Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Aghighi M, Gonzalez RS. Methotrexate. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/liverdrugtoxinmethotrexate.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Methotrexate in liver can cause reactive changes, steatosis or fibrosis and rarely lymphoma
- Duration and dosage of methotrexate impact the risk of liver damage
- Methotrexate is an immunosuppressant medication, mainly used for treatment of cancer and autoimmune diseases
Essential features
- Methotrexate is an antimetabolite and antifolate
- Mild elevation in liver enzymes, fibrosis and cirrhosis may be observed due to extended usage of methotrexate
- Roenigk classification is used to grade liver biopsies
Terminology
- Methotrexate induced liver fibrosis
ICD coding
- ICD-10: K71.9 - Toxic liver disease, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Methotrexate is the first line therapy for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis worldwide
- Incidence rate of liver enzymes elevation in patients with low dose methotrexate therapy is 13 per 100 patient years
- 20% of patients with low dose methotrexate therapy have elevation in liver enzymes during average of 4.6 years of therapy (PLoS One 2018;13:e0203084)
Sites
- Liver
Pathophysiology
- Methotrexate is an antimetabolite and antifolate (World J Hepatol 2017;9:1092)
- Prevents synthesis of tetrahydrofolate in cells by inhibiting dihydrofolate reductase enzyme
- Presence of folic acid is essential for synthesis of nucleosides
- Therefore, methotrexate hinders synthesis of DNA and RNA, resulting in cell cycle arrest in liver
- Methotrexate inhibits an enzyme causing an increase in extracellular adenosine, which promotes liver fibrosis (Psoriasis (Auckl) 2018;8:21)
- In rheumatoid arthritis, methotrexate causes adenosine accumulation by changing purine metabolism (Joint Bone Spine 2019;86:301)
Clinical features
- Clinically, patients may be asymptomatic or present with jaundice, hepatomegaly or constitutional symptoms including weight change and fever
- Symptoms may present after months to years of using methotrexate
- Elevation in liver enzymes may occur due to high dosage of intravenous methotrexate
- Mild elevation in liver enzymes, fibrosis and cirrhosis may be observed due to extended usage of methotrexate (LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Accessed 8 December 2020])
Diagnosis
- Clinical and pathological association is required for diagnosis of liver injuries caused by toxin or drug (LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Accessed 8 December 2020])
Laboratory
- Normal or elevated aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in patients with methotrexate therapy
Radiology description
- Imaging usually reveals a diffuse hepatic steatosis (Br J Radiol 2018;91:20170959)
Prognostic factors
- Risk of liver damage is associated with the dosage and duration of methotrexate therapy
- Risk of liver damage is intensified by obesity or alcohol usage
- Roenigk classification is used to grade liver biopsies (World J Hepatol 2017;9:1092)
- Patients are advised to stop the medication if their liver shows Roenigk stage IIIB (advanced fibrosis) or Roenigk stage IV (cirrhosis) disease; for Roenigk stage IIIA, repeat of biopsy is advised in 6 months (PLoS One 2018;13:e0203084)
Case reports
- 56 year old woman with rheumatoid arthritis and methotrexate treatment developed primary hepatic lymphoma (Intern Med 2015;54:401)
- 64 year old man with rheumatoid arthritis and methotrexate treatment developed primary hepatic lymphoma (Biomark Res 2015;3:10)
- 82 year old man with rheumatoid arthritis and methotrexate treatment developed lymphoproliferative disorders in liver, spleen and lung (J Med Case Rep 2019;13:196)
- 88 year old woman with rheumatoid arthritis under methotrexate therapy for 6 years developed hepatosplenic Hodgkin lymphoma after methotrexate withdrawal (Mod Rheumatol 2017;27:372)
Treatment
- Folic acid supplement of 1 mg per day lowers the risk of liver enzymes abnormality, mouth ulcers and gastrointestinal issues such as nausea and vomiting
- Periodic monitoring of liver enzymes levels is recommended
- Liver biopsy is suggested for monitoring after 1, 3 and 8 grams cumulative methotrexate (PLoS One 2018;13:e0203084)
- Other disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), such as hydroxychloroquine or etanercept, do not show concurrent adverse effect on liver with methotrexate (LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Accessed 8 December 2020])
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Mainly macrovesicular steatosis but sometimes microvesicular
- Reactive changes, such as hyperchromasia and anisocytosis of hepatocyte nuclei or patchy hepatocyte necrosis
- Portal inflammation
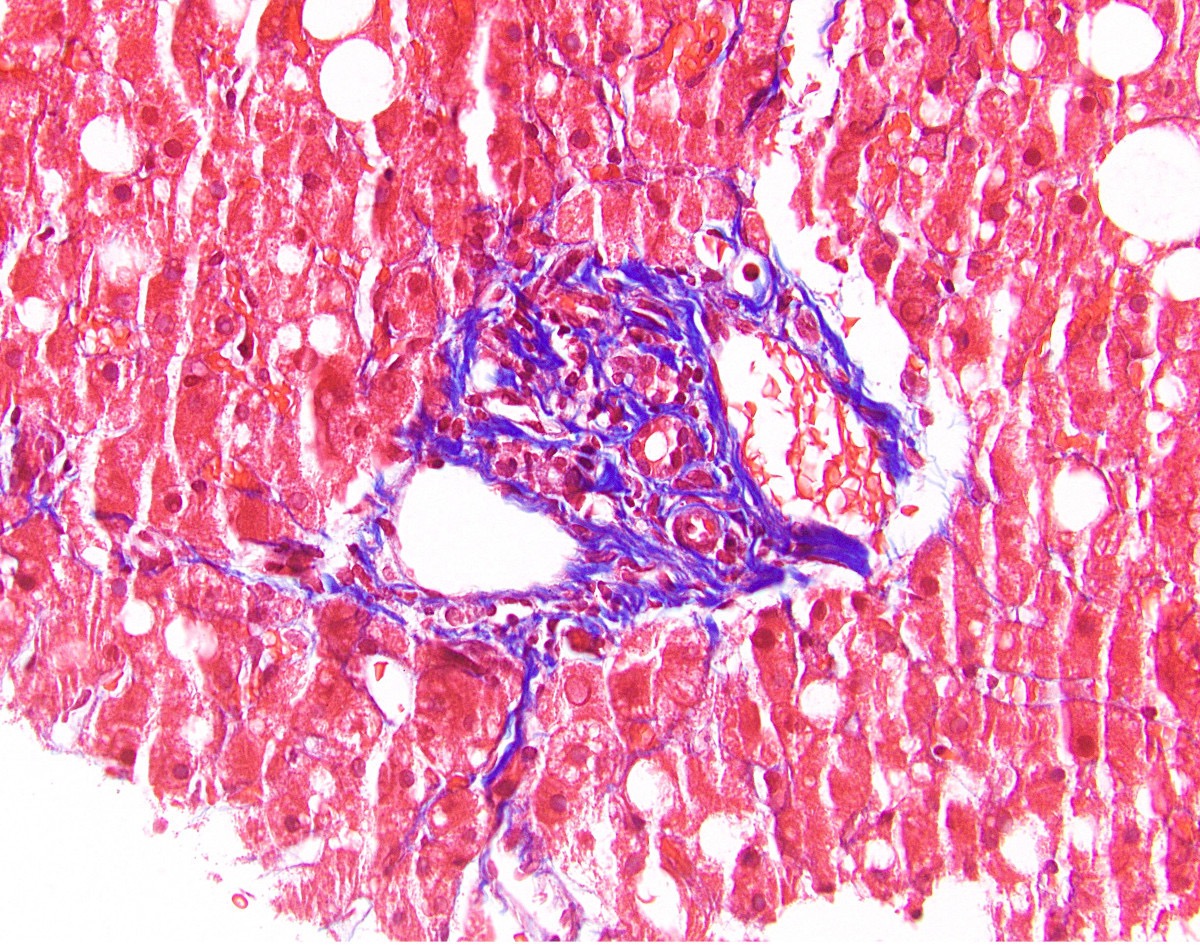
- Periportal fibrosis to central bridging or pericellular fibrosis
- Roenigk classification has 4 grades: grade I (normal to mild fatty changes), grade II (moderate to severe fatty changes), grade IIIA - B (mild to severe periportal fibrosis) and grade IV (cirrhosis) (Arch Dermatol 2007;143:1515)
- Rarely, lymphoproliferative disorders such as primary hepatic lymphoma has been reported after using methotrexate in autoimmune disease patients (Biomark Res 2015;3:10)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Trichrome stain shows an increase in portal, periportal or bridging fibrosis in methotrexate toxicity
Sample pathology report
- Liver, biopsy:
- Macrovesicular steatosis with periportal and bridging fibrosis (see comment)
- Comment: Macrovesicular steatosis involves approximately 50% of the hepatocytes. A trichrome stain demonstrates periportal and bridging fibrosis. The differential diagnosis includes alcoholic hepatitis, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis or drug induced liver injury (the patient's history of methotrexate use is noted).
Differential diagnosis
- Alcoholic hepatitis:
- History of alcohol use is present
- Often more prominent ballooning degeneration and Mallory hyaline
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis:
- Metabolic syndrome is usually a risk factor
- Histologic appearance is generally similar
- Liver injury caused by other drugs:
- Amiodarone can cause steatosis with prominent Mallory hyaline
- Clinical correlation necessary
Board review style question #1
Methotrexate injury in the liver is graded using the Roenigk classification. Which of the following grades indicates methotrexate use should be stopped?
- Stage I
- Stage II
- Stage IIIA
- Stage IIIB
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2