Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Fels Elliott DR, Gill RM. HCC - sarcomatoid variant. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/livertumorsarcomatoid.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) variant, partially or entirely composed of malignant spindle cells
Essential features
- Component of spindle cell morphology
- Area of conventional HCC usually present to support the diagnosis
- Worse prognosis than classic HCC
- Sarcomatoid transformation associated with repeated chemotherapy / chemoembolization
Terminology
- Also called spindle cell HCC, pseudosarcomatous HCC
- May be called carcinosarcoma when heterologous elements are present (Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2017;46:365, J Clin Oncol 2014;32:e63)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C22.7 - other specified carcinomas of liver
Epidemiology
- Incidence ranges from 0.3% of HCC in resected specimens to 9.4% in autopsy series (Cancer Med 2021;10:6227, Cancer 1987;59:310, Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1989;23:S4)
- Patients tend to be older and predominantly male (Hepatology 2019;69:209, J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2022;148:1685)
Sites
- Liver
Pathophysiology
- Associated with expression of genes related to epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) and inflammation (Int J Cancer 2021;149:546)
- Higher expression of PDL1 in tumor cells and infiltration by immune cells compared to conventional HCC (Int J Cancer 2021;149:546, Aging (Albany NY) 2021;13:15126)
Etiology
- Similar etiologic factors to classic HCC (J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2022;148:1685)
- Sarcomatoid change is more frequent in patients undergoing repeated chemotherapy or transarterial chemoembolization (Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1989;23:S4)
Clinical features
- Larger tumor size, advanced stage and higher incidence of extrahepatic disease (e.g., lymph nodes, lungs, bone) compared to classic HCC (Cancer Med 2021;10:6227, World J Gastroenterol 2020;26:4327, J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2022;148:1685)
Diagnosis
- Imaging modalities for diagnosis of HCC: multiphasic computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Tissue biopsy is indicated if imaging is not diagnostic of HCC
Laboratory
- Lower serum alpha fetoprotein (AFP) compared to classic HCC (Surg Pathol Clin 2013;6:367, World J Gastroenterol 2020;26:4327)
Radiology description
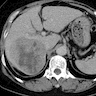
- Large hepatic mass with central necrosis and peripheral rim enhancement (may mimic hepatic abscess or cholangiocarcinoma) (J Comput Assist Tomogr 2008;32:745)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Worse prognosis compared to classic HCC (Hepatology 2019;69:209, Ann Surg Oncol 2015;22:S1048, Cancer Med 2021;10:6227, Int J Cancer 2021;149:546, World J Gastroenterol 2020;26:4327, J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2022;148:1685)
- Prognostic factors for HCC: stage (TNM), single lesion versus multifocal, size, vascular invasion, portal vein thrombosis, severity of underlying liver disease (Liver Int 2009;29:502, J Surg Oncol 2018;117:644)
Case reports
- 56 year old man with abdominal pain and suspected hepatic abscess (Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e22489)
- 62 year old man with a history of hepatitis B (J Cancer Res Ther 2015;11:665)
- 68 year old woman with abdominal distension (World J Surg Oncol 2017;15:219)
- 68 year old man with a right liver mass (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:40)
- 70 year old man with right upper quadrant pain (J Clin Oncol 2014;32:e63)
Treatment
- Surgical resection (Int J Surg 2018;55:145, Ann Surg Oncol 2015;22:S1048)
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE)
- Transplantation (e.g., Milan criteria, modified by some institutions, Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;14:203)
Gross description
- Poorly circumscribed, lobulated mass; may contain areas of necrosis and possibly heterologous elements
Gross images
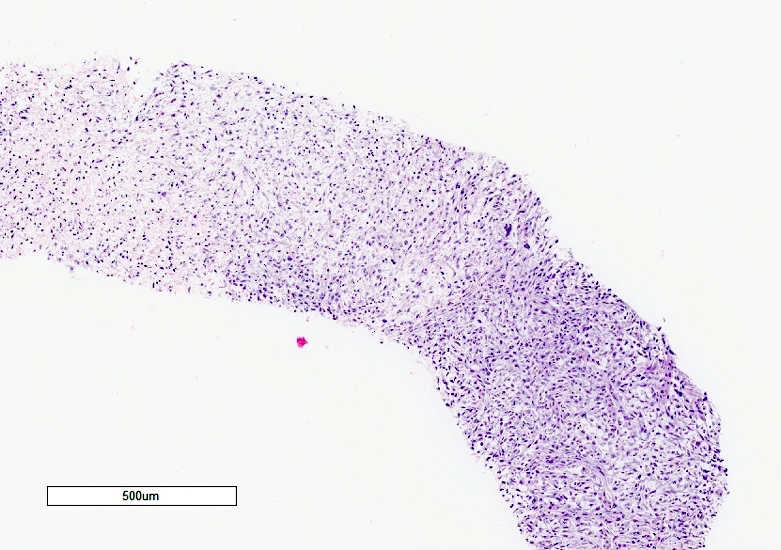
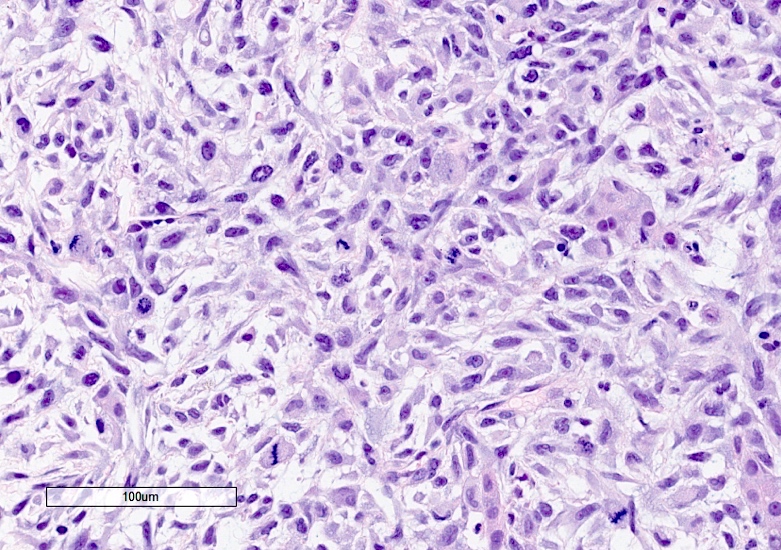
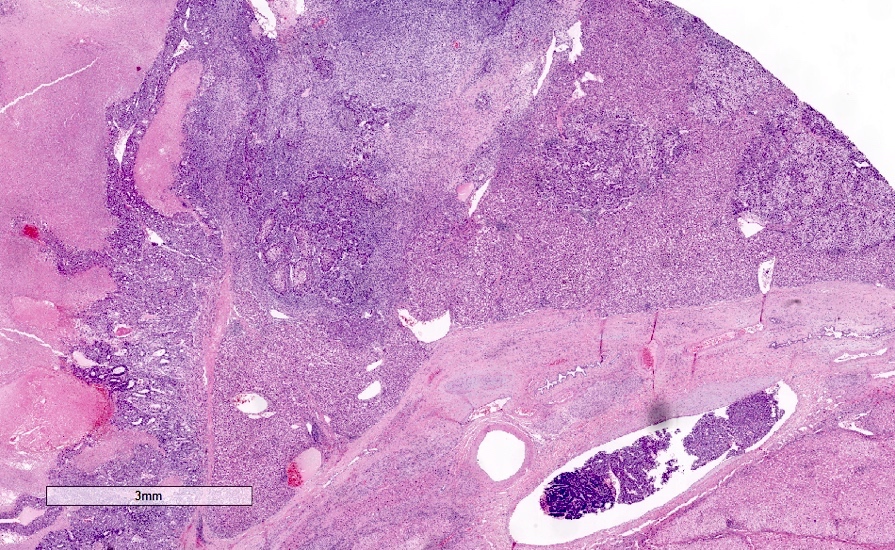
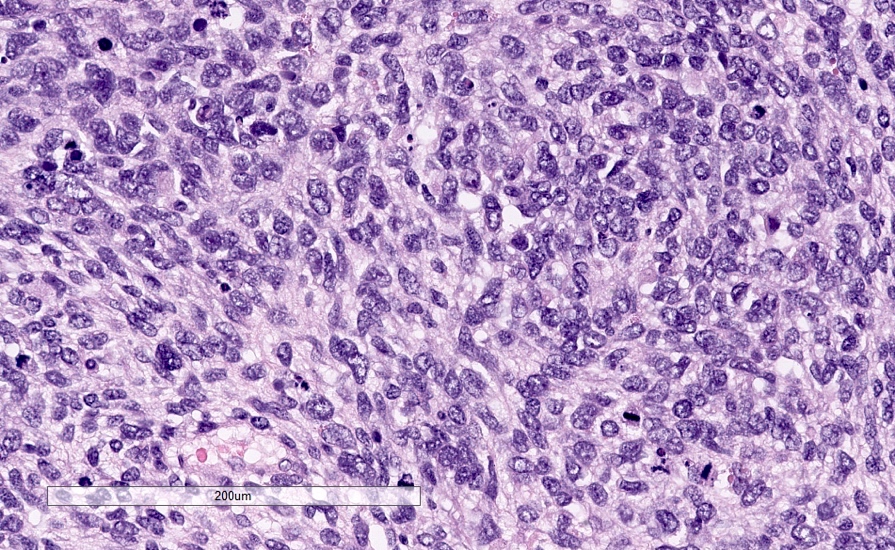
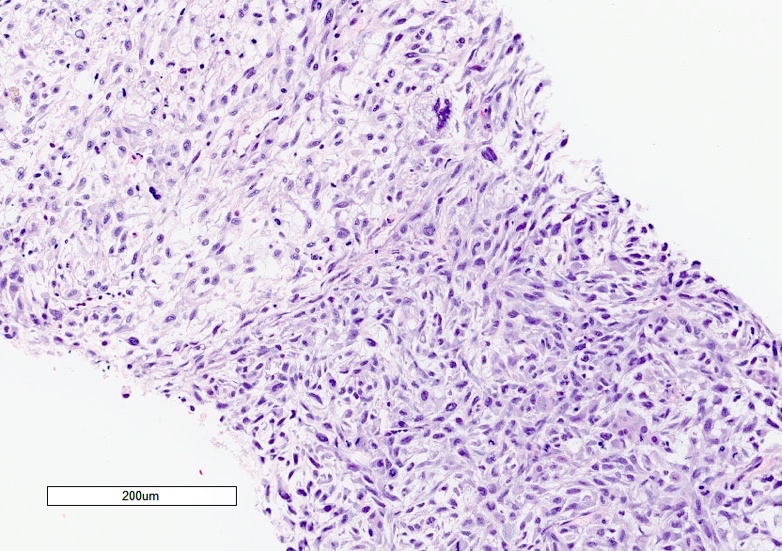
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Partially or entirely composed of malignant spindle cells
- Component of classic HCC is often present to help confirm the diagnosis
- Spindle component may have variable cellularity, nuclear pleomorphism, frequent mitoses
- If heterologous elements are present, the term carcinosarcoma may be used
- Various types of heterologous elements have been reported, including rhabdoid, osteoid and chondroid differentiation; may have pleomorphic and osteoclast-like giant cells (Virchows Arch 1999;434:511, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:817, Pathol Int 2000;50:919, Clin Mol Hepatol 2014;20:313, Diagn Pathol 2015;10:40)
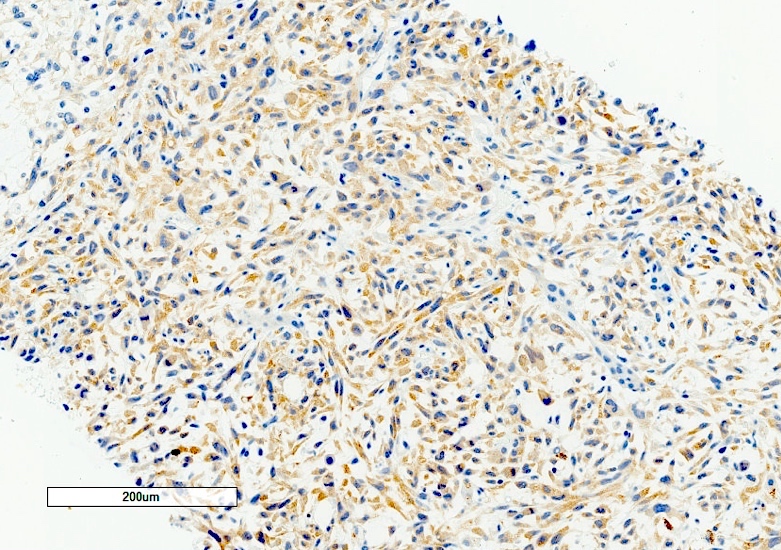
Microscopic (histologic) images
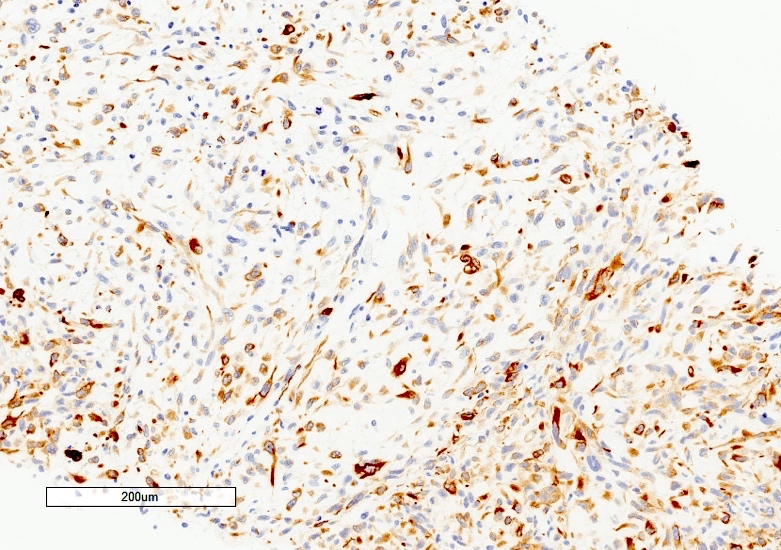
Positive stains
- Cytokeratin variably positive (20 - 60%) (Cancer 1987;59:310, Cancer 1996;77:51)
Negative stains
- Hepatocellular markers (HepPar1, arginase1, glypican 3) typically negative in the sarcomatoid component
- Sarcomatoid markers (e.g., vimentin, actin): typically negative in the carcinomatous component
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Negative albumin mRNA by ISH in the sarcomatoid component (Pathol Res Pract 2013;209:249)
- Molecular alterations: CDKN2A, EPHA5, FANCM, MAP3K1 mutations (Cancer Med 2021;10:6227)
- Common cell of origin of epithelial and sarcomatoid components (same TP53 mutation), with clonal evolution (J Clin Oncol 2014;32:e63)
Sample pathology report
- Liver, mass, core biopsy:
- Hepatocellular carcinoma, sarcomatoid variant (see comment)
- Comment: This tumor shows two distinct morphologies. One component shows features of classic hepatocellular carcinoma, while the second component shows sarcomatoid features, including pleomorphic spindle cells. Cytokeratin is variably positive and hepatocellular markers (HepPar1, arginase1 and glypican 3) are negative in the sarcomatoid component, as is typical for this variant.
Differential diagnosis
- Sarcoma (undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma and fibrosarcoma):
- Clinical history of sarcoma
