Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Pathophysiology | Laboratory | Treatment | Clinical images | Cytology description | Cytology imagesCite this page: Chan A. Ascites. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/liverascites.html. Accessed December 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
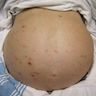
- Ascites is abnormal excessive accumulation of fluid in peritoneal cavity
- It is the most common of the 3 major complications of cirrhosis (ascites, hepatic encephalopathy and bleeding varices) (Hepatology 1987;7:122)
- It is also one of 5 parameters of the Child-Pugh score, the most widely used system for liver function assessment (Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e2877)
- Presence of ascites is associated with poorer overall survival in patients with cirrhosis (1 year 85%, 5 year 56%) (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;4:1385) and hepatocellular carcinoma (Chin J Cancer 2014;33:481)
Essential features
- Pending
Pathophysiology
Combination of these factors, which reinforce each other:
- Elevated hydrostatic pressure due to portal hypertension
- Reduced osmotic pressure due to hypoalbuminemia
- Renal retention of sodium and water due to activation of renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS)
- Decreased effective circulatory volume due to ascites
Laboratory
- Ascitic fluid cell count and differential
- Polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) count > 250 cells/mm3 in the absence of an intra abdominal, surgically treatable source of infection indicates spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (Hepatology 1982;2:399), which complicates about 12% of cirrhotic patients with ascites (Dig Liver Dis 2001;33:41)
- Serum ascites albumin gradient (SAAG) (Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:1401)
- > 1.1 g/dL indicates portal hypertension
- < 1.1 g/dL indicates nonportal hypertension causes including malignancies, tuberculous peritonitis and nephrotic syndrome
- Cytology
- Only positive in peritoneal carcinomatosis (sensitivity of 96.7% if 3 samples from different paracentesis procedures) (Hepatology 1988;8:1104)
- Almost always negative in cirrhotic patients, even those known to have hepatocellular carcinoma (Cytojournal 2009;6:16)
Treatment
- First line (Hepatology 2013;57:1651)
- Cessation of alcohol when present
- Sodium restriction
- Dual diuretics (usually spironolactone and furosemide)
- Discontinue nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drugs
- Evaluation for liver transplantation
- Second line
- Discontinue beta blockers, angiotension converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotension receptor blockers
- Serial therapeutic paracentesis
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt (TIPSS)
- Evaluation for liver transplantation
- Third line
- Peritoneovenous shunt
Cytology description
- Ascites fluid cytology is almost always negative in patients with cirrhosis, even those known or suspected to have hepatocellular carcinoma (Cytojournal 2009;6:16)