Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Flow cytometry images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Gu S, Siddon AJ. AML with t(8;21)(q22;q22); RUNX1::RUNX1T1. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/leukemiaAMLwitht821q22q22.html. Accessed December 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- AML with t(8;21)(q22;q22.1) is defined by a genetic rearrangement that results in the fusion of RUNX1 and RUNX1T1, has characteristic morphologic and immunophenotypic features and is associated with a generally favorable prognosis
Essential features
- AML with t(8;21)(q22;q22.1) is classified in the category of AML with recurrent genetic abnormalities and is diagnostic of AML regardless of blast count
- t(8;21)(q22;q22.1) is a balanced translocation that results in the fusion of RUNX1 and RUNX1T1
- Blasts have distinct morphologic and immunophenotypic features, including abundant basophilic cytoplasm containing azurophilic granules with occasional Auer rods and frequent aberrant expression of B cell markers, such as CD19
- Diagnosis is established by detection of t(8;21) by real time PCR or cytogenetics
- Prognosis is generally favorable, while coexisting KIT mutations adversely affect outcomes
Terminology
- AML with RUNX1-RUNX1T1
- AML with AML1-ETO
- Usually classified as AML M2 subtype in the previous French American British (FAB) classification system
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C92.00 - Acute myeloblastic leukemia, not having achieved remission
Epidemiology
- Typically occurs in younger patients and comprises approximately 1 - 5% of all AML cases
Sites
- Peripheral blood
- Bone marrow
- Myeloid sarcoma soft tissue / organs
Pathophysiology
- t(8;21)(q22;q22.1) results in fusion of the RUNX1 gene on chromosome 21q22.1 with RUNX1T1 gene on chromosome 8q22
- RUNX1 is a member of the core binding factor family of transcription factors, which is critical for the establishment of normal hematopoiesis (Blood 2017;129:2070)
- t(8;21), RUNX1-RUNX1T1 fusion gene expresses a chimeric protein that disrupts the normal function of the core binding factor and predisposes to acute myeloid leukemia (Cell Rep 2013;4:1131)
- Most cases show additional chromosomal abnormalities and cooperating driver mutations that promote transformation to acute myeloid leukemia (Blood 2012;119:e67)
Diagnosis
- Established by detection of t(8;21) by real time PCR or cytogenetics
Prognostic factors
- AML with t(8;21)(q22;q22.1) has a relatively favorable outcome and is associated with high rate of complete remission
- Presence of KIT mutations adversely affects prognosis (J Clin Oncol 2006;24:3904)
Case reports
- 28 year old man with headache was found to have intracranial myeloid sarcoma (Onco Targets Ther 2020;13:237)
- 65 year old woman with epistaxis (Case Rep Hematol 2019;2019:1312630)
- 2 patients with AML also found to have associated systemic mastocytosis (Exp Mol Pathol 2019;108:131)
Treatment
- Typically chemotherapy with induction, followed by intensive cytarabine consolidation
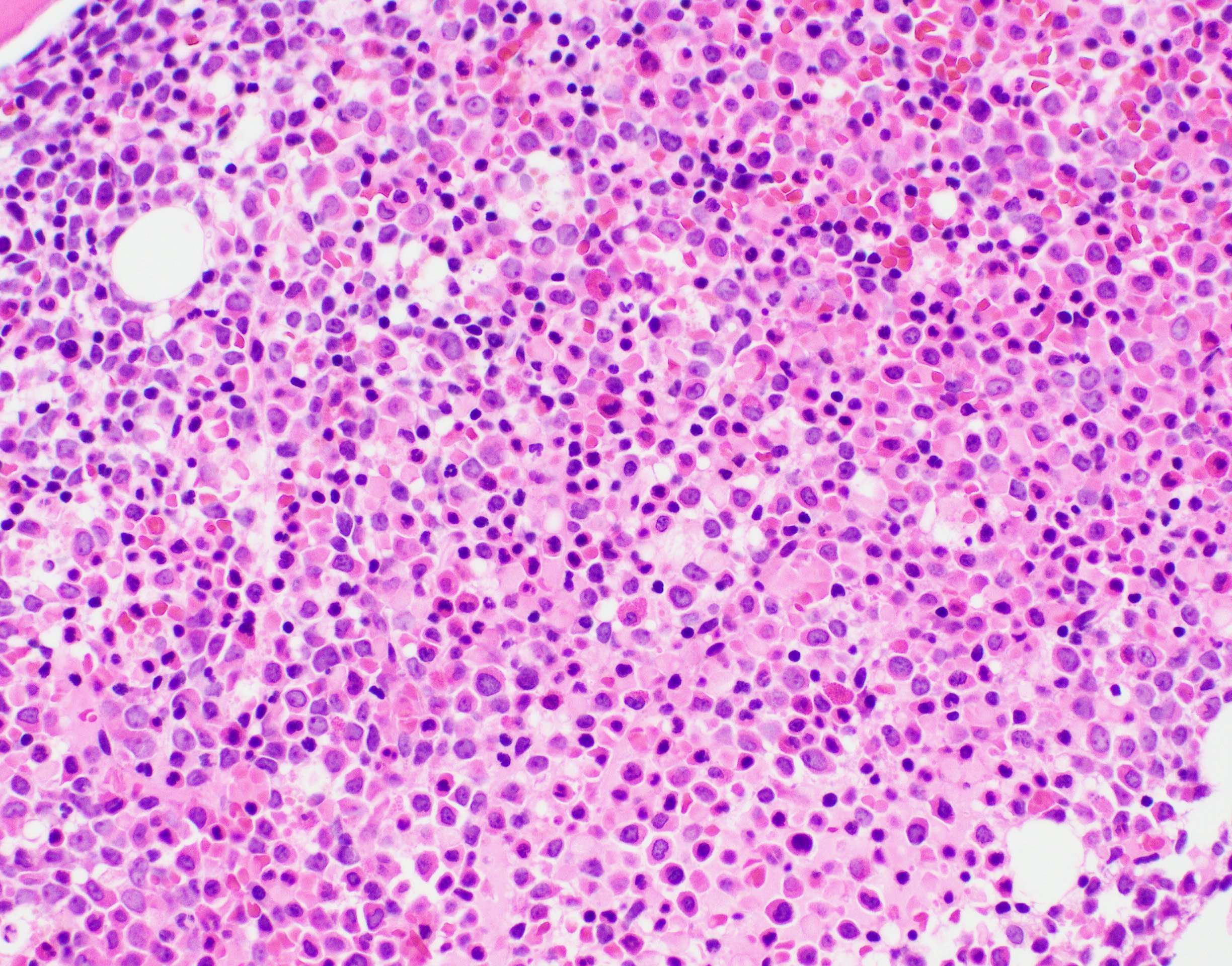
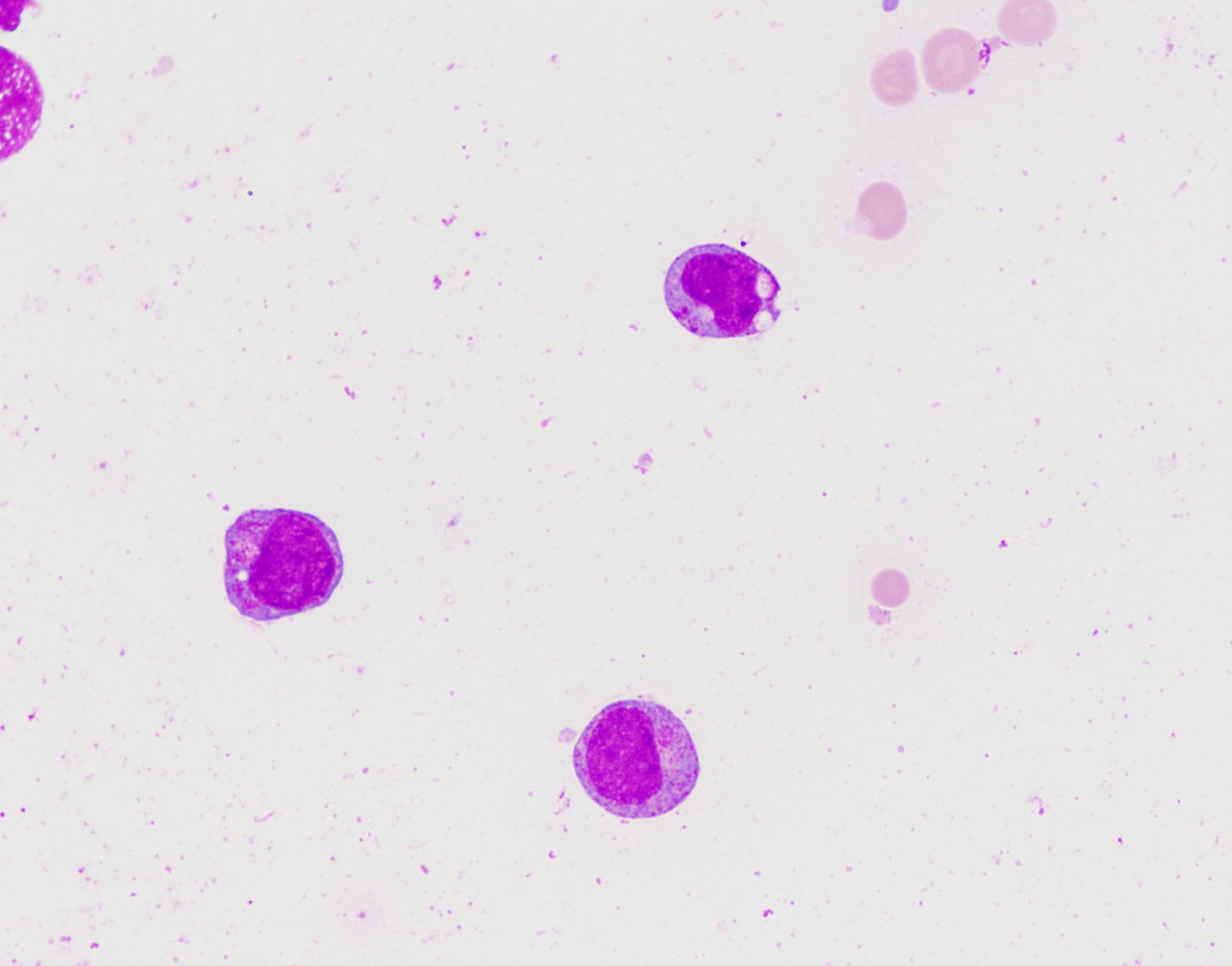
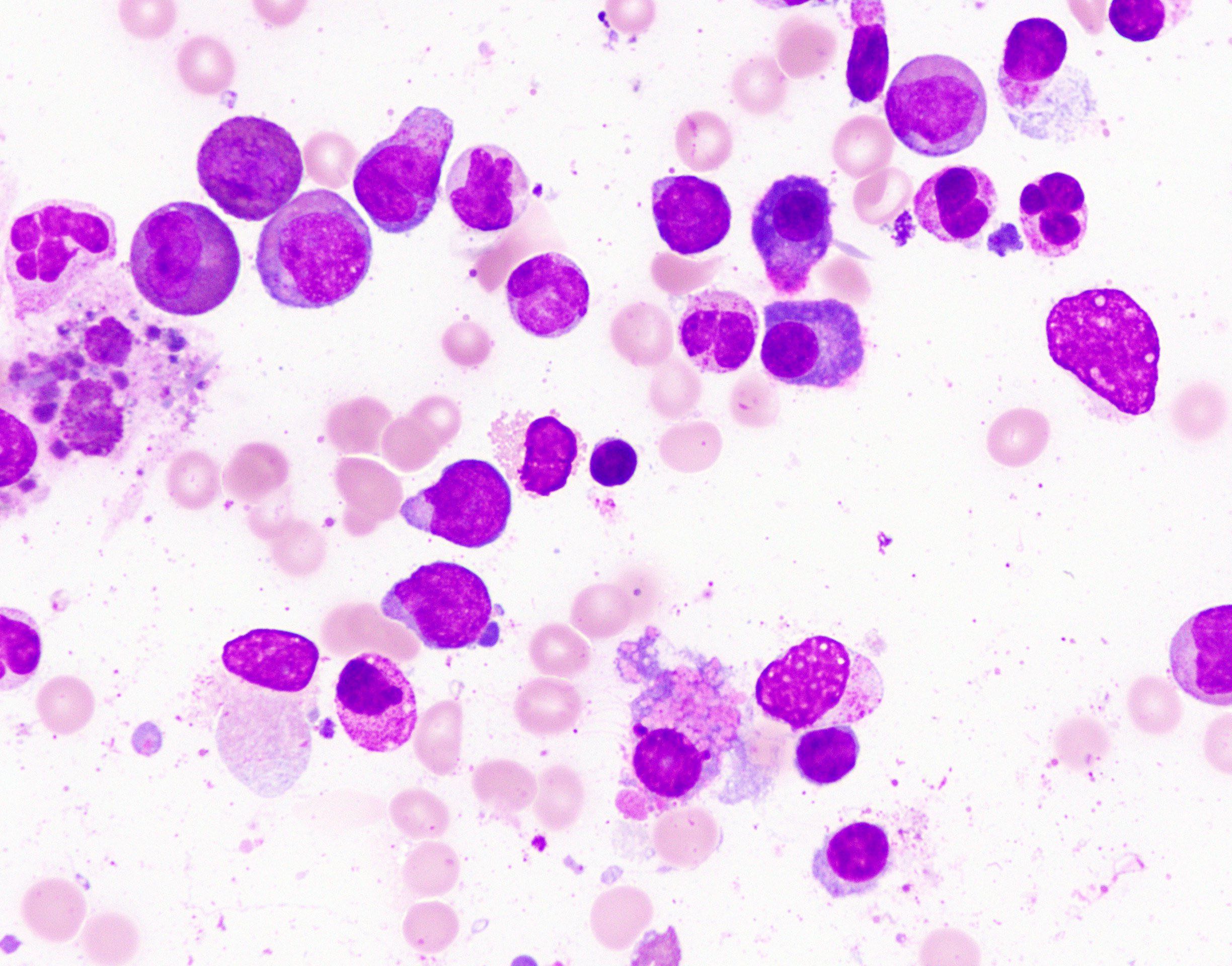
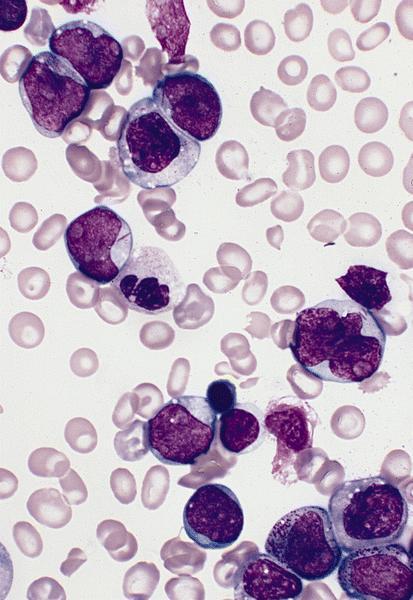
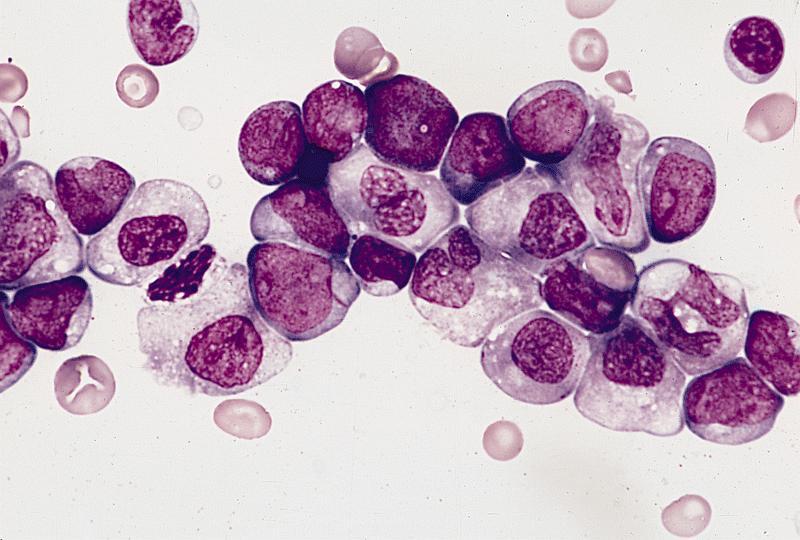
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Blast cells characteristically have slightly basophilic cytoplasm containing abundant azurophilic granules and perinuclear hofs
- Occasionally, large pseudo Chediak-Higashi granules and thin Auer rods may be seen; Auer rods may be seen in neutrophils
- Mature eosinophils that are morphologically normal are often increased in number in the bone marrow
- Mature granulocytes may show dysplastic changes with pseudo Pelger-Huet anomaly
- Generally no dysplasia in the erythroid and megakarocytic lineages
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Negative stains
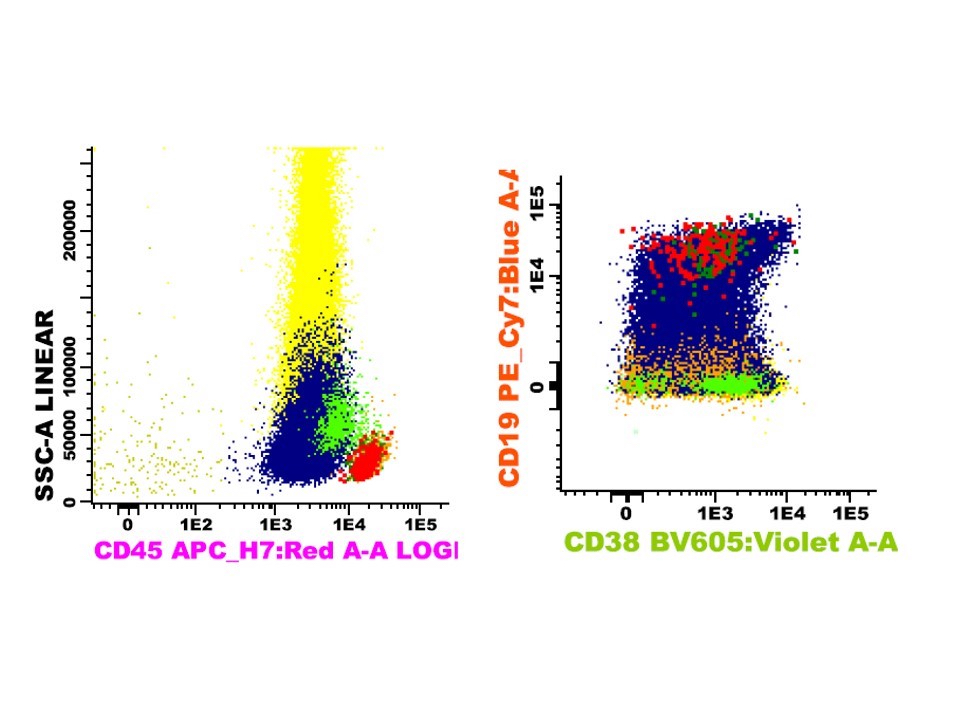
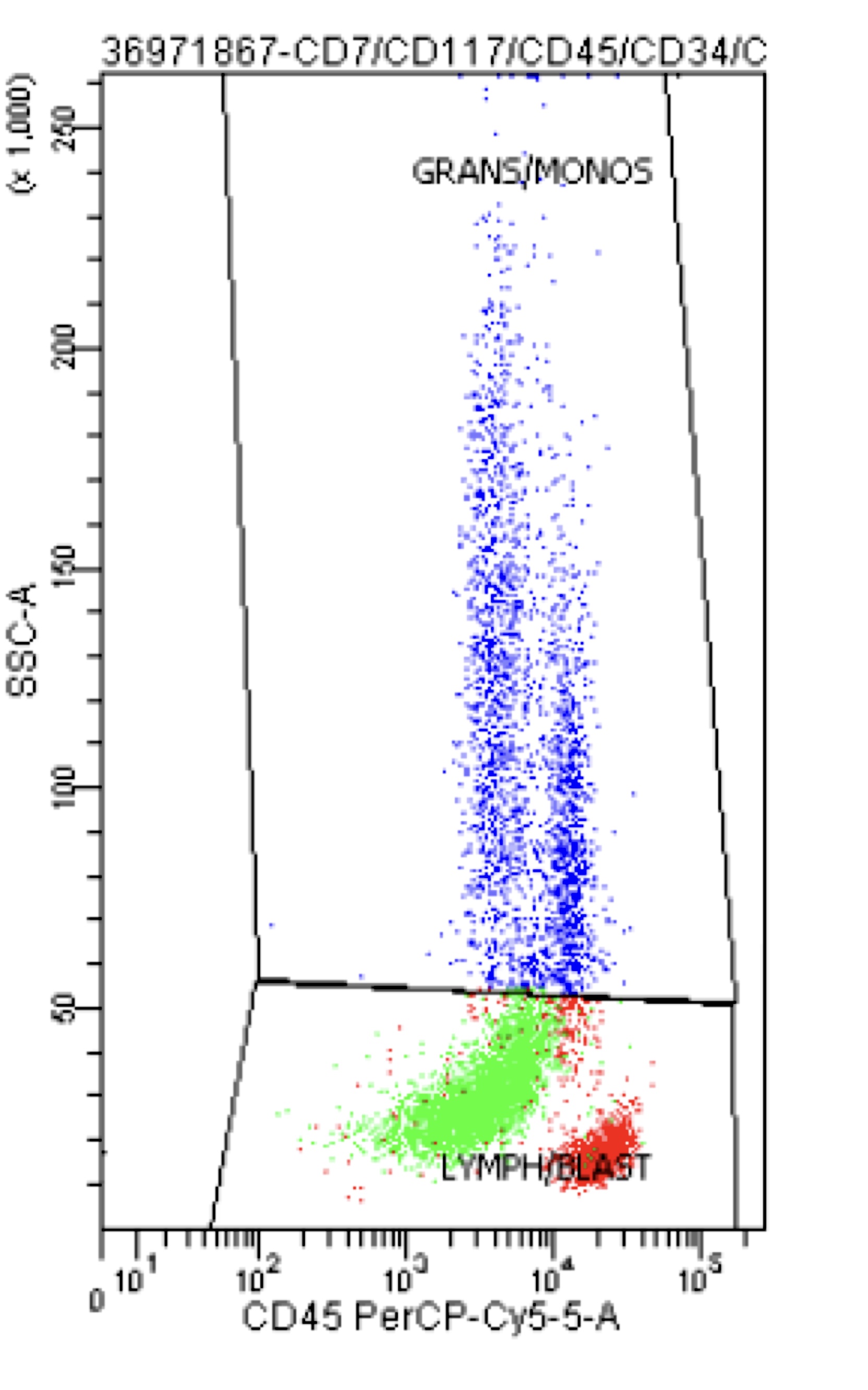
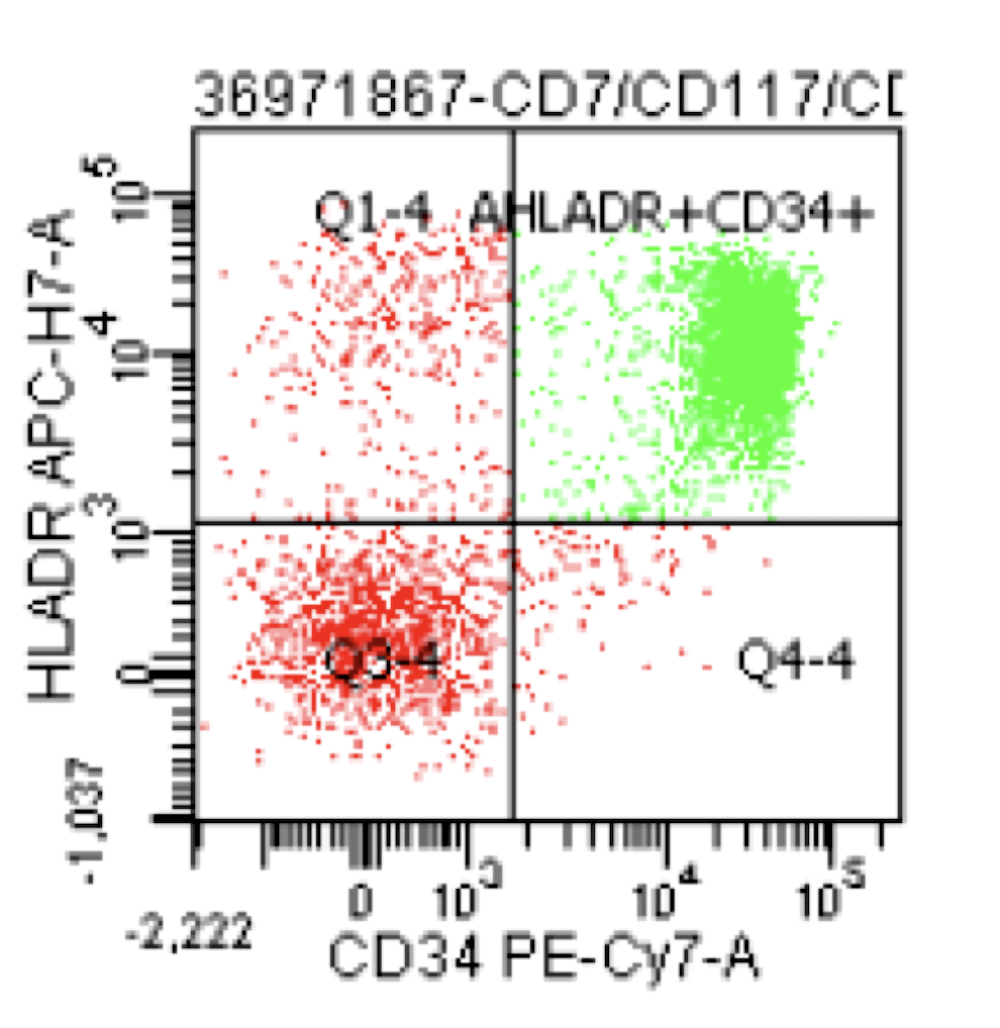
Flow cytometry description
- High levels of CD34, CD13, HLA-DR and myeloperoxidase and weak CD33 expression
- Frequent aberrant expression of B cell markers CD19 and PAX5 (Blood 1992;80:470, Am J Clin Pathol 2006;126:235)
- Expression of CD56 is associated with concomitant KIT mutations and worse prognosis (Blood 1997;90:1643)
Flow cytometry images
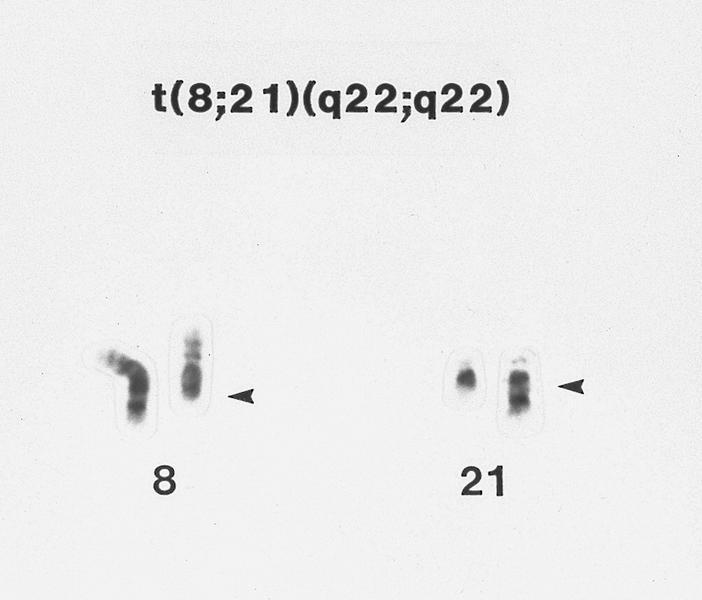
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Demonstration of t(8;21) by real time PCR or cytogenetics
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Left posterior iliac crest, core biopsy and aspirate smear:
- Acute myeloid leukemia with t(8;21)(q22;q22.1); RUNX1-RUNX1T1 (see comment)
- Comment: The bone core biopsy demonstrates an increase in blasts, which are noted to have prominent eosinophilic granules on the aspirate. The presence of t(8;21) by PCR confirms the diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis
- Other AML with recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities:
- AML with t(15;17) may morphologically resemble AML with t(8;21) but would have different flow and molecular findings
- AML with myelodysplasia related changes:
- Lacks t(8;21), often has complex karyotype
- AML with maturation:
- Lacks t(8;21)
- Myelodysplastic syndromes:
- If there are < 20% blasts and no t(8;21), the findings including dysplasia and Auer rods would be compatible with a myelodystplastic syndrome
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true about AML with t(8;21)?
- AML with t(8;21) generally has a poor prognosis
- AML with t(8;21) frequently aberrantly expresses the lymphoid markers CD19 and PAX5
- Auer rods are rare in AML with t(8;21)
- Presence of a concomitant KIT mutation is a good prognostic finding
- Translocation is best identified by microarray
Board review style answer #1
B. AML with t(8;21) frequently aberrantly expresses the lymphoid markers CD19 and PAX5
Comment Here
Reference: AML with t(8;21)(q22;q22)
Comment Here
Reference: AML with t(8;21)(q22;q22)
Board review style question #2
A 26 year old woman is referred to the emergency department when she is noted to have 32% blasts in peripheral blood. Her smear shows large basophilic blasts with prominent eosinophilic granules and rare Auer rods. What will the flow cytometry immunophenotype likely show?
- CD34-, CD117+, HLADR-, MPO++, CD33,
- CD34+, CD33dim+, MPO+, CD71-, CD19dim+
- CD34-, CD13+, CD11b+, CD14+, CD64+, HLA-DR+
- CD34+, CD117+, CD33+, CD19-, CD3-, MPO-
- CD34+, CD19+, CD20-, CD10+, TdT+
Board review style answer #2