Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Cheng L, Tretiakova M. Solitary fibrous tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytumorsolitary.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Fibroblastic mesenchymal tumor with haphazard spindle cells, staghorn vasculature and NAB2::STAT6 gene fusion
Essential features
- Fibroblastic tumor characterized by patternless architecture and staghorn vasculature
- STAT6 expression by immunohistochemistry; NAB2::STAT6 gene fusion
- About 16% of renal solitary fibrous tumors (SFTs) show histological features that may indicate aggressive behavior: hypercellularity, cytological atypia, increased mitosis and necrosis
Terminology
- Hemangiopericytoma (not recommended)
ICD coding
- ICD-O
- ICD-10: D49.519 - neoplasm of unspecified behavior of unspecified kidney
- ICD-11
- 2F7C & XH7E62 - neoplasms of uncertain behavior of connective or other soft tissue & solitary fibrous tumor, NOS
- 2B5Y & XH1HP3 - other specified malignant mesenchymal neoplasms & solitary fibrous tumor, malignant
Epidemiology
- M:F = 1:1.8 (Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:34)
- Mean age: 49 (range: 3 - 85) (Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:34)
Sites
- Any anatomic site; majority are pleural or abdominopelvic (Mod Pathol 2012;25:1298, Ann Surg Oncol 2017;24:3865)
- Rare in kidney; ~105 cases reported (Int J Surg Case Rep 2019;62:112)
