Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Ziadie MS. Nephroblastomatosis / nephrogenic rests. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytumornephroblastomatosis.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Nephrogenic rests: persistent foci of embryonal cells seen after the period of normal nephrogenesis
- Nephroblastomatosis: multifocal or diffuse nephrogenic rests
- May be intralobar or perilobar
Epidemiology
- 1% of neonatal kidneys; florid cases associated with congenital anomalies and hypertension
- Intralobar rests have an increased rate of progression to Wilms tumor, are more commonly associated with WT1 mutations, Denys-Drash syndrome and WAGR syndrome
- Perilobar rests are seen in sporadic tumors and are associated with genetic / epigenetic dysregulation at 11p15 (Clin Cancer Res 2008;14:7635), idiopathic hemihypertrophy and Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
Clinical features
- Precursor lesions of Wilms tumor, seen in 30% - 44% of kidneys resected for Wilms tumor (WT)
Case reports
- 2 week old 'female' infant with nephrotic syndrome and renal failure (Case of the Week #338)
- Male newborn death with bilateral nephroblastomatosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1989;113:729)
- Newborn with lumbosacral ectopic rest (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1389)
- Siblings with universal nephroblastomatosis with nephromegaly (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2009;12:47)
Treatment
- Conservative
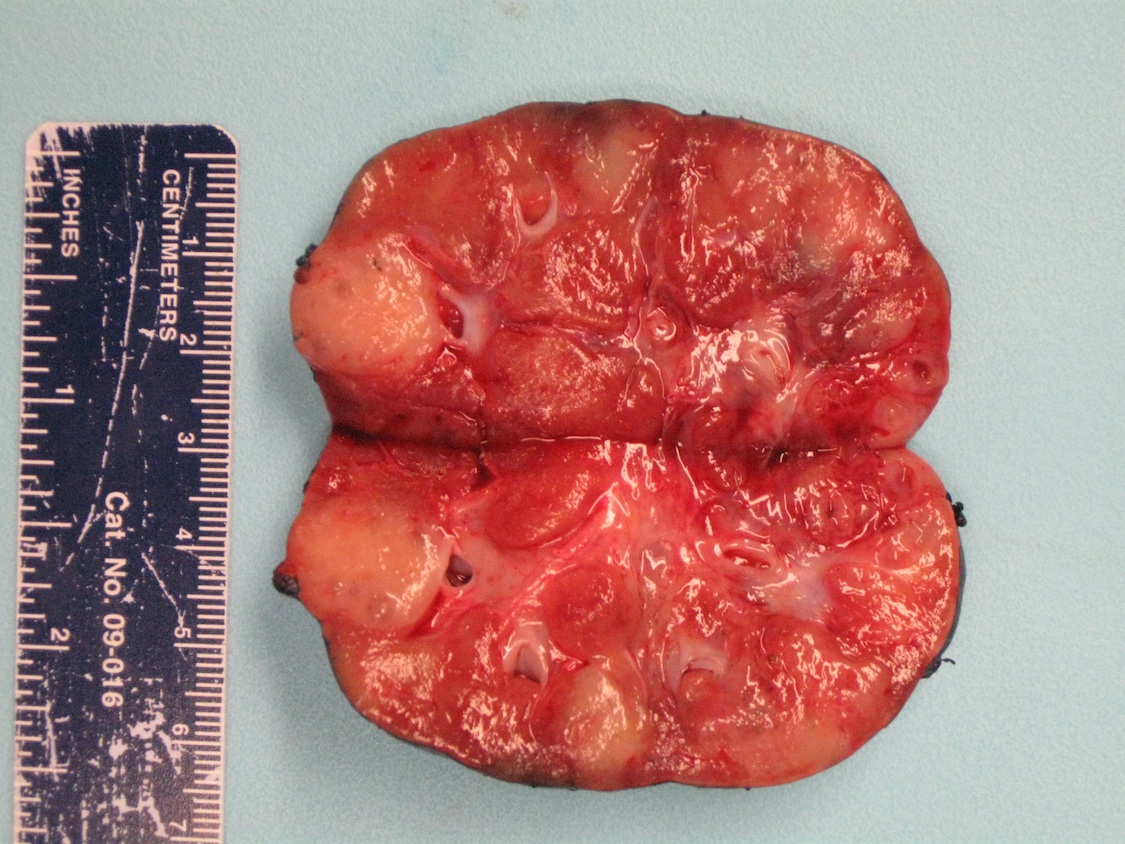
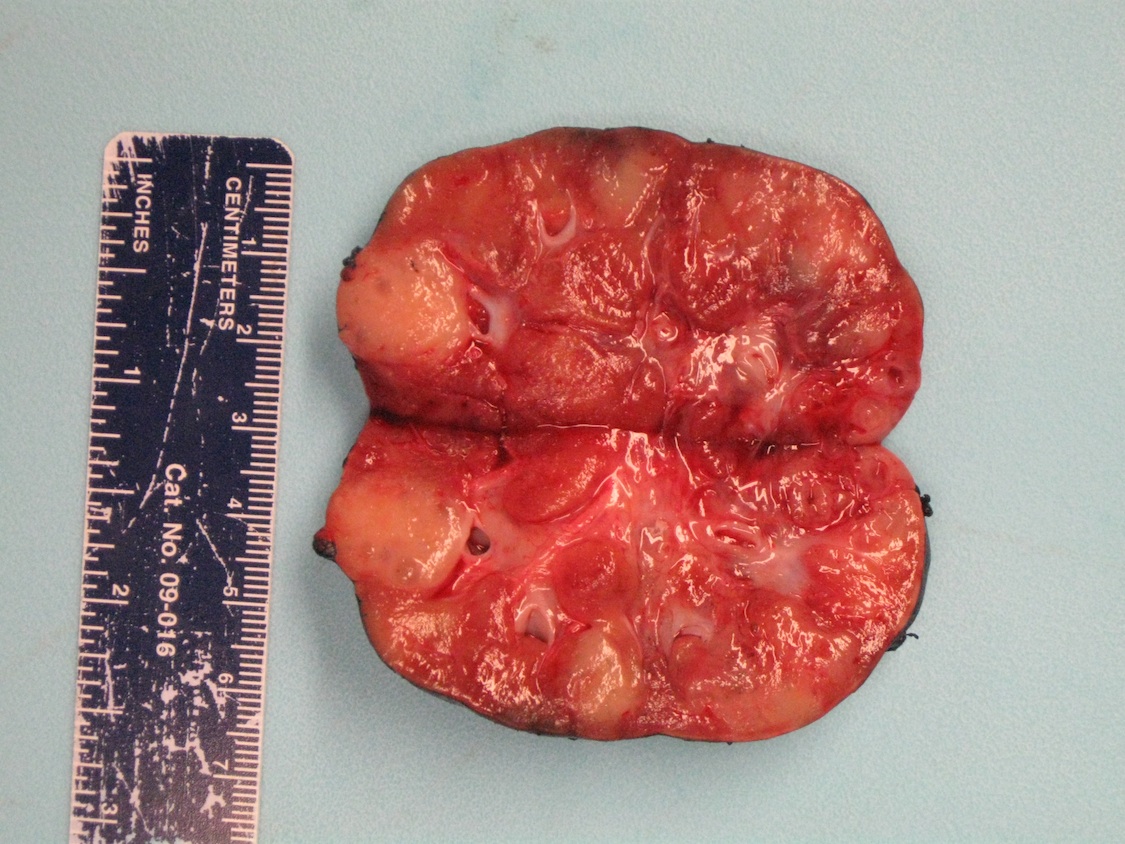
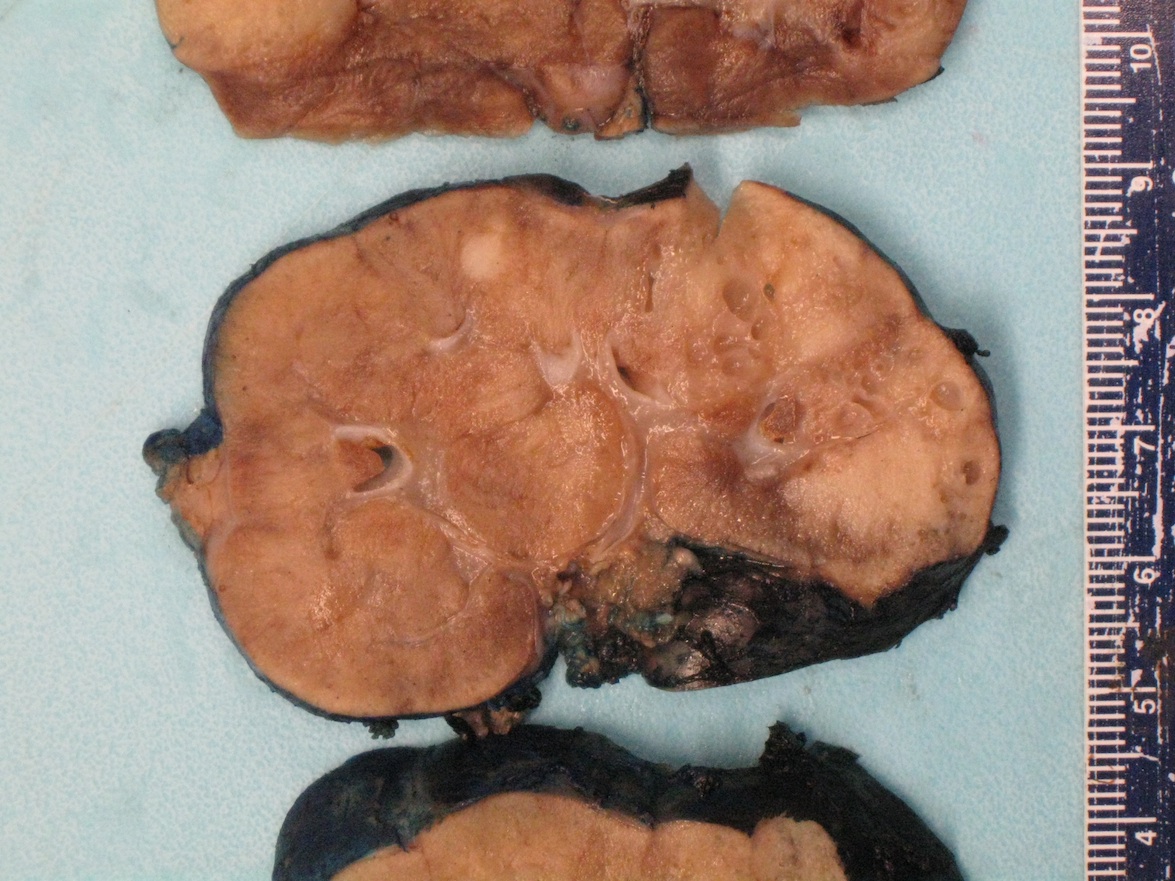
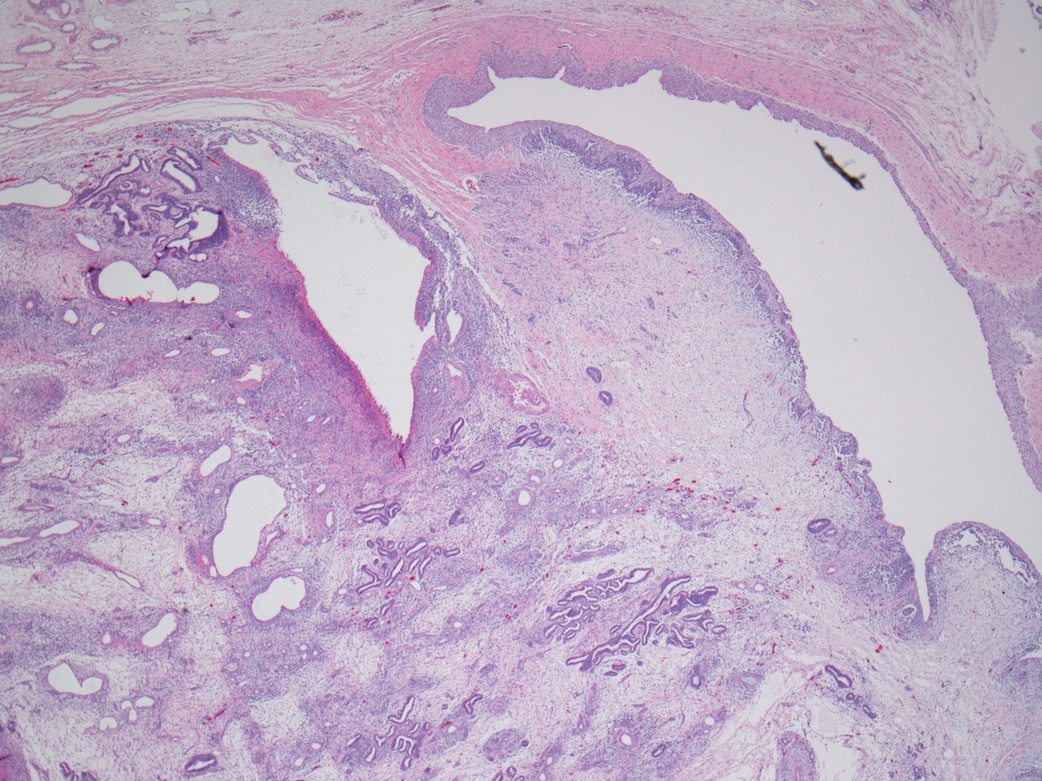
Gross description
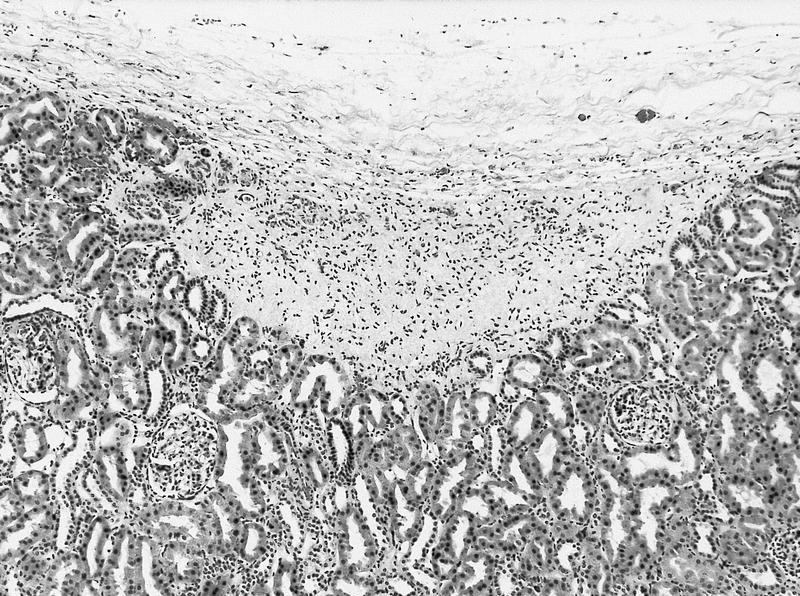
- May be inapparent on gross examination or appear as nodules / foci of capsular thickening / scar beneath the capsule or in the deep cortex / medulla
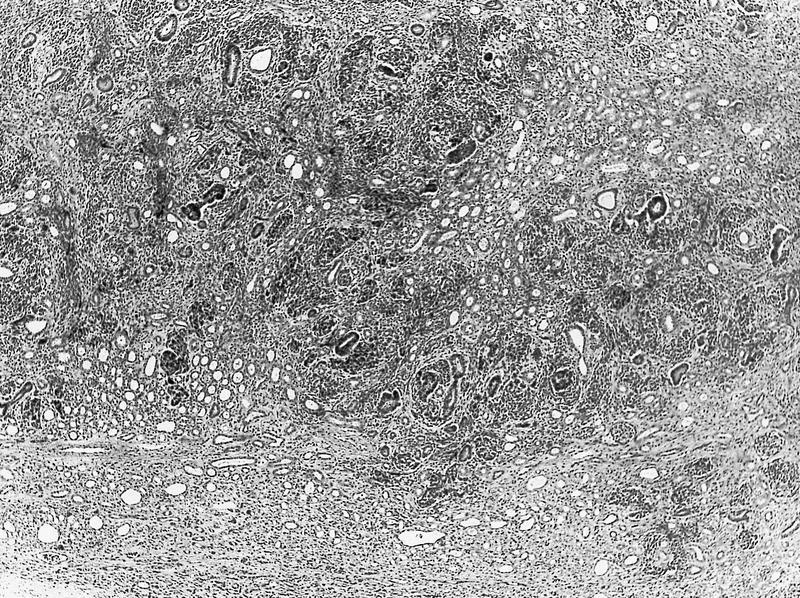
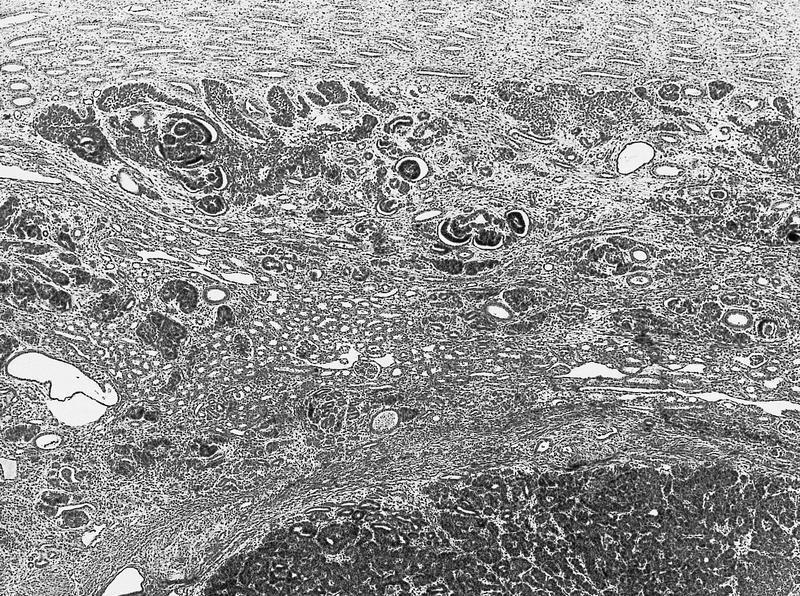
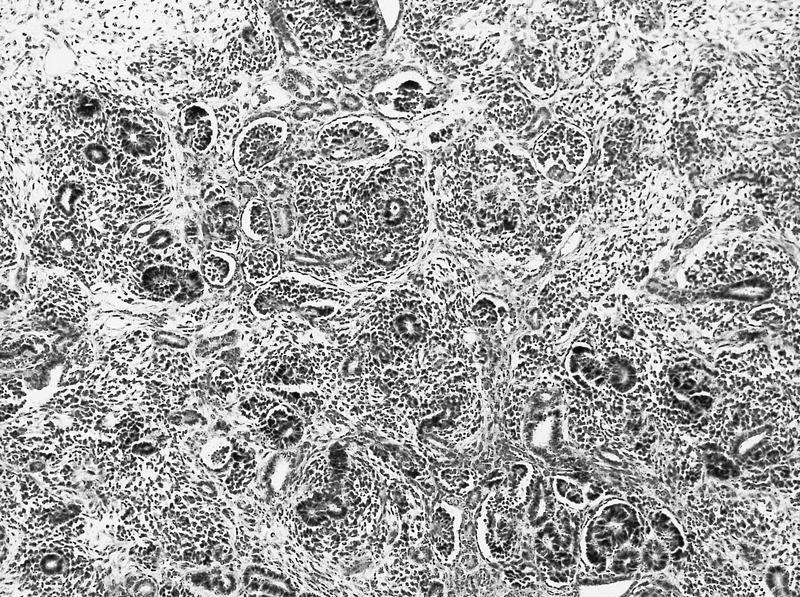
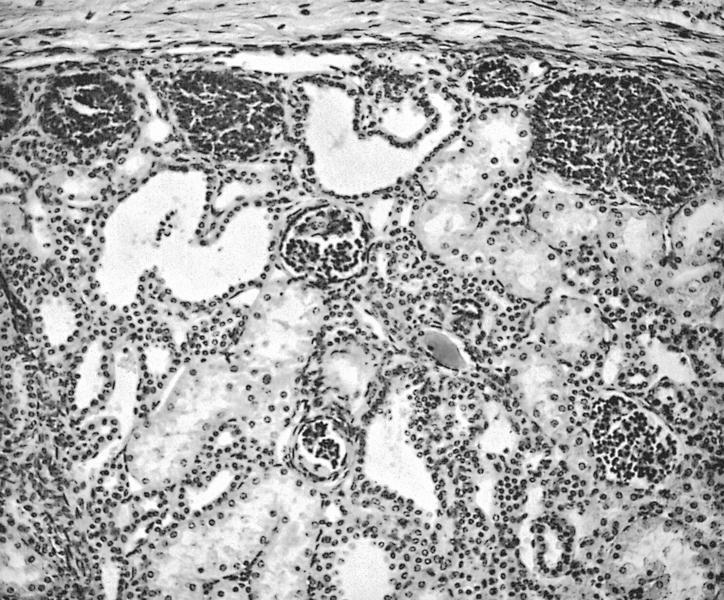
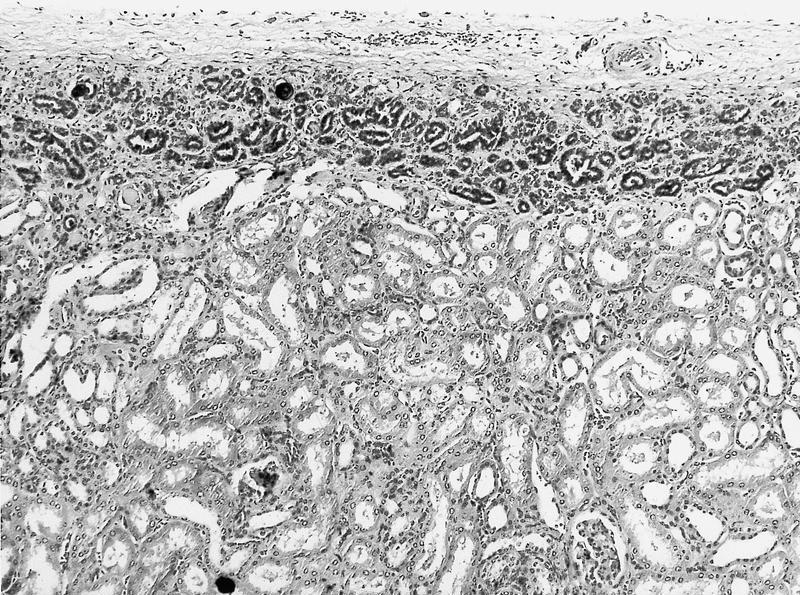
Microscopic (histologic) description
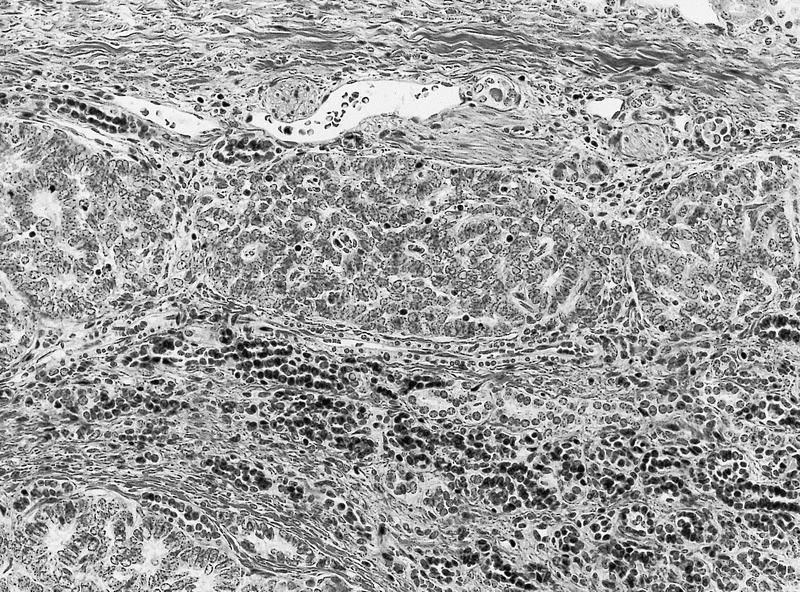
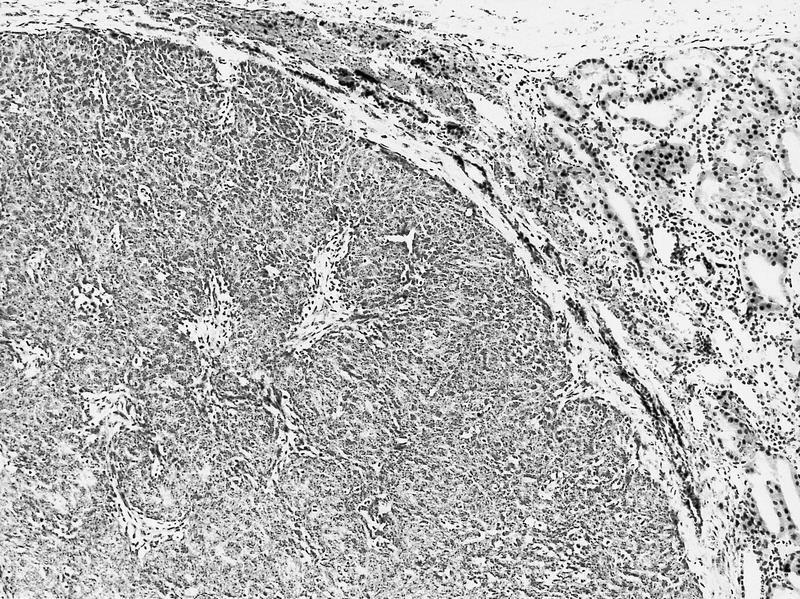
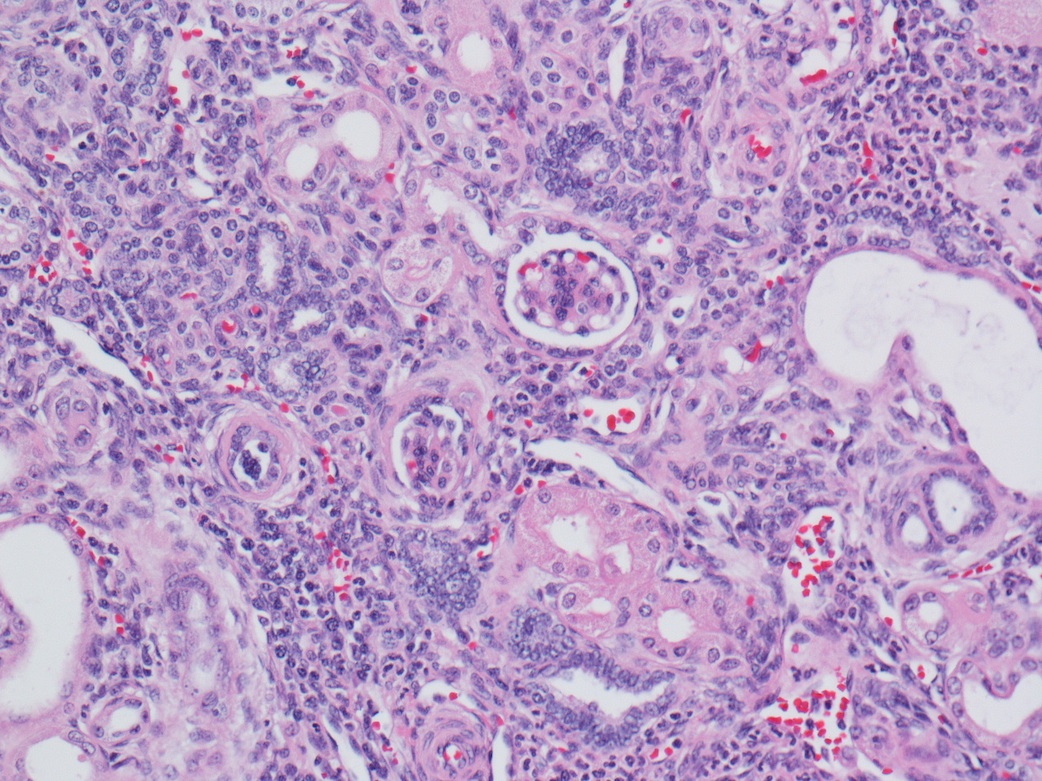
- Tightly packed nests or diffuse sheets of primitive but nonanaplastic blastemal / primitive epithelial cells with scanty stroma
- No cartilage or primitive mesenchyme
- May have a sclerosing or hyperplastic pattern
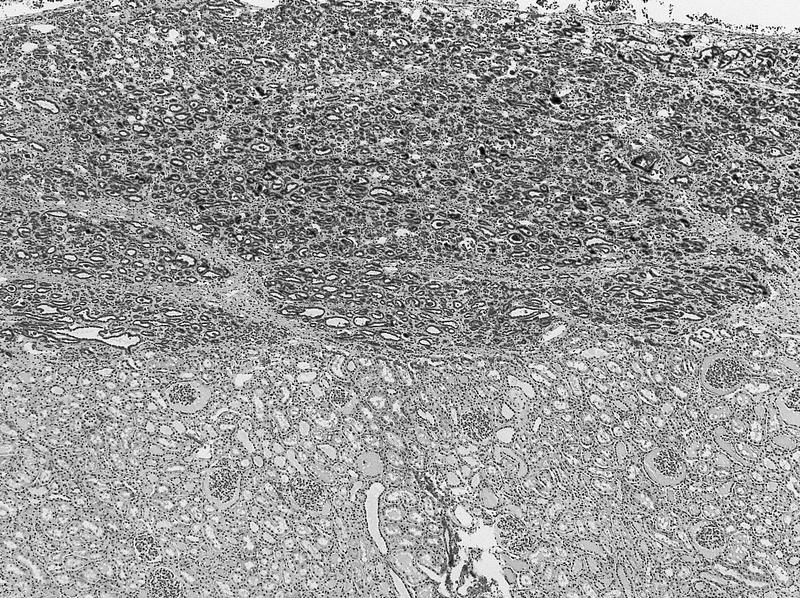
- Intralobar: randomly distributed throughout cortex and medulla with irregular margins, more stroma than blastema or tubules
- Perilobar: peripheral with sharply demarcated margins, composed of blastema and tubules with scanty or sclerotic stroma, often solitary
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
Additional references