Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Assarzadegan N, Gonzalez RS. Liver cell dysplasia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/livertumorlivercelldysplasia.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Premalignant foci in liver characterized by morphologic alterations of hepatocytes and sometimes by architectural changes
- Challenging category that encompasses macroscopic and microscopic patterns of change (see also low grade dysplastic nodule and high grade dysplastic nodule) (Hepatology 2009;49:658)
Essential features
- Dysplastic features in hepatocytes that can progress to malignancy as part of a multistep sequence
- May be incidentally discovered or seen in a discrete nodule
Terminology
- Dysplastic foci are incidental submillimeter microscopic lesions in cirrhotic livers containing dysplastic hepatocytes (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2011;135:704)
- Large cell change and small cell change refer to morphologic changes in hepatocytes; these were formerly called large cell dysplasia and small cell dysplasia
- Iron free foci are areas of hepatocytes lacking iron in a liver otherwise suffering significant iron overload; they appear to be preneoplastic (Hepatology 1993;18:1363)
- Terms adenomatous hyperplasia and atypical adenomatous hyperplasia are no longer in use
Gross description
- Dysplastic foci cannot be identified grossly
Microscopic (histologic) description
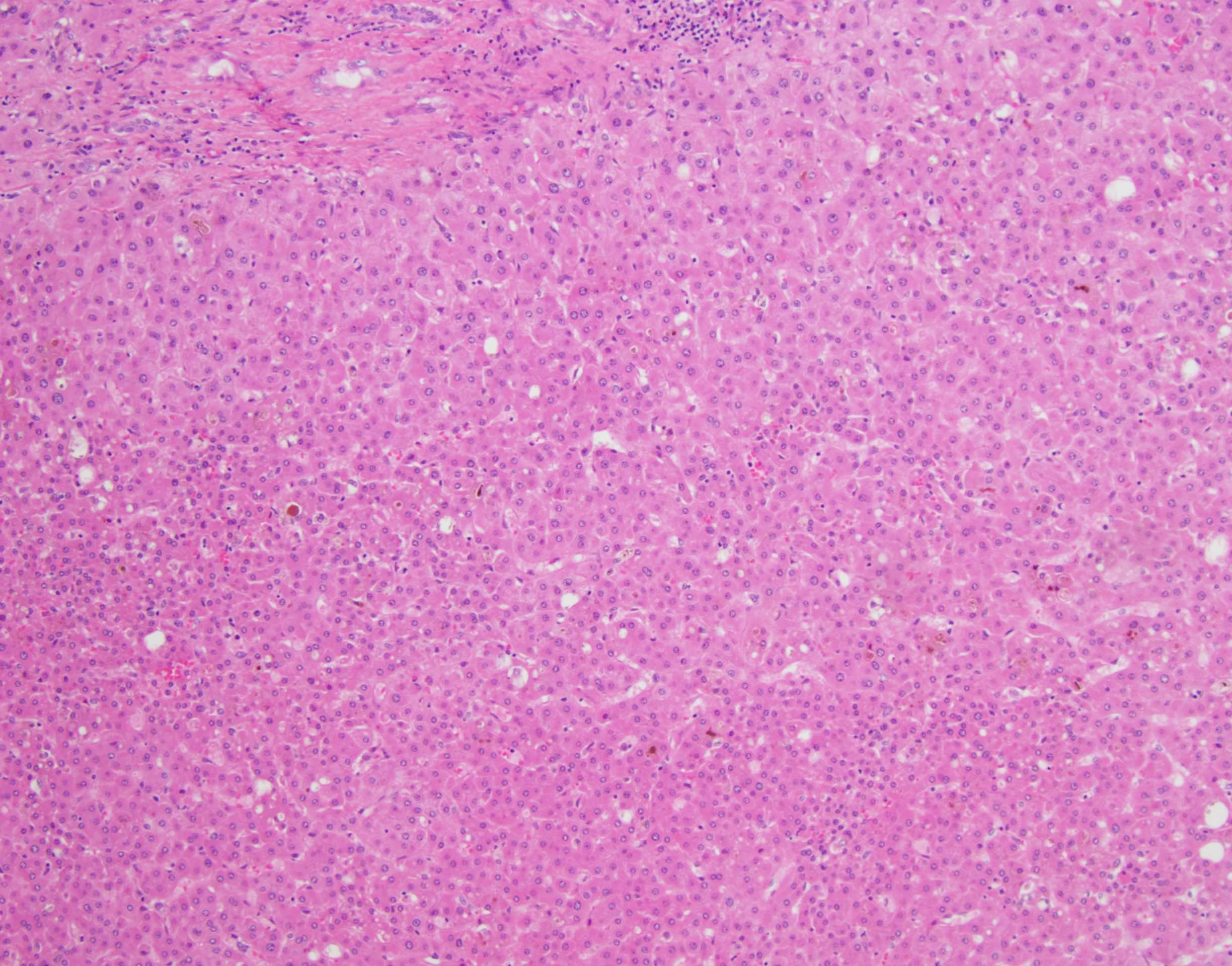
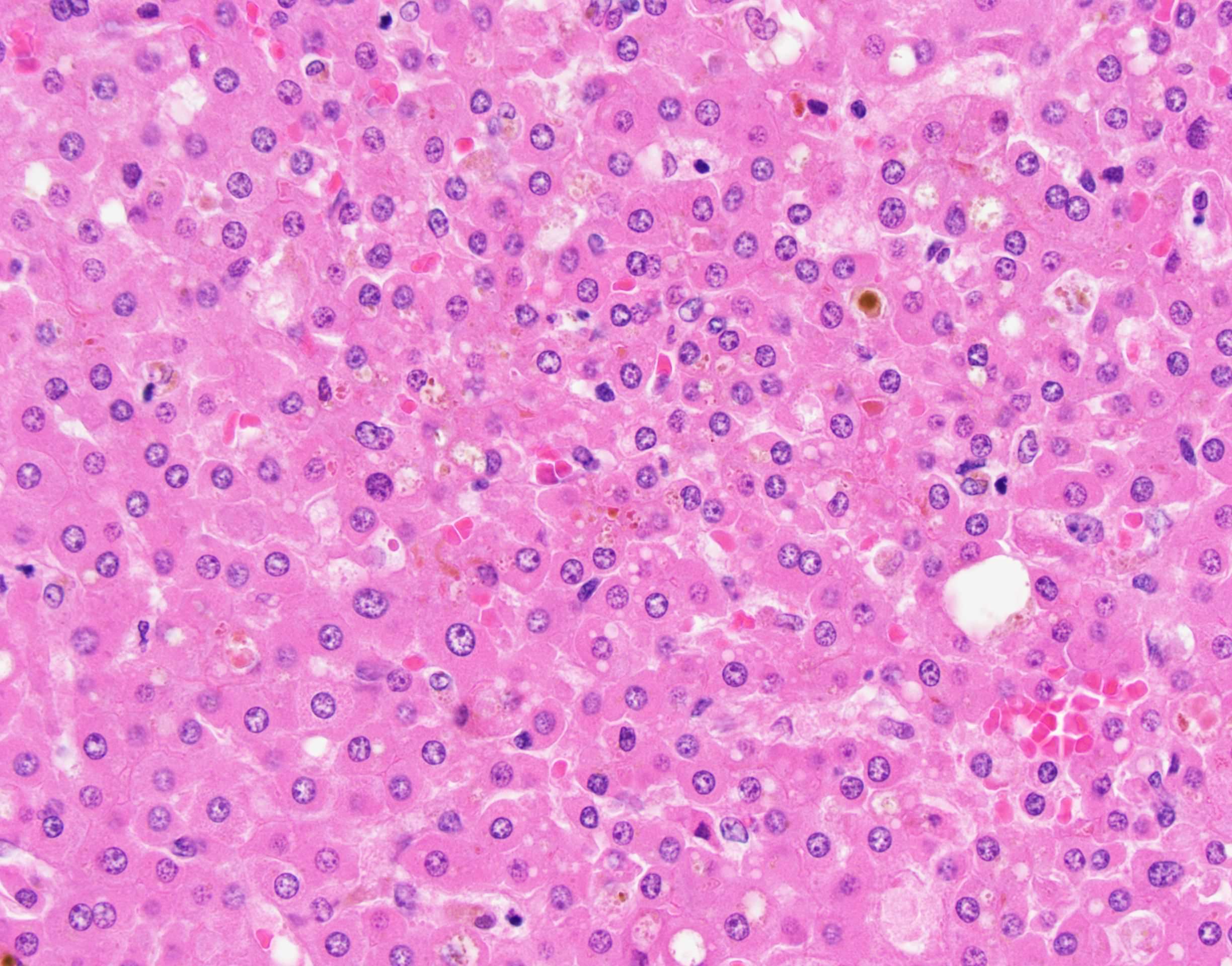
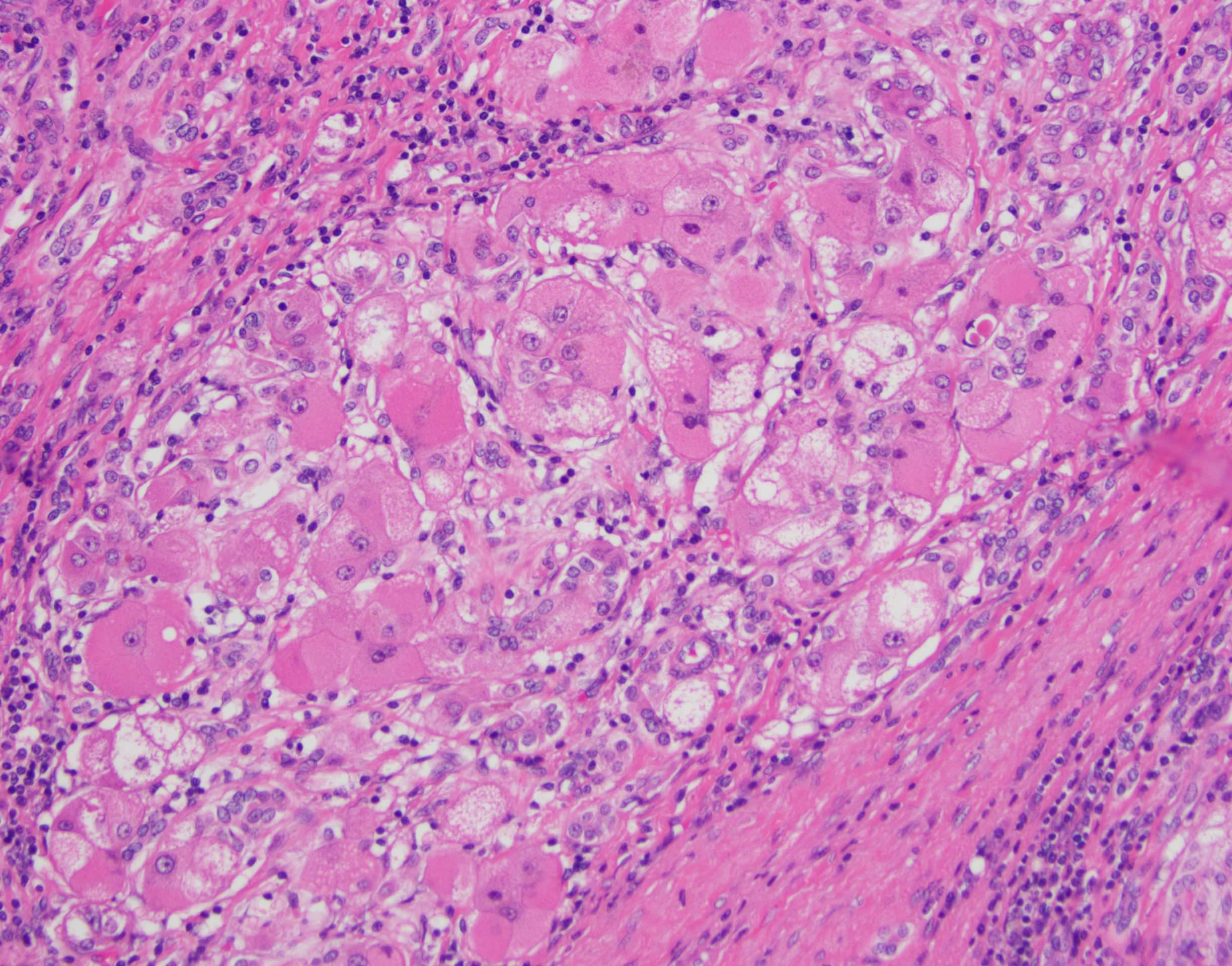
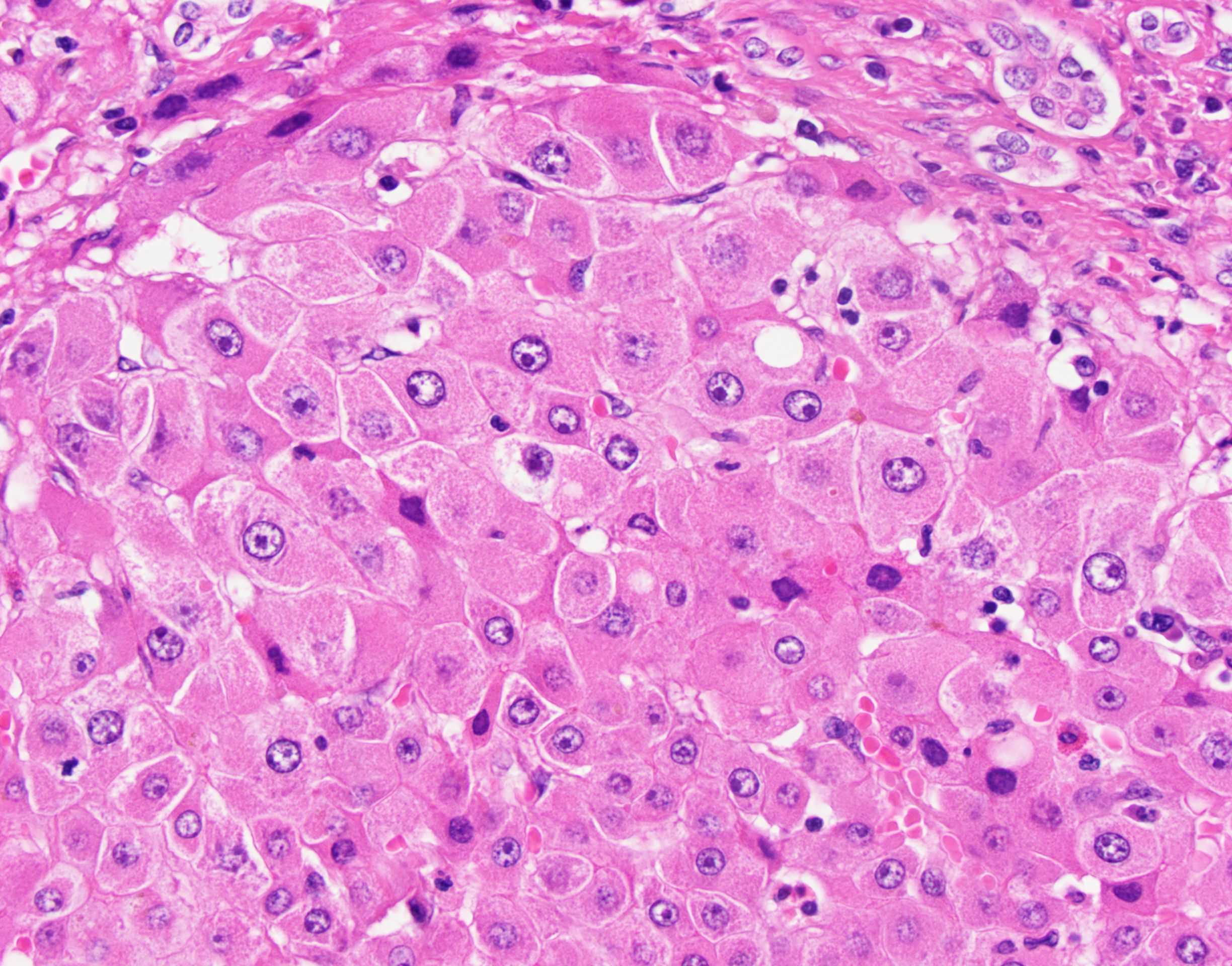
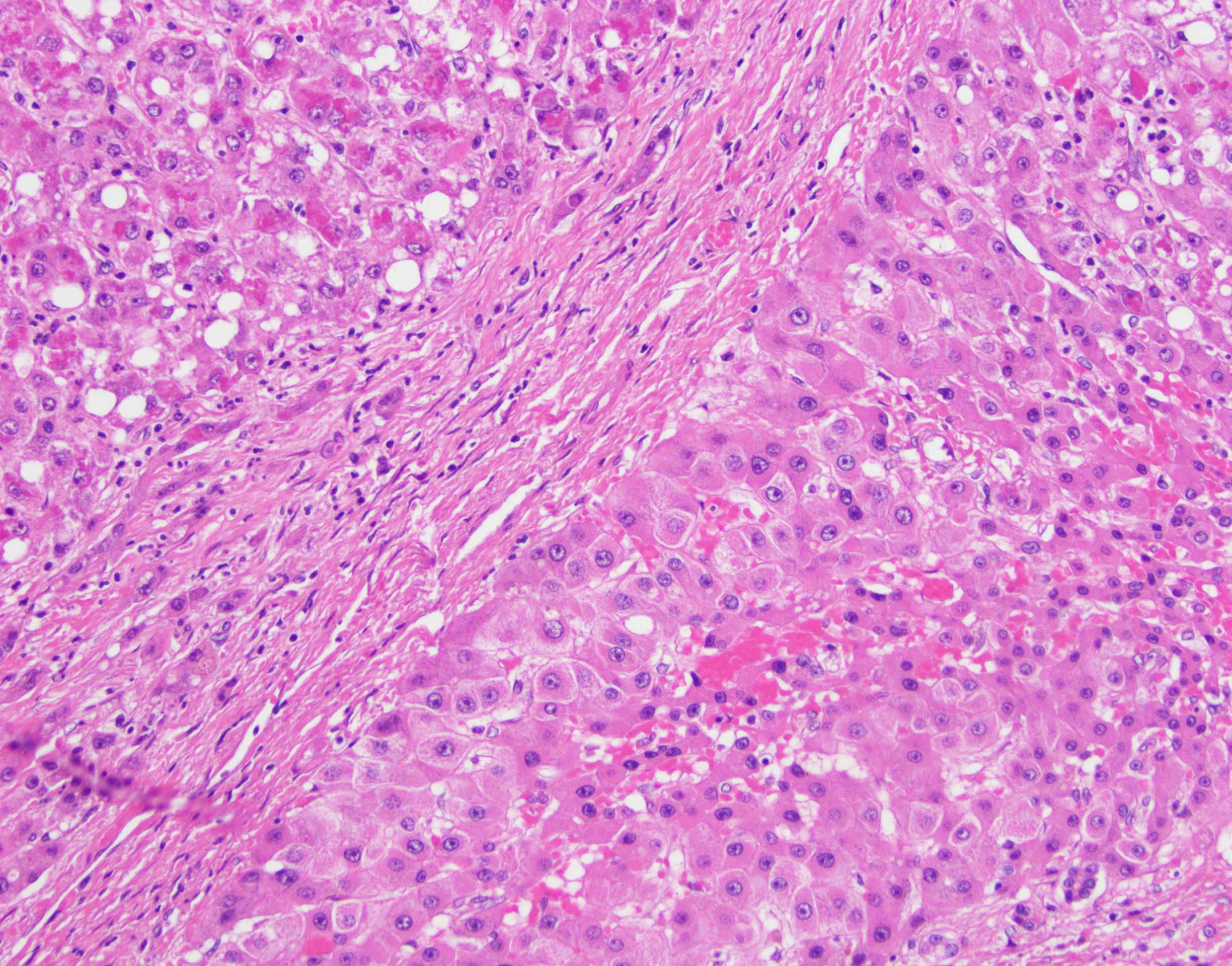
- Large cell change is defined as an increase in both nuclear and cytoplasmic size, preserving nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio; nuclei are hyperchromatic, pleomorphic and frequently multinucleated
- Small cell change is defined as hepatocytes showing decreased cell volume, increased nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio, mild nuclear pleomorphism, hyperchromasia and cytoplasmic basophilia, giving the impression of nuclear crowding; this pattern is typical of high grade dysplastic nodules
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Liver, native, orthotopic transplantation:
- Cirrhosis with mild chronic inflammation and patchy low grade dysplasia (see comment)
- Negative for high grade dysplasia malignancy.
- Margins of resection unremarkable.
- Comment: The findings are consistent with the patient’s reported history of nonalcoholic hepatitis. A trichrome stain confirms cirrhosis. An iron stain is unremarkable.
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true about hepatocellular dysplasia?
- Dysplastic foci can be identified grossly
- It acts as the precursor to cholangiocarcinoma
- Large cell change has an increased nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio
- Small cell change has mild nuclear pleomorphism and cytoplasmic basophilia
Board review style answer #1
D. Small cell change has mild nuclear pleomorphism and cytoplasmic basophilia
Comment Here
Reference: Liver cell dysplasia
Comment Here
Reference: Liver cell dysplasia