- Metachronous SFTs of kidney and synchronous pleurorenal SFTs can happen (Urol Case Rep 2015;4:45, Minerva Chir 2009;64:669)
Pathophysiology
- Intrachromosomal inversion of chromosome 12q results in NAB2::STAT6 fusion (Nat Genet 2013;45:131)
- NAB2 is a transcriptional repressor of early growth response 1 (EGR1), while NAB2::STAT6 is a transcriptional activator of ERG1 (Nat Genet 2013;45:180)
- Overactivation of EGR1 leads to increased expression of its target genes, such as IGF2, FGF2, PDGFD, FGFR1, NTRK1, etc. (Nat Genet 2013;45:180)
Clinical features
- Most asymptomatic, can present with hematuria and flank pain (Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:34)
- Hypoglycemia (Doege-Potter syndrome): in < 5% of patients, due to excess production of IGF2 (Arch Ital Urol Androl 2020;92:392)
Diagnosis
- Histological examination
- NAB2::STAT6 gene fusion by immunohistochemical or molecular studies
Laboratory
- Rare cases showed hypoglycemia and hypokalemia (Asian J Surg 2023;46:1260)
Radiology description
- Ultrasound: heterogeneous, mainly hyperechoic (Cureus 2016;8:e490)
- Computed tomography (CT): heterogeneous enhanced lesion (Mol Clin Oncol 2020;13:39)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): highly variable, may show isointense in T1 and hyperintense in T2 (Int J Surg Case Rep 2019;62:112)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Histological