Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Tretiakova M. ELOC (TCEB1) mutated. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytumortceb1mutatedrcc.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) composed of clear cells separated by thick fibromuscular bands and associated with mutation of TCEB1 gene
Essential features
- Low grade clear cells with voluminous cytoplasm
- Transecting thick fibromuscular septae imparting multilobular appearance
- Biallelic inactivation of TCEB1 gene: mutation with concurrent monosomy 8 or loss of heterozygosity at 8q21
- Lack VHL mutations, hypermethylation or loss of heterozygosity at 3p (Histopathology 2019;74:31, Mod Pathol 2015;28:845, Histopathology 2019;74:60)
Terminology
- Transcription Elongation Factor B (TCEB1) mutated renal cell carcinoma
- Monosomy 8 renal cell carcinoma
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C64 - malignant neoplasm of kidney, except renal pelvis
Epidemiology
- Rare; < 20 cases described
- Age range: 32 - 77 year old (Mod Pathol 2015;28:845, Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1135, Mod Pathol 2017;30:1603, Virchows Arch 2016;469:81)
Sites
- Solitary kidney mass
- Renal cortex
Pathophysiology
- TCEB1 located at chromosome 8q21.11 and encodes 112-residue protein elongin C, subunit 1 of transcription factor B (SIII) complex