- Will not have area of classic HCC
- Immunohistochemistry (entirely negative for pancytokeratin) and potentially molecular testing (e.g., next generation sequencing cancer gene panel) are necessary for diagnosis
- Undifferentiated primary liver carcinoma:
- Shows no specific differentiation except epithelial based on morphology and immunohistochemistry (pancytokeratin+)
- No evidence of differentiation towards HCC or cholangiocarcinoma
- May be albumin ISH+
- Metastatic sarcomatoid carcinoma:
- Will not have area of classic HCC
- Clinical history of carcinoma
- Usually multiple nodules
- Immunohistochemistry (pancytokeratin+) and potentially molecular testing (e.g., next generation sequencing cancer gene panel) are necessary for diagnosis
- Negative for hepatocellular markers, positive keratin staining (usually patchy, perhaps only for high molecular weight keratins, e.g., as detected on MNF116)
Board review style question #1
Which of the following histologic features is characteristic of the sarcomatoid variant of hepatocellular carcinoma?
- Contains components of conventional HCC and spindle cell morphology
- Cytokeratin is always negative in the sarcomatoid component
- Hepatocellular markers are usually positive in the sarcomatoid component
- Must be entirely composed of malignant spindle cells
- Necrosis is not a common feature
Board review style answer #1
A. Contains components of conventional HCC and spindle cell morphology
Comment Here
Reference: Sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is true regarding the sarcomatoid variant of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)?
- Associated with a better prognosis than classic HCC
- Higher serum AFP in comparison to classic HCC
- More common in patients undergoing repeated chemotherapy or transarterial chemoembolization
- Patients are predominantly female
- There is a lower incidence of extrahepatic spread in comparison to classic HCC
Board review style answer #2
C. More common in patients undergoing repeated chemotherapy or transarterial chemoembolization
Comment Here
Reference: Sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma