Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Ascending cholangitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/liverascendingcholangitis.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Infection of the extrahepatic biliary system, often due to obstruction (Infect Dis Clin North Am 2000;14:521)
Essential features
- Highly morbid infection of large bile ducts
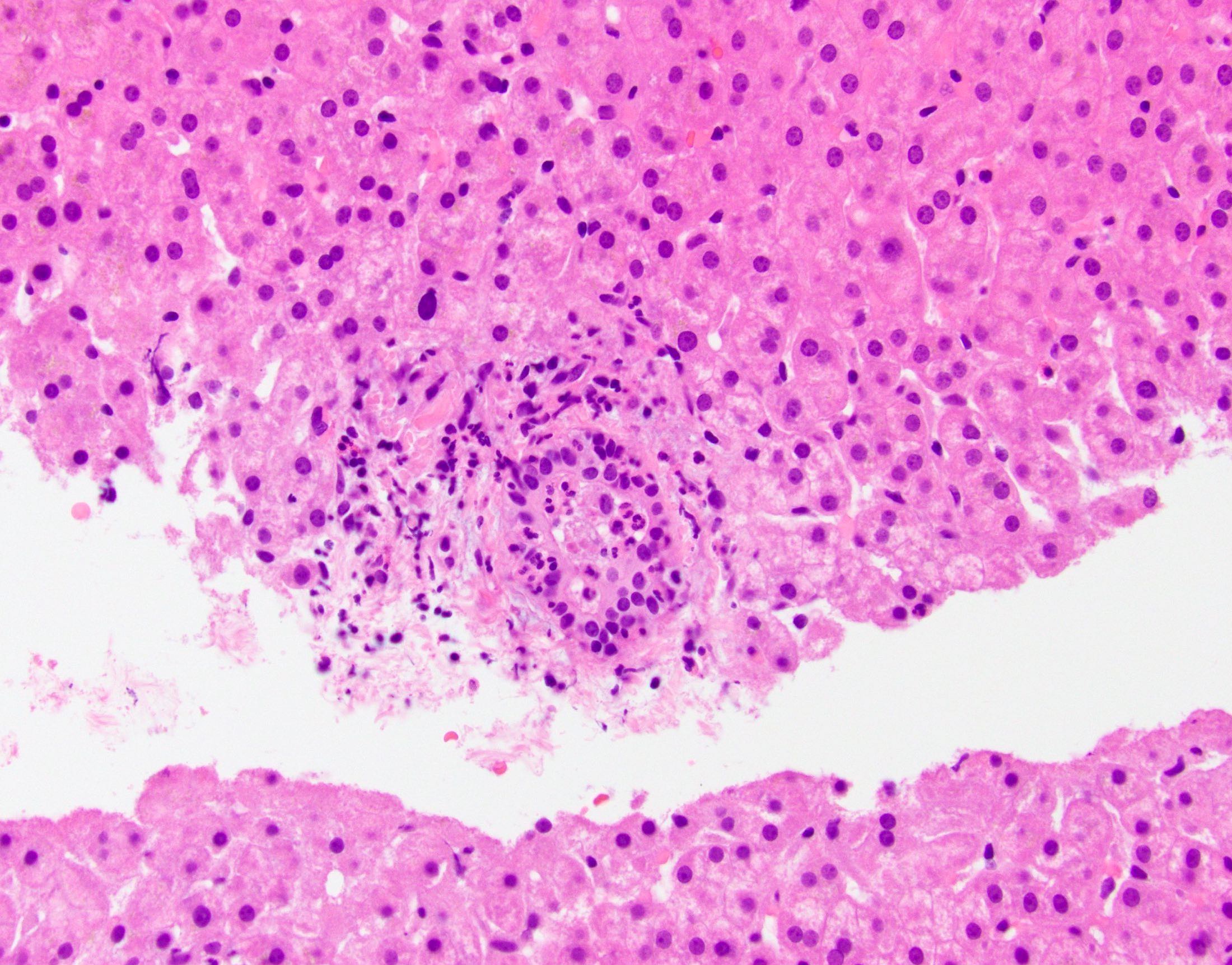
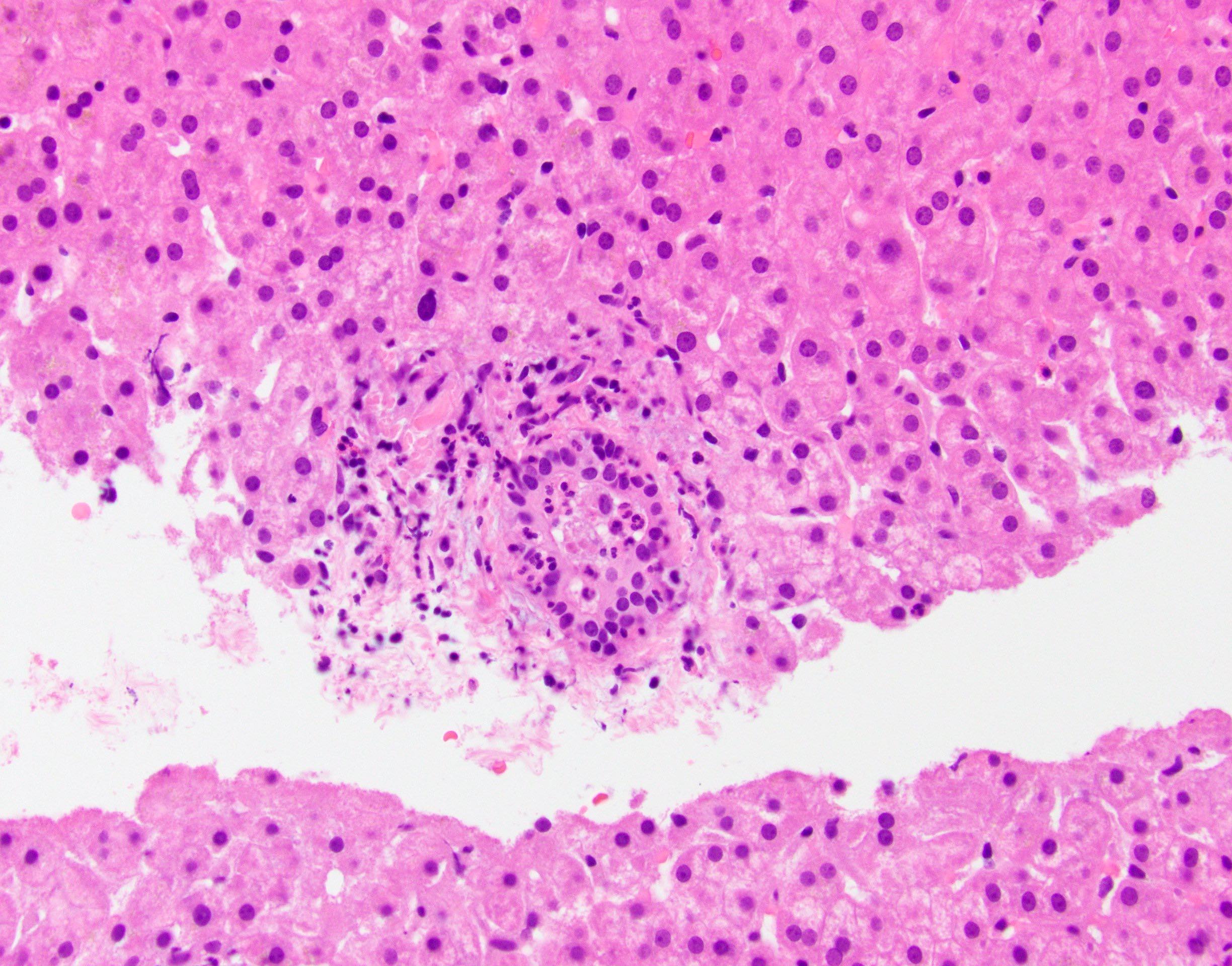
- Histologic correlate is neutrophils within epithelium and lumen of interlobular bile ducts
Terminology
- Also called acute cholangitis, suppurative cholangitis
ICD coding
- ICD-10: K83.09 - other cholangitis
Epidemiology
- Typically a secondary process that occurs in an already diseased bile duct (stricture, etc.) (Postgrad Med J 2007;83:773)
- Can occur following the Kasai procedure to correct extrahepatic biliary atresia (J Pediatr Surg 1989;24:729, J Pediatr Surg 2004;39:1800)
Etiology
- Common infectious causes include E. coli, Klebsiella, enterococci (Postgrad Med J 2007;83:773)
- Rarely due to adenovirus (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2003;6:156)
Clinical features
- Symptoms include Charcot cholangitis triad: jaundice, fever and right upper quadrant abdominal pain (World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2018;9:1)
- May lead to a hepatic pyogenic abscess
Diagnosis
- Based on the Tokyo Guidelines, which incorporate systemic inflammation, cholestasis and imaging (J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2018;25:17, ANZ J Surg 2017;87:554)
Laboratory
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) obtained bile can be cultured to guide antibiotic therapy (Dig Dis 2019;37:155)
- Blood culture may be less successful
Case reports
- 64 year old woman with Ascaris infection (Eur J Intern Med 2016;34:e7)
- 72 year old man with Lactococcus lactis cremoris bacteremia (J Med Case Rep 2009;3:3)
- 73 year old man who has recently done heavy lifting (Case Rep Gastroenterol 2017;11:500)
- 93 year old woman with biliary enteric fistula (ACG Case Rep J 2018;5:e60)
Treatment
- Biliary drainage and antibiotic therapy
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Neutrophils within lumens of interlobular bile ducts and also infiltrating duct (not ductule) epithelium (Lefkowitch: Scheuer's Liver Biopsy Interpretation, 9th Edition, 2015)
- Note: neutrophils sprinkled throughout ductular reaction is a typical component of ductular reaction and should NOT be considered evidence of infection or of ascending cholangitis
- Larger ducts often unaffected
- Findings of other concomitant biliary processes (e.g. large duct obstruction) may also be present
Sample pathology report
- Liver, biopsy:
- Hepatic parenchyma with cholestasis and neutrophils involving bile duct lumens and epithelium (see comment)
- Comment: The findings are concerning for acute (ascending) cholangitis in the proper clinical context.
Differential diagnosis
- Acute cellular rejection of liver transplant:
- Neutrophils within duct lumen may rarely be present
- Clinical correlation necessary, as duct complications / infection can also occur in the posttransplant setting
- Sepsis:
- May occur alongside ascending cholangitis
- Nonspecific cholestasis and acute / chronic inflammation, though ductular cholestasis is highly suggestive of sepsis
Board review style question #1
Neutrophils filling the lumens of native interlobular bile ducts are most suggestive of which diagnosis?
- Ascending cholangitis
- Cholangiocarcinoma
- Primary biliary cholangitis
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Recurrent pyogenic cholangitis
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
A patient presents with fever, jaundice and abdominal pain. Liver enzymes are elevated and a liver biopsy is performed. Findings are visible in the figure above. Based on this, which of the following steps may be included in the patient's therapy?
- Antibiotics
- Bile duct excision
- Platinum based chemotherapy
- Steroids
- Ursodeoxycholic acid
Board review style answer #2