- Elongin C is part of VHL complex responsible for proteosomic degradation (ubiquitination) of hydroxylated HIF
- Loss of Elongin C leads to HIF1α stabilization, accumulation, activation of hypoxia inducible growth factors and tumor development
- Downregulate other genes in ubiquitination complex including POLR2E, POLR2C, CDK7, TCEA1 and TCEB2
- Increase the POL II transcription elongation past template encoding arresting sites (Nat Genet 2013;45:860, Mod Pathol 2015;28:845)
Etiology
- Hotspot mutations in TCEB1 gene always accompanied by loss of chromosome 8 (loss of heterozygosity at 8q or monosomy 8)
- TCEB1 mutations and VHL abnormalities are mutually exclusive (Nat Genet 2013;45:860)
Clinical features
- Vast majority are incidental: pT1a
- Rare tumors are pT3a
Prognostic factors
- No recurrence or metastasis reported to date
Case reports
- Not available at this time
Treatment
- Surgical: partial or radical nephrectomy
Gross description
- Unifocal, well circumscribed, partly encapsulated
- Pale-tan cut surface with traversing fibrous bands
- Could have nodular or lobulated appearance
- Size: reported 1.6 - 3.5 cm (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1135, Virchows Arch 2016;469:81)
Microscopic (histologic) description
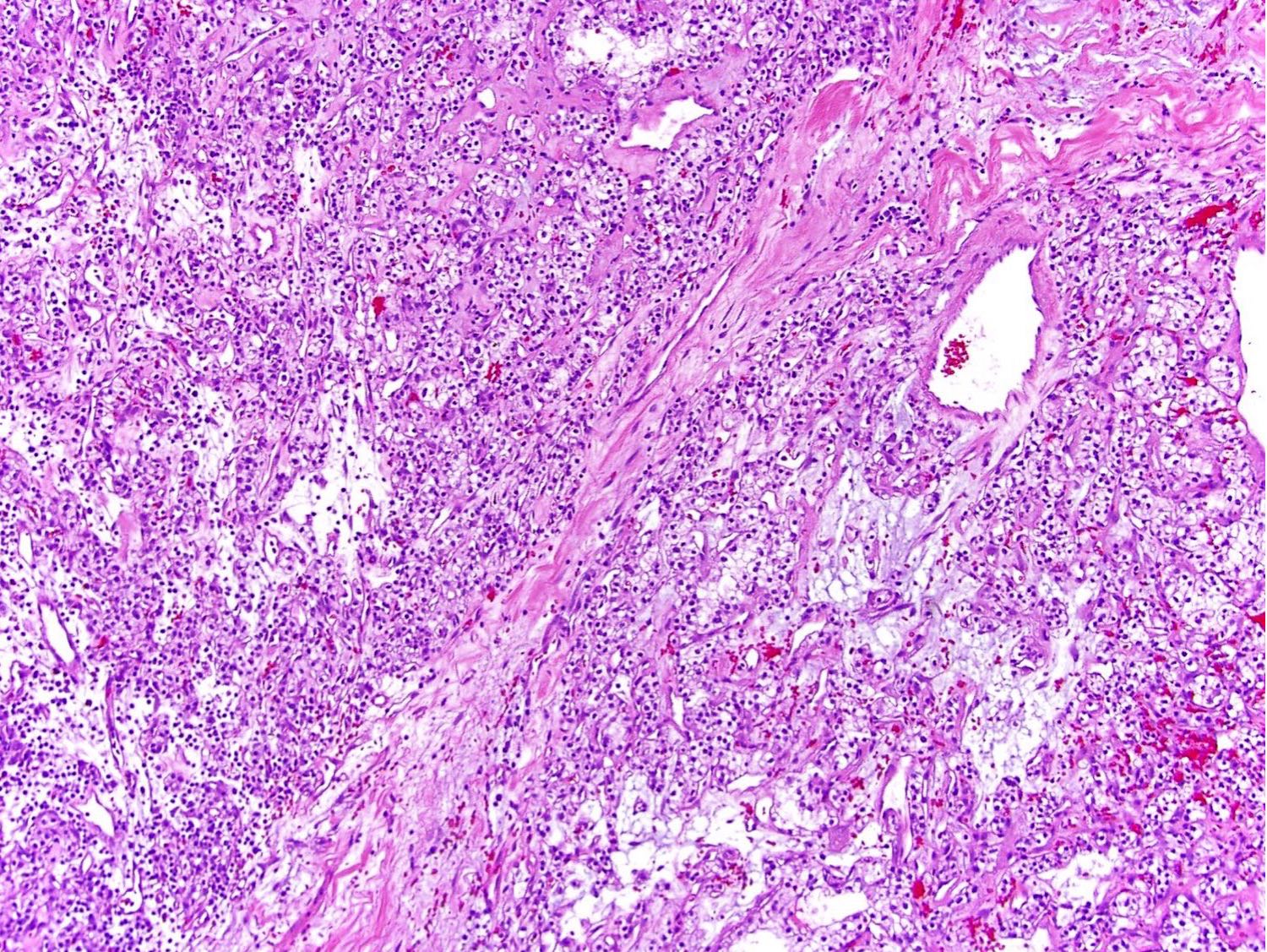
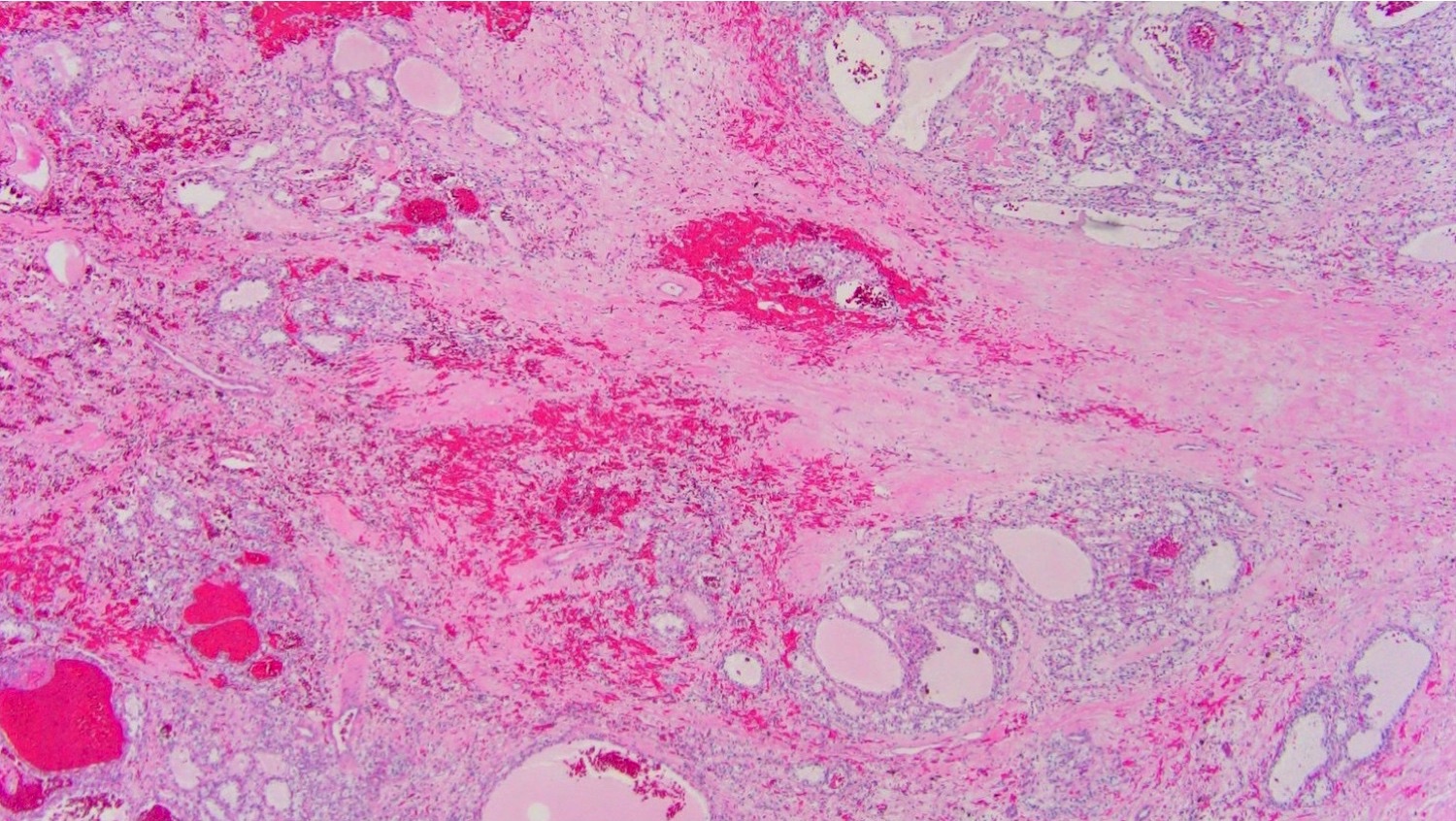
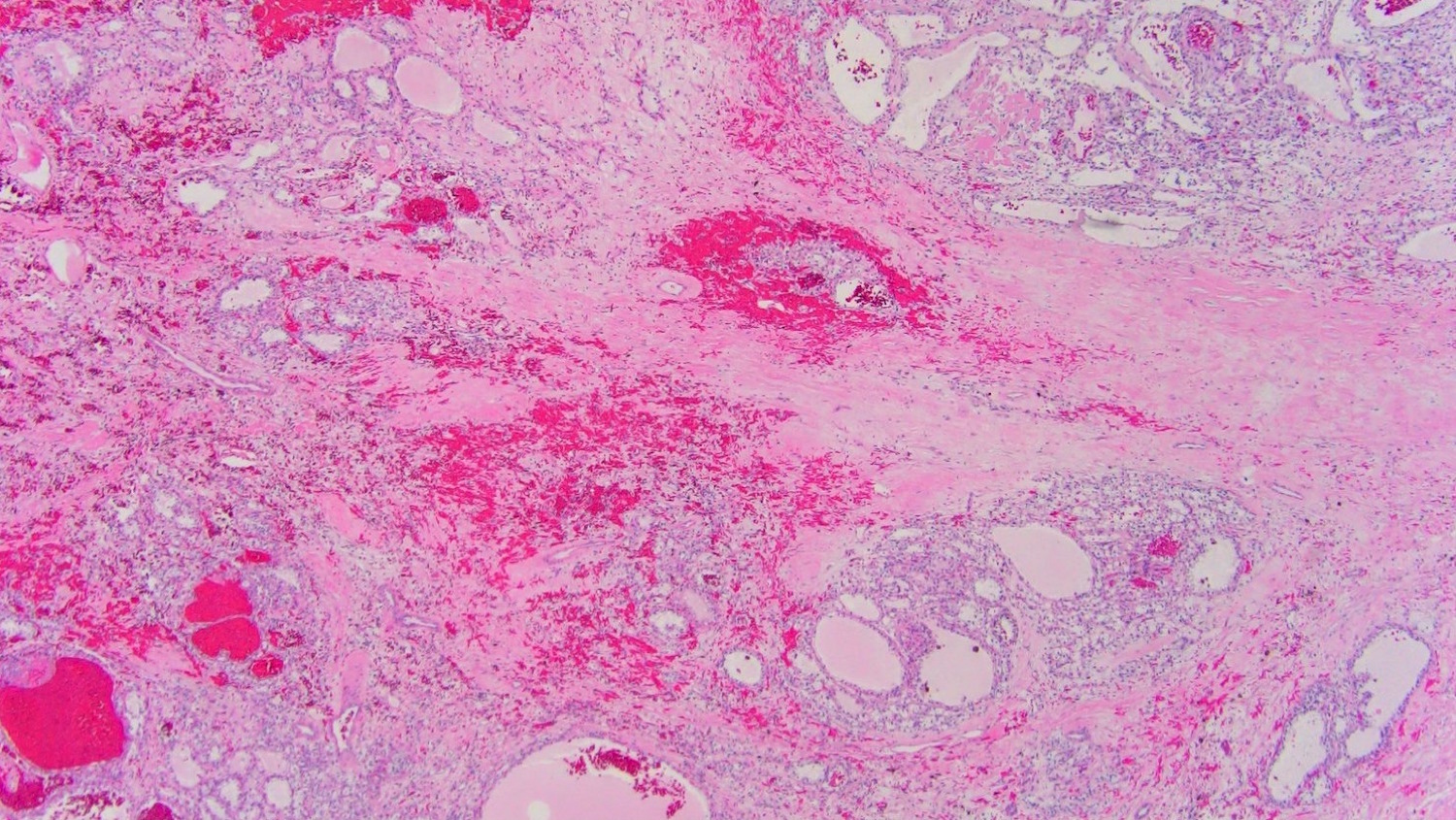
- Clear cell tumor with multinodular appearance at low power due to transecting thick fibrous or fibromuscular bands
- Variable architecture combining solid, alveolar, nested patterns with occasional cystic and tubulopapillary features
- Cells with predominantly clear voluminous cytoplasm, prominent cell membranes and low nucleolar grade (WHO / ISUP grade 1 or 2)
- No necrosis, lymphovascular invasion or heavy inflammatory infiltrate (Mod Pathol 2015;28:845, Histopathology 2019;74:31)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
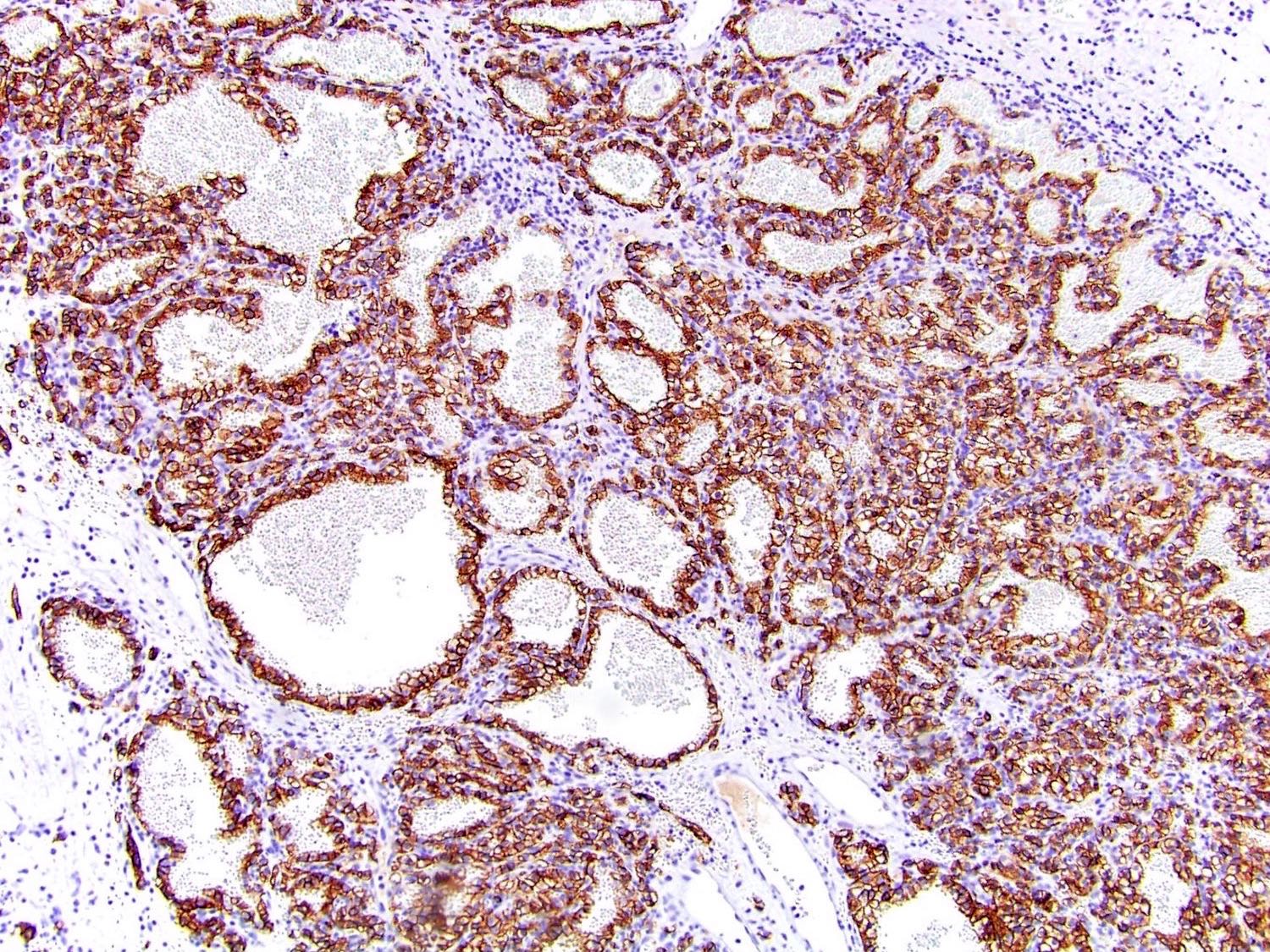
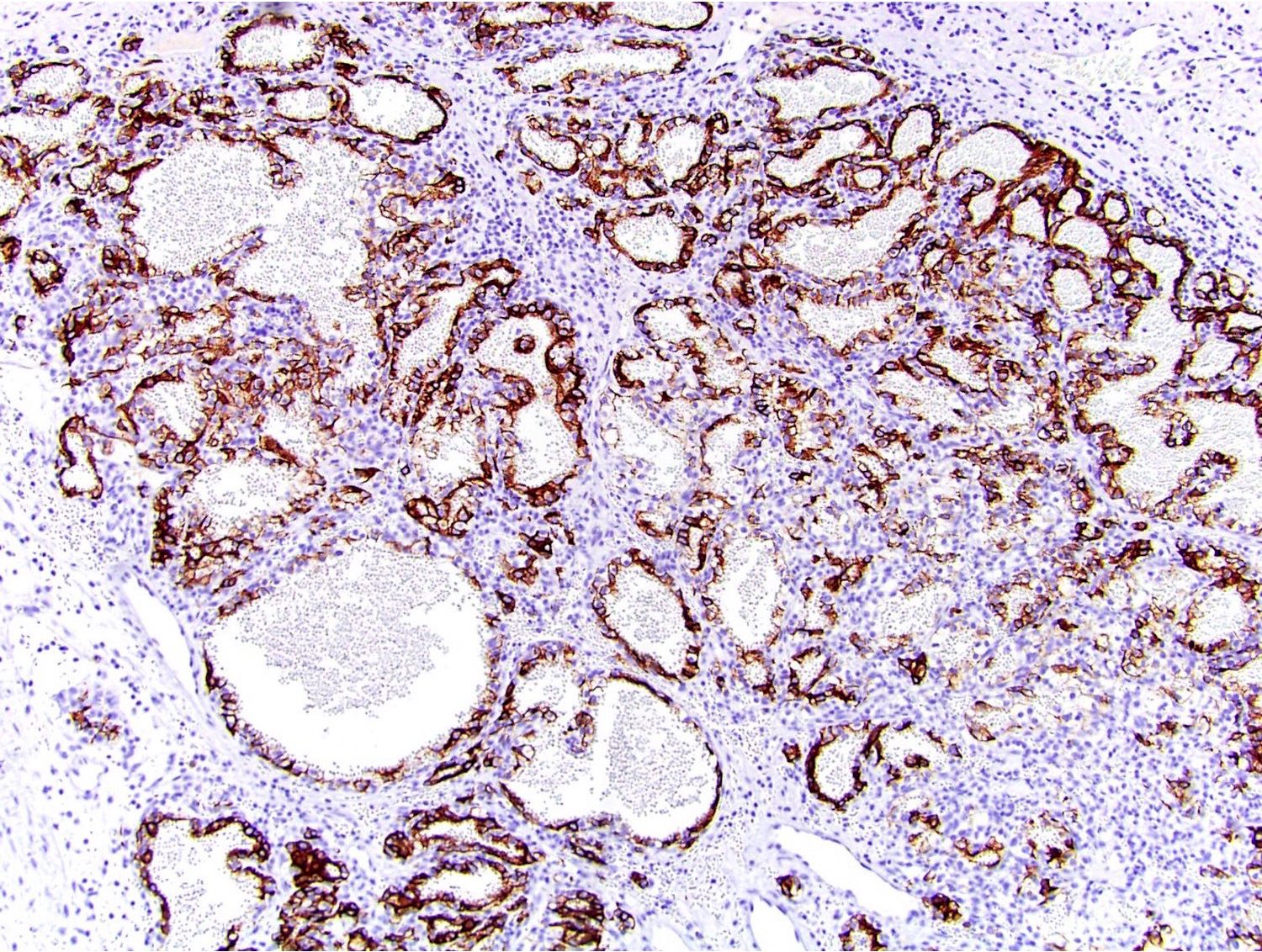
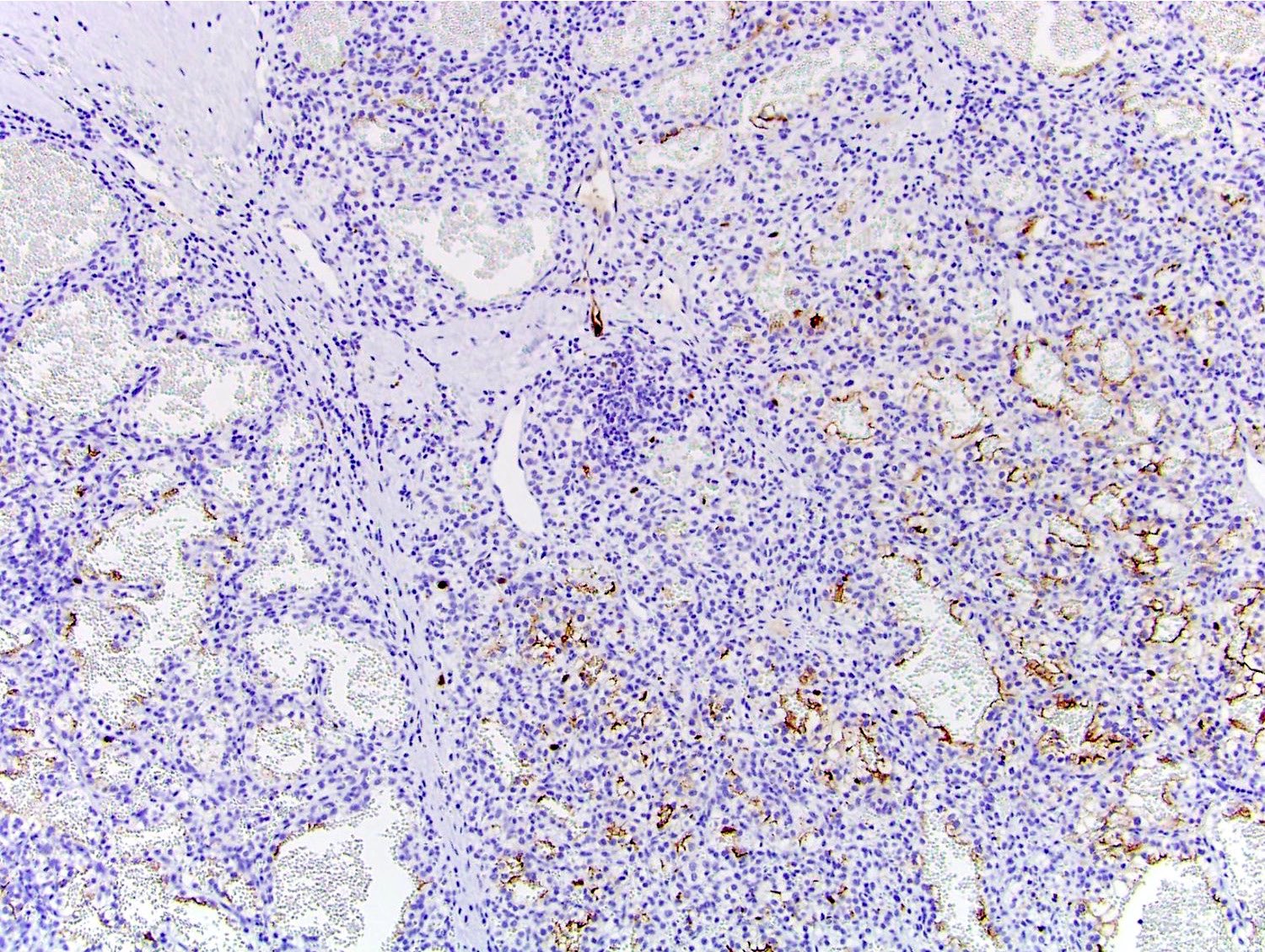
- CAIX (diffuse membranous, box shape pattern) like in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- CK7 (strong in majority of cells)
- CD10 (focal weak to moderate)
- SDHB (retained but weak due to cell clearing)
- HIF1α (Virchows Arch 2016;469:81, Pathology 2019;51:453)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- TCEB1 mutations (NGS): Tyr79 (> 80%), Ala100, Ala 106 and Ser23
- Copy number analysis: loss of heterozygosity of chromosome 8, copy neutral loss of heterozygosity
- RNA expression analysis: mRNA downregulation of POLR2E, POLR2C, CDK7, TCEA1 and TCEB2 (Mod Pathol 2015;28:845, Nat Genet 2013;45:860, Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1135)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Left kidney, mass, partial nephrectomy:
- Renal cell carcinoma with clear cell features, unclassified (see synoptic report and comment)
- Comment: The carcinoma is morphologically consistent with clear cell renal cell carcinoma but contains prominent fibromuscular stroma. The immunohistochemical stains demonstrate that the neoplastic cells are positive for CAIX, variably positive for CK7 and CD10 but negative for TFE3. The tumor histology and variable CK7 positivity raise the possibility of a recently described TCEB1 mutated renal cell carcinoma. Molecular characterization can be attempted to confirm the histologic impression.
Differential diagnosis
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma with prominent stromal component:
- CK7 usually negative or only focally positive
- Loss of heterozygosity at 3p or VHL alteration (biallelic loss)
- Clear cell (tubulo)papillary renal cell carcinoma:
- Renal cell carcinoma with (angio)leiomyomatous stroma:
- Provisional / emerging entity in IARC: WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs (Medicine), 4th Edition, 2016
- Prominent vascular and smooth muscle stroma, branching tubules / papillary tufts of clear cells
- Positive for CAIX, HMWCK, CK7 and CD10
- No TCEB1 abnormalities or monosomy 8; absence of VHL/3p alterations, no trisomy 7/17
- Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) associated renal cell carcinoma:
- Often multifocal, bilateral and associated with multiple cysts and angiomyolipomas
- TSC gene related alterations
- Family history
- MiT family translocation renal cell carcinoma:
- Usually with papillary architecture and higher nuclear grade
- Positive for TFE3
- Negative for CK7 / CAIX
- Histopathology 2019;74:31, Pathology 2019;51:453, Mod Pathol 2017;30:1603, Pathology 2017;49:10, Hum Pathol 2017;66:152, Mod Pathol 2015;28:845, Histopathology 2019;74:60
Additional references
Board review style question #1
- Which is true about TCEB1 mutated renal cell carcinoma?
- Definitive diagnosis is based on documenting either TCEB1 mutation or absence of chromosome 8 (monosomy 8)
- Morphologically identical to clear cell renal cell carcinoma with prominent fibromuscular stroma
- Multiple reports indicate relatively high incidence of this tumor type
- TCEB1 and TFEB genes belong to the same family of transcription factors
- Typically pursue aggressive course
Board review style answer #1
B. TCEB1 mutated renal cell carcinoma is a distinct genomic entity of RCC with clear cell phenotype, mutations of TCEB1 gene with concurrent loss of heterozygosity at chromosome 8. Histologically these tumors are similar to conventional clear cell renal cell carcinoma but contain thick traversing fibromuscular bands transecting the tumor parenchyma and imparting multinodular appearance. Based on peculiar stromal prominence, these tumors were included into the 2016 World Health Organization Classification as a provisional entity of RCCs with (angio)leiomyomatous stroma. Grossly tumors are unifocal, small, well circumscribed and often encapsulated with tan nodular cut surface. On microscopy, neoplastic cells have voluminous clear cytoplasm, low grade nuclei and could be arranged in several architectural patterns in various combinations: solid alveolar, nested, cystic or tubulopapillary. Immunostaining shows a characteristic pattern: diffuse membranous box-like expression of CAIX, diffuse HIF1α, strong CK7 in the majority but not 100% of tumors cells, patchy and weak CD10, negative HMWCK, GATA3 and TFE3. Virtually all reported cases are incidental low stage indolent tumors with no recurrences or metastases.
Comment Here
Reference: TCEB1 mutated renal cell carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: TCEB1 mutated renal cell carcinoma
Board review style question #2
- Which immunohistochemical results will raise concern of TCEB1 mutated renal cell carcinoma in 45 year old patient with 3 cm encapsulated tumor having prominent stroma and clear cell morphology, shown here?
- HMWCK-, CD10-, TFE3+, RCC+
- HMWCK-, CK7-, CAIX+, CD10+
- HMWCK-, CK7+, CAIX+, CD10-
- HMWCK+, CK7+, CAIX+, GATA3+
Board review style answer #2
C. The microscopic image shows a clear cell tumor with solid alveolar and microcystic areas with abundant fibromuscular stroma separating tumor into nodules. These features are often seen in conventional clear cell renal cell carcinoma but also raise a suspicion of rare indolent tumor entity of renal cell carcinoma with (angio)leiomyomatous stroma including TCEB1 mutated RCC. From the above panels, only answer B is consistent with TCEB1 mutated RCC; but definitive diagnosis requires molecular studies confirming mutation of TCEB1 gene and loss of heterozygosity at 8q21/monosomy 8.
Comment Here
Reference: TCEB1 mutated renal cell carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: TCEB1 mutated renal cell carcinoma