Cite this page: Sangle N. Urate nephropathy. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneyurate.html. Accessed January 7th, 2025.
Definition / general
-
Three types:
- Acute uric acid nephropathy due to precipitation of uric acid crystals in tubules, causing acute renal failure; associated with chemotherapy for leukemia / lymphoma
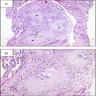
- Chronic urate nephropathy, associated with gout and lead exposure from drinking “moonshine”
- Uric acid stones, in 22% with gout and 42% with secondary hyperuricemia
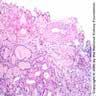
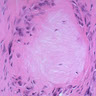
- Gout causes deposition of monosodium urate crystals with tophus formation that obstructs tubules, leading to cortical atrophy and scarring (eMedicine: Gout and Pseudogout [Accessed 02 January 2018])
- Kidney injury molecule-1 expression identifies proximal tubular injury in urate nephropathy (Ann Clin Lab Sci 2008;38:210)