Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Choy B. Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytumormixedepithelial.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Uncommon neoplasm composed of variable cystic and solid components with morphologically diverse epithelial and stromal elements
- Classified as part of MEST family, with adult cystic nephroma at opposite end of spectrum, by the 2016 World Health Organization (WHO) classification
Essential features
- Typically occur in perimenopausal women, often with long term hormonal treatment
- Solitary, well circumscribed tumors, with variable solid and cystic components
- Versus adult cystic nephroma - predominantly cystic tumors with no solid components
- Stroma and epithelium with wide variety of histologic features
- Versus adult cystic nephroma - noncommunicating epithelial-lined cysts separated by fibrous septae
- Mostly benign but rare malignant transformation of epithelial or stromal component
- Stromal cells typically positive for ER / PR
Terminology
- Renal epithelial and stromal tumor (REST) (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:489)
- Cystic hamartoma of the renal pelvis - term not currently recommended (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:1169, Semin Diagn Pathol 1998;15:2, Mod Pathol 1999;12:417)
- Leiomyomatous renal hamartoma - term not currently recommended (Eur Urol 1988;14:80)
- Adult mesoblastic nephroma - term not currently recommended (J Urol 1973;110:380, Arch Pathol Lab Med 1990;114:533, Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:1029, Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:827)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8959/0 - Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor
Epidemiology
