Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Tripathy A, Husain AN. Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lunghyalinizingclearcellcarcinoma.html. Accessed December 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Low grade and indolent malignant neoplasm rarely seen in lung
- Head and neck is the most common location of this neoplasm
Essential features
- Rare, malignant, low grade neoplasm that arises in the bronchial glands of the middle aged population but is more common in salivary glands of the oral cavity
- Composed of trabeculae and solid areas separated by dense hyalinizing stroma
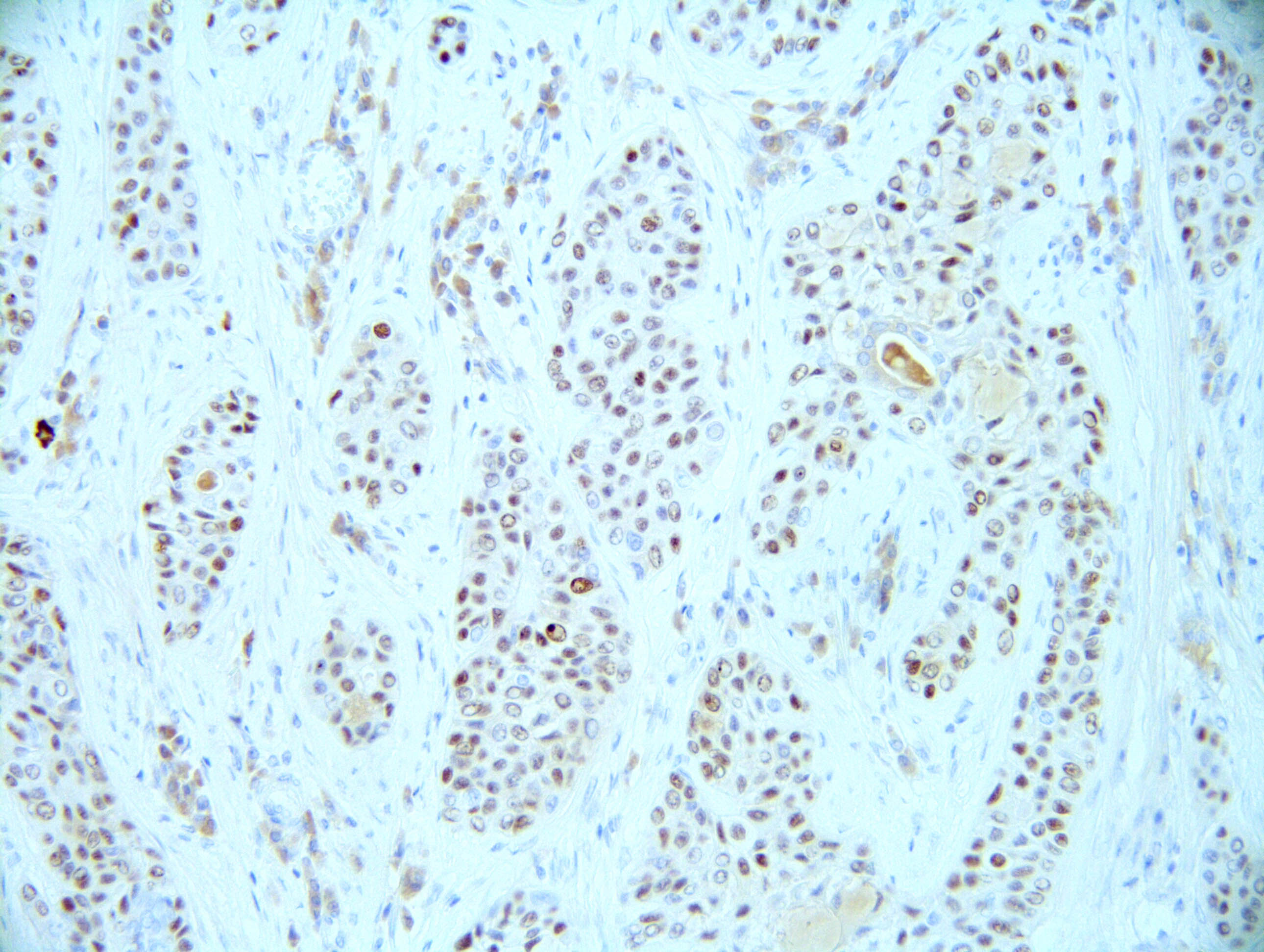
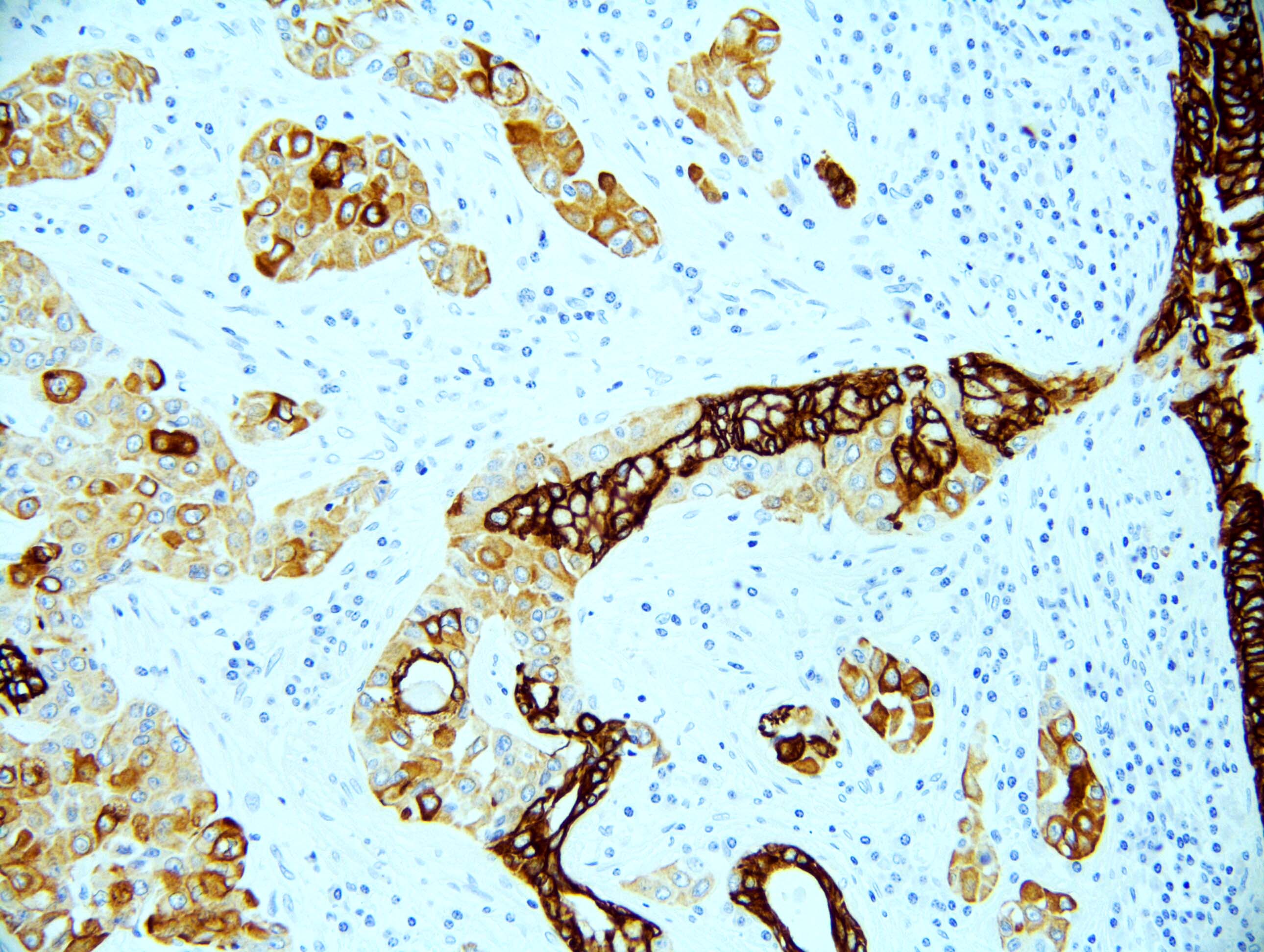
- Keratin and p40 positive
- Most important differential diagnosis is squamous cell carcinoma, which also stains positively with the same immunohistochemical markers but is much more aggressive
- Diagnosis can be confirmed by demonstrating EWSR1::ATF1 fusion
Terminology
- Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma of lung (HCCC)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8310/3 - clear cell adenocarcinoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Commonly seen in middle aged group (32 - 75 years), nonsmokers, with a M:F ratio of 2:3 (Int J Surg Pathol 2023;31:1187)
Sites
- These tumors are commonly located in the oral cavity, followed by uncommon locations, such as trachea, bronchi and nasopharynx (Int J Surg Pathol 2023;31:1187)
Pathophysiology
- Chimeric gene EWSR1::ATF1 transcripts have been seen in soft tissue sarcomas (including hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma of salivary glands) (Hum Pathol 2015;46:471, Am J Clin Pathol 2017;148:73, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2011;50:559)
- Although rare, hyalinizing clear cell carcinomas have also been identified in submucosal bronchial glands
Etiology
- Etiology of this neoplasm remains unclear
Clinical features
- Most cases are detected incidentally during regular physical examination and a few present with dyspnea, chest pain and hemoptysis (Front Oncol 2023;13:1175279)
Diagnosis
- These tumors are identified as masses incidentally on radiological imaging and on tumor cells with demonstration of EWSR1::ATF1 gene rearrangement being used as a confirmatory test (Am J Clin Pathol 2017;148:73)
Laboratory
- Cytogenetic or molecular study: Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1 (EWSR1) fluorescence in situ hybridization is a helpful ancillary test in diagnosing pulmonary hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma; most of these tumors demonstrate EWSR1::ATF1 fusion transcript (Am J Clin Pathol 2017;148:73)
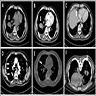
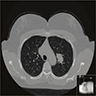
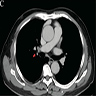
Radiology description
- Solitary, solid, well circumscribed / lobulated and noncalcified (Malays J Pathol 2022;44:509, Front Oncol 2023;13:1175279, Am J Clin Pathol 2017;148:73)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Excellent prognosis
- Long term follow up may be helpful in cases having lymph node metastasis, perineural invasion and tumor necrosis, as there is limited data on the prognosis of these cases (Int J Surg Pathol 2023;31:1187)
Case reports
- 54 year old woman with 2.5 cm right lung hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma, which demonstrated EWSR1::ATF1 gene fusion (Medicine (Baltimore) 2023;102:e34101)
- 58 year old male smoker with right upper lobe mass, which was diagnosed to be pulmonary hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma of salivary gland type (PPS: May 2020 Case of the Month [Accessed 11 March 2024])
- 70 year old man with pulmonary hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma harboring EWSR1::CREM fusion combined with a previously unreported IRF2::NTRK3 fusion (Front Oncol 2023;13:1175279)
- 81 year old man with synchronous existence of squamous cell carcinoma of right vocal cord and 2.9 cm hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma in the right upper lung (Diagn Pathol 2023;18:90)
- 81 year old female smoker with left upper lobe hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma (PPS: December 2022 Case of the Month [Accessed 11 March 2024])
Treatment
- Surgical resection is curative
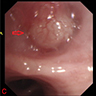
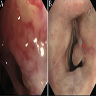
Clinical images
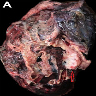
Gross description
- Solitary, solid, well circumscribed / lobulated and creamy white
Gross images
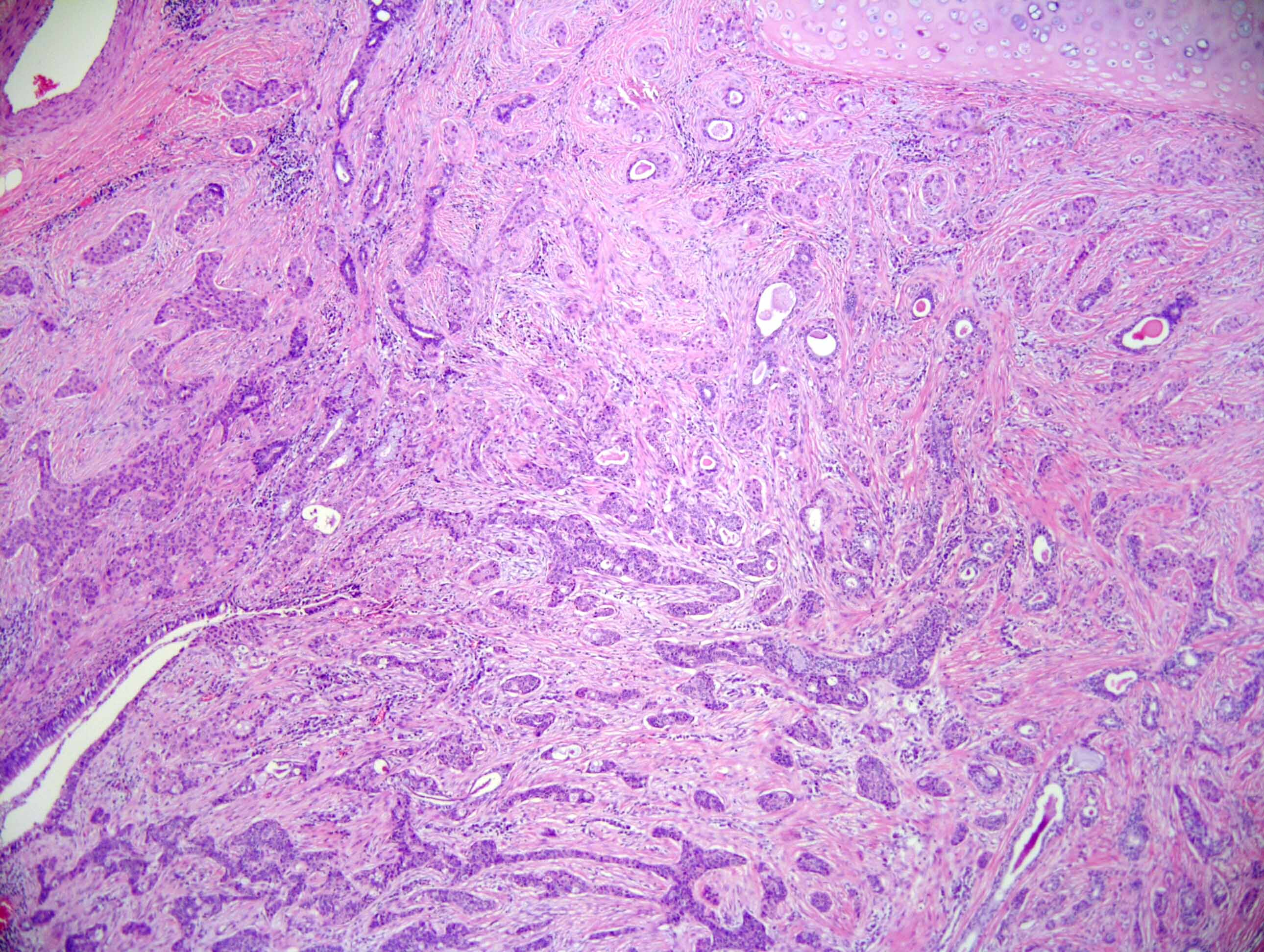
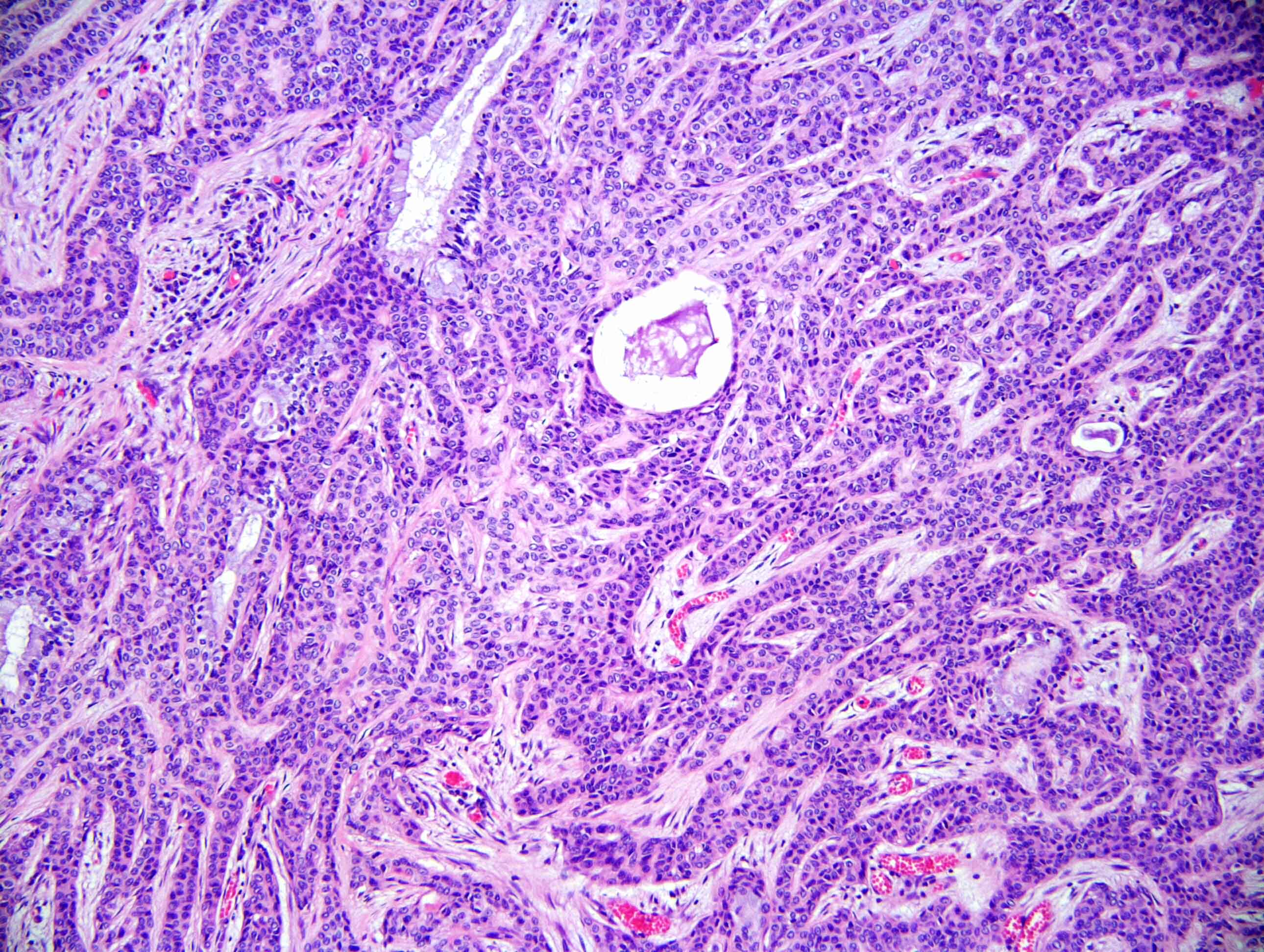
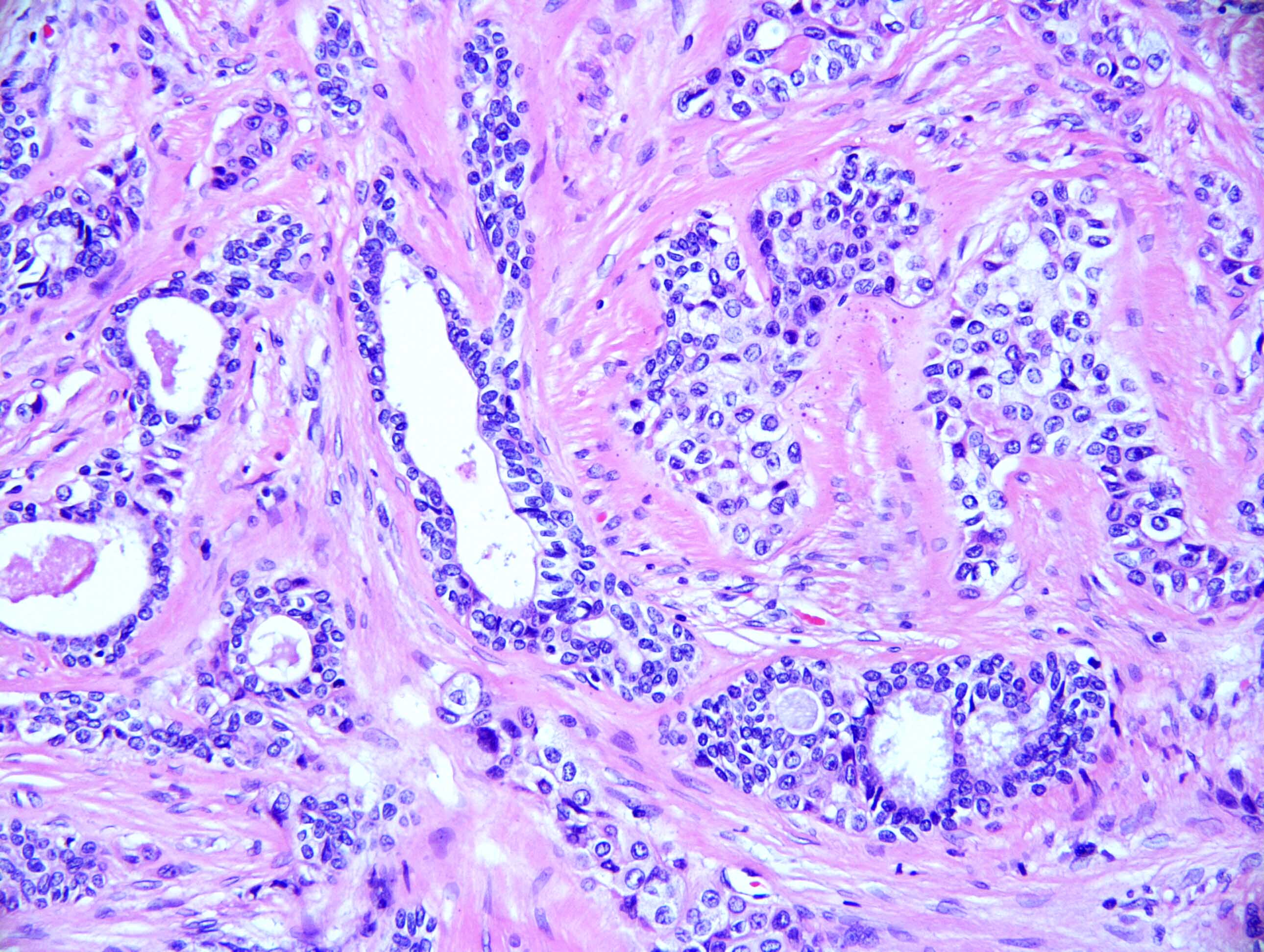
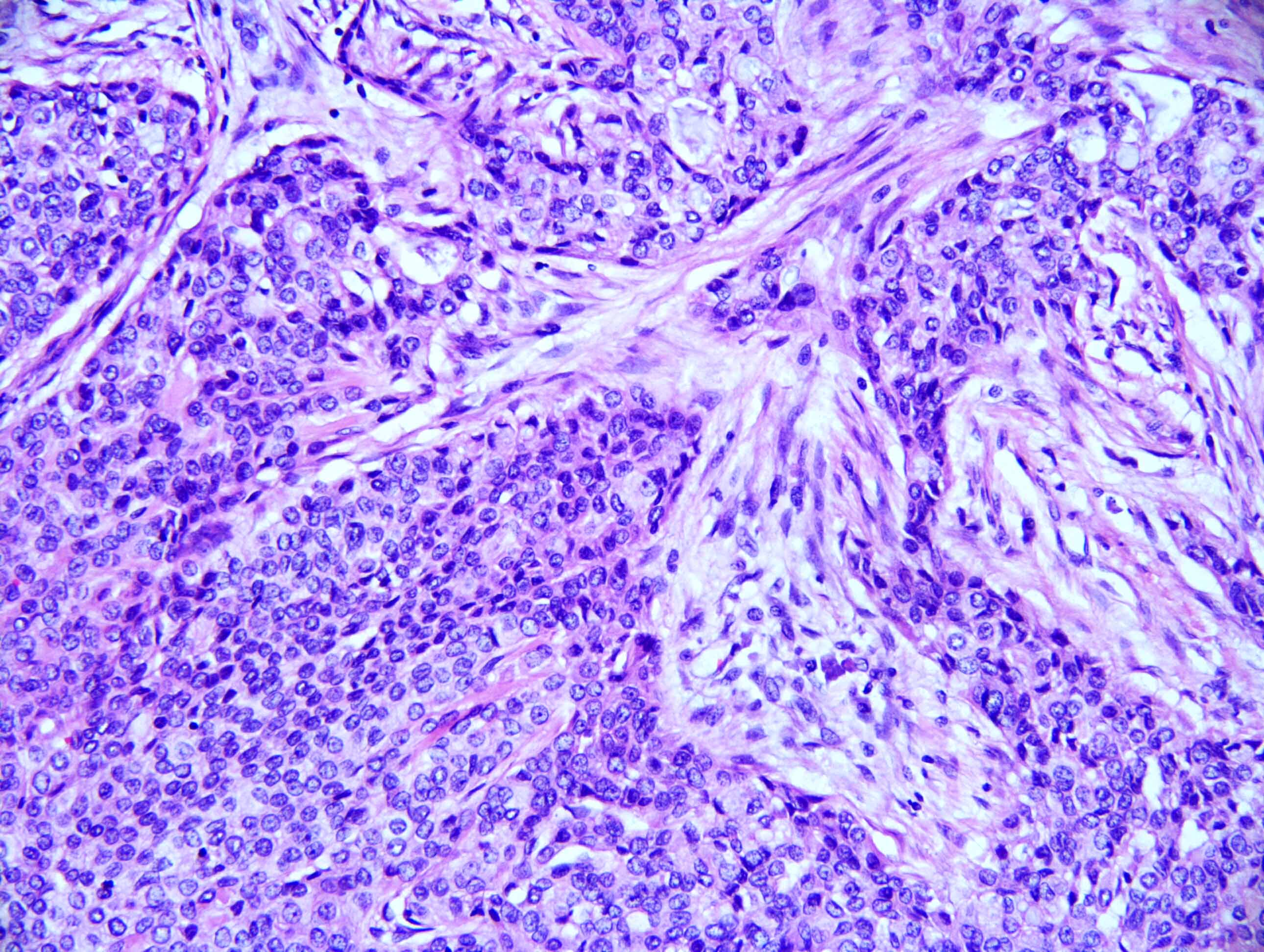
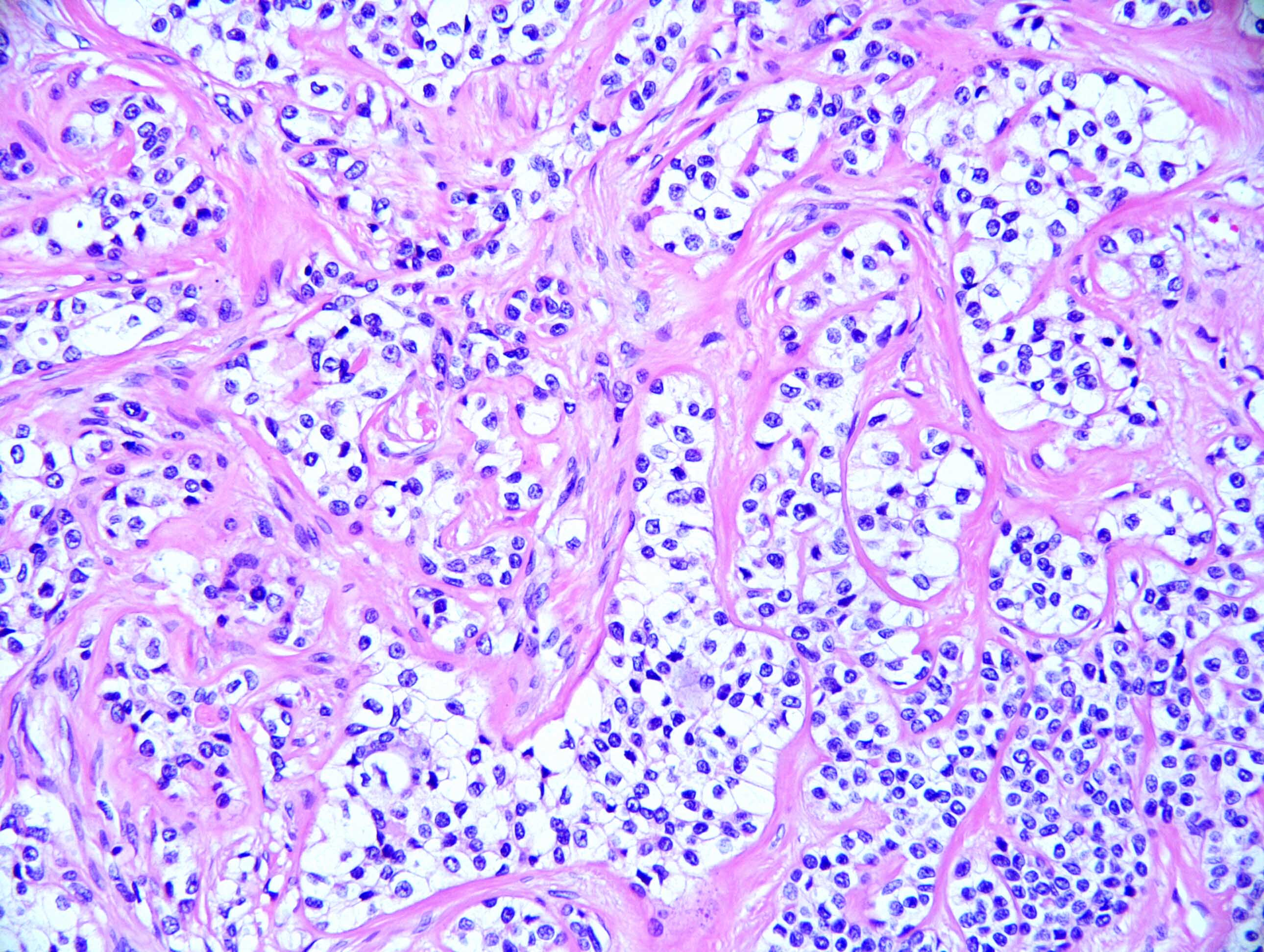
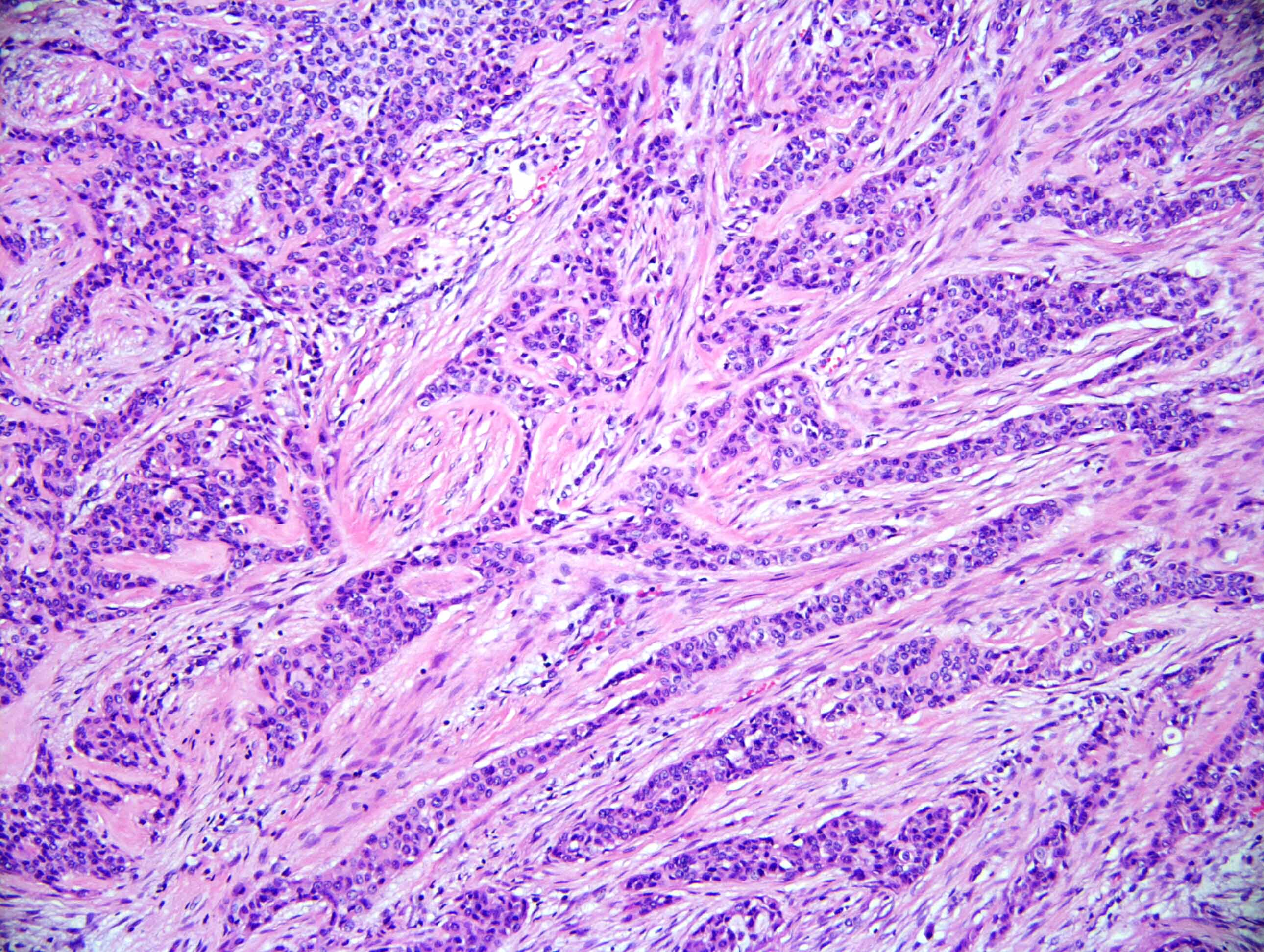
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Neoplasm with well demarcated borders composed of tumor cells arranged in nests, trabeculae and occasional glands
- Background stroma is composed of hyalinized collagen bands
- Tumor cells have clear or eosinophilic cytoplasm, round to oval nuclei with inconspicuous nucleoli (Mod Pathol 2018;31:923)
- Neural invasion is commonly seen in this neoplasm when compared with mucoepidermoid carcinoma (Mod Pathol 2018;31:923)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Negative stains
- TTF1, HMB45, PAX8, myoepithelial markers (smooth muscle actin, SOX10, smooth muscle myosin heavy chain, calponin, S100), neuroendocrine markers (chromogranin and synaptophysin) and markers for metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC, CD10)
- References: Mod Pathol 2018;31:923, Am J Clin Pathol 2017;148:73, Malays J Pathol 2022;44:509
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) assay using EWSR1 gene break apart probe was performed in all cases as a specific diagnostic ancillary technique; all cases harbored the characteristic EWSR1 gene rearrangement
Sample pathology report
- Lung, left, CT guided biopsy:
- Malignant neoplasm with clear cell features (see comment)
- Comment: Immunohistochemical studies (done with appropriate controls) showed that the tumor cells are immunoreactive for AE1 / AE3, p63 and negative for PAX8, TTF1, S100, SOX10 and HMB45. The morphology and staining pattern are most consistent with hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma. Fluorescence in situ hybridization assay using EWSR1 gene break apart probe to demonstrate presence of EWSR1 gene rearrangement can be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma:
- Only occasional cells in hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma may have intracellular mucin in contrast to mucoepidermoid carcinoma, which has abundant mucin cells (Mod Pathol 2018;31:923)
- Gene testing helps in difficult cases (Malays J Pathol 2022;44:509)
- Squamous cell carcinoma with prominent clear cell feature:
- These tumors have keratinization, high grade features, apparent dysplasia and high mitotic activity (Mod Pathol 2018;31:923)
- Metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma:
- PAX8 positivity
- Lung adenocarcinoma with clear cells:
- PEComa:
- Myoepithelial carcinoma:
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
A. EWSR1::ATF1 fusion. 93% of hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma cases demonstrate EWSR1::ATF1 fusion transcript. Answer B is incorrect because EWSR1::CREM fusion is rarely seen (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1182). Answers C and D are incorrect because EWSR1::ETV1 and EWSR1::FEV fusions have not been demonstrated in this neoplasm.
Comment Here
Reference: Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma