Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Clinical features | Radiology description | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Assarzadegan N, Gonzalez RS. Macroregenerative nodule. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/livertumormacroregenerativenodule.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Discrete regenerative hepatocellular nodule that often arises in the background of cirrhosis
Essential features
- May represent a precursor of hepatocellular carcinoma (Hepatology 1992;16:949)
- Classified into type I and type II, based on cytological and architectural atypia (Cancer 1998;61:99)
- Macroregenerative nodule (MRN) II shows atypical cytologic or architectural features that are insufficient for a diagnosis of malignancy
Terminology
- Also called hepatocellular pseudotumor, adenomatous hyperplasia, adenomatous hyperplastic nodule or adenomatous regeneration
Clinical features
- Most MRNs are seen in cirrhotic livers
- Occurs in about 10% of cirrhotic livers at autopsy or at time of transplantation
- Role of MRN in hepatocarcinogenesis varies in different studies and the true biologic nature of these nodules is uncertain (Int J Hepatol 2016;2016:4390434)
Radiology description
- Well defined isointense nodules relative to the background liver
Gross description
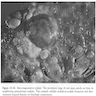
- Usually multiple, large, discrete, tumor-like hepatocellular masses > 1 cm in diameter (rarely > 5 cm)
- Often differ from surrounding nodular parenchyma in color, texture or degree to which they bulge beyond the cut liver surface
Gross images
Microscopic (histologic) description
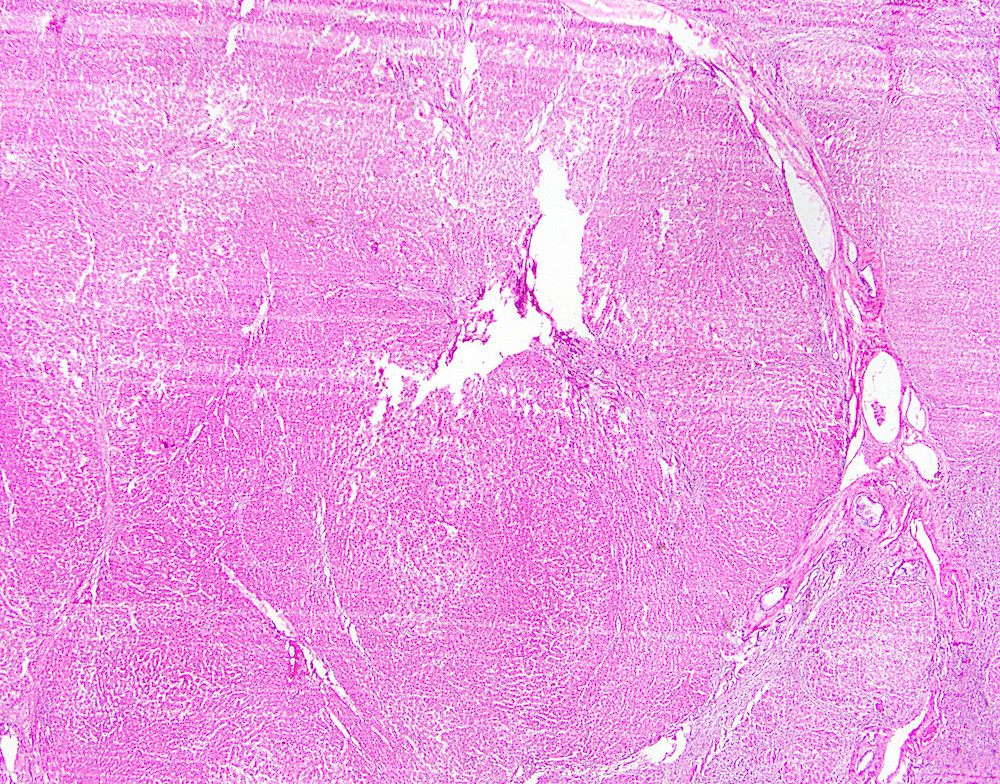
- Liver cell plates 1 - 2 cells thick, reduced and scattered portal tracts with variable structural distortion (prominent bile ductules, absent interlobular bile ducts)
- Hepatocytes resemble those in adjacent liver and may reflect any disease process there
- MRN type II may have architectural and cytologic atypia
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Liver, native, orthotopic transplantation:
- Cirrhosis with mild to moderate chronic inflammation and occasional macroregenerative nodules (see comment)
- Negative for dysplasia or malignancy.
- Margins of resection unremarkable.
- Comment: The findings are consistent with the patient’s reported history of autoimmune hepatitis. A trichrome stain confirms cirrhosis. An iron stain is unremarkable.
Differential diagnosis
- Early hepatocellular carcinoma:
- Can be difficult or impossible to distinguish from MRN type II with cytological atypia
- Large regenerative nodule:
- Low malignant potential
- Less commonly arises in cirrhosis
- Similar if not identical by morphology
Board review style question #1
- Which of these liver lesions is the least likely to arise in the background of cirrhosis?
- High grade dysplastic nodule
- Large regenerative nodule
- Low grade dysplastic nodule
- Macroregenerative nodule
Board review style answer #1