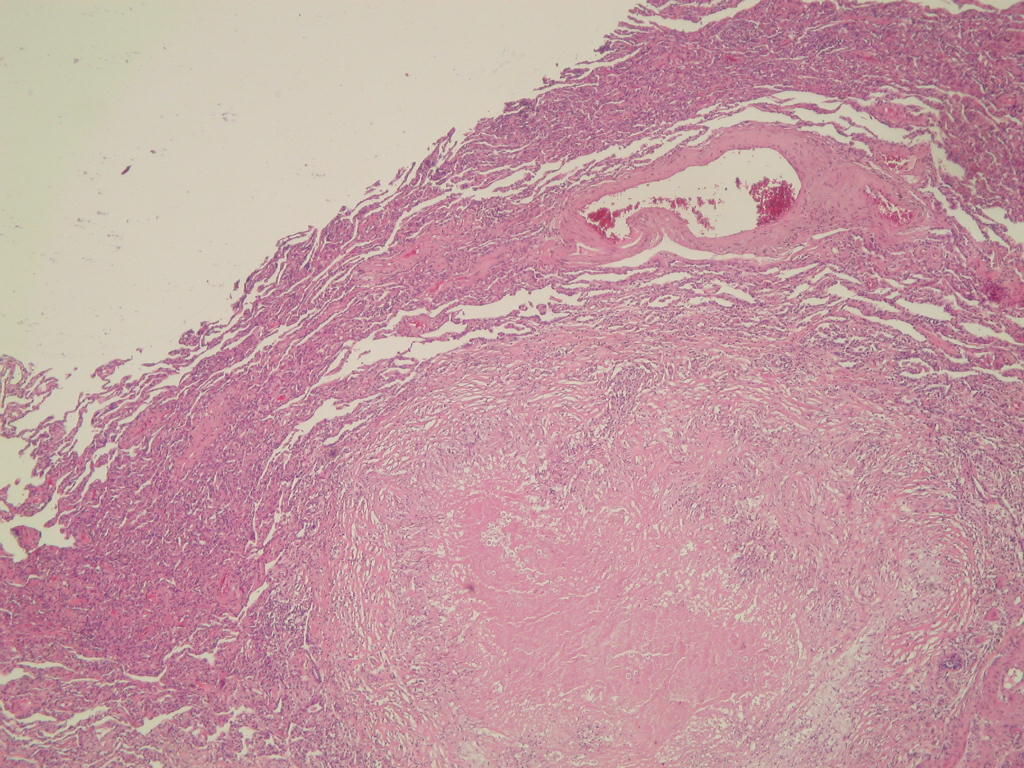
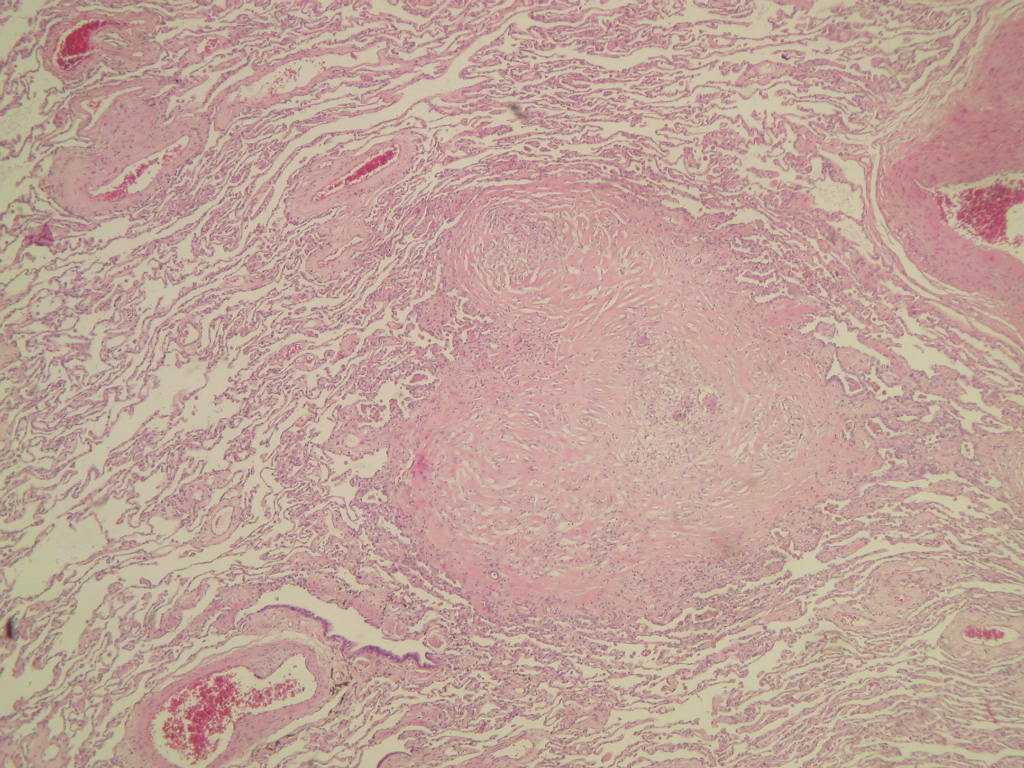
Blastomyces
Clinical features
- See also Skin - nontumor chapter
- Dimorphic fungus found in soil in Central and Southeastern United States and Canada (bordering Great Lakes, St. Lawrence River, Mississippi River and Ohio River basins), Mexico, Africa, India, Middle East
- More common in males
- Due to inhalation of soil containing microfoci of mycelia (Clin Microbiol Rev 2010;23:367)
- Difficult to isolate in clinical microbiology laboratory
- May present as consolidative pneumonia, ARDS or nodules resembling carcinoma; prefers upper lobes
- May also infect skin and bone
- Grossly often resembles tuberculosis
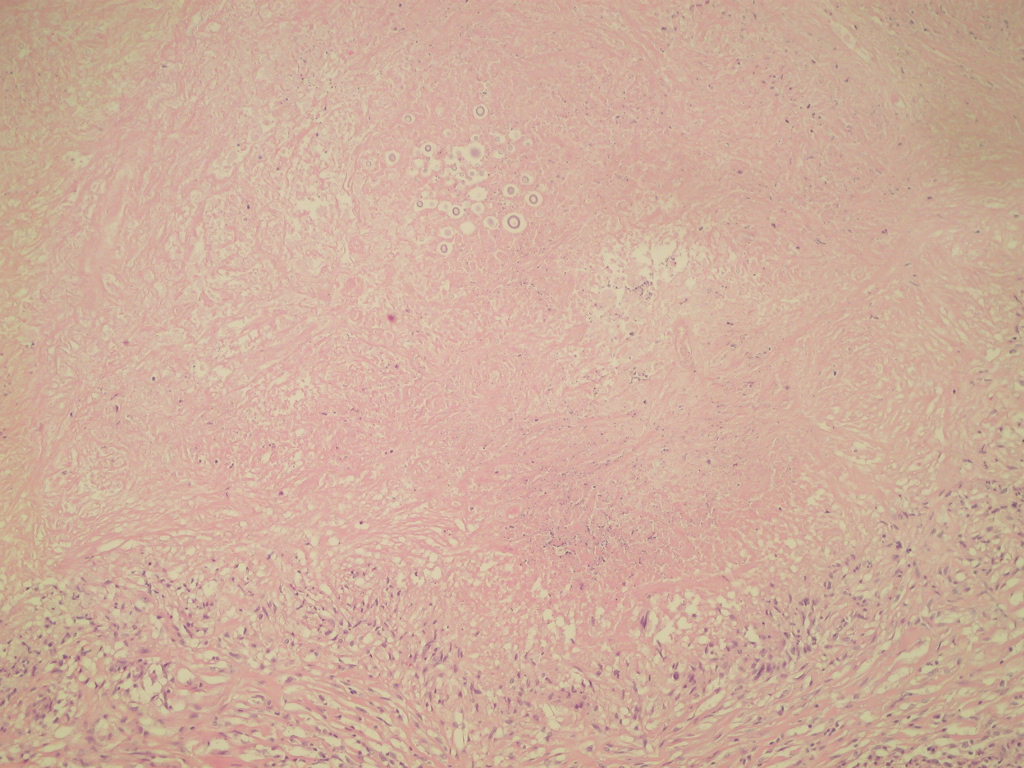
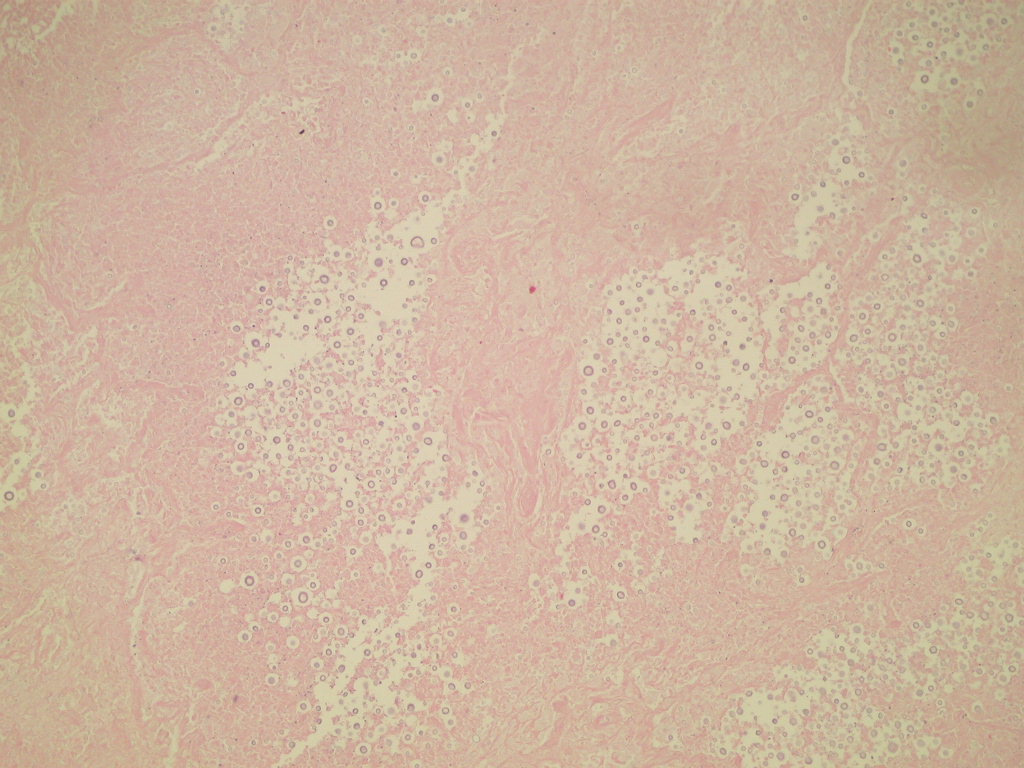
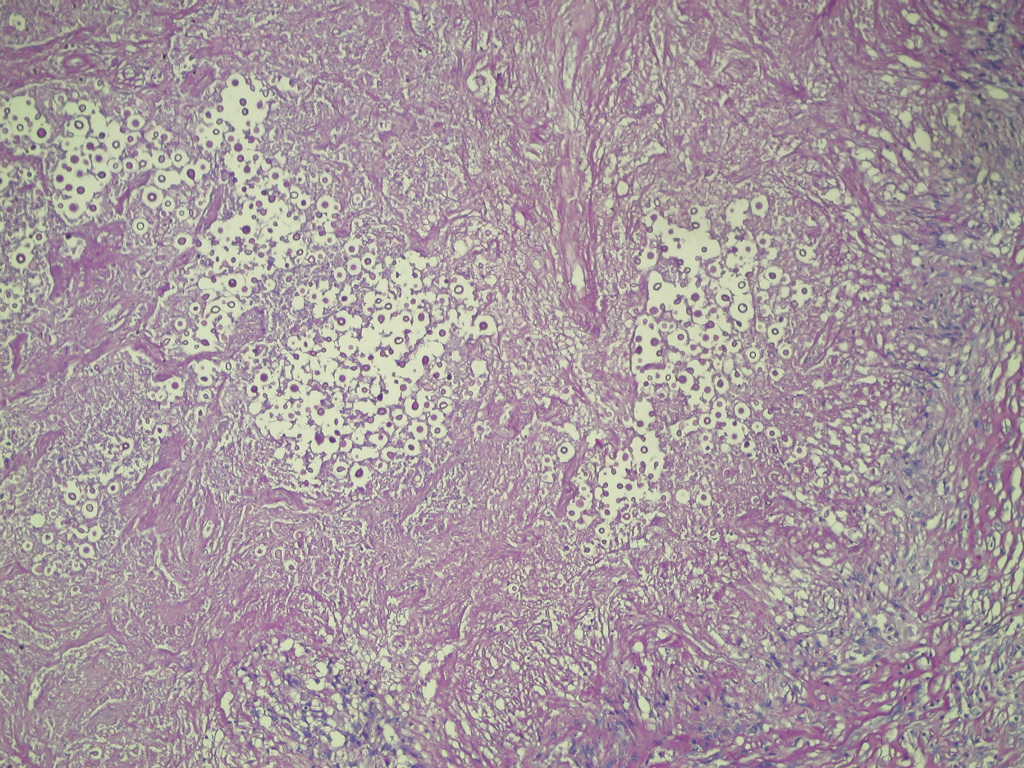
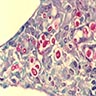
Microscopic (histologic) description
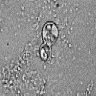
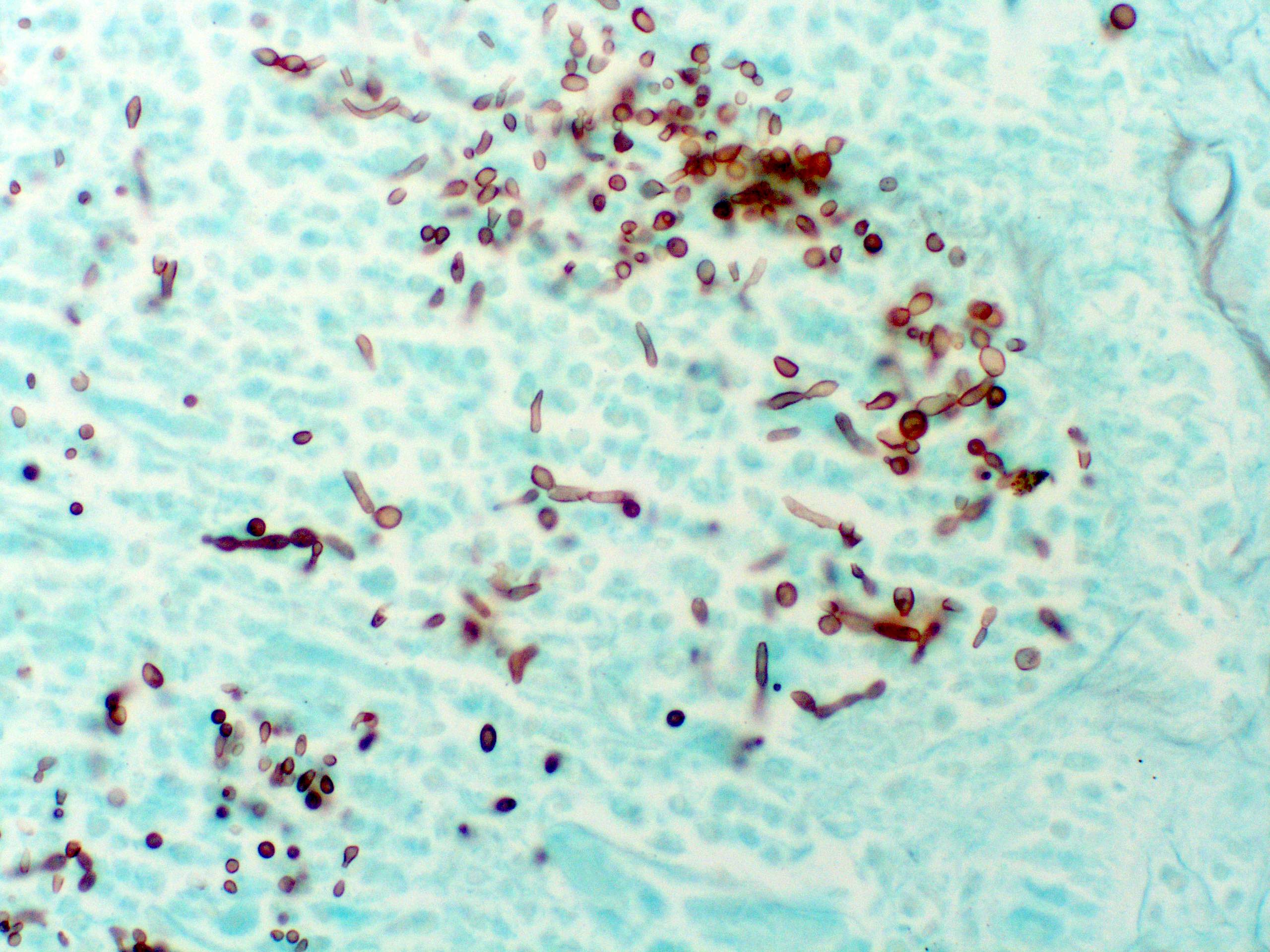
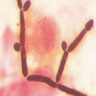
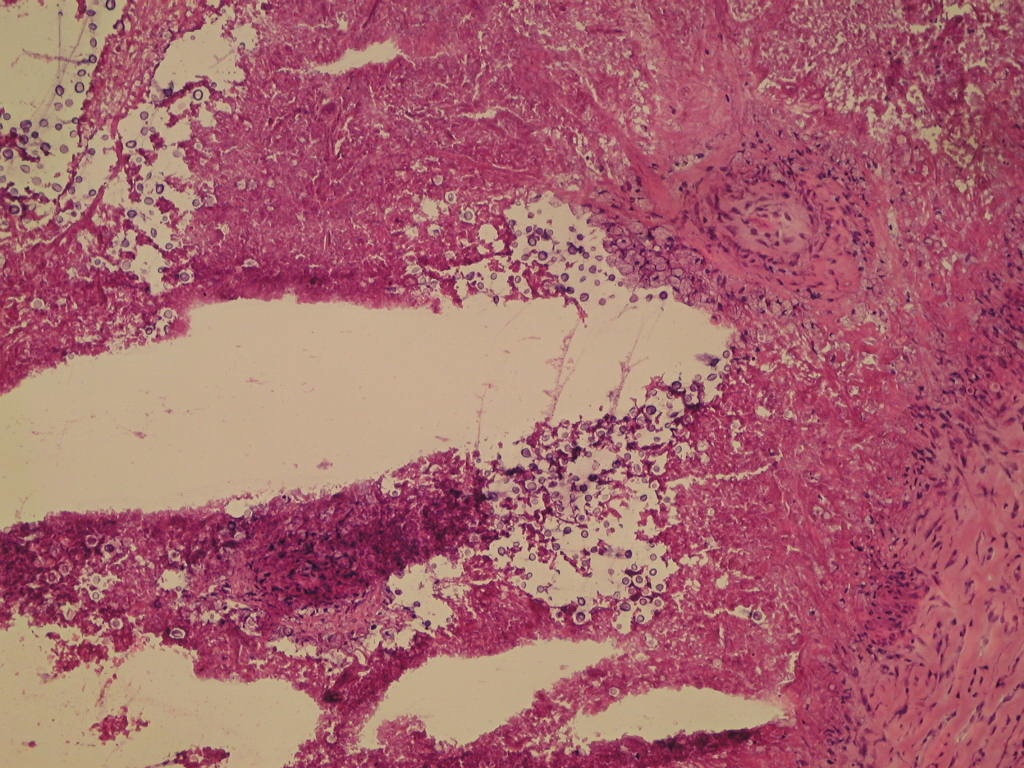
- Mixed acute and granulomatous inflammation caused by large budding yeasts (15 - 10 μm) with broad based buds and refractile walls
- Easily seen with H&E
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Candida
Definition / general
- See also Skin - nontumor chapter
- Normal flora of mouth, GI tract, vagina
- May be commensal or pathogen
- Commonly present in upper airways
- Often present in aspiration pneumonia or pulmonary abscess due to colonization but invasive disease due to candida is rare in lung except in setting of candidal sepsis
- Candida pneumonia associated with malignancy or immunosuppression (West J Med 1979;131:196)
Microscopic (histologic) description
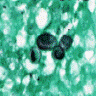
- Pseudohyphae, occasionally true hyphae and budding yeasts
- In some cases, only yeast may be present
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Yale Rosen, M.D.
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
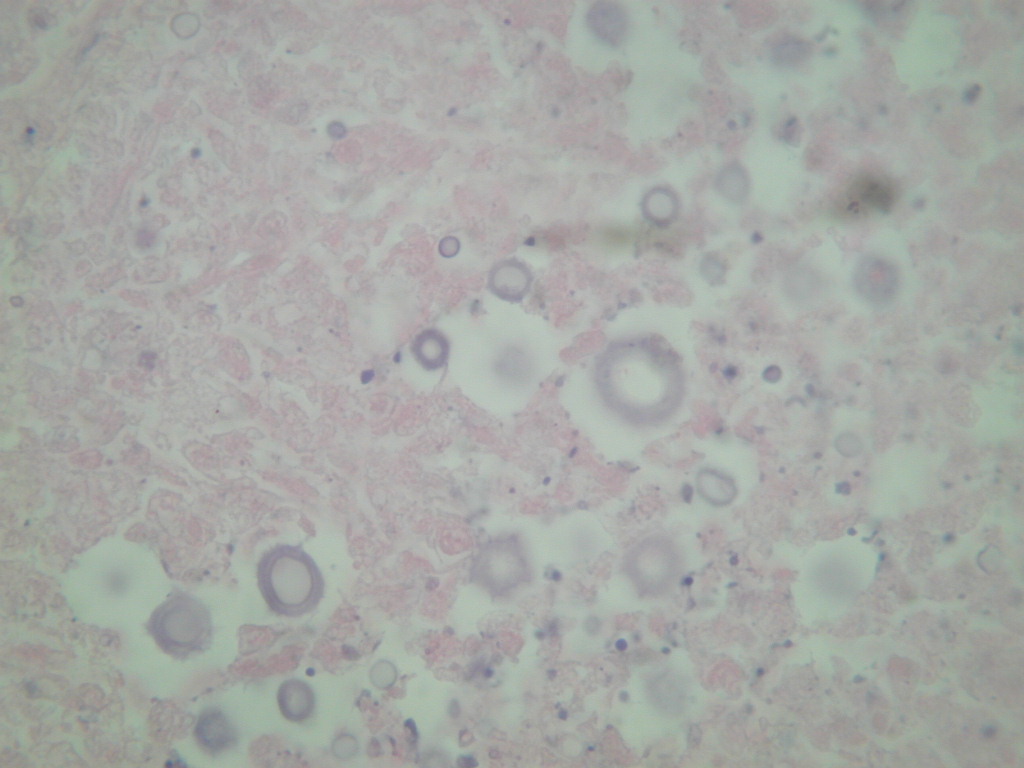
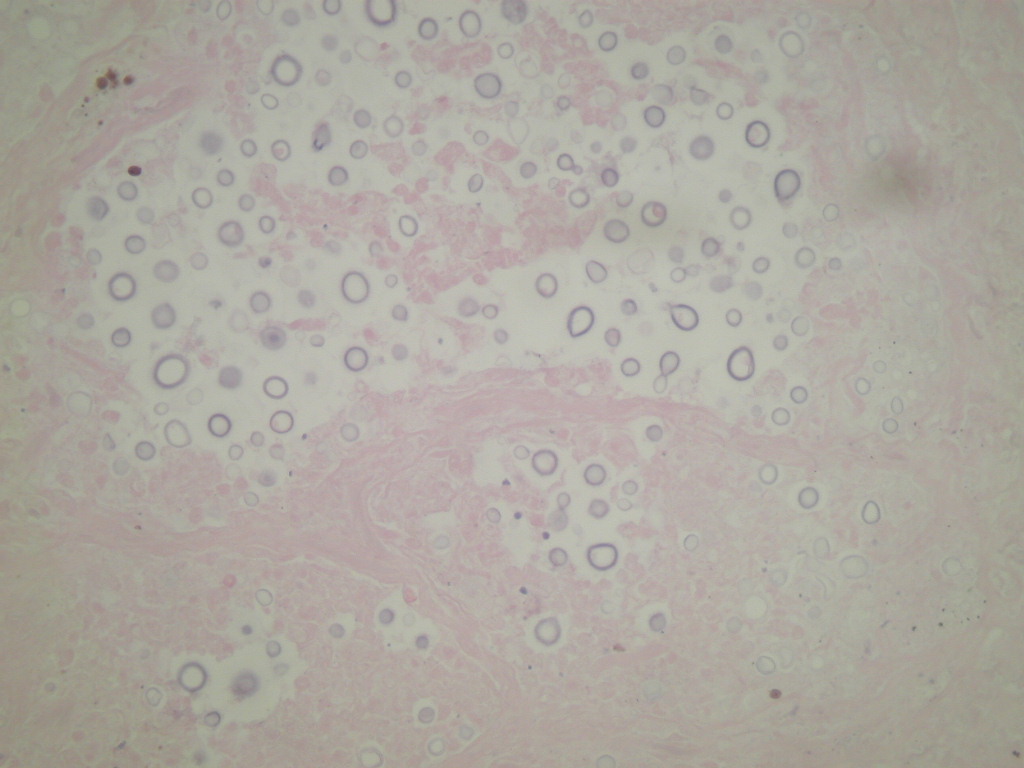
Cryptococcus
Clinical features
- Yeast, mostly encapsulated, found in pigeon droppings, that may cause mild infection after inhalation; usually confluent bronchopneumonia with "yeast lakes" of microorganisms and possibly coin lesions but no evident host response (eMedicine: Cryptococcosis [Accessed 22 March 2021])
- May also cause meningitis
- Latent infections can reactivate in immunosuppressed
- CNS disease is a major concern in immunocompromised
- Most commonly an opportunistic infection but disease may occur in immunocompetent patients
- Major virulence factor is capsular polysaccharide glucuronoxylomannin, which hinders phagocytosis by alveolar histiocytes and inflammatory cell recruitment and migration
- Other virulence factors include melanin production (Fontana-Masson stain may be positive; melanin may have antioxidant properties) and enzymes that increase invasiveness
Case reports
- 65 year old woman with arthritis and lung mass (Case of the Week #298)
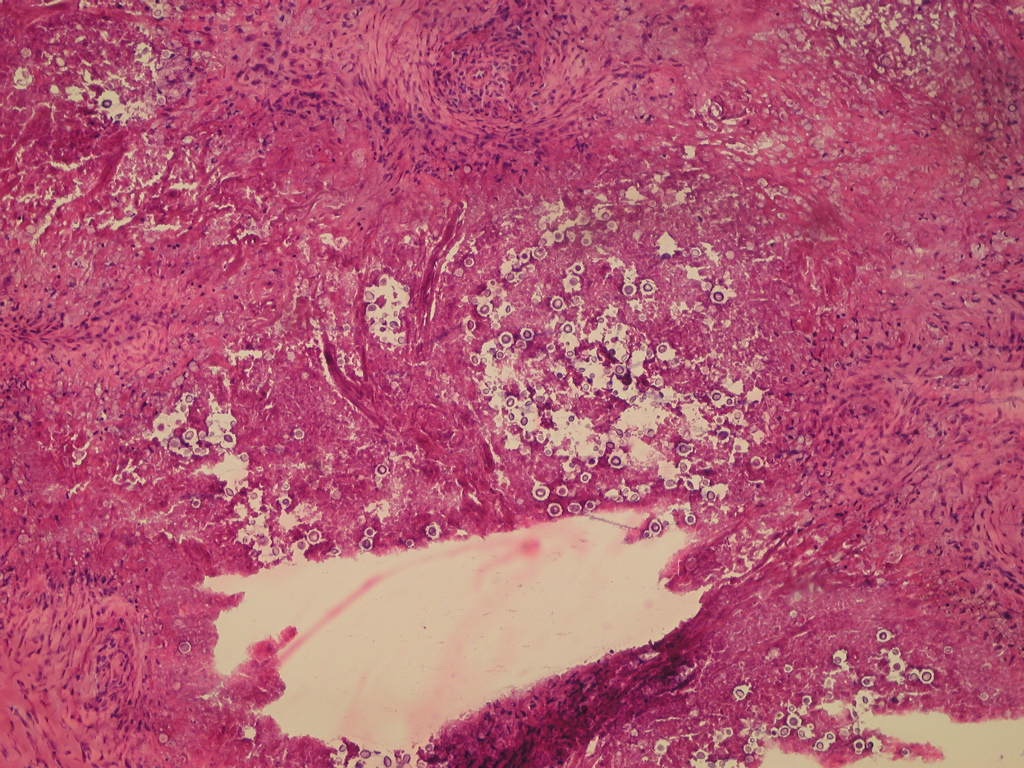
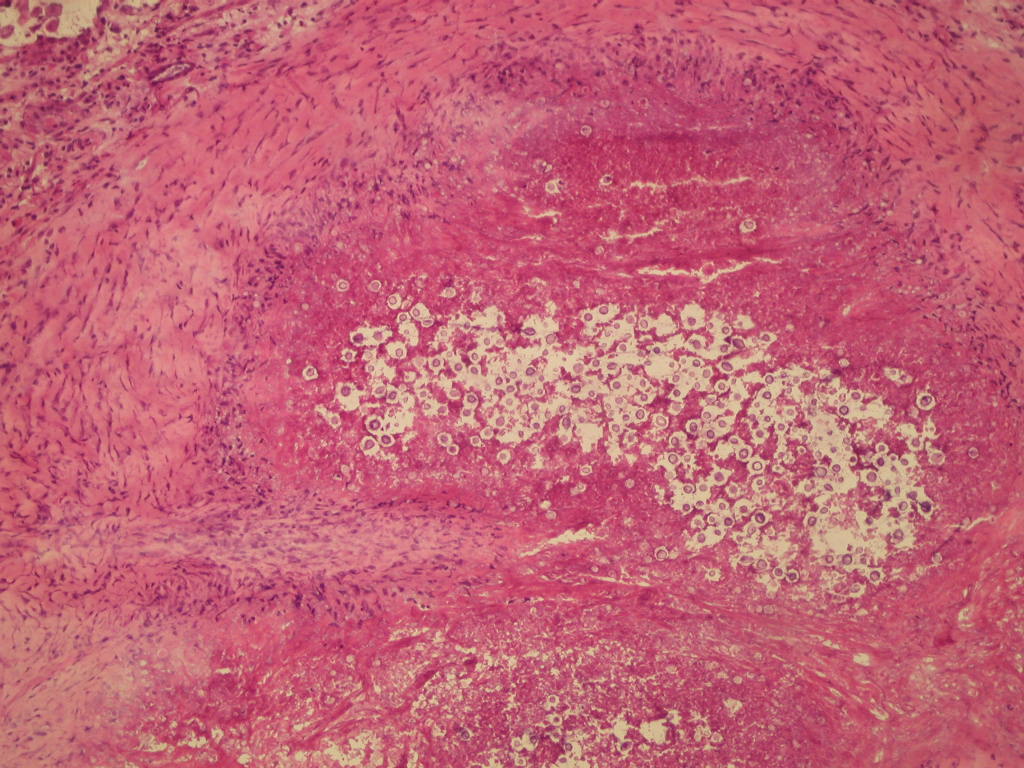
Microscopic (histologic) description
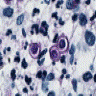
- Somewhat pleomorphic, round / oval yeast, 4 - 10 microns
- Thick, mucinous capsule stains bright red with mucicarmine; some are unencapsulated
- Narrow necked budding takes place
- Smaller, unencapsulated forms resemble Histoplasma capsulatum
Microscopic (histologic) images
Case #298
Images hosted on other servers:
Mucor
Definition / general
- Also known as zygomycosis or mucormycosis
- Ubiquitous fungi of class Zygomycetes, includes Mucor, Rhizopus, Absidia and Cunninghamella
- Opportunistic infection especially associated with diabetes; other predisposing factors are neutropenia, corticosteroid therapy, iron overload and mucocutaneous trauma
- Pulmonary and sinusoidal infection caused by inhaled spores or secondary to rhinocerebral mucormycosis
Case reports
- 39 year old man with necrotizing pneumonia (University of Pittsburgh: Case 181 [Accessed 22 March 2021])
Microscopic (histologic) description
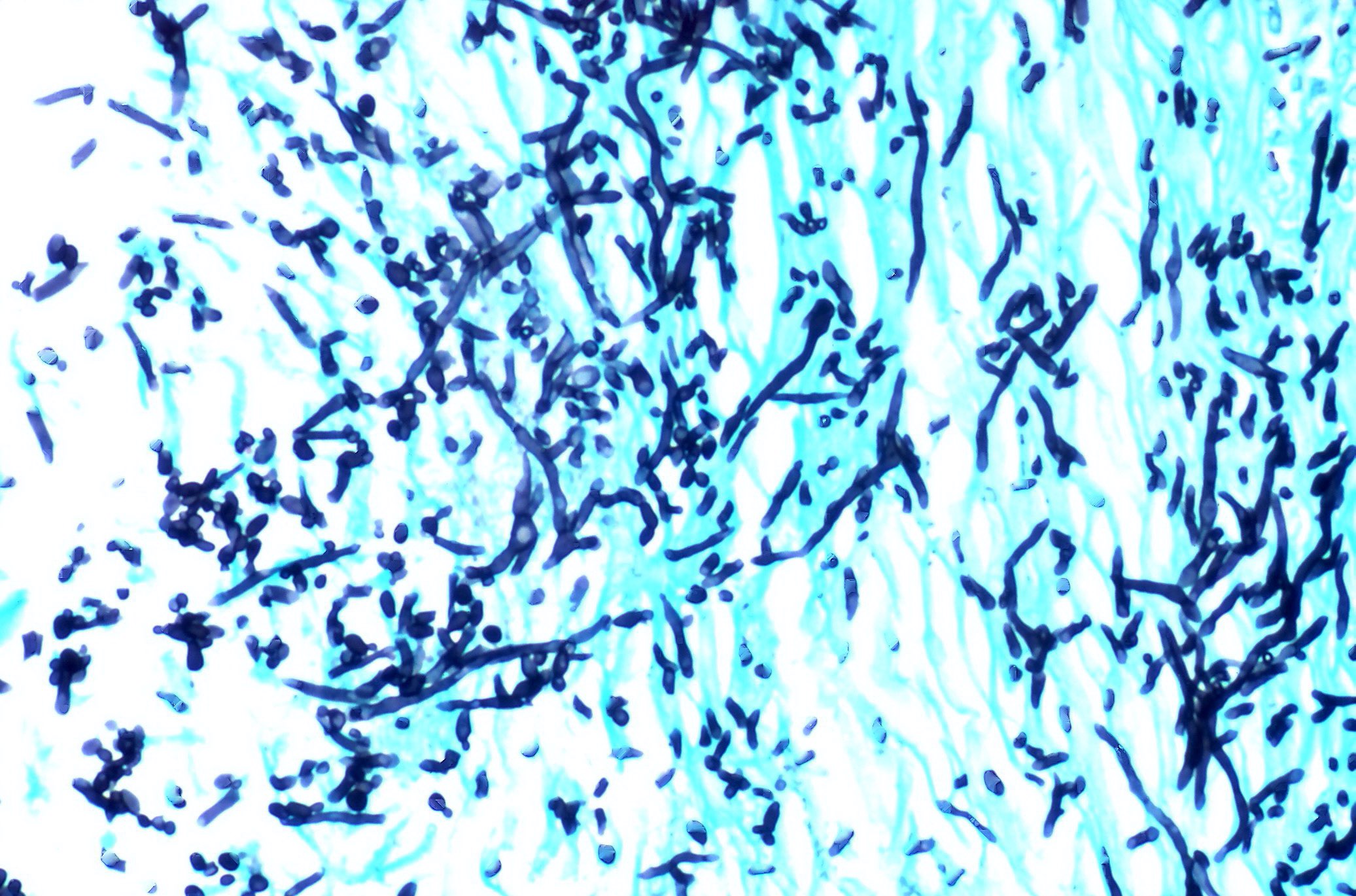
- Large, nonsepta hyphae with 90 degree angle branching and nonparallel walls, angioinvasive causing tissue necrosis and hemorrhage
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers: