Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Pernick N, Handra-Luca A. Conventional squamous cell carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/larynxcarcinomageneral.html. Accessed January 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- 9,000 new cases annually in US; 40% mortality
- Represents 90% of all laryngeal cancers
- 96% male; usually ages 40+ (but can occur in younger patients)
- Major risk factors are smoking, enhanced by heavy alcohol consumption
- HPV is not an early factor but positive in 20%, usually HPV 16 (Hum Pathol 1999;30:274)
- EBV a factor in 40% of hypopharyngeal carcinomas (Hum Pathol 1999;30:1071)
- Site influences histology and clinical behavior - either glottic, supraglottic or transglottic
- Spread is limited by tough membranes / ligaments
- Recurrence rate of 3% per year, second primary rate is 5% per year, usually in lung
- Metastases to regional lymph nodes and lungs; direct extension to thyroid gland and jugular vein
Clinical features
- Trachea:
- Exophytic, obstructive tumor usually in smokers but also children (J Am Coll Surg 2006;202:237)
- Most common primary malignancy of trachea (40 - 75%) (Cancer 1990;66:894)
- Usually arises in lower third of trachea (Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 1993;250:383, Acta Otolaryngol 1991;111:1162)
- May be extension of other head and neck primary
- May be associated with pneumoconiosis or posttracheotomy scar (Respiration 1993;60:250)
- Rapid clinical course, poor prognosis (Am J Clin Oncol 2011;34:32, Virchows Arch 2009;455:423, Jpn J Clin Oncol 1997;27:305)
Prognostic factors
- TNM; also tumor grade, tumor size, mitotic count, vascular invasion and margins
- 5 year survival by site:
- Glottic: I: 90%; II: 85%; III: 60%; IV: < 5%
- Supraglottic: I: 85%; II: 75%; III: 45%; IV: < 5%
- Transglottic: 50%
- Subglottic: 40%
Case reports
- 11 month old boy with severe dyspnea and stridor (Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 1998;43:163)
- 37 year old woman with hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (J Laryngol Otol 2002;116:742)
- 50 year old man with unresectable basaloid squamous cell carcinoma (J Cancer Res Ther 2010;6:321)
- 52 year old woman with HPV and squamous cell carcinoma in a solitary tracheal papilloma (Ann Thorac Surg 2004;77:2201)
- 54 year old man with dyspnea, hemoptysis, cough and weight loss (Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 2010;30:209)
- 70 year old woman with double primary cancer of the lung and trachea (Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi 1996;34:216)
- 78 year old man with spindle cell sarcomatoid carcinoma (Tuberk Toraks 2009;57:337)
- Nodal metastasis occurring postradiation therapy with mixture of squamous cell carcinoma and rhabdomyosarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:415)
Treatment
- Surgical excision with end to end anastomosis, radiation therapy (Med Princ Pract 2004;13:69)
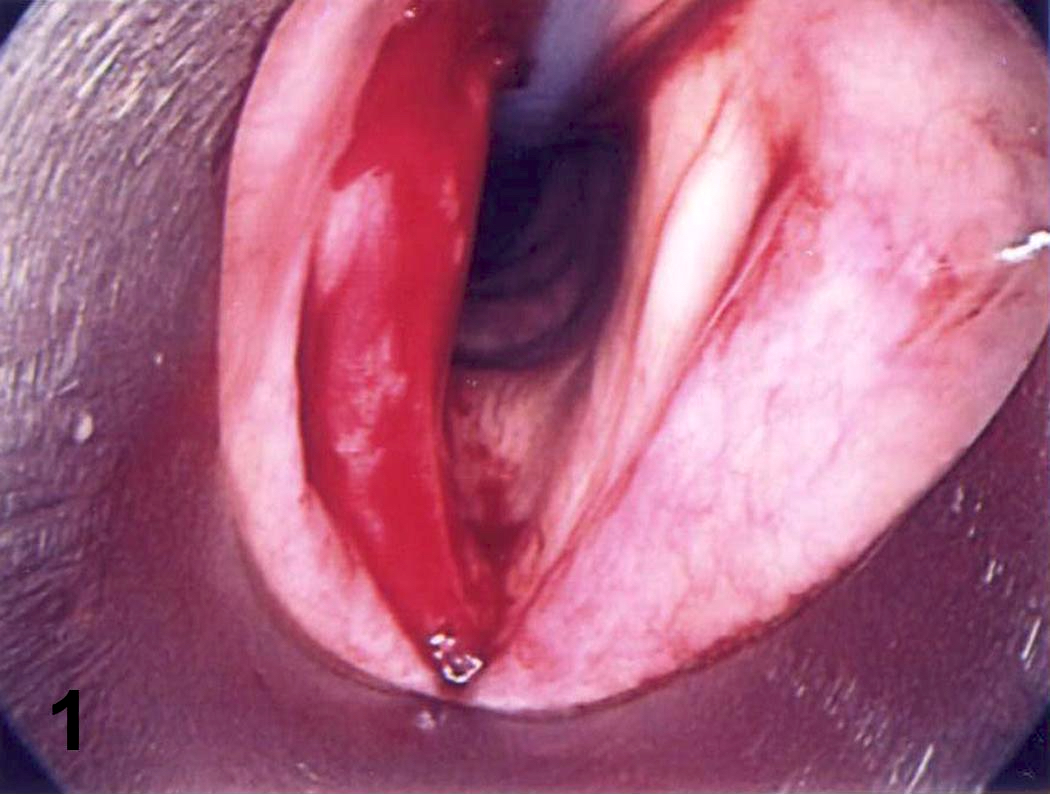
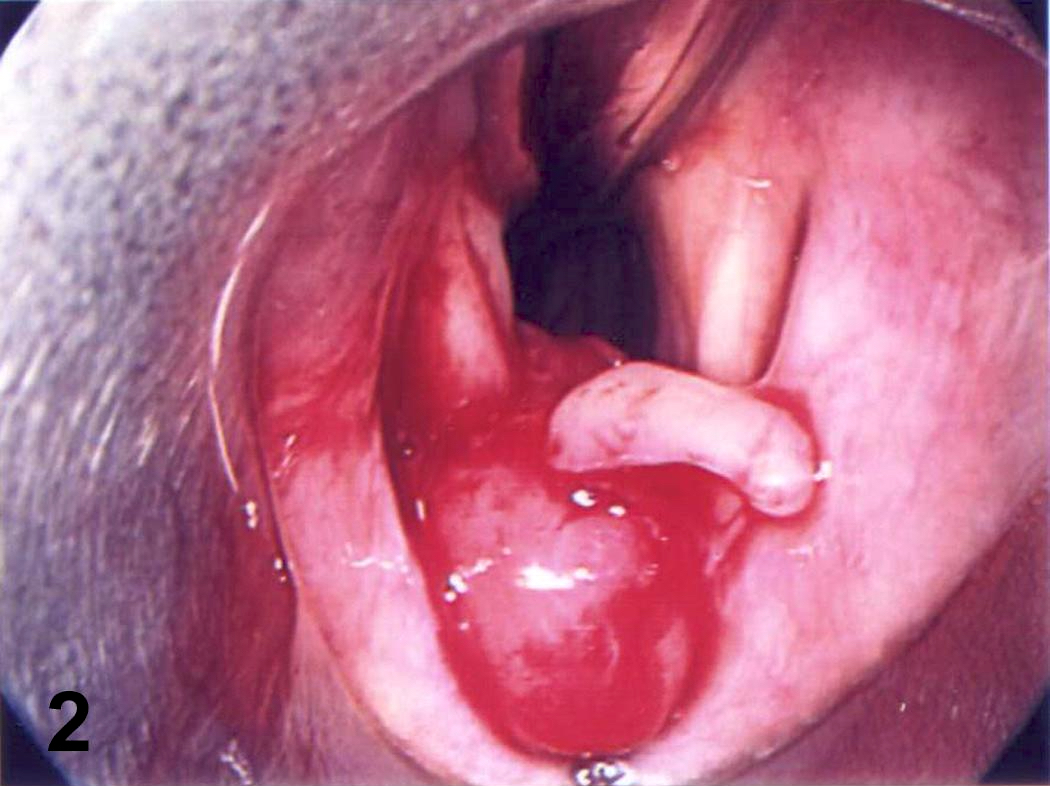
Clinical images
Gross description
- Pink to gray ulcerated mass; vocal cord lesions often keratotic
Microscopic (histologic) description
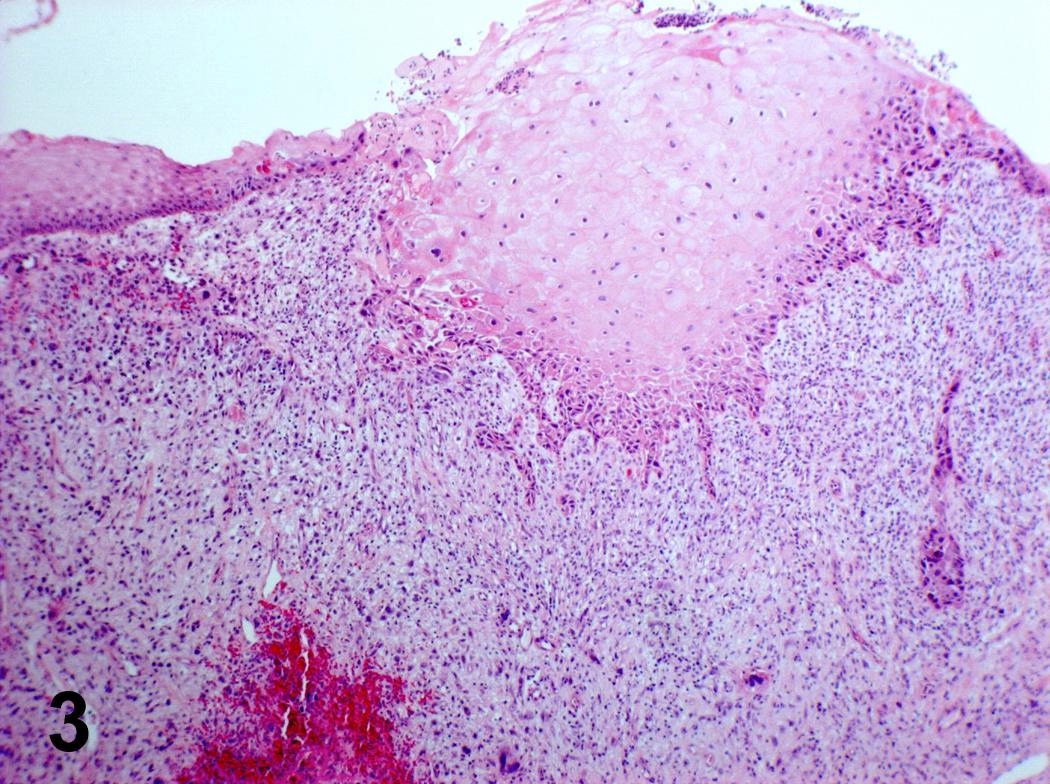
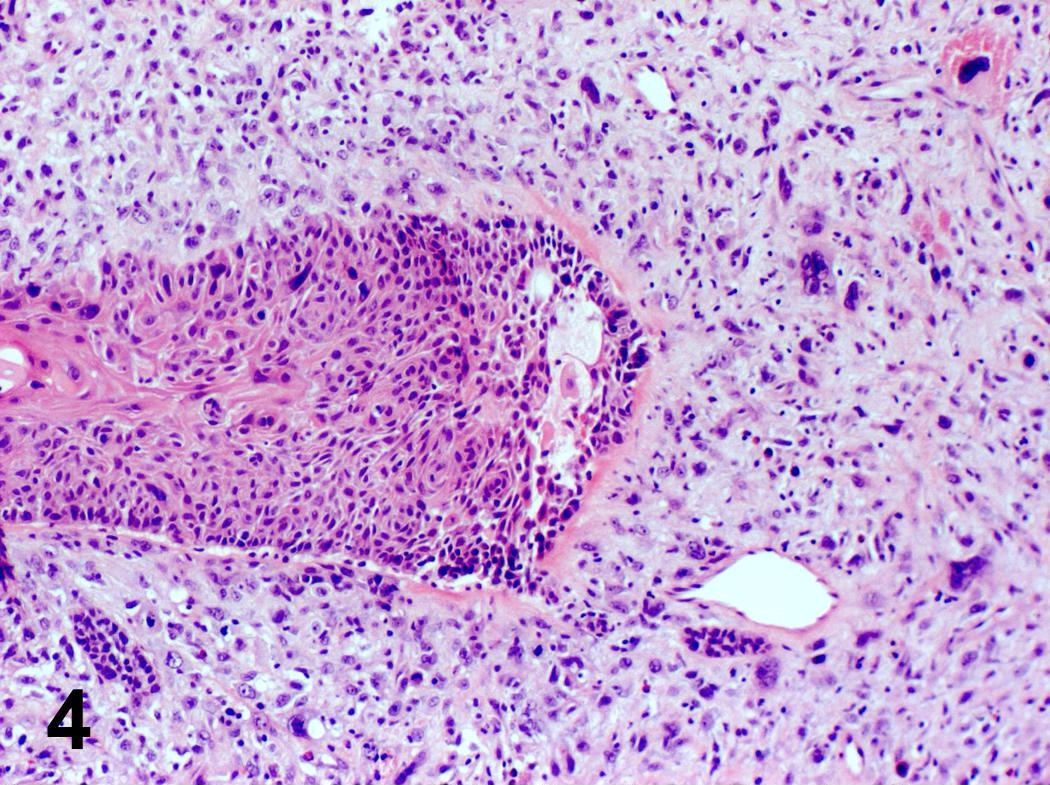
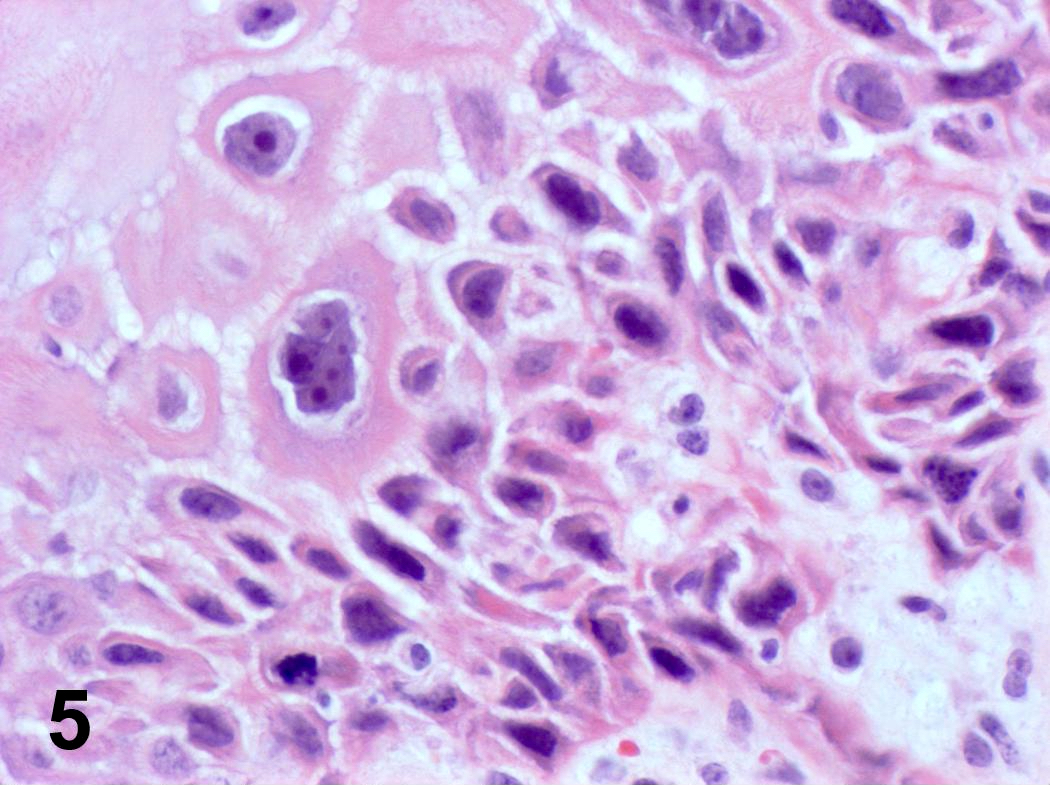
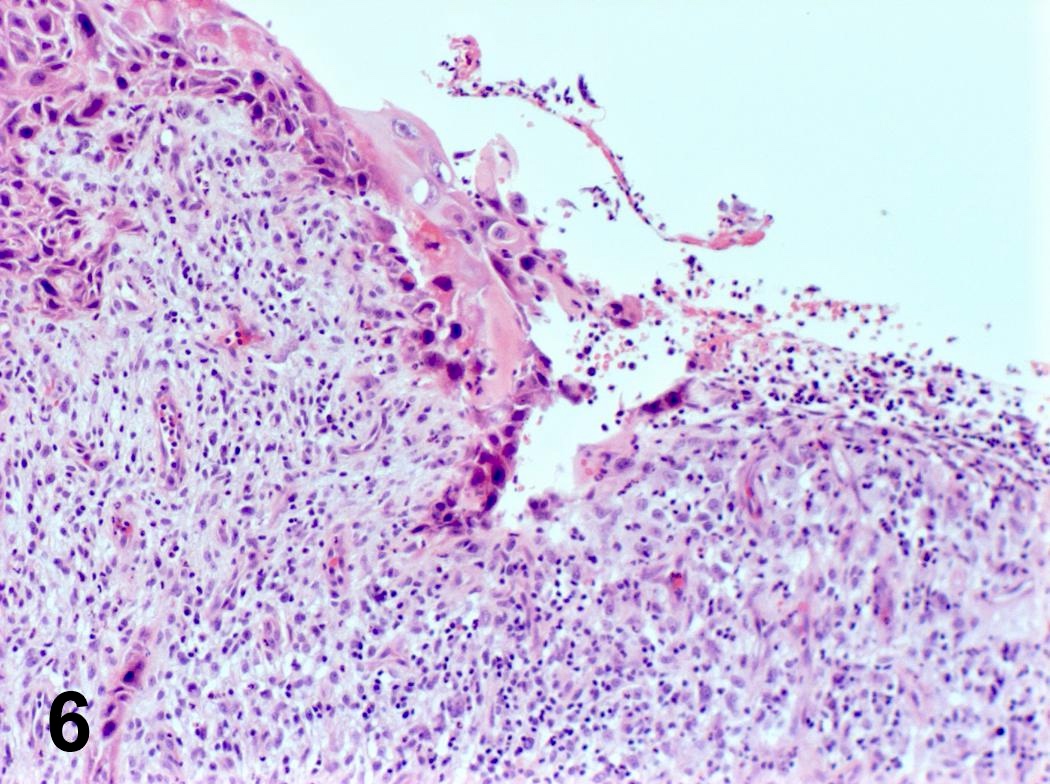
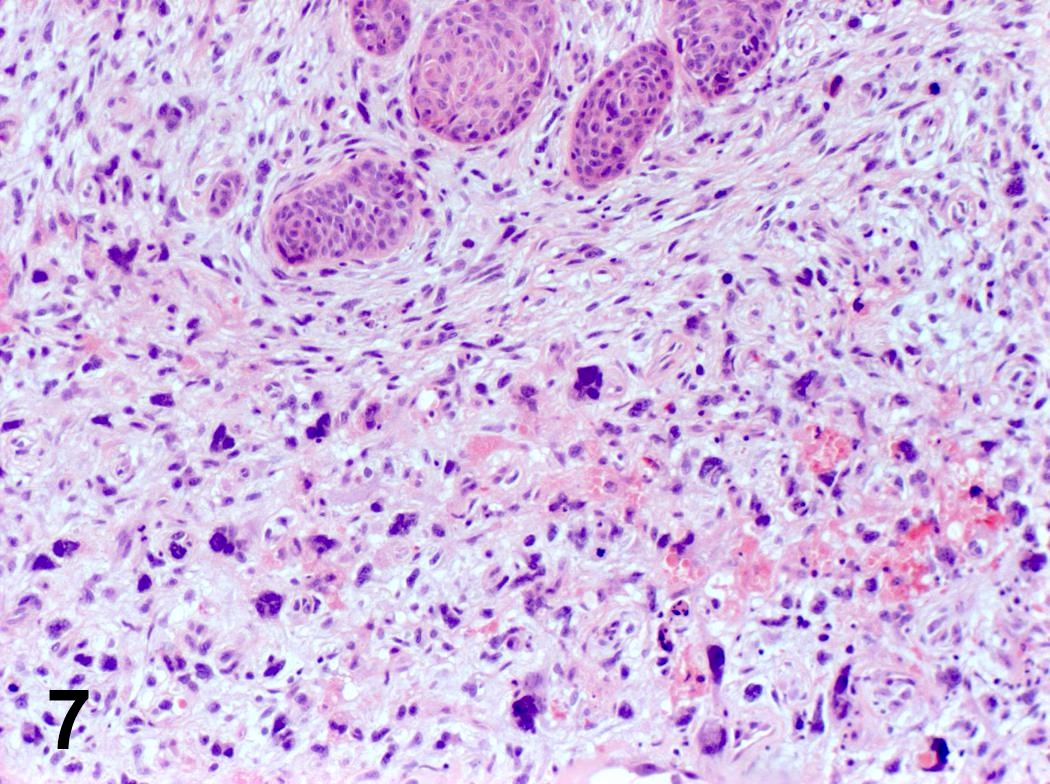
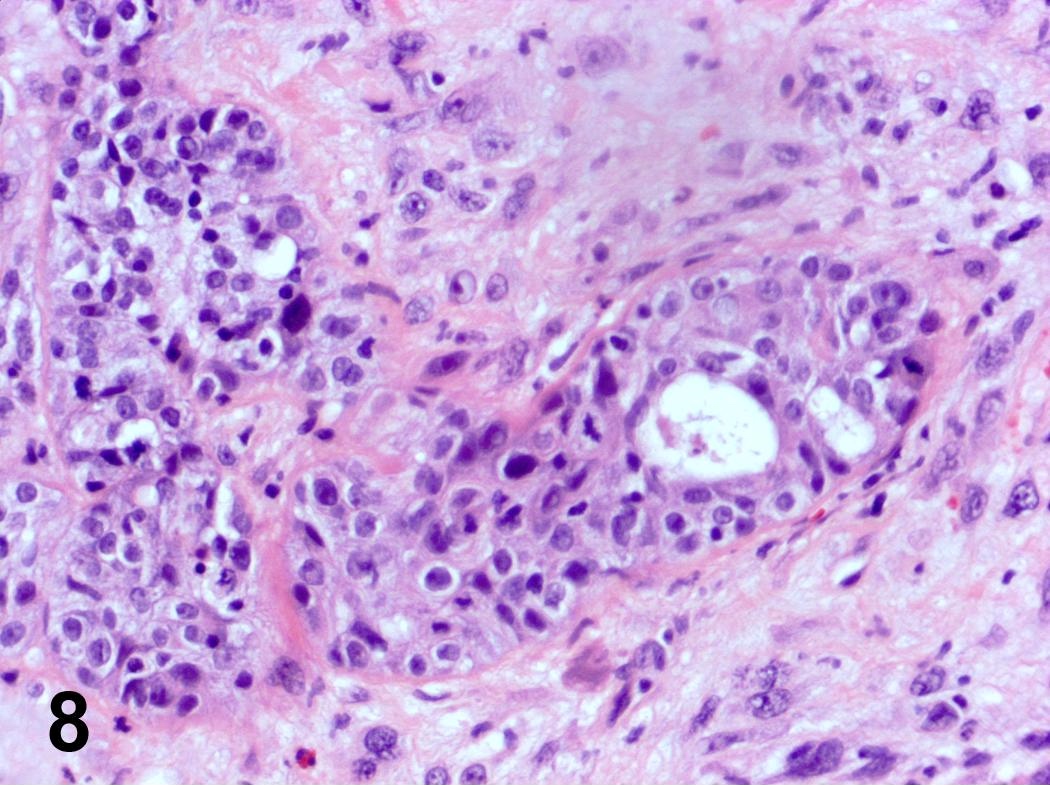
- Invasion indicated by desmoplasia around malignant squamous cells, often with keratinization at periphery
- Progression of columnar epithelium areas is similar to squamous cell carcinoma of cervical or lung
- Progression of vocal cord tumors is similar to squamous cell carcinoma of skin or esophagus
- Well, moderate or poorly differentiated, based on degree of keratinization, pearl formation, intercellular bridges and mitotic activity
- Smaller tumors are usually better differentiated
- Trachea:
- Variants include spindle cell, sarcomatoid
- May arise in papilloma
- May be combined with small cell and giant cell carcinoma
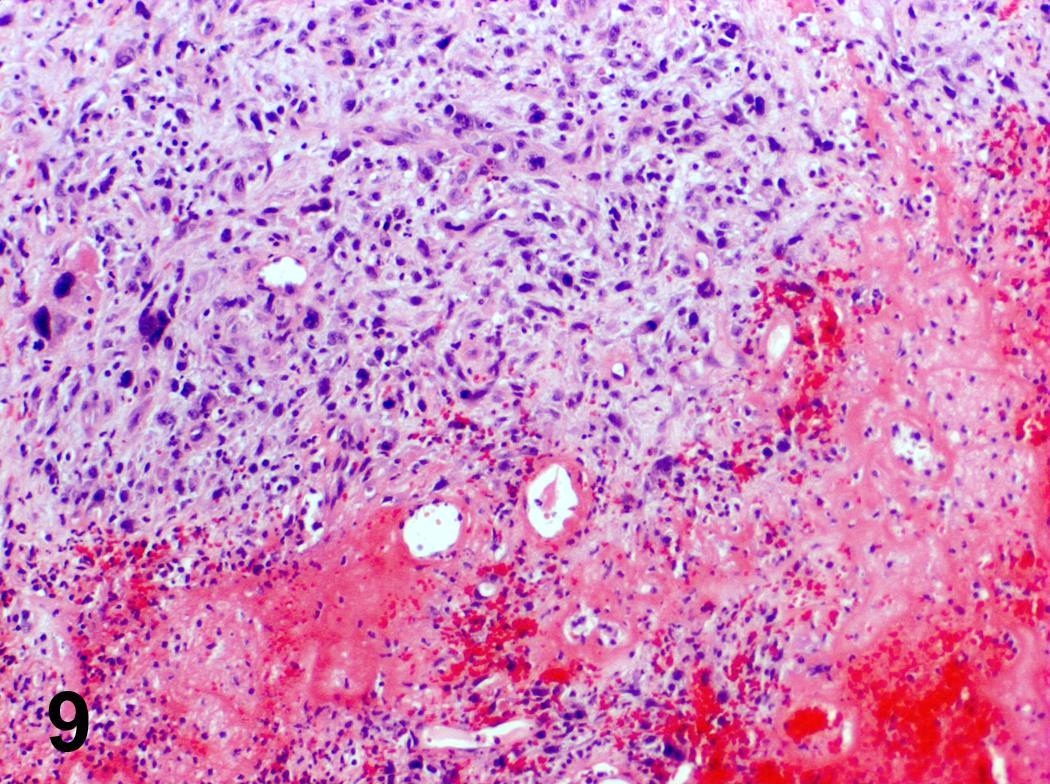
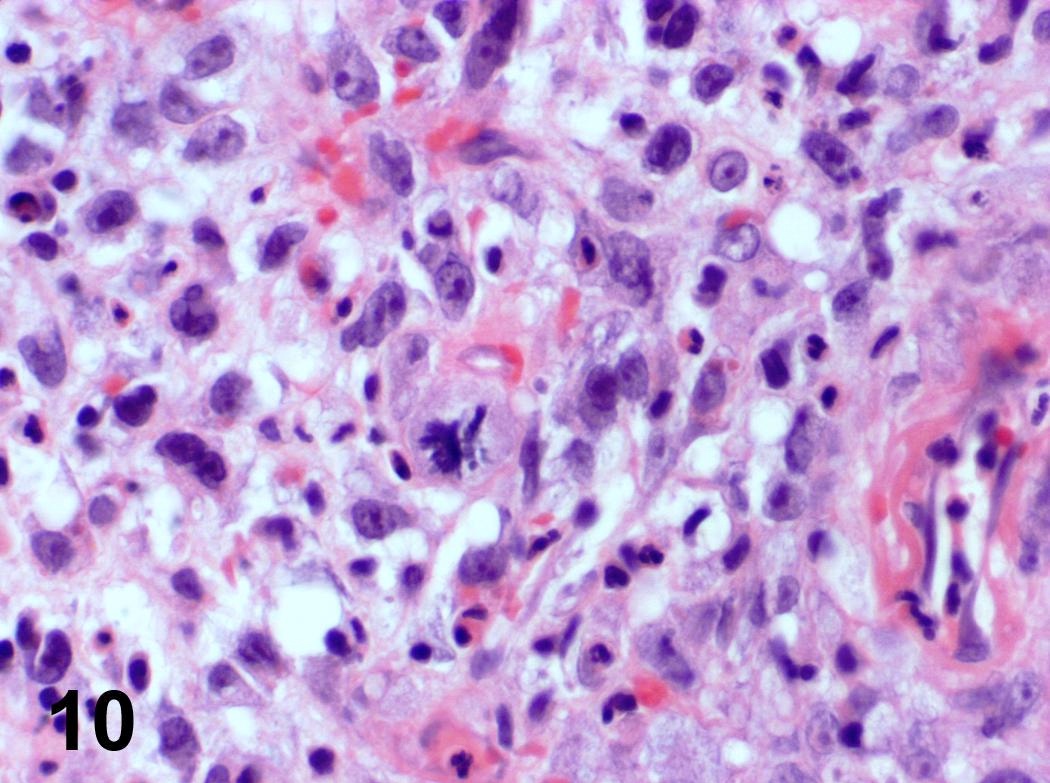
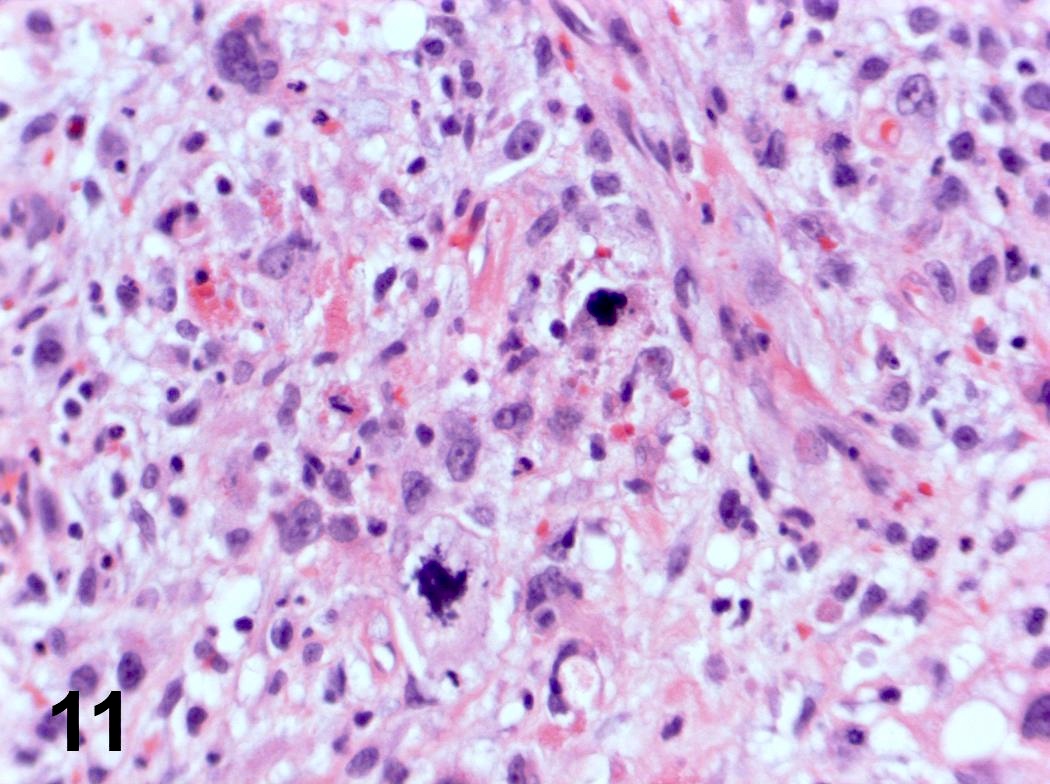
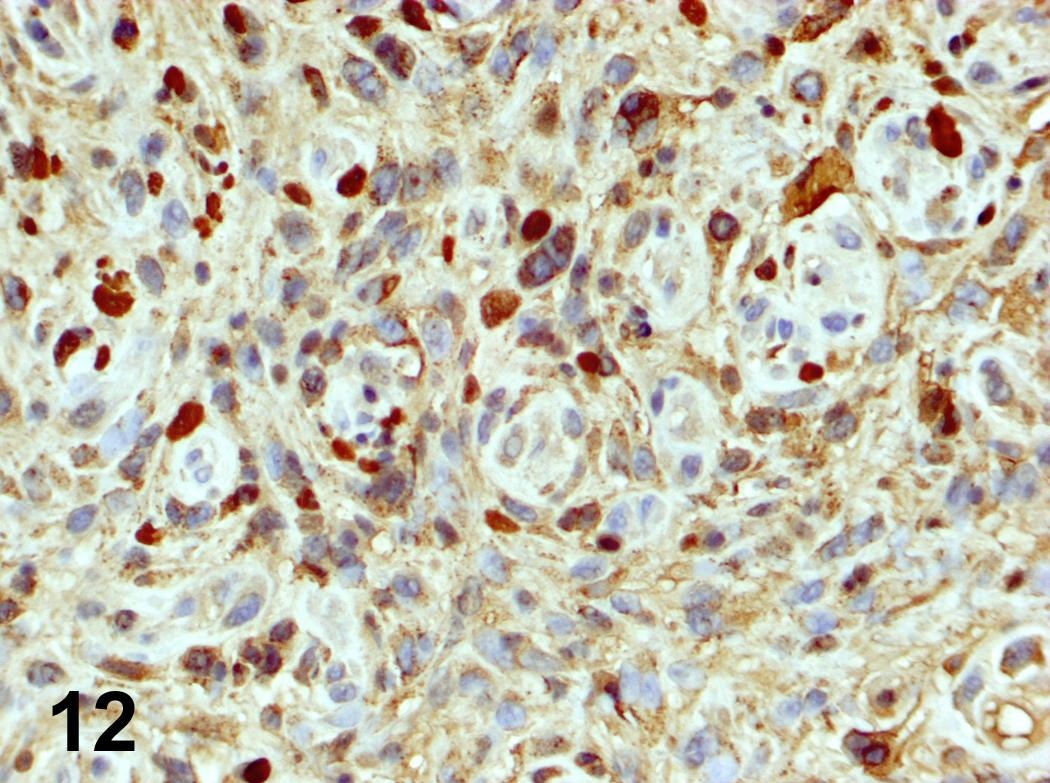
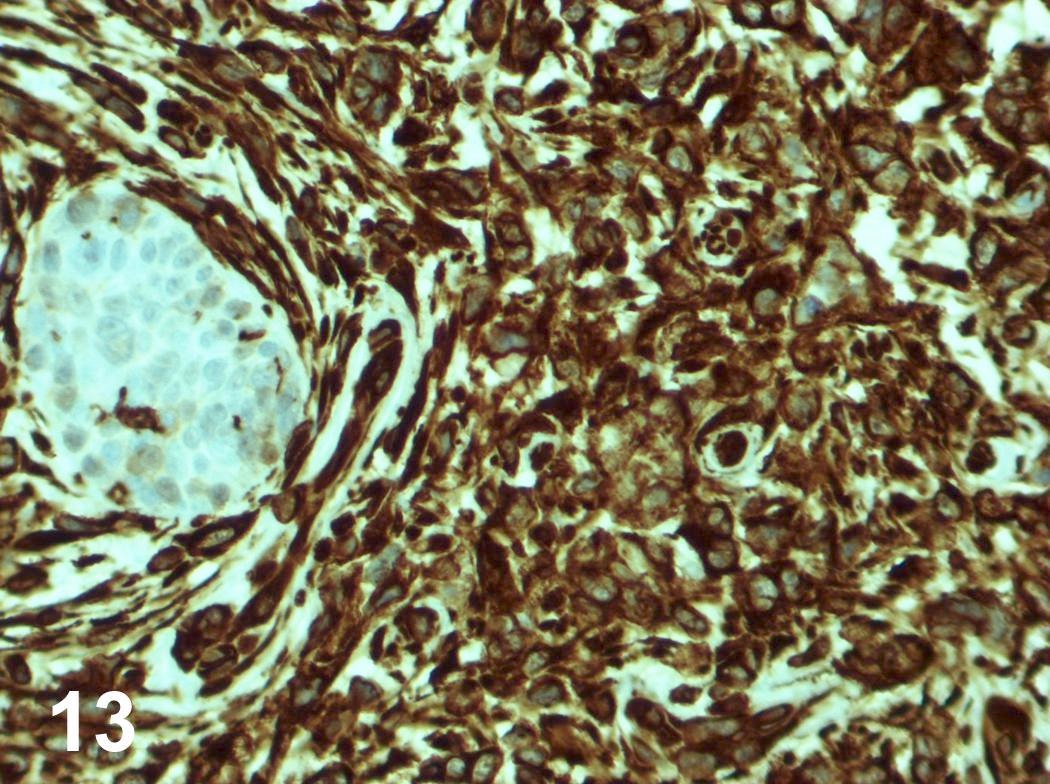
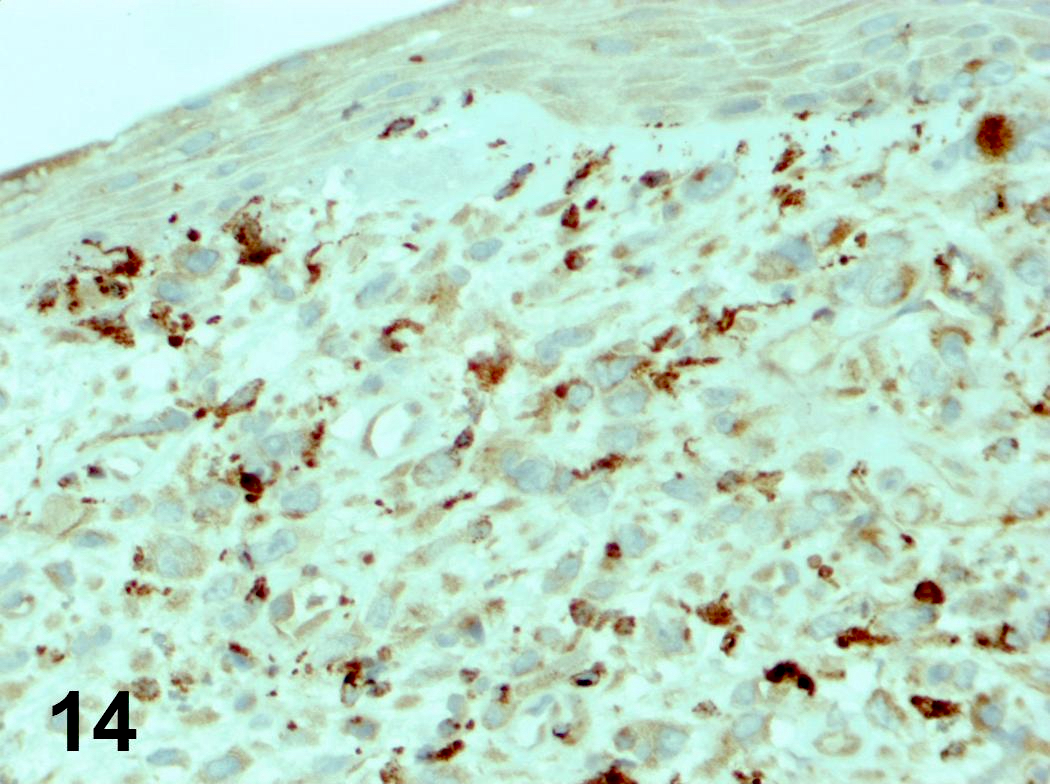
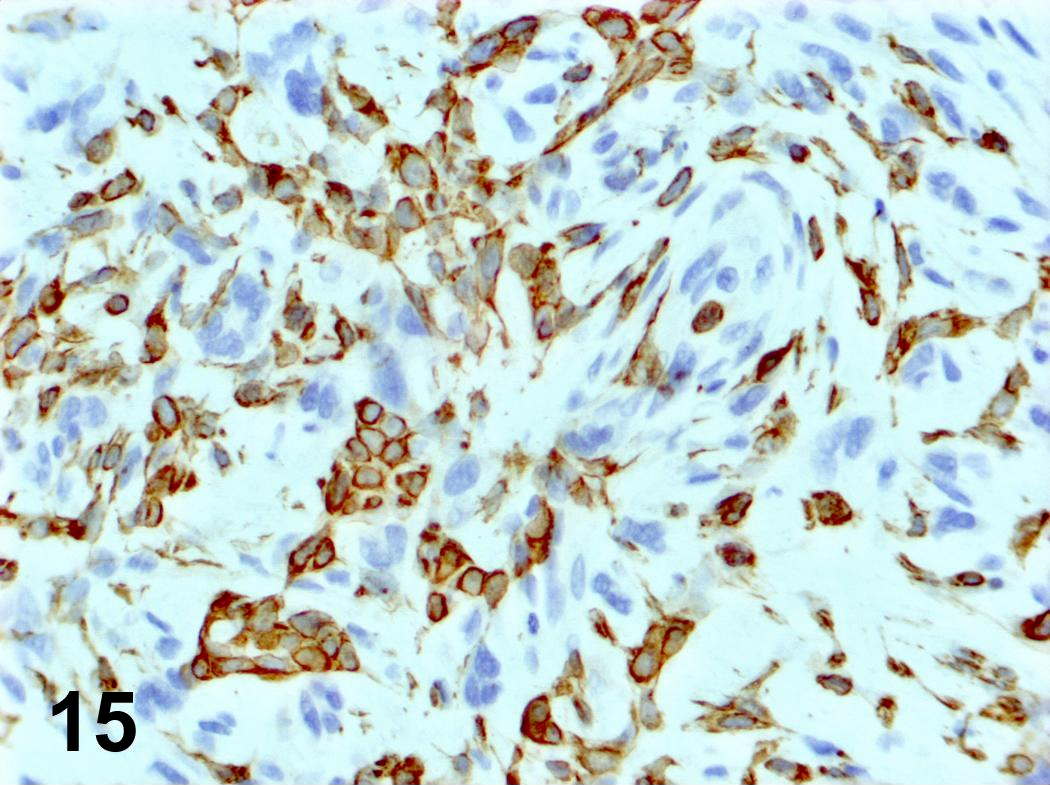
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Steven Catinchi-Jaime, M.D.
Images hosted on other servers:
Differential diagnosis
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Extension of esophageal tumor (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1984;108:983)
- Metastasis from colon carcinoma (Can Assoc Radiol J 1989;40:198)
Additional references