features cannot precisely predict aggressive behavior; only 36% of histologically malignant kidney SFT patients presented with recurrent / metastatic disease (Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:34)
- Multivariable risk stratification model has shown to more accurately predict prognosis
- Variables in risk stratification model of SFTs from all anatomic sites are: age ≥ 55, tumor size ≥ 10 cm, mitotic count ≥ 4/10 high power fields, tumor necrosis ≥ 10% (Mod Pathol 2017;30:1433)
Case reports
- 39 year old woman with left kidney mass (Cureus 2023;15:e46475)
- 52 year old woman with right kidney tumor (Mol Clin Oncol 2020;13:39)
- 55 year old man with left kidney mass (Int J Surg Case Rep 2019;62:112)
- 66 year old woman with new onset hematuria (Cureus 2016;8:e490)
- 83 year old man with kidney mass and Doege-Potter syndrome (Arch Ital Urol Androl 2020;92:392)
Treatment
- Complete surgical resection
- Ablation or systemic chemotherapy for unresectable tumors
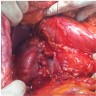
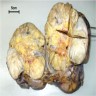
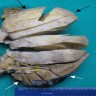
Gross description
- Average tumor size of benign kidney SFTs: 8 cm (Int J Surg Pathol 2016;24:281)
- Firm, rubbery, usually well circumscribed
- White-tan or yellow-tan cut surface
- Myxoid changes, hemorrhage and necrosis can be seen
Gross images
Frozen section description
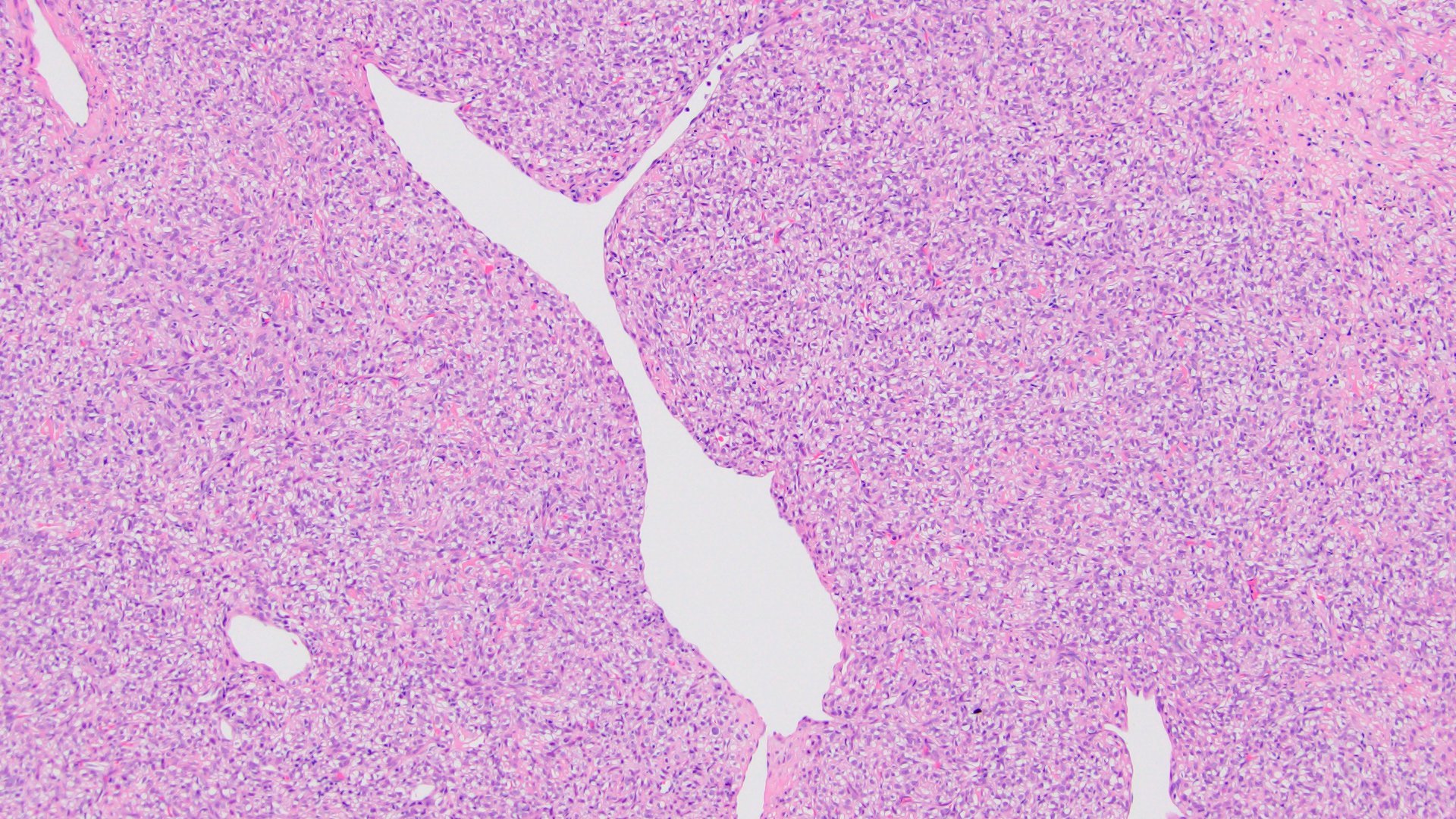
- Spindle cell neoplasm with patternless architecture and staghorn vessels
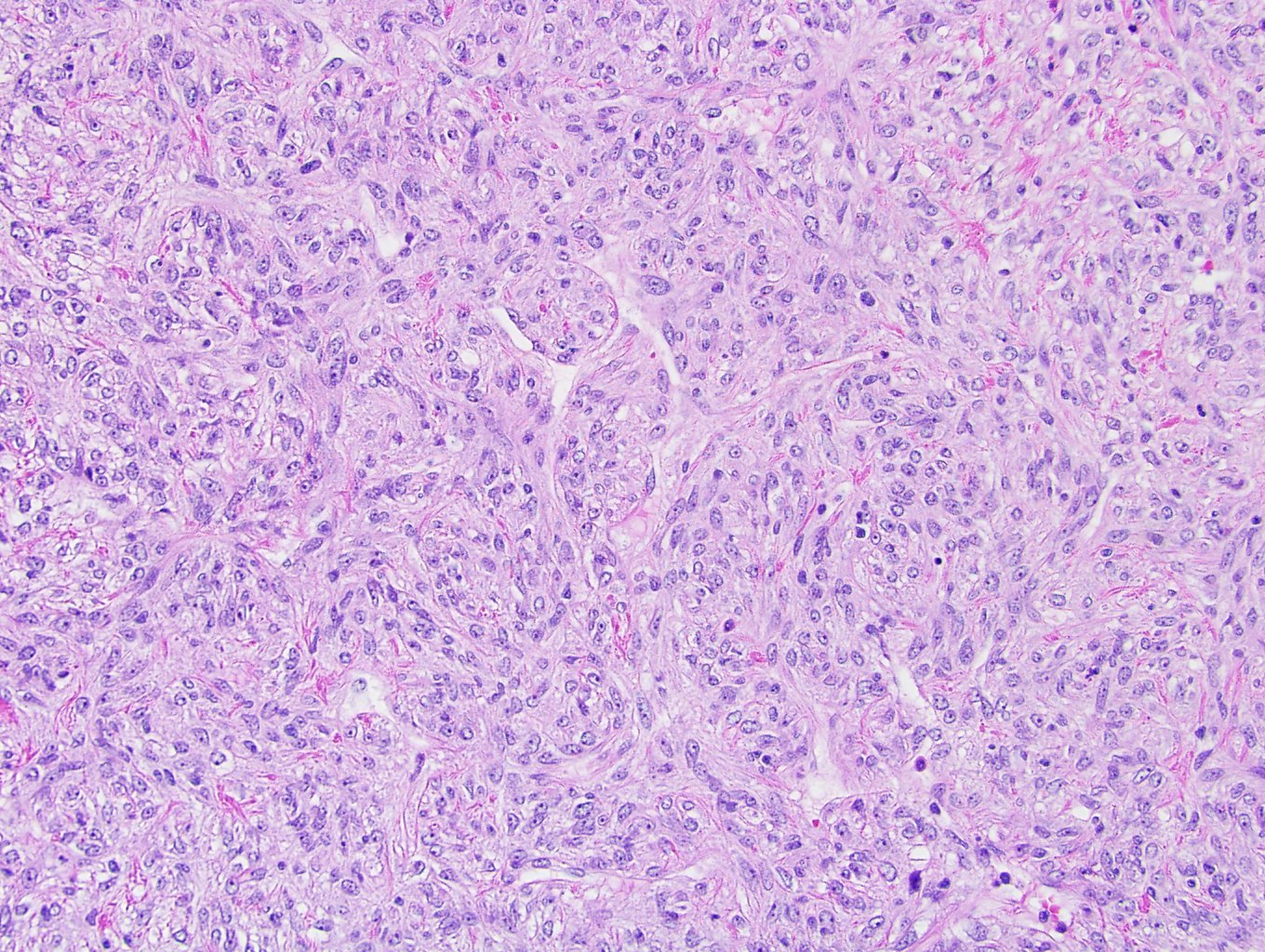
Microscopic (histologic) description
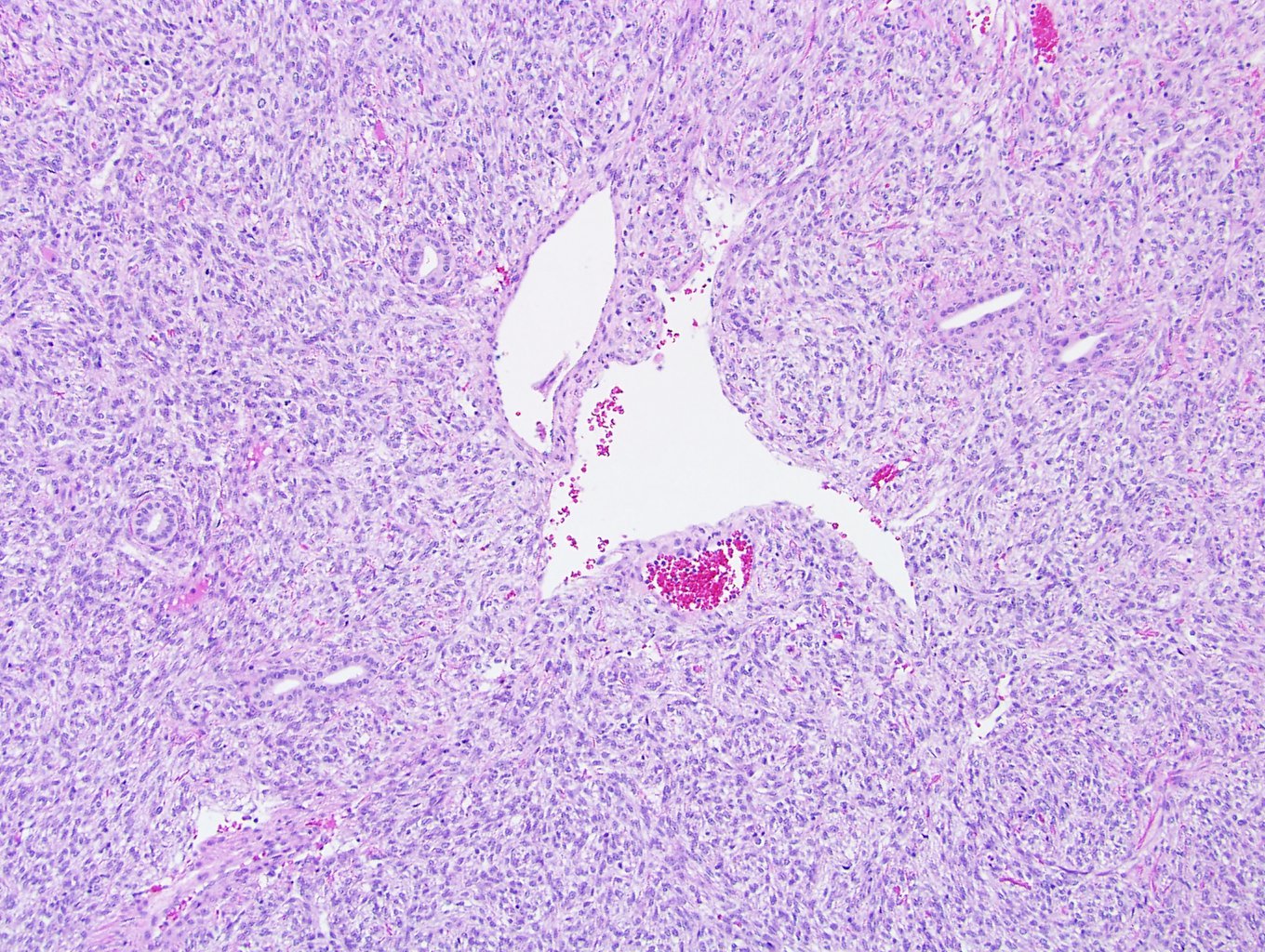
- Haphazard arrangement of spindle to oval shaped cells (patternless architecture)
- Both hypo and hypercellular areas
- Staghorn branching vasculature
- Intertwined collagen bands
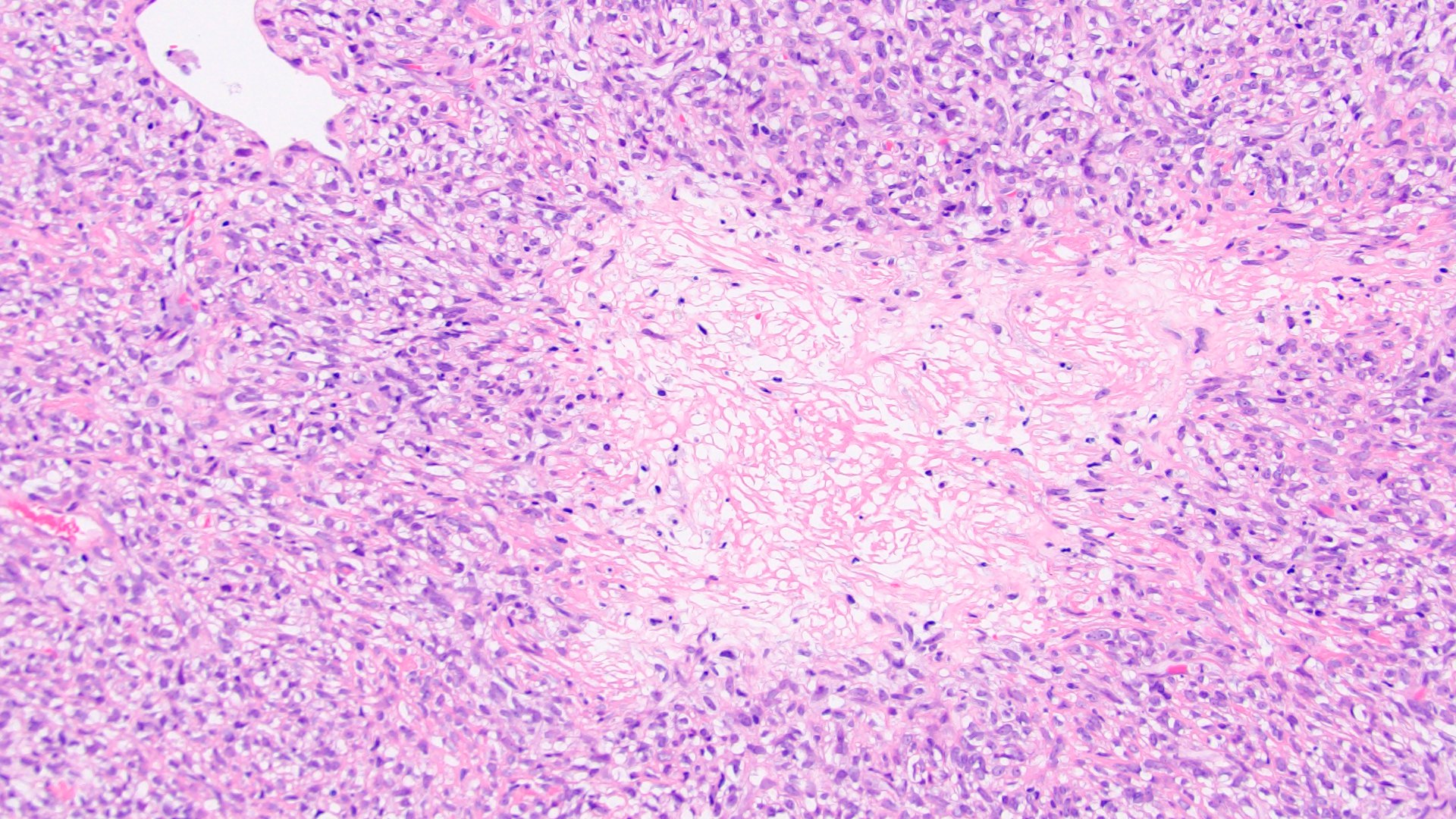
- Myxoid areas and pseudocystic areas can be present (J Clin Pathol 2017;70:508)
- Features with increased risk for malignancy: high cellularity, cytological atypia, increased mitosis, necrosis (Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:640, J Clin Pathol 2017;70:508)
- Round cell histological subtype (Genitourinary Pathology Society: Case of the Week [Accessed 25 October 2024])
- Fat forming histological subtype (In Vivo 2018;32:649)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
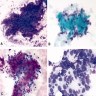
- SFTs with low risk of aggressive behavior: low to moderate cellularity of clusters and single cells, spindle, oval or stellate cells with monotonous nuclei, wispy cytoplasm, collagenous intercellular stroma (Cancer Cytopathol 2018;126:36)
- SFTs with high risk of aggressive behavior: hypercellular, crowded clusters, focal nuclear pleomorphism, mitoses, necrosis (Cancer Cytopathol 2010;118:83)
Cytology images
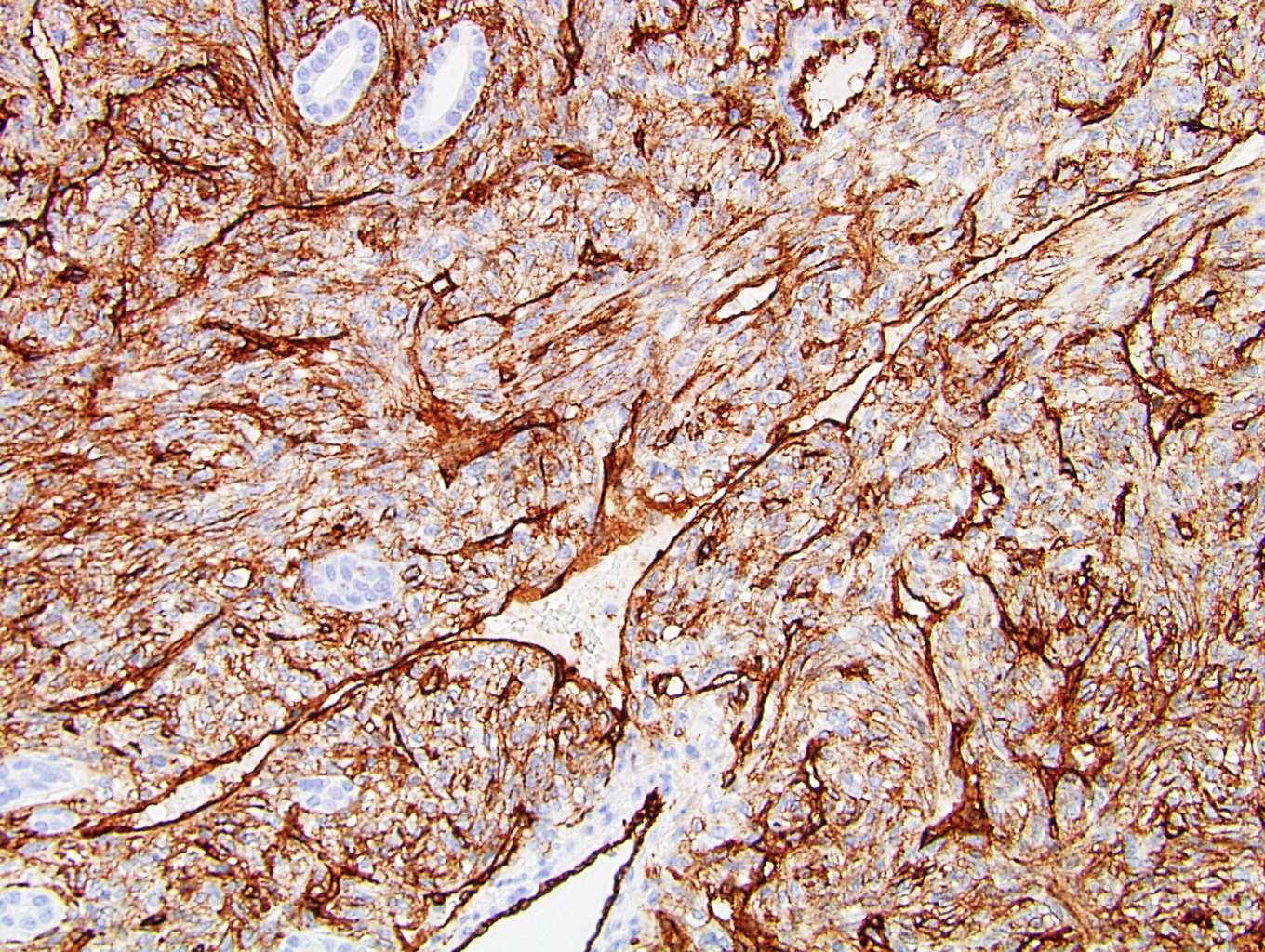
Positive stains
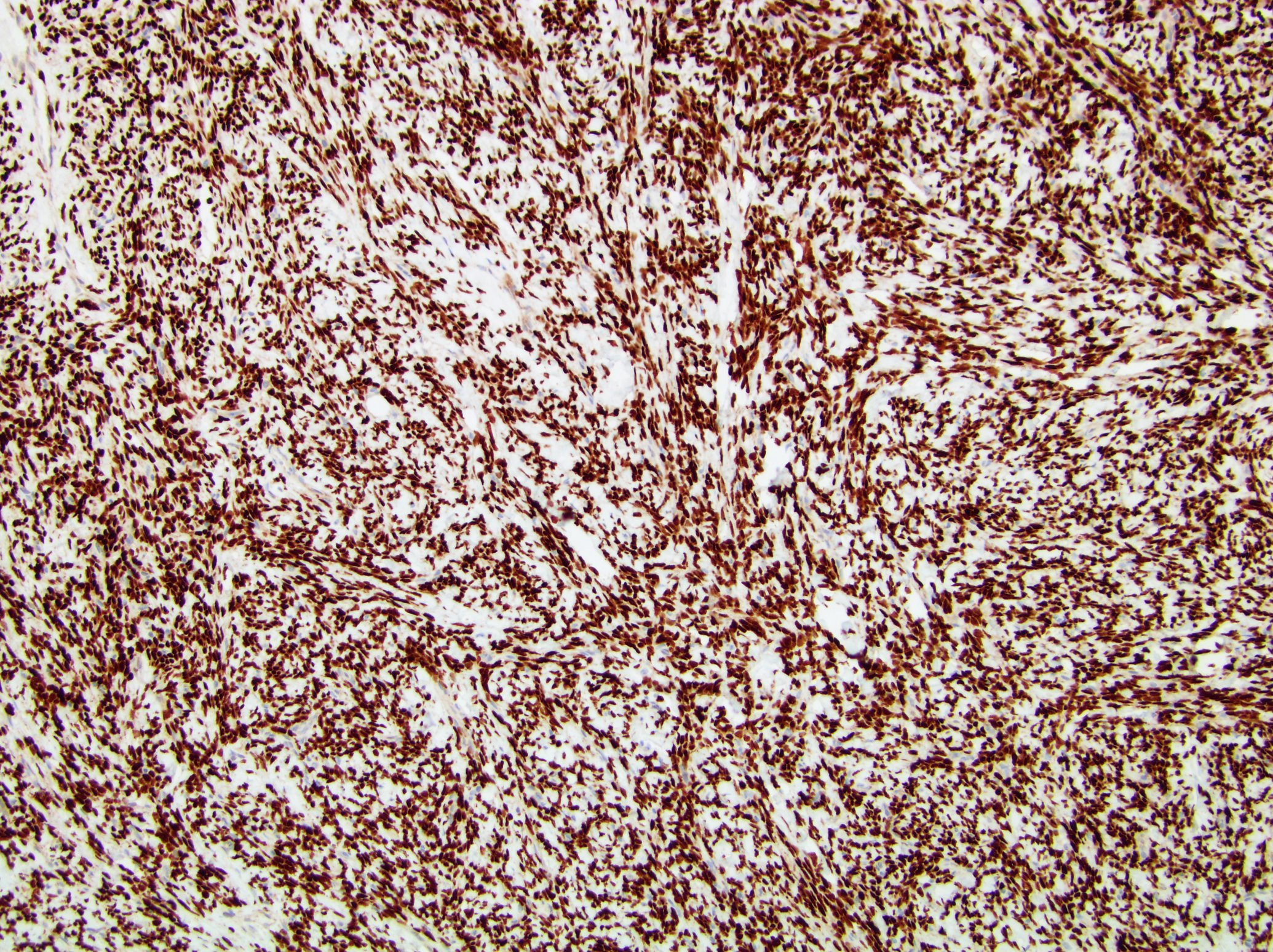
- STAT6: 99 - 100% in benign SFTs of soft tissue, 93% in retroperitoneal SFTs (Iran J Pathol 2016;11:195, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019;27:195)
- CD34: 96.1% in benign SFTs of kidney, 76.5% in malignant SFTs (Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:34)
- BCL2: 68% in benign SFTs of kidney, 53.8% in malignant SFTs (Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:34)
- CD99: 83.3% in benign SFTs of kidney, 75% in malignant SFTs (Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:34)
- Vimentin: 98.3% in benign SFTs of kidney, 100% in malignant SFTs (Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:34)
Negative stains
- PAX8: positive in 43% of cases (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019;27:195)
- S100: positive in 1.8% of cases (Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:34)
- MDM2 (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019;27:195)
- Pancytokeratin (Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:34)
- CD31 (Int J Surg Pathol 2015;23:34)
Electron microscopy description
- Cells with fibroblastic features, well developed rough endoplasmic reticulum, surrounded with collagen fibers (Med Mol Morphol 2009;42:239)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Multiple NAB2::STAT6 gene fusion variants detected by whole exome sequencing (Nat Genet 2013;45:131, Nat Genet 2013;45:180)
- Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) based tests are more sensitive than STAT6 FISH due to close proximity of the 2 genes (J Clin Pathol 2017;70:508)
- STAT6 FISH is more sensitive than STAT6 immunostain (J Clin Pathol 2017;70:508)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Left kidney, nephrectomy:
- Solitary fibrous tumor, 3.5 cm, margins of resection free of involvement (see comment)
- Comment: Clinically, this patient presented with hematuria and flank pain. CT showed a left renal mass. No other lesions or history of any malignancies are identified. The histological sections of the renal mass show both hypo and hypercellular areas composed of monotonous spindle cells in haphazard pattern with staghorn vascular network. No mitosis or necrosis is seen. Immunohistochemistry studies show that the spindle cells are positive for STAT6, CD34, BCL2 and vimentin and negative for PAX8, CK8/18, MDM2 and S100. The overall findings favor a solitary fibrous tumor, likely renal primary. According to the modified risk stratification criteria, this tumor is classified as low risk. Clinical correlation is recommended (Mod Pathol 2017;30:1433).
Differential diagnosis
- Angiomyolipoma / PEComa:
- Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma:
- High grade cytological atypia
- Positive for PAX8 and cytokeratin
- Negative for STAT6
- Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor (MEST):
- Most are benign, well circumscribed, with solid and cystic areas
- Stromal and epithelial components showing diverse morphology and minimal cytological atypia
- Stroma positive for ER, PR and smooth muscle markers
- Epithelium positive for cytokeratin and PAX8
- Renomedullary interstitial cell tumor (RMICT):
- Well differentiated liposarcoma (WDL):
- Contains adipose tissue and mimics fat forming SFTs but usually no staghorn vessels
- Positive for MDM2 and CDK4
- Dedifferentiated liposarcoma may be positive for STAT6, when amplification of CDK4 and MDM2 genes involves contiguous STAT6 gene (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019;27:195)
- Synovial sarcoma:
- Schwannoma:
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT):
- Myofibroblastic proliferation with mixed inflammation
- Most show spindle cells with haphazard arrangement but no staghorn vessels
- Positive for vimentin, SMA and ~60% are positive for ALK1 (cytoplasmic staining in spindle cells, nuclear membrane or perinuclear staining in epithelioid variant)
- Negative for STAT6 and CD34
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following are the most commonly seen histological features of solitary fibrous tumor of kidney?
- Admixture of adipose tissue, smooth muscle and thick wall vessels
- Haphazard arrangement of spindle cells and staghorn vasculatures
- Spindle cells with cytoplasmic microvacuoles and complex capillary network
- Storiform fibrosis
- Sustentacular cells wrap around chief cells and form zellballen pattern
Board review style answer #1
B. Haphazard arrangement of spindle cells and staghorn vasculatures are seen in solitary fibrous tumors.
Answer A is incorrect because these are features of angiomyolipoma / PEComa.
Answer C is incorrect because these are features of renal hemangioblastoma.
Answer D is incorrect because storiform fibrosis is commonly seen in IgG4 related diseases.
Answer E is incorrect because these are features of paraganglioma / pheochromocytoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Solitary fibrous tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Solitary fibrous tumor
Board review style question #2
Which immunostain is usually negative in solitary fibrous tumor of kidney?
- BCL2
- CD34
- CD99
- MDM2
- STAT6
Board review style answer #2
D. MDM2 is usually negative in solitary fibrous tumors. It is commonly positive in well differentiated liposarcoma.
Answers A, B, C and E are incorrect because these markers are positive in most solitary fibrous tumors.
Comment Here
Reference: Solitary fibrous tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Solitary fibrous tumor