- F:M = 7:1 (Moch: WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs, 4th Edition, 2016)
- Mean age = 52 years
Sites
- Confined to kidney
- Located in renal medulla, with some bulging into renal pelvis, involves both renal cortex and medulla or centered within renal pelvis (Virchows Arch 2004;445:359, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:80, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:489)
Pathophysiology
- Little is known
- Epithelial and stromal components appear to arise from common cell of origin; same pattern of nonrandom inactivation of X chromosome seen in both components (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1114)
Etiology
- Possible role of hormones in pathogenesis (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:958)
Clinical features
- Often incidentally found
- Others present with abdominal / flank pain, hematuria, urinary tract infection (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:958)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis by histologic examination of tissue
Radiology description
- CT (Urology 2008;71:1142, J Comput Assist Tomogr 2010;34:177, Radiographics 2010;30:1541, Abdom Imaging 2012;37:873, J Chin Med Assoc 2016;79:554):
- Cystic with heterogeneous and delayed contrast enhancement of septations and solid components
- Most classified into Bosniak category III or IV
- MRI (BJU Int 2010;105:932):
- Cystic areas: T1 hypointensity and T2 hyperintensity
- Solid areas: T1 hyperintensity and T2 hypointensity
Prognostic factors
- Mostly benign, with rare local recurrence reported
- Rarely aggressive
- Malignant transformation of either epithelial or stromal component (Hum Pathol 2008;39:463)
- Metastasis of malignant component (Anal Quant Cytopathol Histpathol 2015;37:199)
Case reports
- 22 year old woman with 25 cm giant tumor (J Clin Diagn Res 2015;9:XD01)
- 27 year old man with tumor extending into inferior vena cava (Case Rep Pathol 2018;2018:8234295)
- 38 year old woman with peritoneal seeding following incomplete resection (Urol Ann 2016;8:114)
- 42 year old woman with thyroid-like follicular renal cell carcinoma arising within MEST (Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:80)
- 43 year old woman with bilateral and multiple tumors (Mol Clin Oncol 2017;7:1005)
- 61 year old man with malignant tumor and 2 additional malignant epithelial components (Int J Surg Pathol 2018;26:56)
Treatment
- Nephron sparing surgery (partial nephrectomy), whenever feasible; radical nephrectomy if not possible
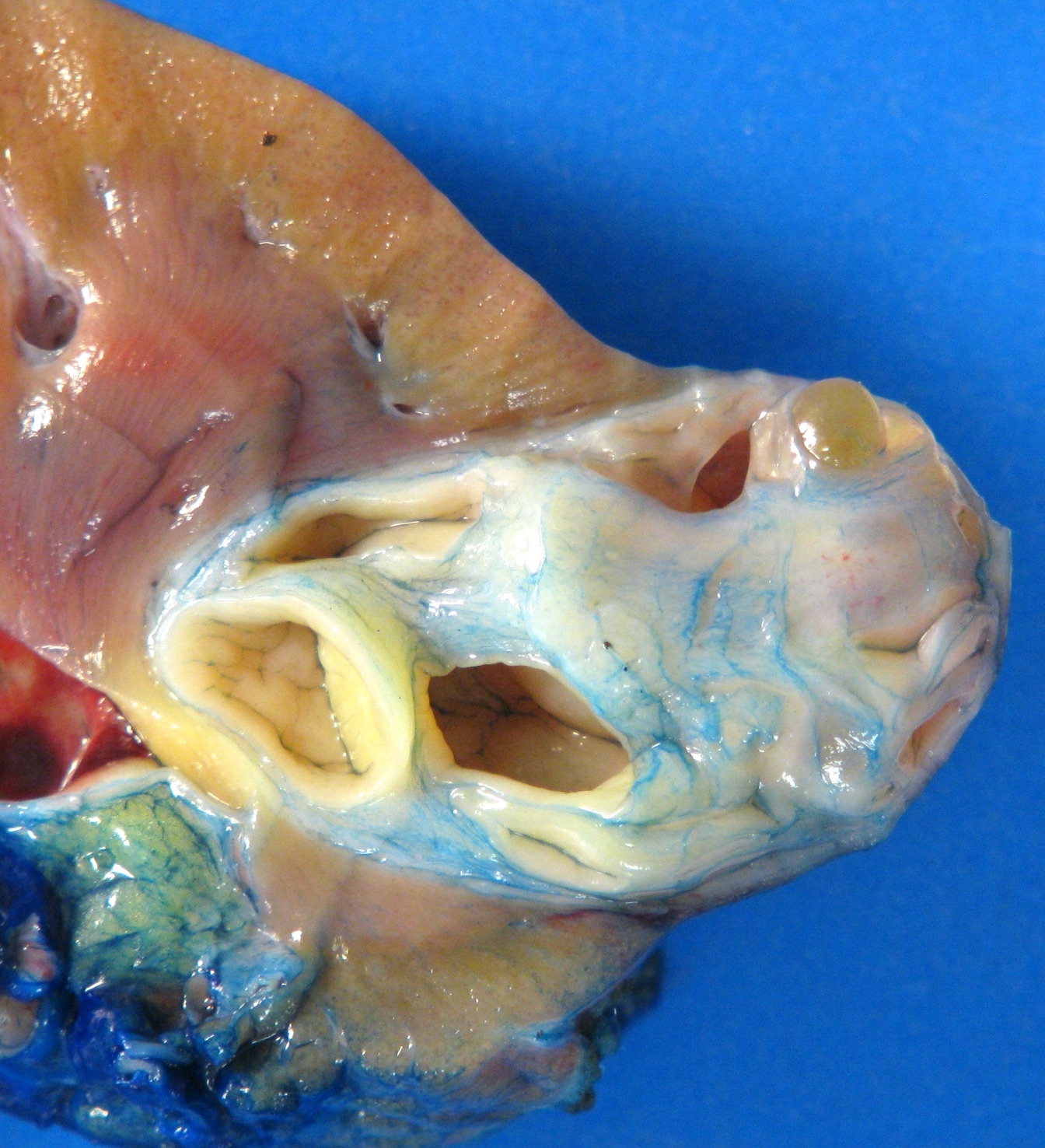
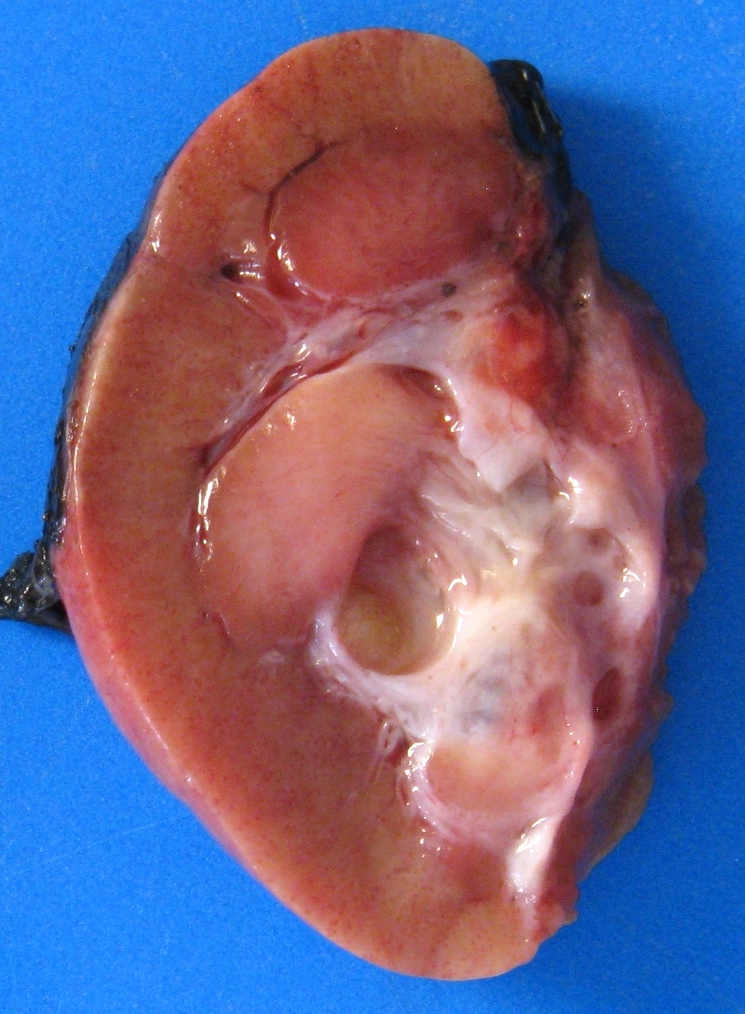
Gross description
- Solitary, rarely bilateral (Urology 2008;71:1142, J Chin Med Assoc 2016;79:554, Mol Clin Oncol 2017;7:1005)
- Unencapsulated but well circumscribed
- Mean size: 9 cm
- Mixture of solid and cystic areas
- Solid areas: firm and white to softer and tan (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:958)
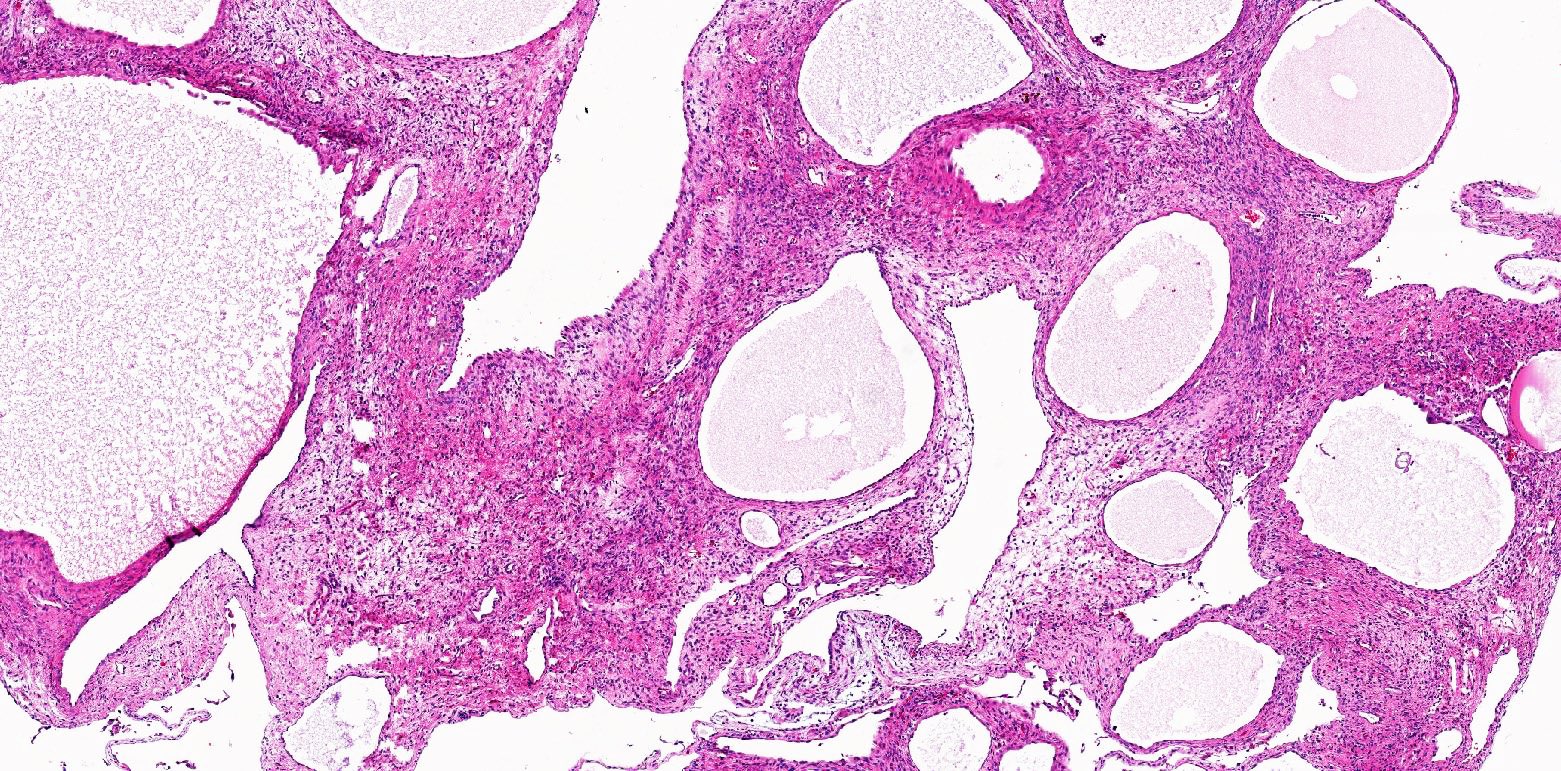
- Cystic areas:
- Cysts of different sizes and shape
- Smooth and glistening linings (Virchows Arch 2004;445:359)
- Contain clear serous fluid (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:489)
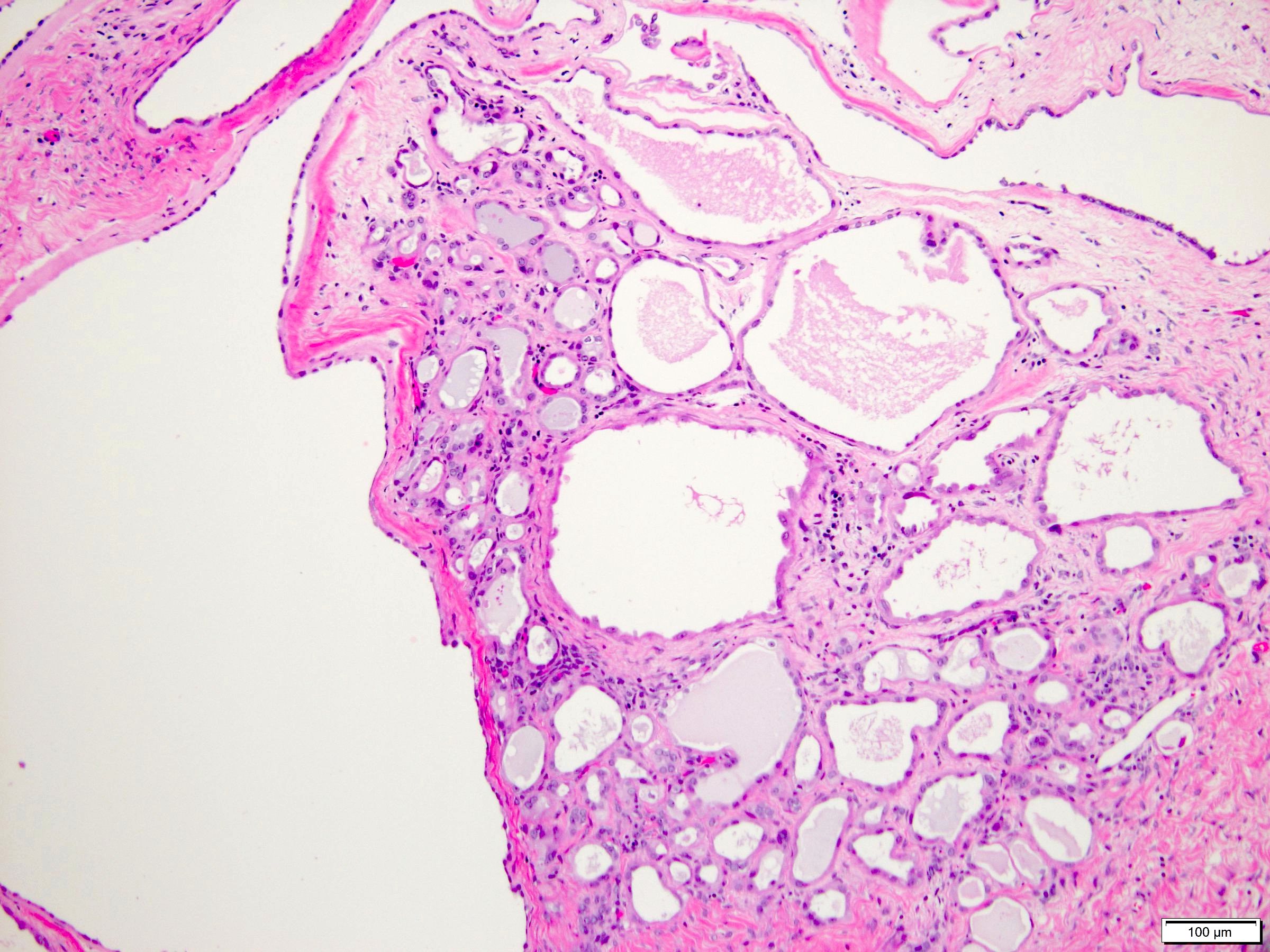
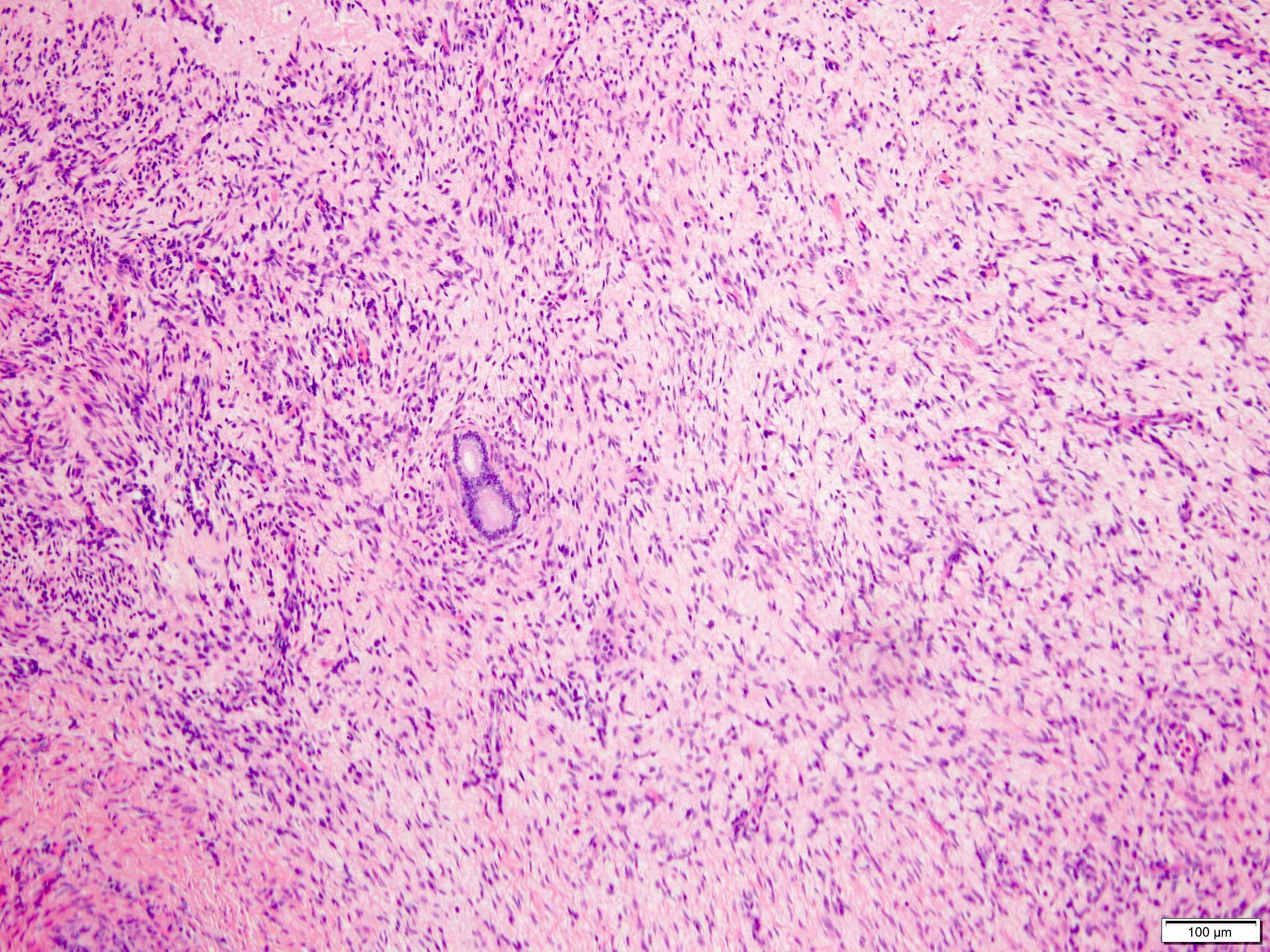
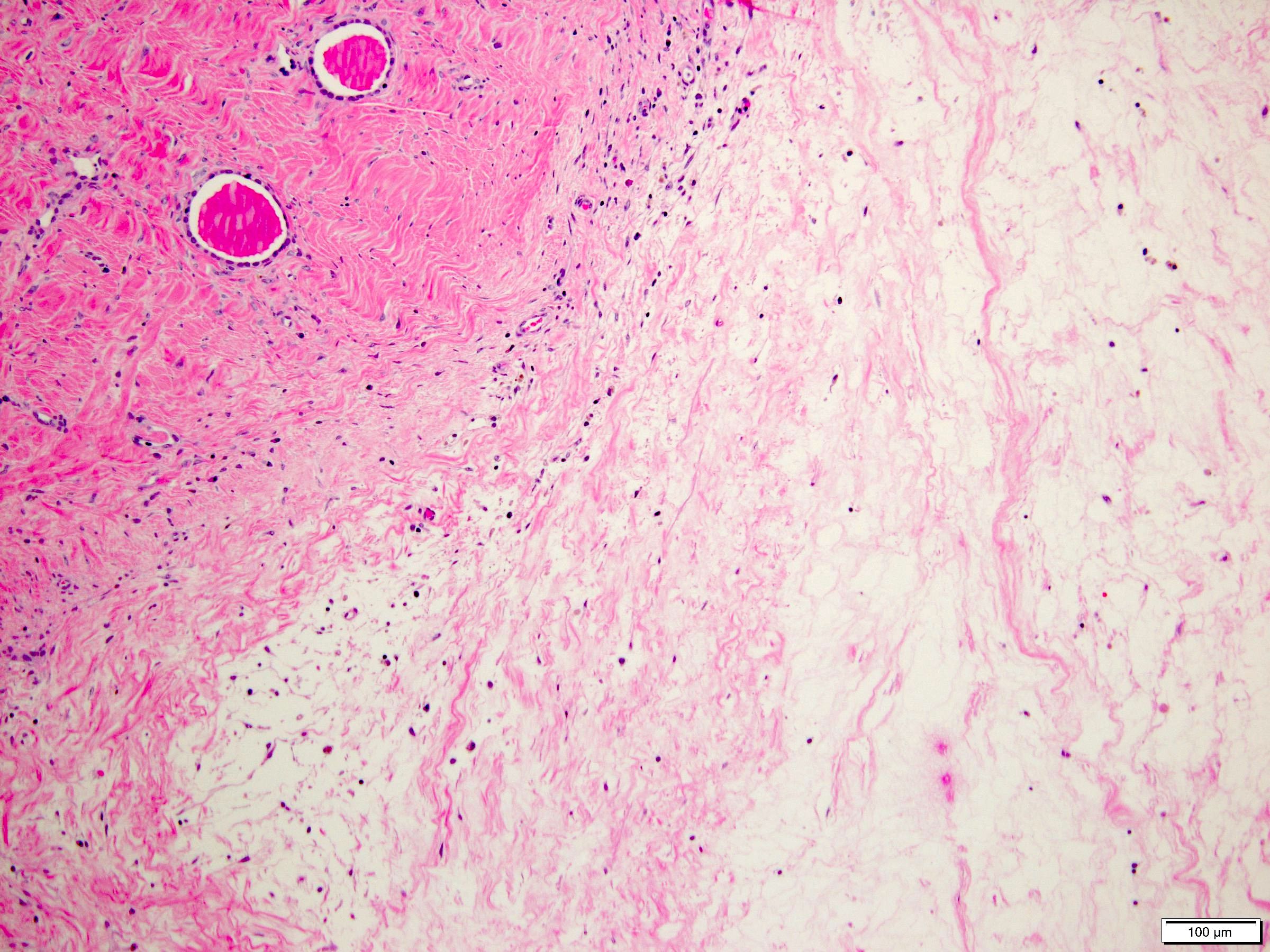
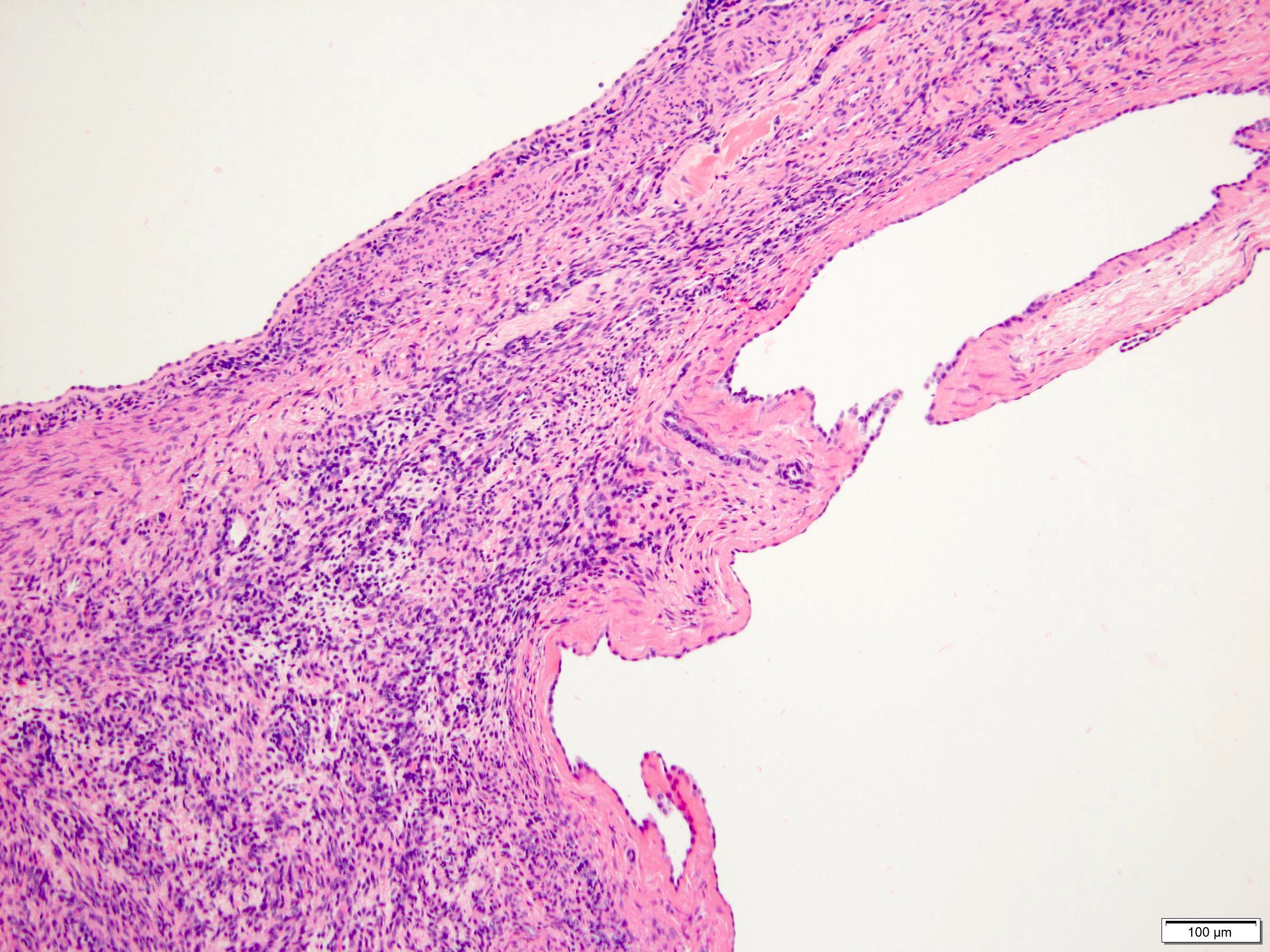
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Combination of diverse stromal and epithelial elements (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:958, Virchows Arch 2004;445:359, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:489, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:80, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1538)
- Stroma:
- Paucicellular to hypercellular
- Wide spectrum of morphology:
- Dense and collagenous to edematous and fibrous
- Spindle cells from slender to plump
- Areas may show smooth muscle differentiation or ovarian type stroma with luteinization
- Adipose tissue occasionally seen
- Condensation of spindle cells around epithelial component
- Slit-like to thick walled vessels
- Foamy histiocytes and calcifications
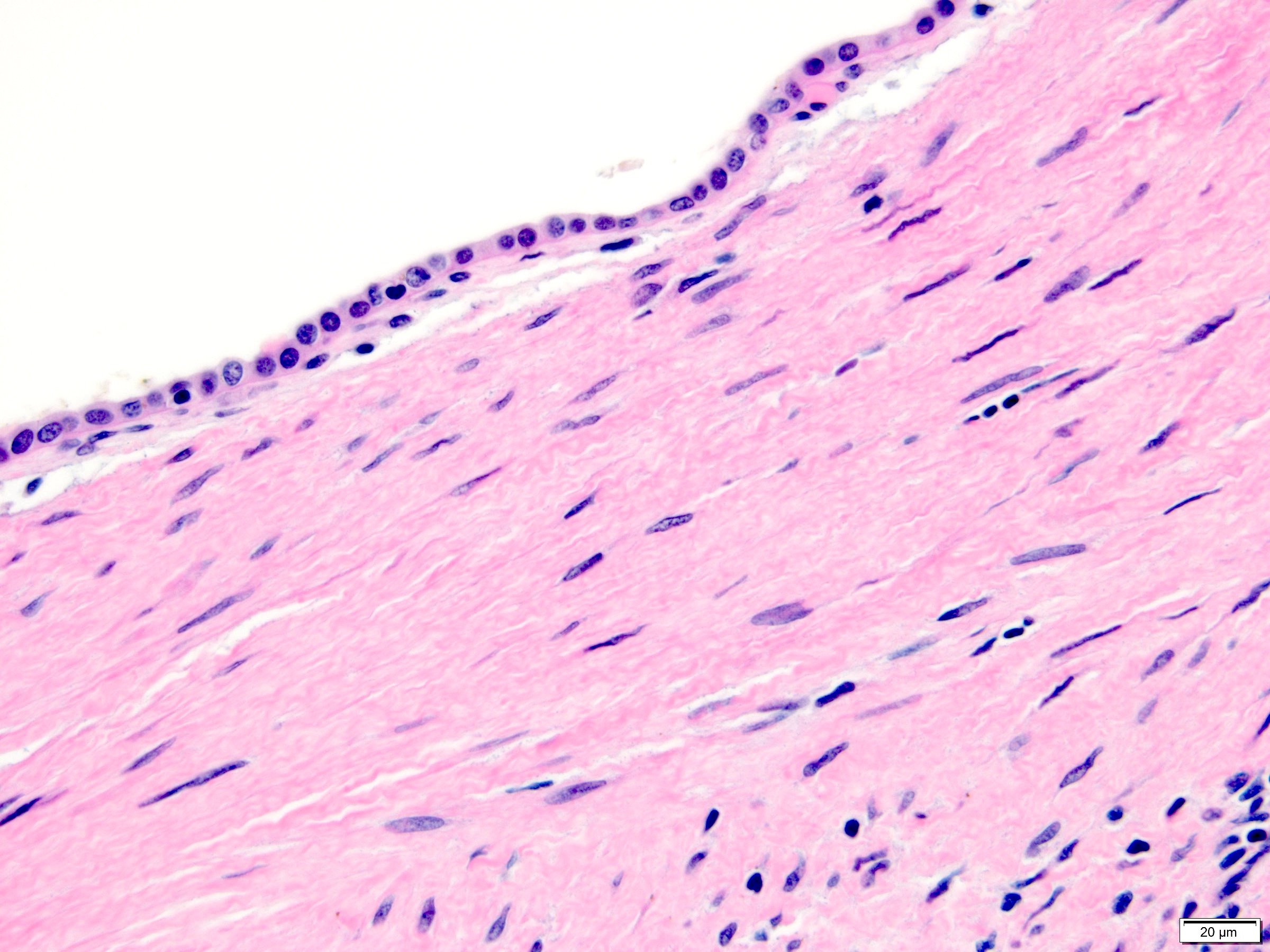
- Epithelium:
- Cysts and glands of varying size and architecture; scattered or clustered
- Lining cells with broad spectrum of morphology: flat, cuboidal, columnar, hobnail, urothelial-like, clear cell, ciliated
- Cytoplasm can be eosinophilic, amphophilic, vacuolated
- Combinations of different epithelial elements commonly seen
- Stroma:
- Versus adult cystic nephroma, which consists of multilocular cysts lined by flat to cuboidal epithelium and separated by fibrous septae
- Minimal cytologic atypia
- Mitoses, necrosis and hemorrhage rare
- Rare cases of malignant transformation reported: undifferentiated sarcoma, synovial sarcoma, sarcoma with rhabdoid differentiation, rhabdomyosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, carcinosarcoma, papillary renal cell carcinoma (Virchows Arch 2001;439:700, Lancet Oncol 2004;5:747, Hum Pathol 2007;38:1432, Hum Pathol 2008;39:463, APMIS 2008;116:1013, Int J Urol 2013;20:448, Int J Surg Pathol 2014;22:266, Int J Surg Pathol 2018;26:56)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- FNA: hypocellular specimen, rare epithelial cells in clusters (Diagn Cytopathol 2014;42:680)
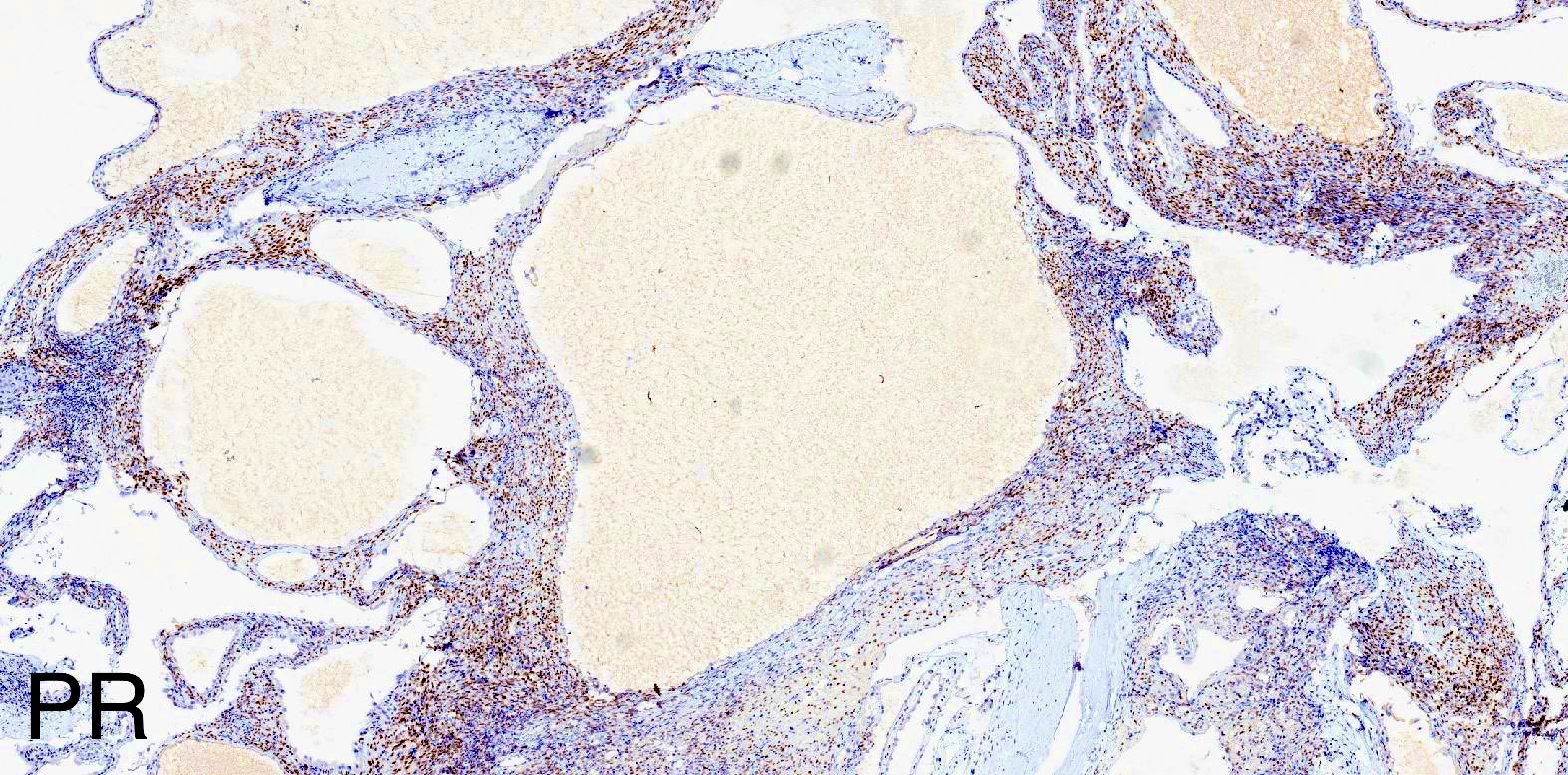
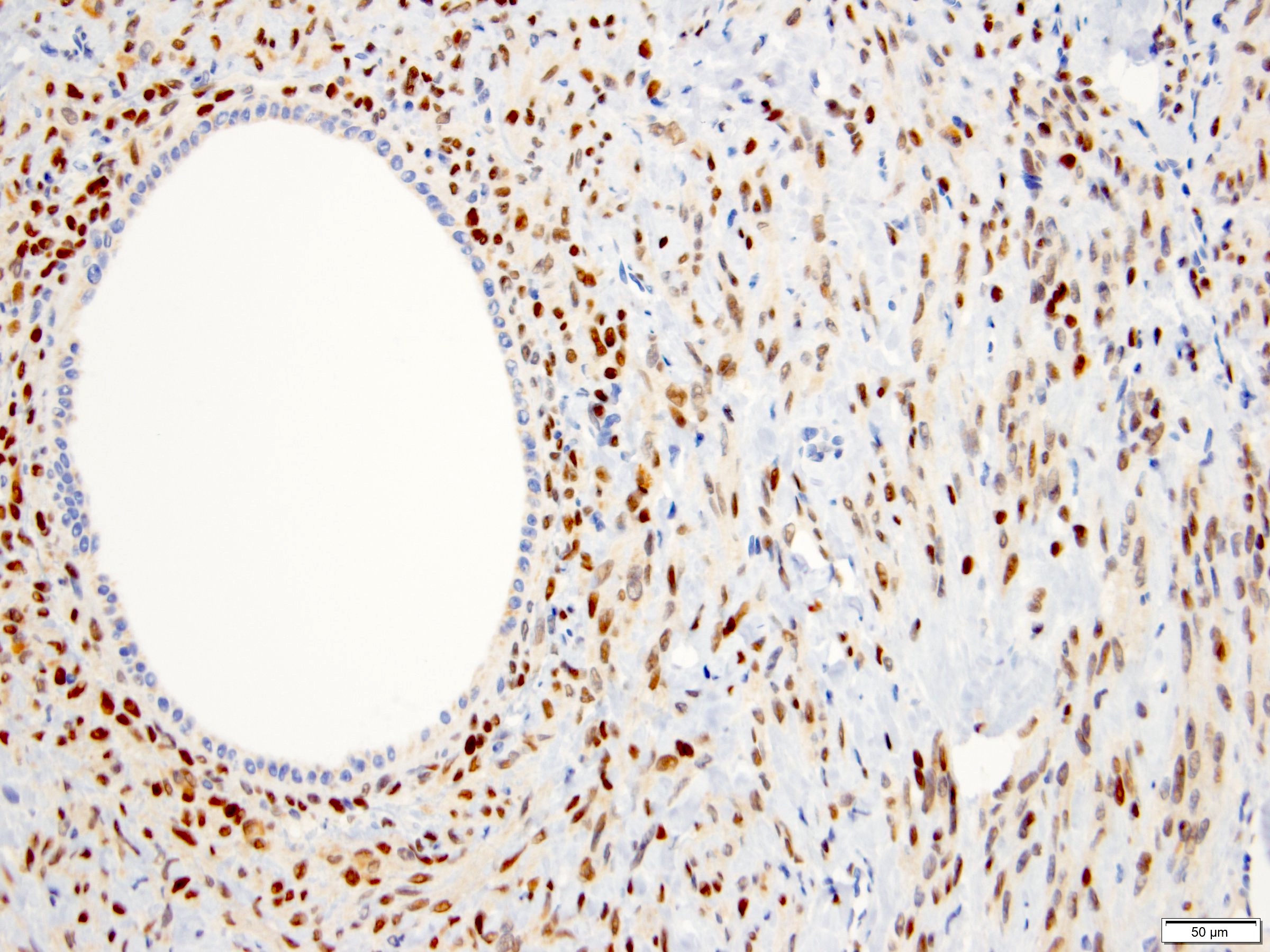
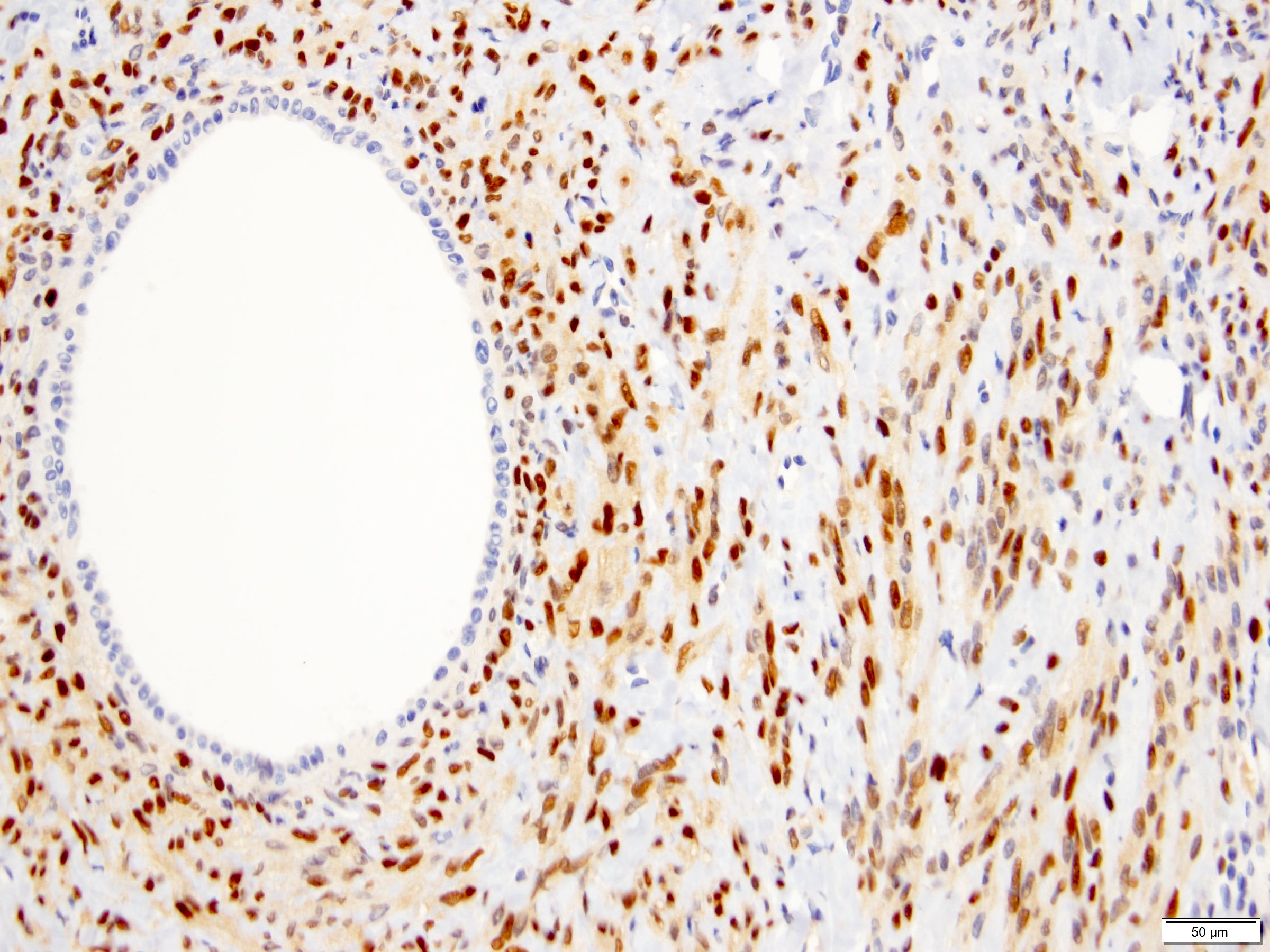
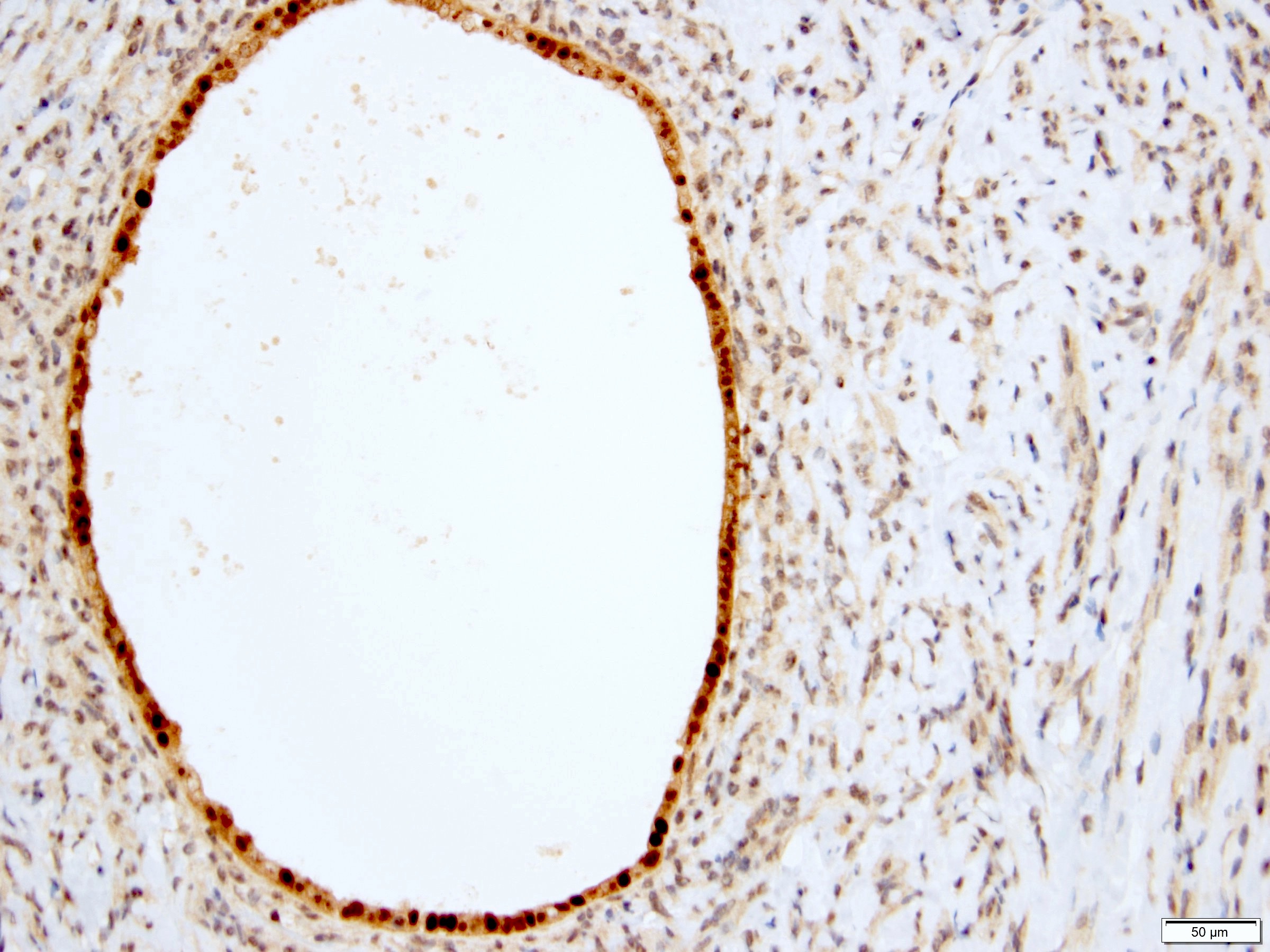
Positive stains
- Stroma:
- SMA: strong and diffuse, 97% (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:958, Virchows Arch 2004;445:359, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1538)
- Desmin and caldesmon: more variable, focal to diffuse, 89% and 88%, respectively (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:958, Virchows Arch 2004;445:359, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1538)
- ER and PR: 88% and 95%, respectively (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:958, Virchows Arch 2004;445:359, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1538)
- CD10: often concentrated around epithelial elements, 90% (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1538)
- Inhibin and calretinin: in ovarian type stroma, particularly in luteinized cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:489)
- FOXL2: in ovarian type stroma, 90% (Hum Pathol 2014;45:1010)
- Epithelium:
- Cytokeratins
- PAX2, PAX8 (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1264)
- GATA3: coexpression with PAX8, 57% (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1538)
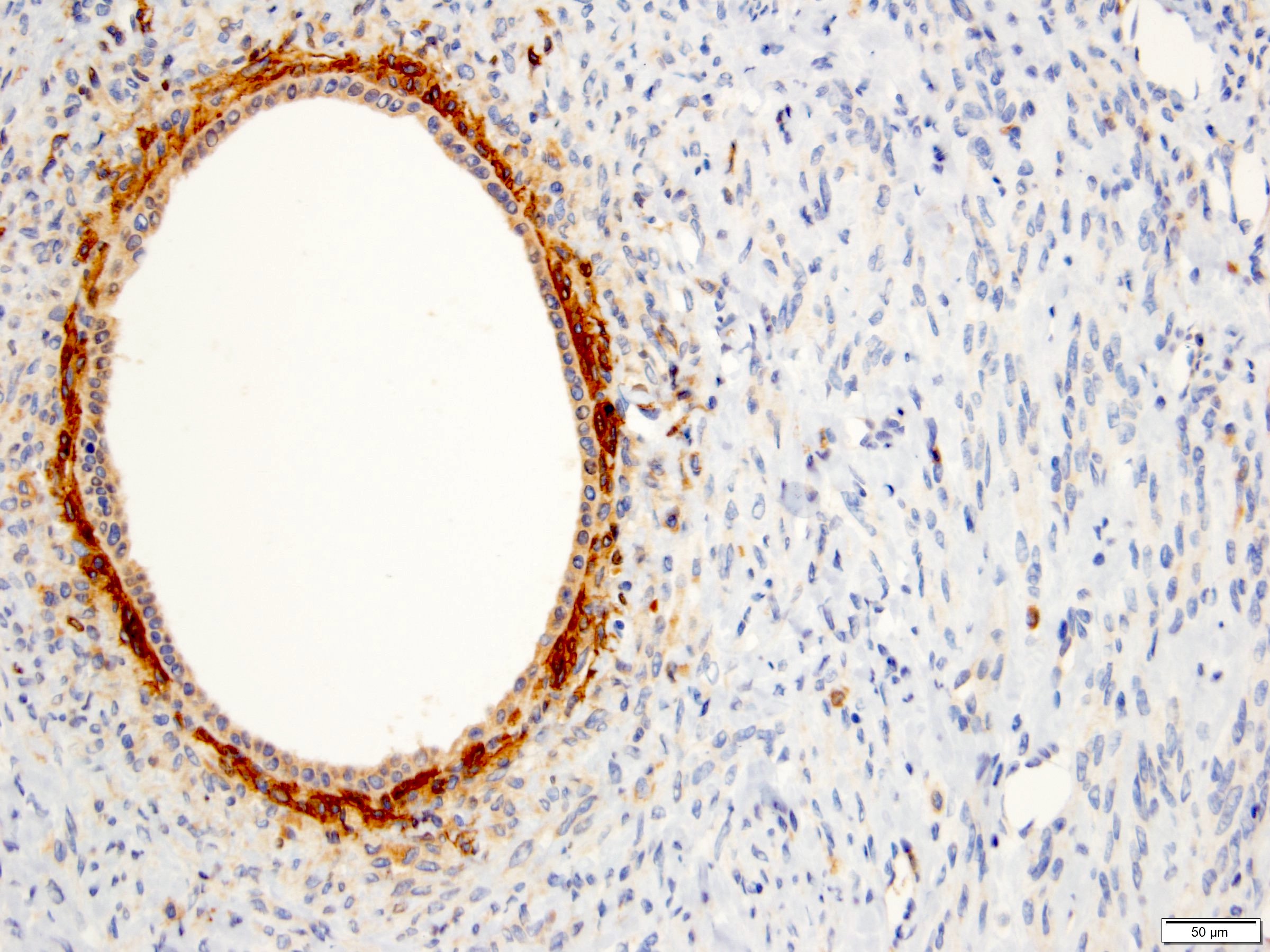
Negative stains
- HMB45
- MelanA
- S100: only positive in adipocytes in stroma when present
- WT1: may show positivity in stromal cells, 26% (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:80, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1538)
- CD34: may show positivity in pericystic stromal cells, 47% (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:1538)
Electron microscopy description
- Spindle cells in stromal component:
- Nonspecific features of fibrocystic cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:958)
- Myogenic features: cytoplasmic fibrils consistent with myofilaments, subplasmalemmal aggregates of thin filaments
- Characteristics of smooth muscle differentiation: number of pinocytic vesicles and dense plaques, near continuous external lamina and relative paucity of rough endoplasmic reticulum
- Intercellular spaces in stromal component:
- Filled with collagen fibrils
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Similar mRNA expression profile between MEST and adult cystic nephroma may represent opposite ends of same spectrum of tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:72)
- Highest differentially expressed gene: insulin-like growth factor 2
- Lowest differentially expressed gene: carbonic anhydrase II
- Lack abnormalities in chromosomes 8, 11 or 17 seen in congenital cellular mesoblastic nephroma (Hum Pathol 2001;32:513)
- CDC73 germ line mutation, associated with hyperparathyroidism jaw tumor syndrome, in family with MESTs (Urology 2019;124:91)
Sample pathology report
- Right kidney, mass, partial nephrectomy:
- Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor, measuring 2.5 cm in greatest dimension (see comment)
- Surgical margins, negative for tumor
- Comment: The sections show a well circumscribed tumor composed of occasional glands and cysts embedded in a variably cellular stroma. Immunohistochemical stains for ER and PR are positive in the stromal component of the tumor. Overall, the morphologic and immunohistochemical findings support the diagnosis of mixed epithelial and stromal tumor.
Differential diagnosis
- Adult cystic nephroma:
- Part of the MEST family, with MEST at opposite end of spectrum, on basis of comparable clinical features (sex and age distribution), overlapping morphologic findings and similar immunohistochemical profile
- No solid component
- Multilocular cysts lined by flat, hobnail or columnar epithelium
- Fibrous septae with ovarian-like stroma in areas
- Angiomyolipoma with epithelial cysts (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:593):
- Renomedullary interstitial cell tumor (Hum Pathol 2018;82:46):
- Metanephric adenofibroma:
- Cystic partially differentiated nephroblastoma:
- Most occur in patients < 24 months old
- Nephroblastematous tissue (e.g. blastema, immature stromal cells, primitive epithelial elements) present
- Mesoblastic nephroma:
- Multilocular cystic neoplasm of low malignant potential:
- Clusters or nests of clear cells present in cystic septa
- No cellular stroma
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma with prominent spindle cell stroma (Ann Diagn Pathol 2020;44:151441):
- Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma:
- Infiltrative borders
- Marked cytologic atypia
- Necrosis and mitotic figures frequent
- Synovial sarcoma:
- Most are monophasic type with entrapped renal tubules; biphasic type is rare
- t(X;18)(p11;q11), resulting in SS18-SSX2 gene fusion
Board review style question #1
A 60 year old woman with hematuria was found to have a 3.5 cm variably cystic and solid renal mass on CT imaging. Partial nephrectomy showed a well circumscribed tumor with the above morphology. The stromal component is positive for ER and PR. What is the likely diagnosis?
- Angiomyolipoma
- Cystic partially differentiated nephroblastoma
- Metanephric adenofibroma
- Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor
- Multilocular cystic neoplasm of low malignant potential
Board review style answer #1
D. Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor
Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor is a well circumscribed, variably solid and cystic mass. Cystic partially differentiated nephroblastoma and metanephric adenofibroma typically occur in children. Multilocular cystic neoplasm of low malignant potential does not have a cellular stroma. None of the above choices, except for mixed epithelial and stromal tumor, demonstrate immunoreactivity for ER and PR.
Comment Here
Reference: Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor
Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor is a well circumscribed, variably solid and cystic mass. Cystic partially differentiated nephroblastoma and metanephric adenofibroma typically occur in children. Multilocular cystic neoplasm of low malignant potential does not have a cellular stroma. None of the above choices, except for mixed epithelial and stromal tumor, demonstrate immunoreactivity for ER and PR.
Comment Here
Reference: Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is true about mixed epithelial and stromal tumor of the kidney?
- Commonly bilateral and multiple
- Harbor DICER1 gene mutations
- Most behave in benign fashion
- Typically occur in male patients
Board review style answer #2
C. Most behave in benign fashion
Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor is typically seen in perimenopausal women. These tumors are solitary, with very rare exceptions. Most of these tumors have benign behavior following surgical resection. Unlike pediatric cystic nephroma, DICER1 gene mutations are not found in mixed epithelial and stromal tumor.
Comment Here
Reference: Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor
Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor is typically seen in perimenopausal women. These tumors are solitary, with very rare exceptions. Most of these tumors have benign behavior following surgical resection. Unlike pediatric cystic nephroma, DICER1 gene mutations are not found in mixed epithelial and stromal tumor.
Comment Here
Reference: Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor