Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Ward SC. HCC - steatohepatitic. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/liversteatohepatiticHCC.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- WHO recognized histological variant of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in which the tumor cells show histologic features resembling nonneoplastic steatohepatitis
- This variant usually arises in the setting of steatohepatitis (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1630)
Essential features
- Variant of hepatocellular carcinoma with histologic features resembling nonneoplastic steatohepatitis (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1630)
- Arises in the setting of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis as well as alcoholic steatohepatitis (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1630, Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1406)
- May have yellow appearance on cut surface of tumor
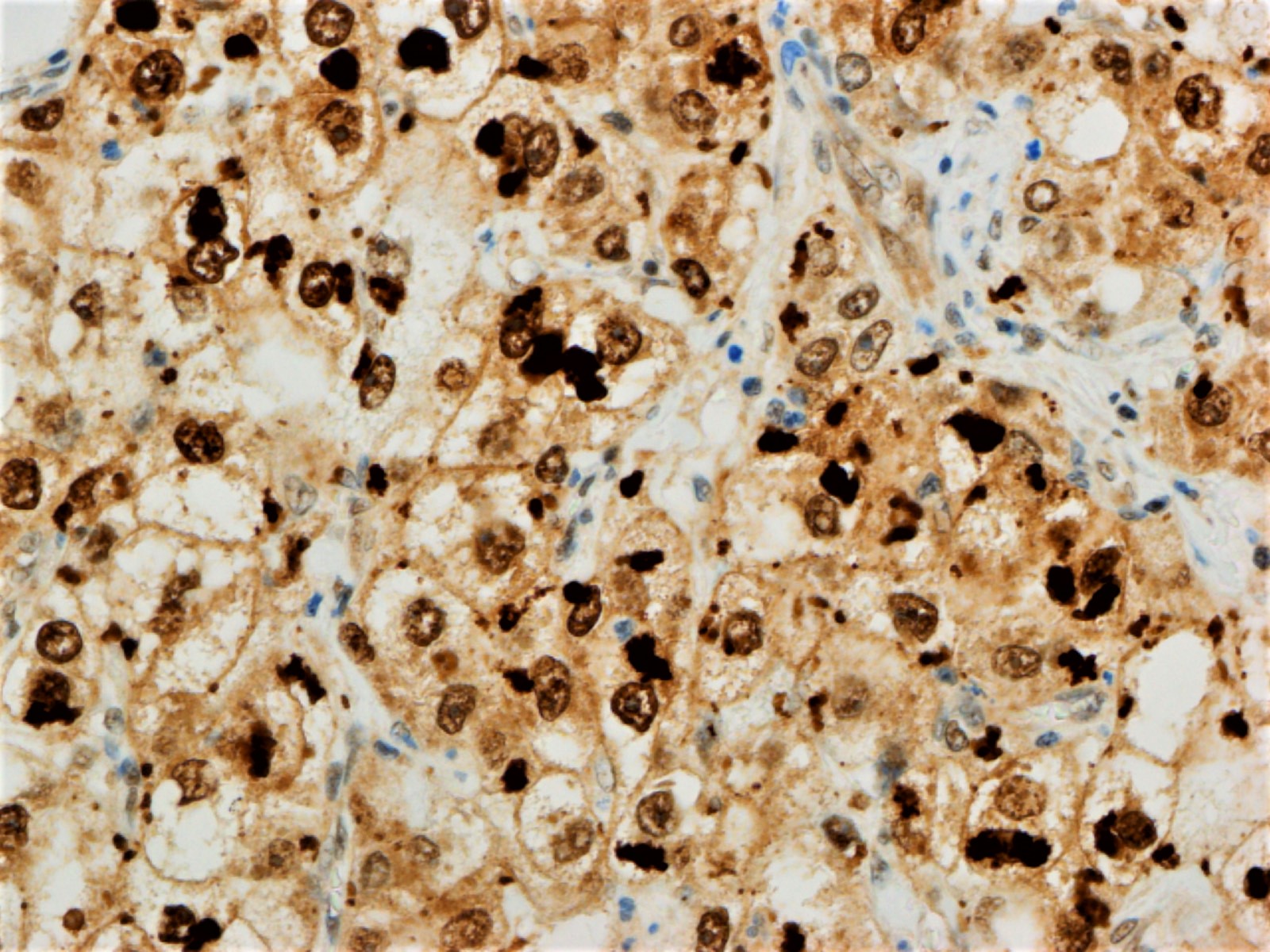
- Ubiquitin immunohistochemical stain can be used to highlight Mallory-Denk bodies
- Associated with S1 molecular subclass (TGFβ pathway activation) (Liver Int 2016;36:108)
Terminology
- Steatohepatic variant of hepatocellular carcinoma
ICD coding
- No specific code for steatohepatitic HCC
Epidemiology
- Age sixth to seventh decade (similar to conventional HCC) (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1630)
- M > F (similar to conventional HCC) (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1630)
- Represents 5 - 20% of HCC
Sites
- Liver
Pathophysiology
- Similar to HCC
Etiology
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1630)
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Hypertension
- Dyslipidemia
- Alcoholic steatohepatitis (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1406)
- May arise in absence of fatty liver disease or metabolic syndrome (Hum Pathol 2015;46:1769)
Clinical features
- See Etiology
Diagnosis
- Similar to HCC
Laboratory
- Similar to HCC
Radiology description
- Prominent fatty deposits on MRI (Clin Radiol 2021;76:160.e15)
Prognostic factors
- Similar prognosis to conventional HCC
Case reports
- 49 year old woman with hepatitis C related chronic liver disease (Trop Gastroenterol 2014;35:49)
- 65 year old man with history of diabetes and hypertension with 4.8 cm liver mass (Indian J Surg Oncol 2014;5:161)
Treatment
- Similar to HCC
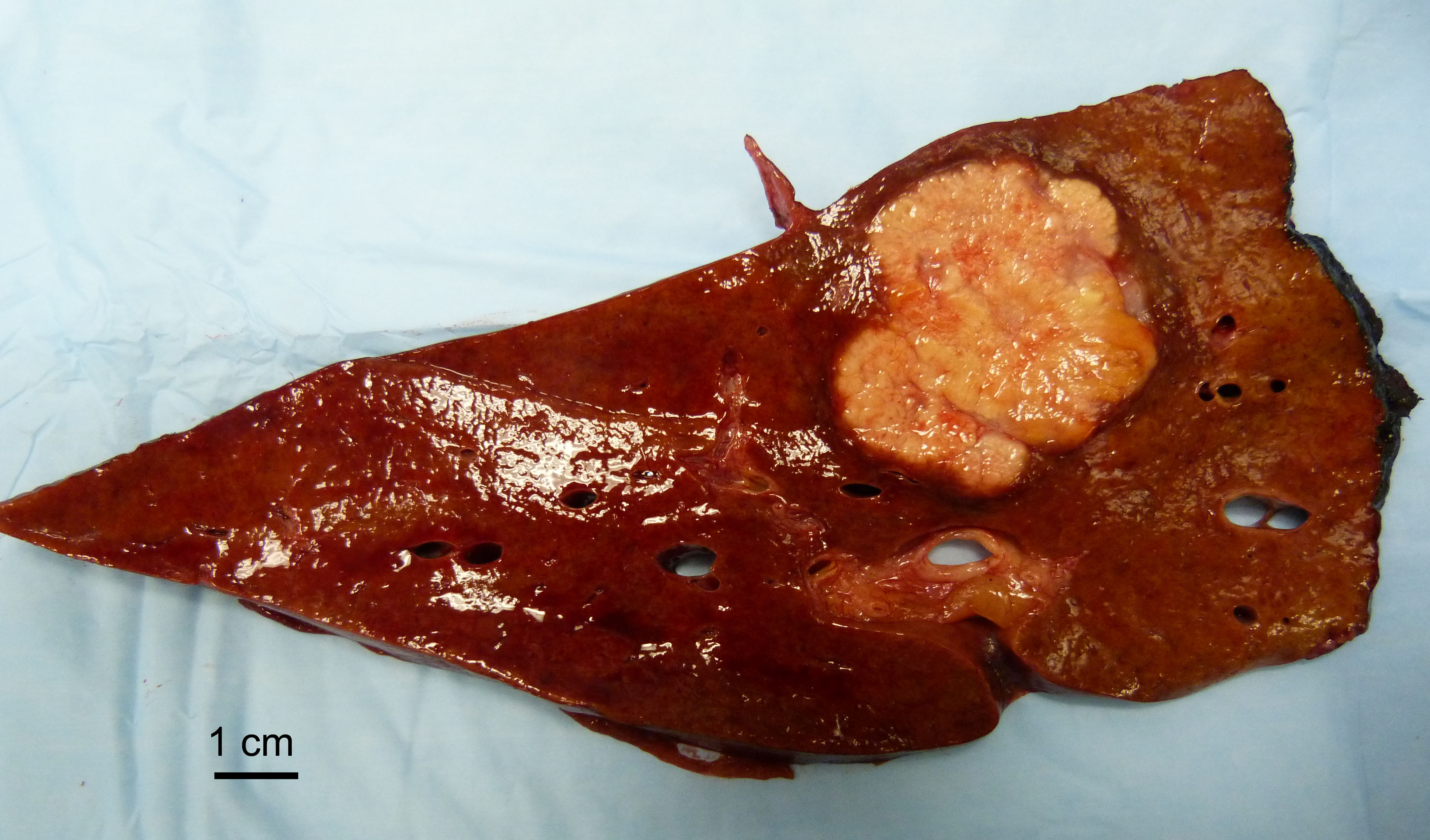
Gross description
- May show yellow cut surface
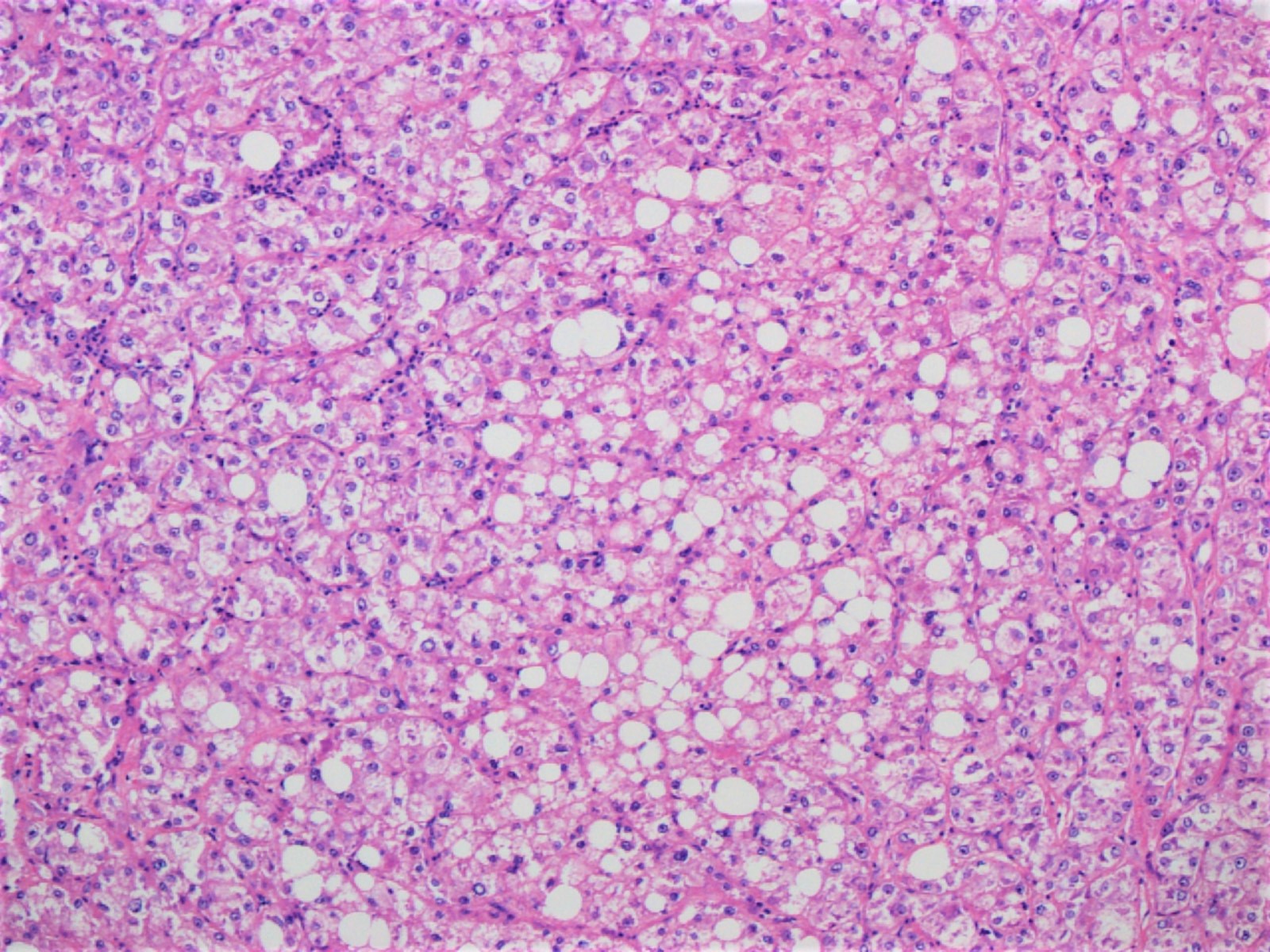
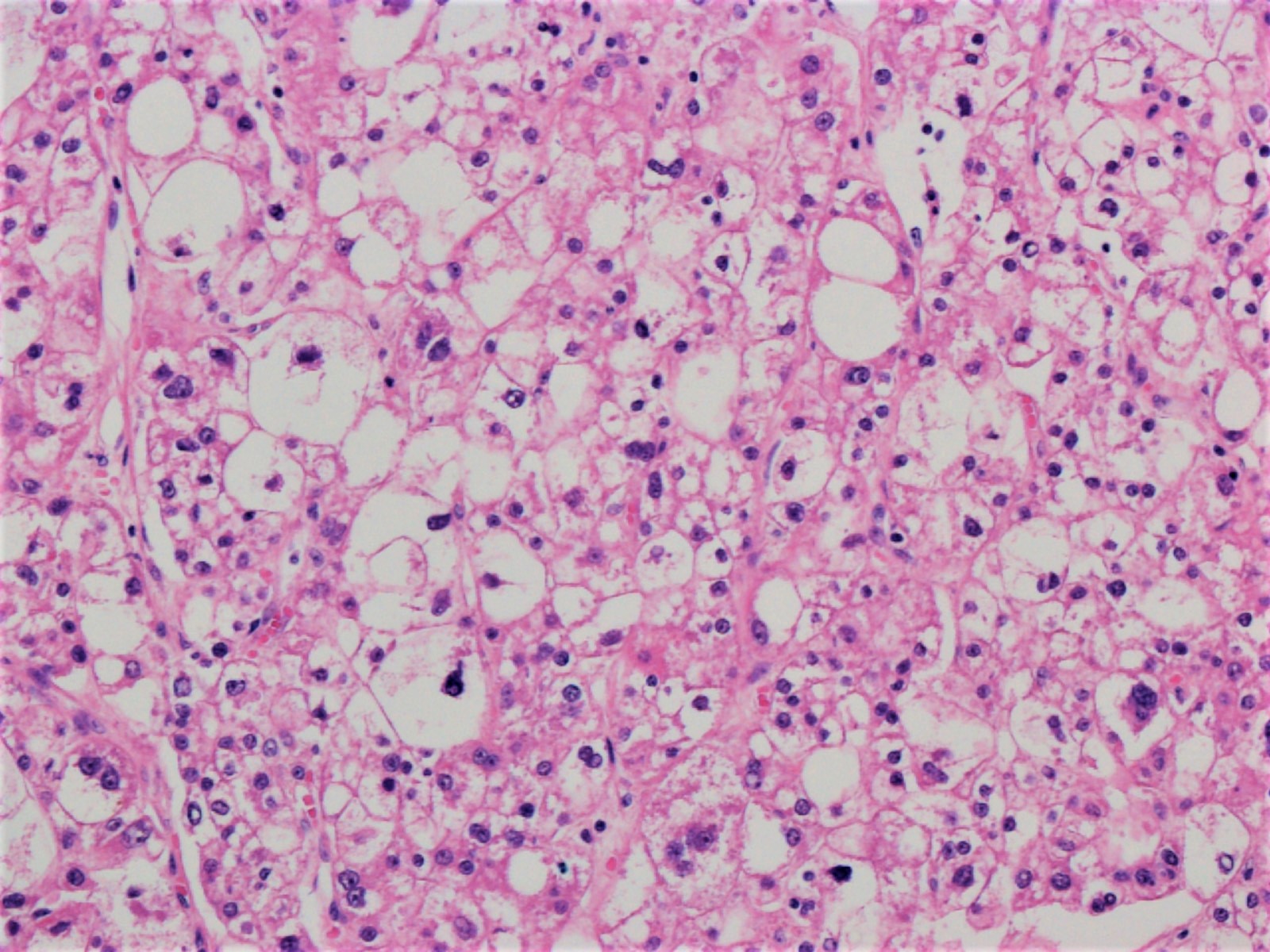
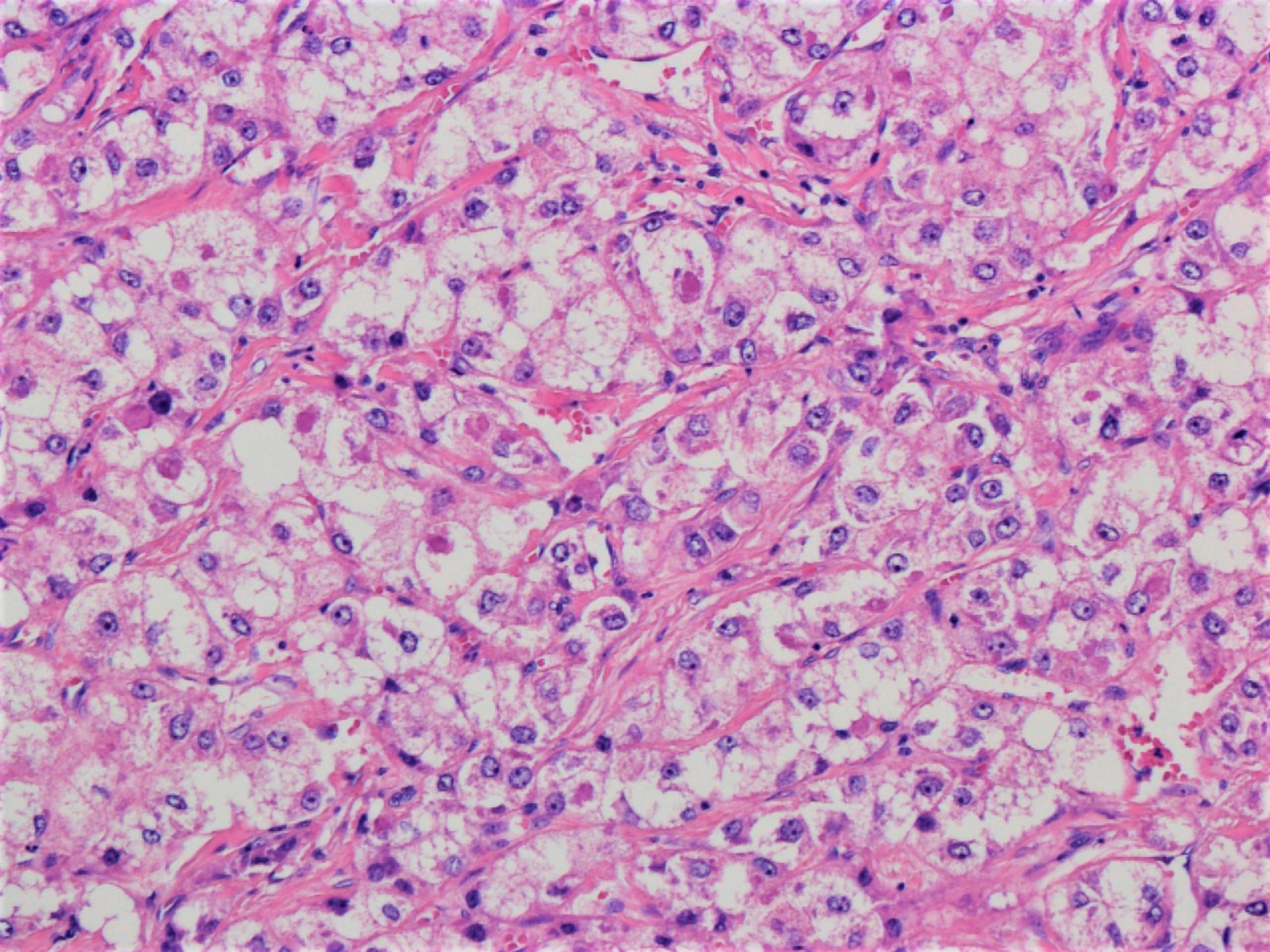
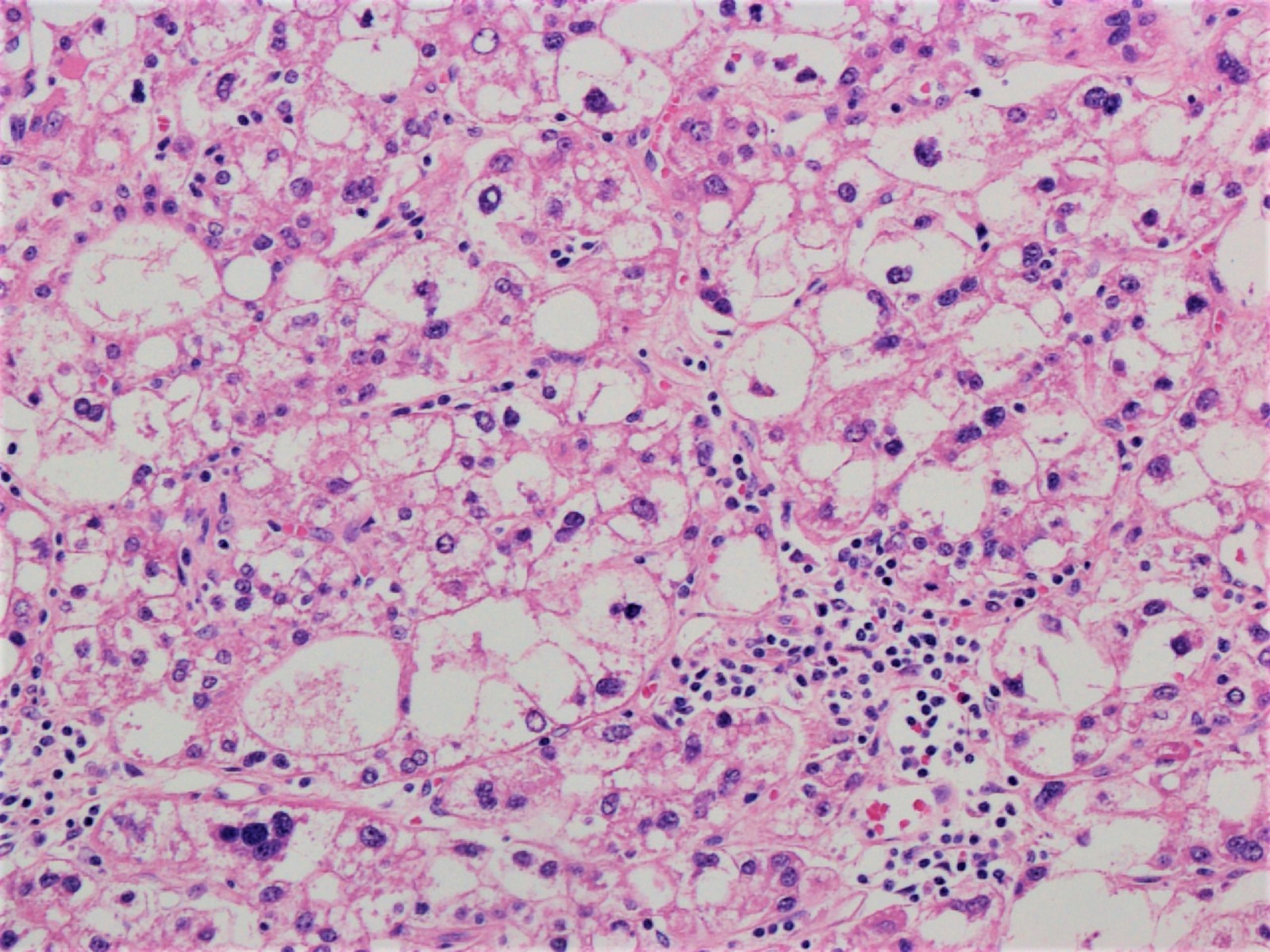
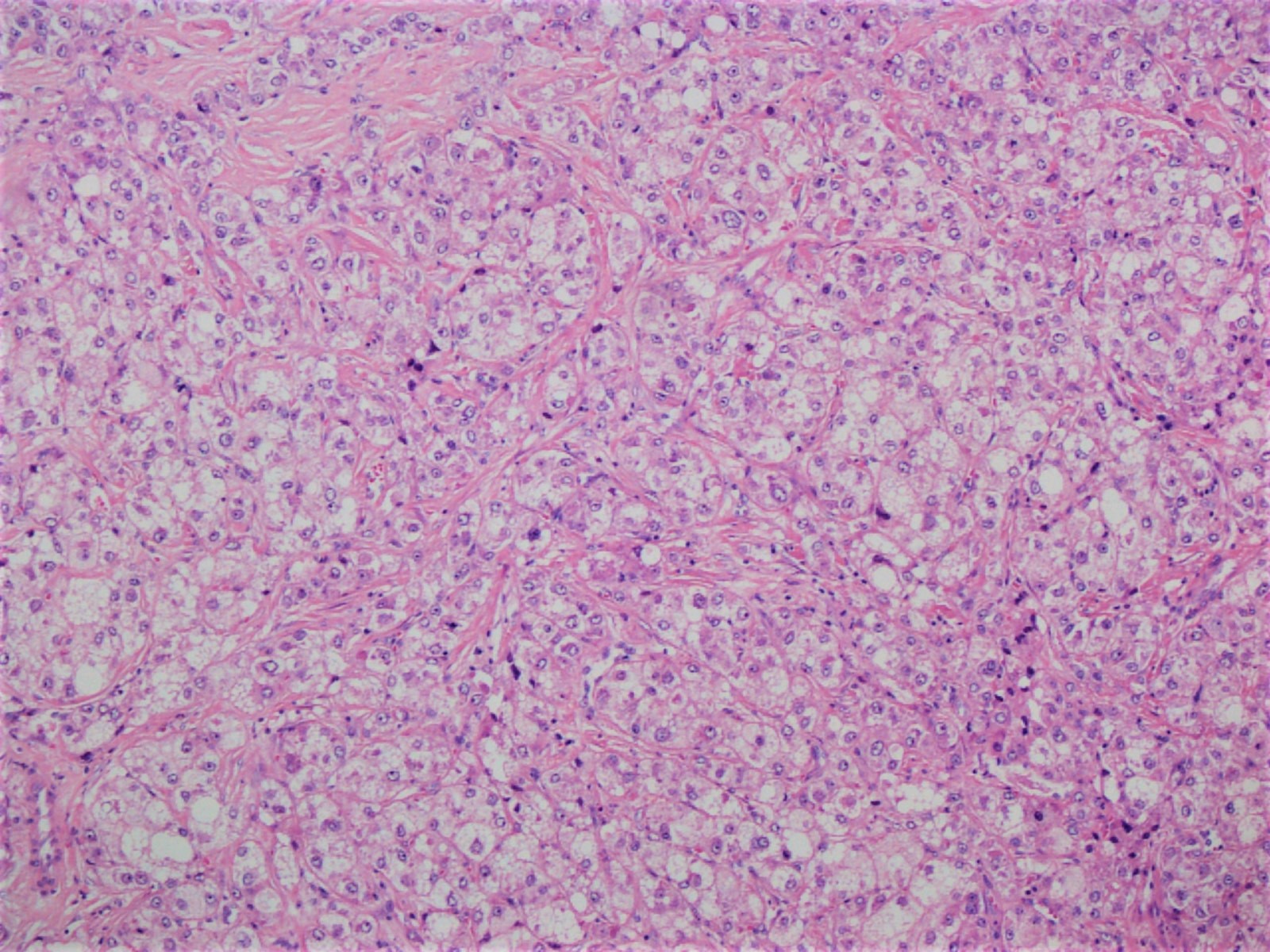
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Hepatocellular carcinoma with ≥ 50% of tumor showing 3 or more of the following steatohepatitis-like features (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1630):
- Steatosis
- Hepatocyte ballooning
- Mallory-Denk bodies
- Inflammation
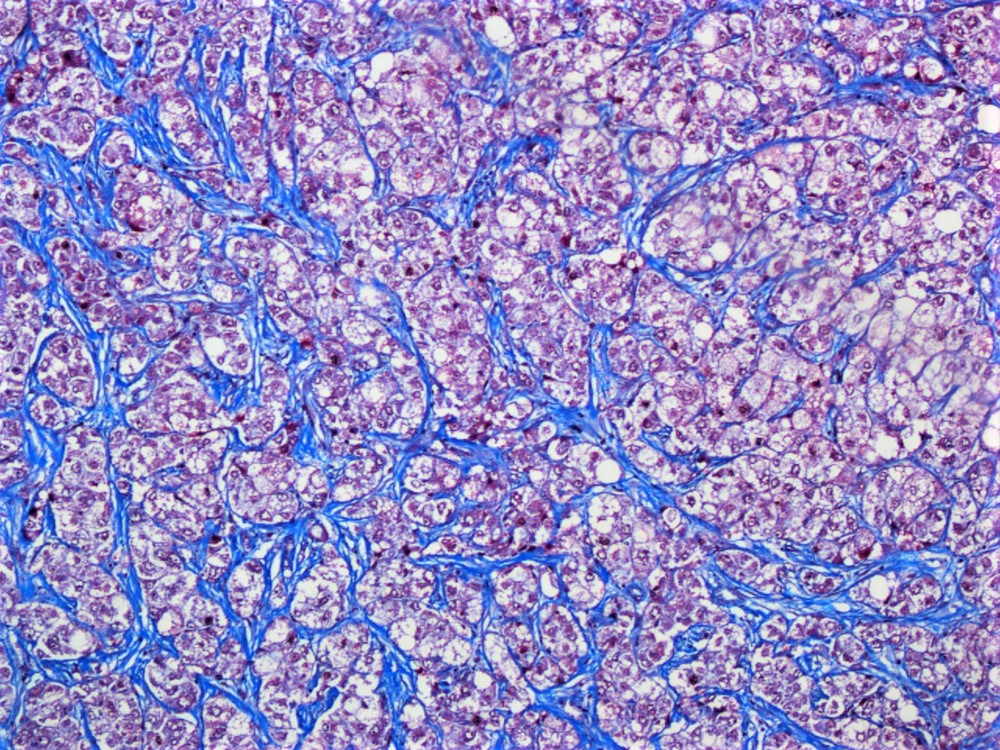
- Pericellular fibrosis
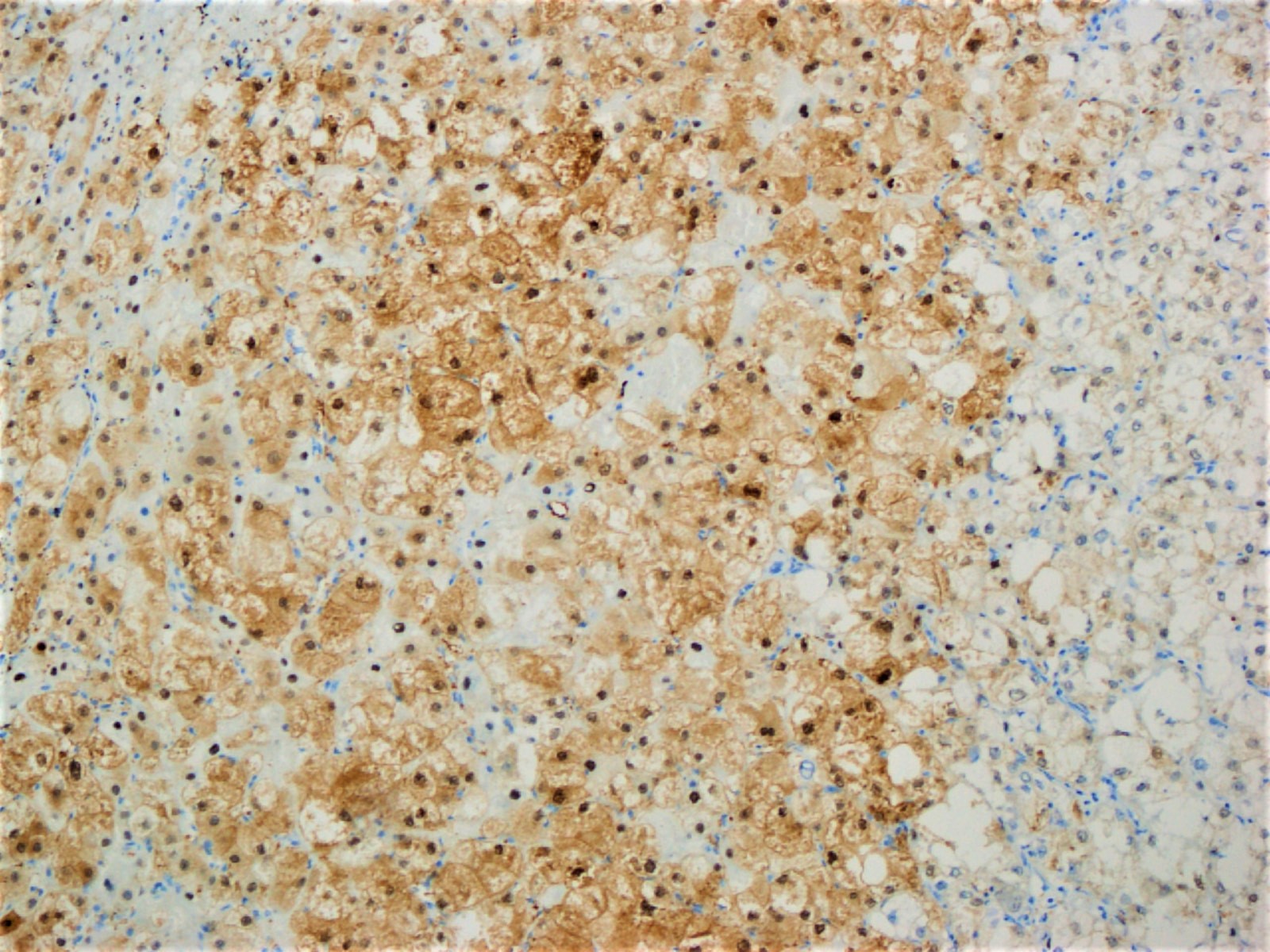
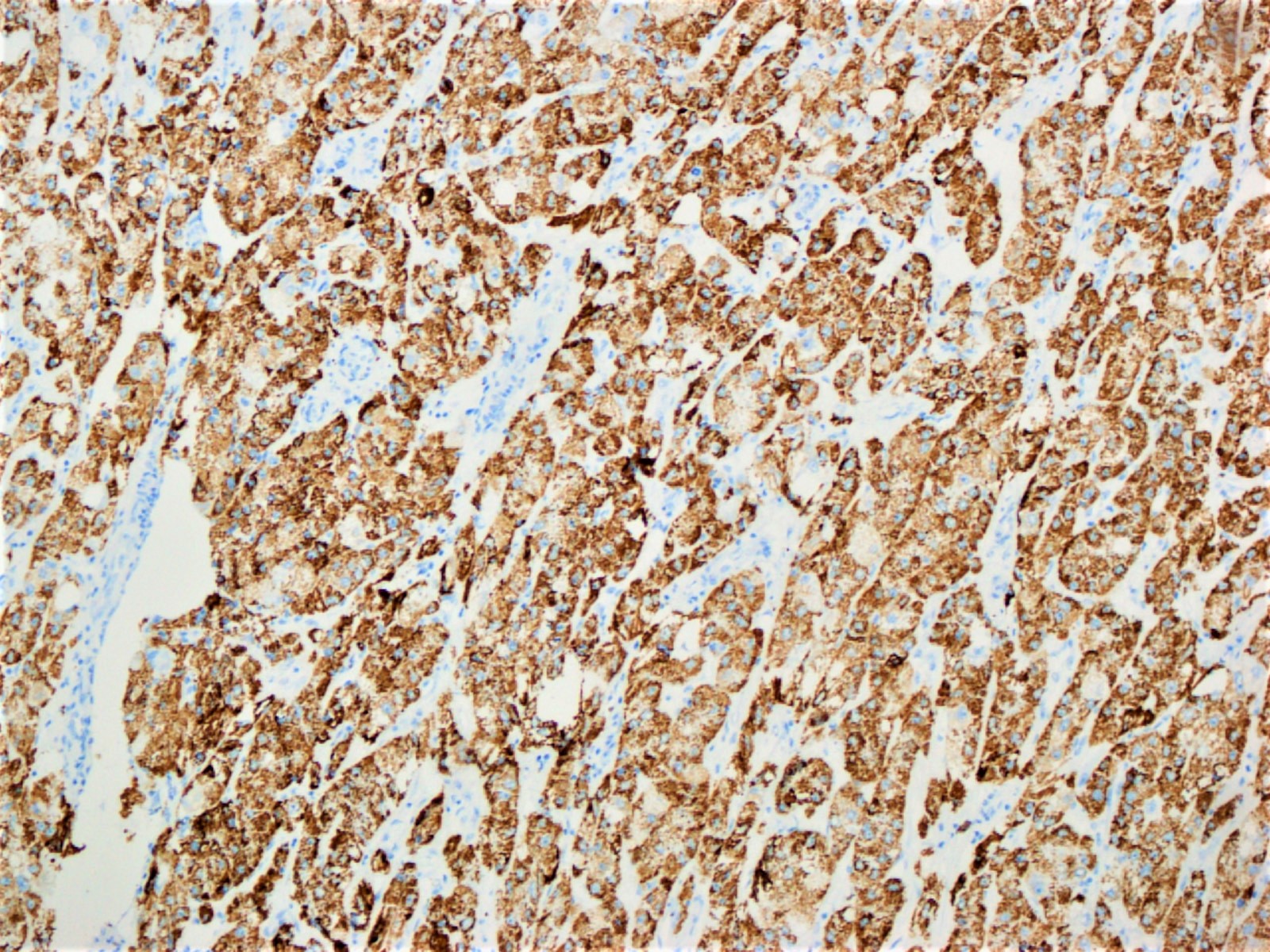
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Trabecular fragments of atypical hepatocytes with steatotic vacuoles (Indian J Surg Oncol 2014;5:161)
Positive stains
- Similar to conventional hepatocellular carcinoma (arginase1, HepPar1, glypican 3, canalicular staining pattern with CD10 and polyclonal CEA, albumin in situ hybridization, reticulin can highlight thickened trabeculae)
- Ubiquitin stain highlights Mallory-Denk bodies
- C reactive protein (J Hepatol 2017;67:727)
- Trichrome stain highlights pericellular fibrosis
- Oil red O or Sudan Black stains can highlight fat content but must be performed on frozen tissue section
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Associated with S1 molecular subclass (TGFβ pathway activation) (Liver Int 2016;36:108)
- Associated with G4 subgroup (JAK / STAT pathway activation, lack of mutations in CTNNB1, TP53 and TERT promoter) (J Hepatol 2017;67:727)
Sample pathology report
- Liver mass, needle biopsy:
- Moderately differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma, steatohepatitic variant
Differential diagnosis
- Clear cell variant of hepatocellular carcinoma:
- Tumor cells contain glycogen, may contain some fat
- Will not show inflammatory features, such as ballooning degeneration of hepatocytes or Mallory-Denk bodies
- Benign liver with steatohepatitis:
- Lacks features of malignancy, such as increased N/C ratio, thickened trabeculae, unpaired arteries
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
E. Steatohepatitis. Steatohepatitic hepatocellular carcinoma most commonly arises in the setting of steatohepatitis, either alcoholic or nonalcoholic.
Comment Here
Reference: HCC - steatohepatitic
Comment Here
Reference: HCC - steatohepatitic
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is true regarding staining of steatohepatitic hepatocellular carcinoma?
- Oil red O stain must be performed on formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissue
- PAS stain will show that the clear droplets contain dense glycogen
- Trichrome stain generally shows a thick fibrous capsule with minimal intratumoral fibrosis
- Ubiquitin stain can be used to highlight Mallory-Denk bodies
Board review style answer #2
D. Ubiquitin stain can be used to highlight Mallory-Denk bodies. Mallory-Denk bodies may not be present in all cases of steatohepatitic hepatocellular carcinoma but immunohistochemical stain for ubiquitin can be used to confirm or highlight their presence. The cytoplasmic vacuoles in steatohepatitic hepatocellular carcinoma contain predominantly lipid, not glycogen, so they would not be expected to stain with PAS. Oil red O and Sudan Black stains must be performed on frozen tissue (most fat is removed during tissue processing for paraffin embedding). Steatohepatitic hepatocellular carcinoma classically shows a pericellular fibrosis pattern.
Comment Here
Reference: HCC - steatohepatitic
Comment Here
Reference: HCC - steatohepatitic