Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Laboratory | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Electron microscopy description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Gonzalez R. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome / venoocclusive disease (SOS / VOD). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/liverVOD.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Drug induced liver injury causing toxic damage to sinusoids and zone 3 hepatocytes (Bone Marrow Transplant 2015;50:781)
Essential features
- Form of sinusoidal injury first described in Jamaican bush tea drinkers; now usually occurs following hematopoietic stem cell transplant (J Clin Exp Hepatol 2014;4:332)
Terminology
- Previously called veno-occlusive disease (Semin Liver Dis 2002;22:27)
- Sometimes called blue liver syndrome
ICD coding
- ICD-10: K76.5 - Hepatic veno-occlusive disease
Pathophysiology
- Toxic agent damages sinusoidal endothelial cells, likely via depletion of glutathione and nitric oxide
- Injury related sloughing of sinusoidal endothelial cells leads to embolic sinusoidal obstruction around central veins
- Hepatocytes also injured, contributing to disease process
Etiology
- First described in Jamaica, where the causative agent was imbibed bush tea
- Now seen primarily in stem cell transplant patients, secondary to alkylating myeloablative drugs (cyclophosphamide, etc.)
- Other causative agents include chemotherapy drugs such as oxaliplatin
Clinical features
- Occurs after a few weeks in up to 25% of patients receiving allogeneic bone marrow transplant; biopsy is risky in these patients
- Leads to mortality in 40% of patients; worse if multiple organ failure also occurs (J Med Econ 2017;20:871)
- Acute symptoms include marked weight gain, tender hepatomegaly, ascites and jaundice
- Portal hypertension may occur
- Rarely progresses to cirrhosis
Laboratory
- Increase in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) with little change in alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
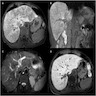
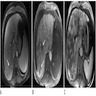
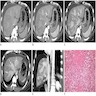
Radiology images
Case reports
- 2 year old boy after stem cell transplant (Indian Pediatr 2017;54:765)
- 9 year old girl after chemotherapy (Cancer Res Treat 2016;48:1443)
- 27 year old man after tacrolimus (World J Gastroenterol 2015;21:6422)
Treatment
- Largely supportive, depending on severity of disease (Blood 2014;123:4023)
- Defibrotide can be used in high risk patients (Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 2018;11:113, J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2017;39:e373)
Gross description
- Liver may appear blue if a resection or autopsy case is received
Microscopic (histologic) description
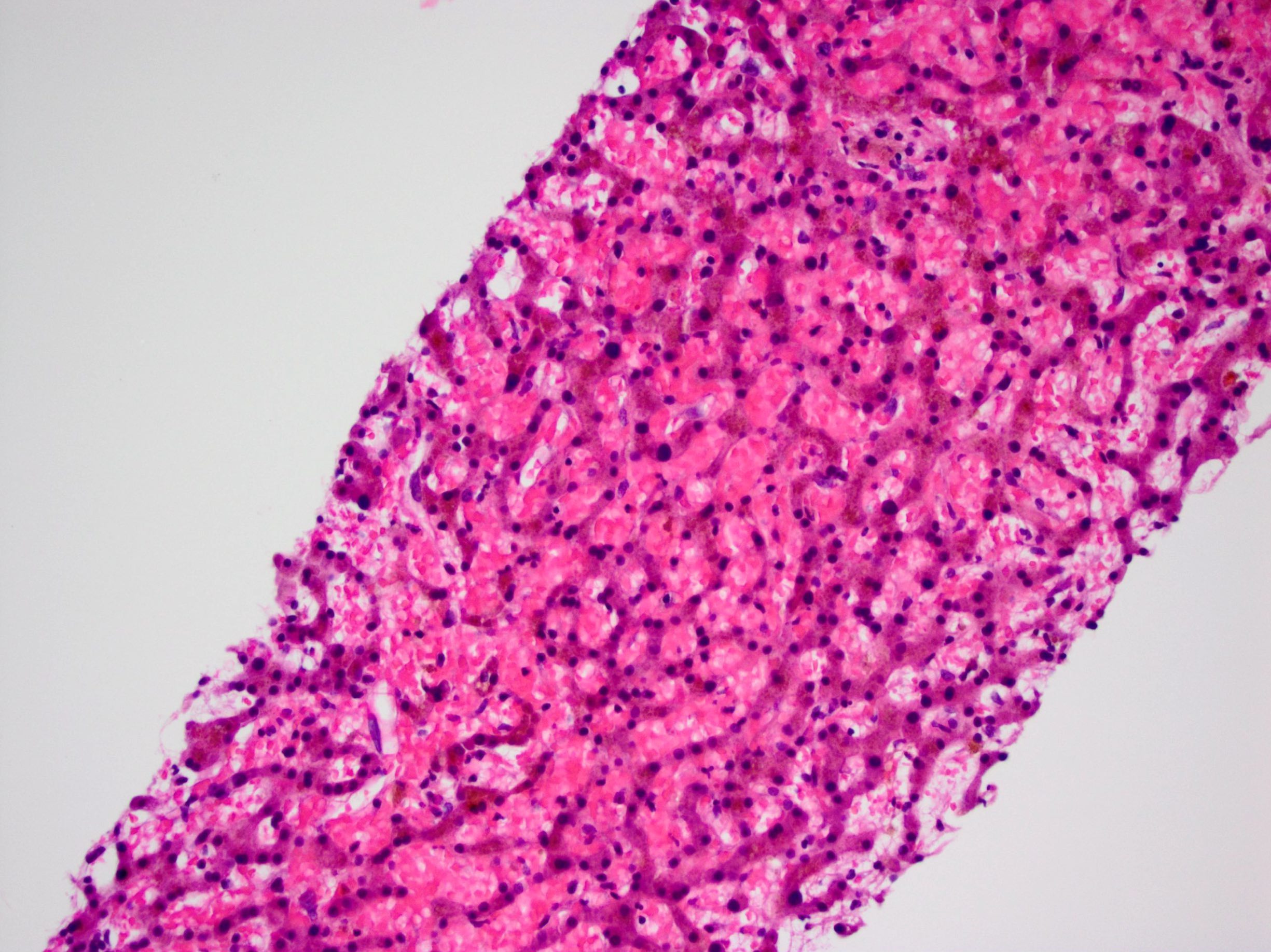
- Acutely, hemorrhage into markedly dilated sinusoids with hepatocyte atrophy; sinusoids are denuded, though this may be difficult to see clearly
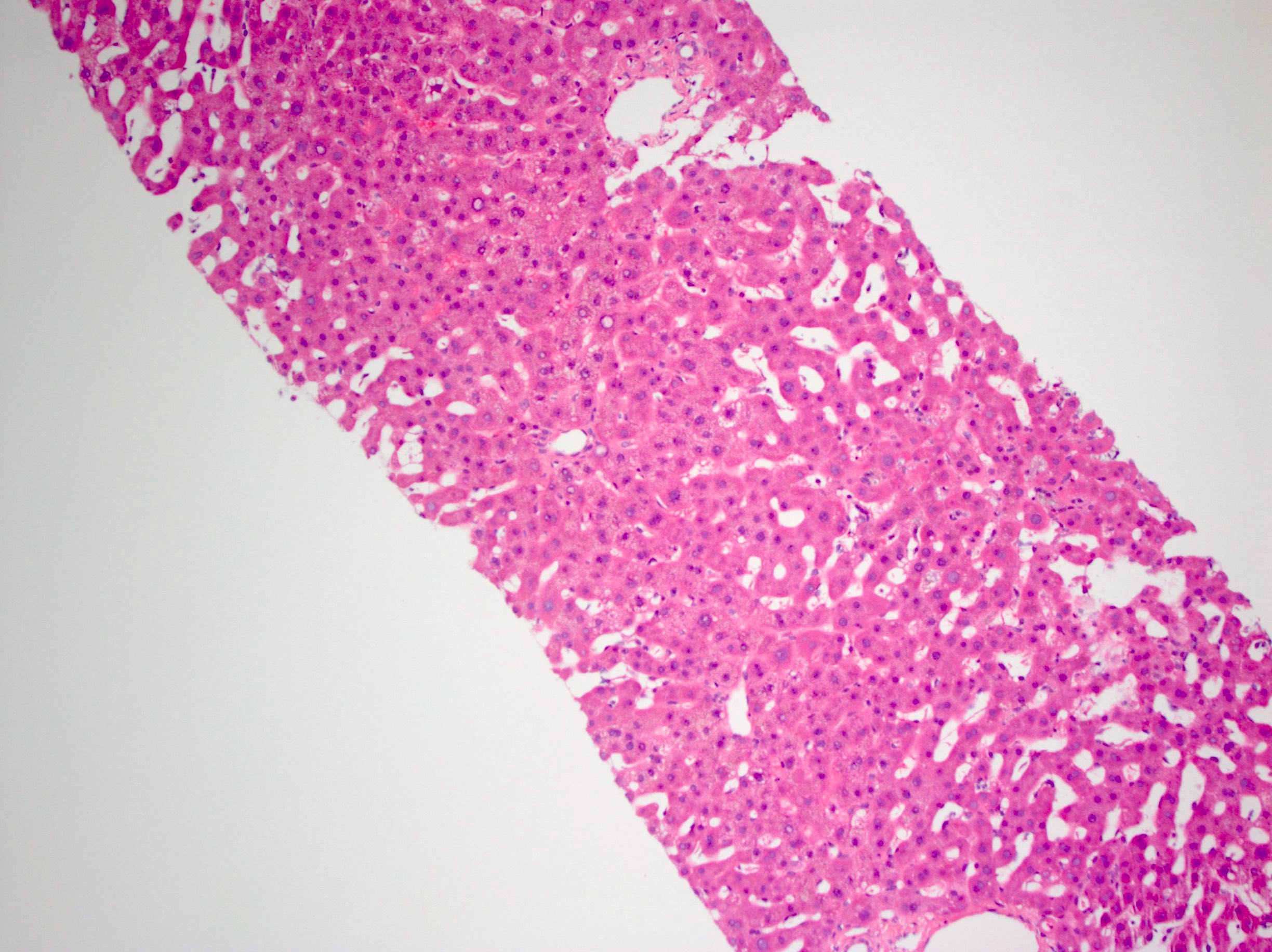
- Later, some regions of liver heal while others show collapse; constriction / obliteration of small central veins by subendothelial swelling / fibrosis can be seen
- Sinusoidal fibrosis and nodular regeneration may occur
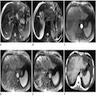
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Trichrome stain may be necessary to observe scant evidence of completely obliterated central veins
Electron microscopy description
- Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS): a light and electron microscopy study in human liver (Micron 2016;84:17)
Sample pathology report
- Liver, biopsy:
- Liver with dilated, congested sinusoids and hepatic plate atrophy (see comment)
- Comment: The patient’s reported history of hematopoietic stem cell transplant is noted. The findings are consistent with sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. A trichrome stain demonstrates focal central vein narrowing. An iron stain highlights hemosiderin deposition.
Differential diagnosis
- Budd-Chiari syndrome:
- Different clinical scenario / presentation
- Sinusoids may be dilated but not denuded
- Central veins should not show collapse
- Sickle cell disease:
- Red blood cells filling sinusoids appear sickled on high power
Additional references
Board review style question #1
53 year old man with leukemia undergoes myeloablative therapy and allogeneic stem cell transplant. One week later, he presents with jaundice, hepatomegaly and weight gain. Which of the following would be the most likely finding on liver biopsy?
- Bile duct injury
- Cytomegalic inclusions
- Hepatic artery obliteration
- Massive sinusoidal dilation
- Mixed portal inflammation
Board review style answer #1
D. Massive sinusoidal dilation
Comment Here
Reference: Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome / venoocclusive disease (SOS / VOD)
Comment Here
Reference: Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome / venoocclusive disease (SOS / VOD)