Table of Contents
Definition / general | Trade name | Indications | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical information | Uses by pathologists | Side effects | Drug administration | Molecular theory | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Yeh YA. Alectinib. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lungalectinib.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Alectinib is a therapeutic agent that inhibits the activity of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)
- Developed by Hoffmann-La Roche, Inc. and Genentech, Inc.
Trade name
- Alecensa®
Indications
- To treat patients with advanced or recurrent ALK positive non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) or who could not tolerate crizotinib (Xalkori®) - approved by U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in December 2015
- First line treatment of patients with ALK positive metastatic NSCLC - approved by U.S. FDA in November 2017
Pathophysiology
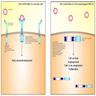
- In normal cells, ALK is activated by dimerization of extracellular ligands and autophosphorylation of intracellular tyrosine kinase, mostly involved in the neurodevelopment of CNS, gut and testes (Figure 1)
- ALK has been found to fuse with other genes in NSCLC, more commonly with EML4 gene; the resulting EML4-ALK fusion gene occurred in 3 - 6% of lung adenocarcinoma
- ALK is activated by the 5' fusion partner (e.g. EML4) that serves as a functional promotor and expresses a domain in the fusion protein for dimerization (Figure 1)
- Dimerized ALK rearranged fusion proteins activate downstream signaling pathways including STAT3, mTOR, PI3K, Ras and MEK to enhance cell survival, angiogenesis and cell cycle progression (Figure 1)
- Alectinib inhibits ALK tyrosine kinase by binding to its ATP binding site and blocking autophosphorylation of the EML4-ALK fusion protein, thereby inhibiting downstream STAT3, Ras and PI3K signaling pathways (Figure 2)
- Reference: Semin Cancer Biol 2017;42:81
Diagrams / tables
Clinical information
- Hepatotoxicity: monitor liver function tests every 2 weeks for first 3 months, then monthly
- Not recommended in patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment
- Withhold the drug if patients develop interstitial lung disease
- Withhold the drug if patients develop renal impairment
- Bradycardia: monitor heart rate and blood pressure regularly
- Myalgia: monitor creatine phosphokinase (CPK) every 2 weeks in first month
- Embryo fetal toxicity: advise females to use elective contraception
- Pharmacokinetics (Drug Saf 2019;42:199)
- Bioavailability: 37% (taken with a meal)
- Protein binding: > 99%
- Metabolism: CYP3A4 and other CYP enzymes and aldehyde dehydrogenase
- Plasma half life: 32.5 hours
- Excretion: mainly via feces (98%), minor fraction in urine (< 1%)
- Steady states: reached within 7 days
- Reference: FDA: Highlights of Prescribing Information [Accessed 8 October 2020]
Uses by pathologists
- ALK immunohistochemistry: cytoplasmic staining for altered ALK protein expression (N Engl J Med 2010;363:1693, Mod Pathol 2013;26:1545)
- Clone ALK1, Dako mouse monoclonal ALK1 antibody CD246, sensitivity 100%, specificity 99%
- Clone 5A4, Novocastra mouse monoclonal antibody p80 ALK, sensitivity 100%, specificity 98%
- Clone D5F3, Cell Signaling Technology rabbit monoclonal ALK XP, sensitivity 100%, specificity 99%
- Clone 1A4, Zeta mouse monoclonal anti-ALK antibody
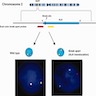
- ALK FISH: gold standard for evaluating ALK rearrangement
- ALK 2p23 dual color break apart FISH probe for detecting ALK gene rearrangement (Figure 3)
- ALK / EML4 tricolor FISH probe for detecting EML4-ALK gene fusion
- ALK RT-PCR and next generation sequencing
- Detecting point mutations, usually occur within tyrosine kinase domain
- Detecting gene amplifications (gene copy gain)
- Detecting rearranged ALK fusion genes and identifying fusion gene partners in chromosomal translocations, which include the following:
Chromosomal translocation Fusion gene References inv(2)(p21;p23)del(2)(p21;p23) EML4-ALK Nature 2007;448:561 t(2;2)(p23;p22) STRN-ALK J Pathol 2013;230:270 t(2;3)(p23;q12) TFG-ALK Cell 2007;131:1190 t(2;9)(p23;q31) PTPN3-ALK Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2012;51:590 t(2;10)(p23;p11) KIF5B-ALK Nat Med 2012;18:378 t(2;14)(p23;q32) KLC1-ALK PLoS One 2012;7:e31323 t(1;2)(q31;p23) TPR-ALK J Thorac Oncol 2014;9:563 t(2;7)(p23;q11) HIP1-ALK J Thorac Oncol 2014;9:419
Side effects
- Fatigue (> 20%)
- Constipation (> 20%)
- Anemia (20%)
- Peripheral edema (17%)
- Myalgia (16%)
- Increased blood bilirubin (15%)
- Increased ALT (15%)
- Increased AST (14%)
- Nausea (14%)
- Diarrhea (12%)
- Increased weight (10%)
- Dizziness (8%)
- Musculoskeletal pain (7%)
- Vomiting (7%)
- Photosensitivity reaction (5%)
- Dysgeusia (3%)
- Blurred vision (2%)
- Visual impairment (1%)
- Alopecia (1%)
- Increased γ glutamyltransferase (1%)
- References: N Engl J Med 2017;377:829, FDA: Highlights of Prescribing Information [Accessed 8 October 2020]
Drug administration
- 600 mg po bid with food
- 450 mg po bid with food for patients with severe hepatic impairment
- Discontinue if patients cannot tolerate 300 mg po bid
- Reference: ALECENSA: Dosing and Administration [Accessed 8 October 2020]
Molecular theory
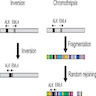
- ALK is located at chromosome 2p21 and EML4 at 2p23.1-23.2
- EML4-ALK fusion gene can be caused by chromosomal inversion or a complicated chromosomal translocation (chromothripsis) (Figure 4) (J Thorac Oncol 2014;9:1638)
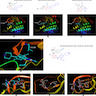
- Alectinib weakly interacts with the P loop of rearranged ALK protein shown in the cocrystal structures (Figure 5) (Lung Cancer 2017;110:32)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following lung primary tumors could be treated with alectinib?
- Adenocarcinoma with ALK rearrangement
- Adenocarcinoma with c-MET rearrangement
- Adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations
- Small cell carcinoma with MYC rearrangement
Board review style answer #1