Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Antic T. Metanephric adenoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytumormetanephric.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Member of the metanephric tumor family, which also includes metanephric adenofibroma and metanephric stromal tumor
- Most tumors have BRAF gene mutation
Essential features
- Benign tumor composed of cytologically bland embryonic looking epithelium with frequent psammomatous calcifications
- Can be seen in patients from pediatric to older adult age
Terminology
- Metanephroid renal tumor, nephroblastoma-like adenoma, nephrogenic nephroma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8325/0 - metanephric adenoma
- ICD-11: 2F35 & XH0JC7 - benign neoplasm of urinary organs & metanephric adenoma
Epidemiology
- Uncommon, usually asymptomatic, incidentally discovered renal neoplasm
- Rare, < 0.5% of all renal neoplasms
- Age range: 5 - 84 years (mean: ~54) (Oncotarget 2016;8:54096)
- 60% are female
Sites
- Renal cortex
Pathophysiology
- Considered to arise from different forms of maturation arrested embryonal rests, persistent blastema or maturing nephroblastoma due to its resemblance to nephrogenic rests / maturing Wilms tumor (Anticancer Res 2018;38:6663, Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:1290)
- Recently it has been suggested that at least a subset originates from an adult Wilms tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2022;46:988)
Clinical features
- Usually discovered incidentally with no presenting symptoms
- If presenting with symptoms, it can demonstrate hematuria, pyrexia, flank pain, abdominal mass and polycythemia (Oncol Lett 2016;11:352)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosed by histopathologic examination of excised tissue
- If diagnosis is questionable, immunohistochemistry can differentiate metanephric adenoma from its mimics
Laboratory
- Routine laboratory within normal limits in incidental cases
- Polycythemia might be suggestive of renal tumor
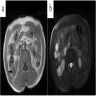
Radiology description
- CT: usually solid and hypovascular and shows prolonged and homogenous mild enhancement (Clin Radiol 2019;74:408.e9)
Prognostic factors
- Benign course
- Seeding of lymph nodes has been reported (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:1317)
Case reports
- 9 year old boy with multifocal tumor (Pathol Int 2009;59:49)
- 15 year old girl with large cystic metanephric adenoma (Urology 2017;101:147)
- 23 year old man with diffuse calcifications in metanephric adenoma (Oncol Lett 2015;10:1816)
- 30 year old woman with passive seeding of hilar lymph node (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:1317)
- 39 year old woman with partial nephrectomy (Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e3486)
- 54 year old woman with a metanephric adenoma associated with polycythemia (Oncol Lett 2016;11:352)
Treatment
- Surgical resection is curative
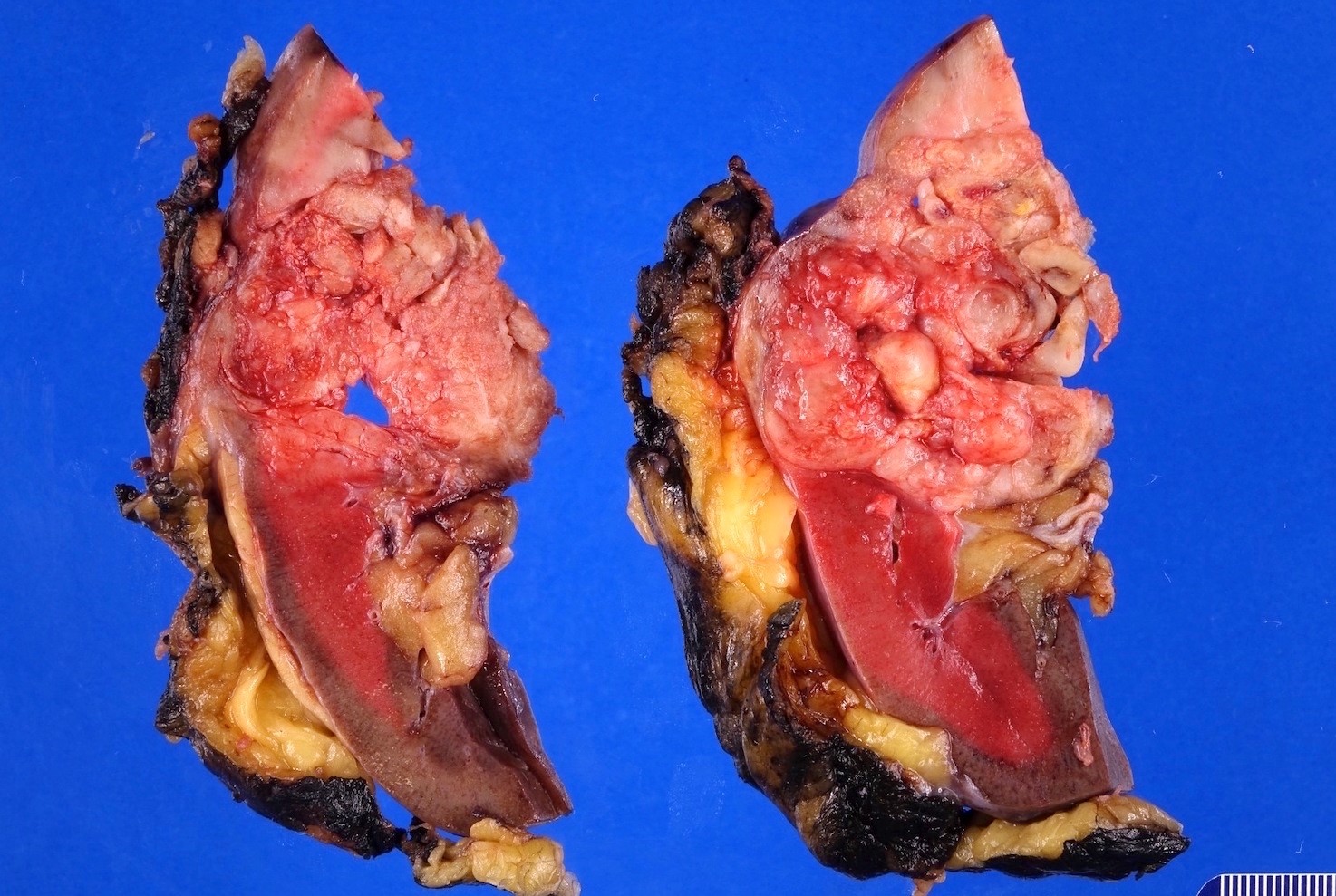
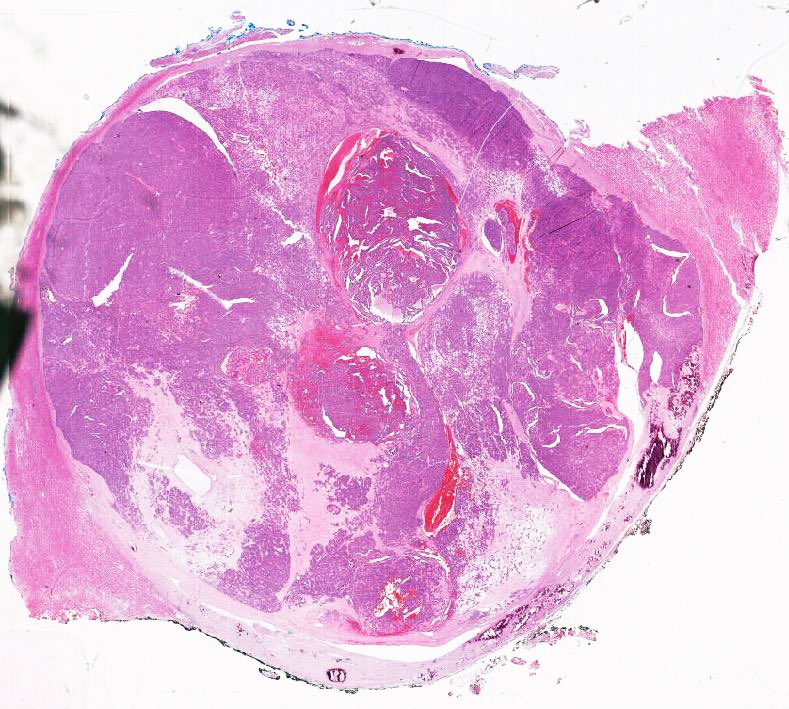
Gross description
- Most are 3 - 6 cm in diameter although 15 cm tumor has been reported (Urology 2017;101:147)
- Mostly unilateral and unifocal
- Rare cases with cystic change (Urology 2017;101:147)
- Circumscribed, not encapsulated, with pushing border
- Cut surface is tan to grey and can be soft or firm; occasionally, hemorrhage and necrosis can present in larger tumors
- Calcifications are often seen grossly
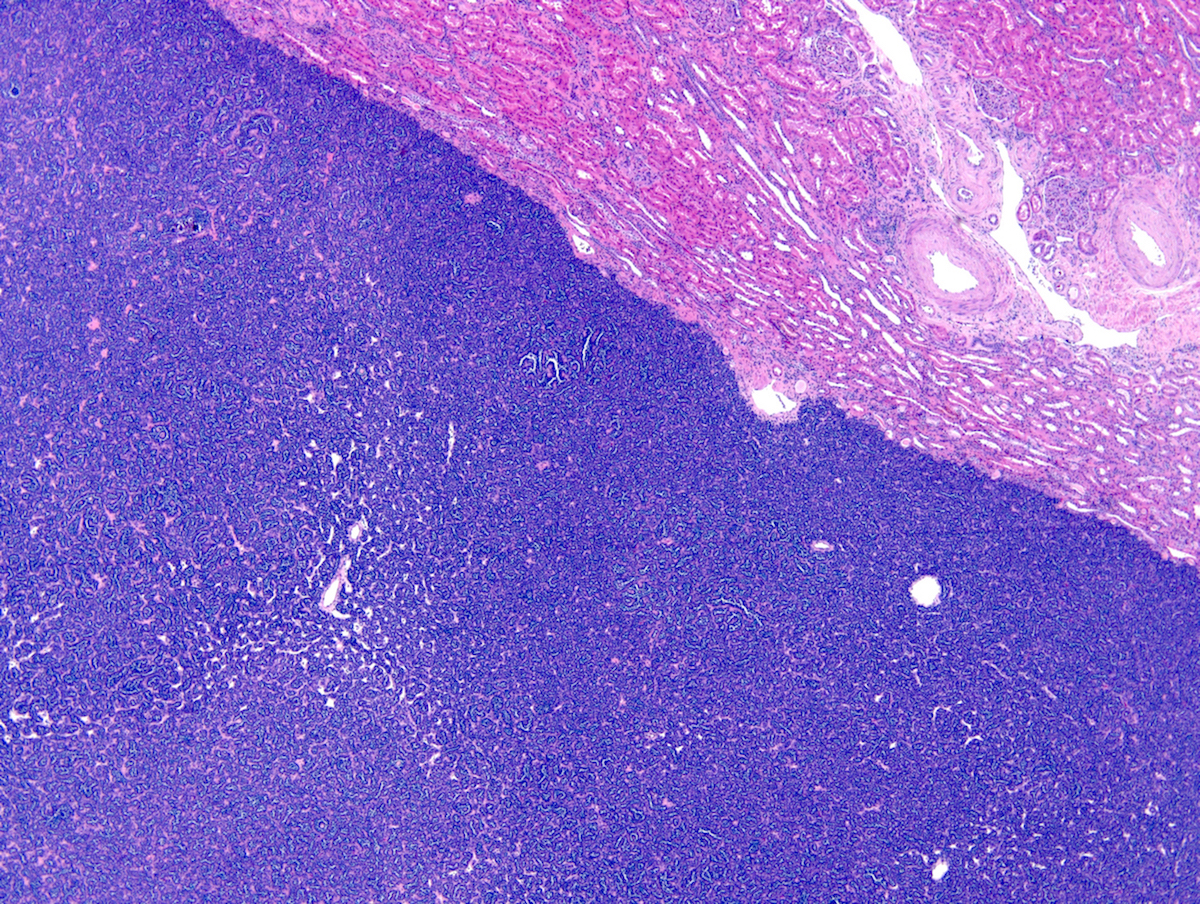
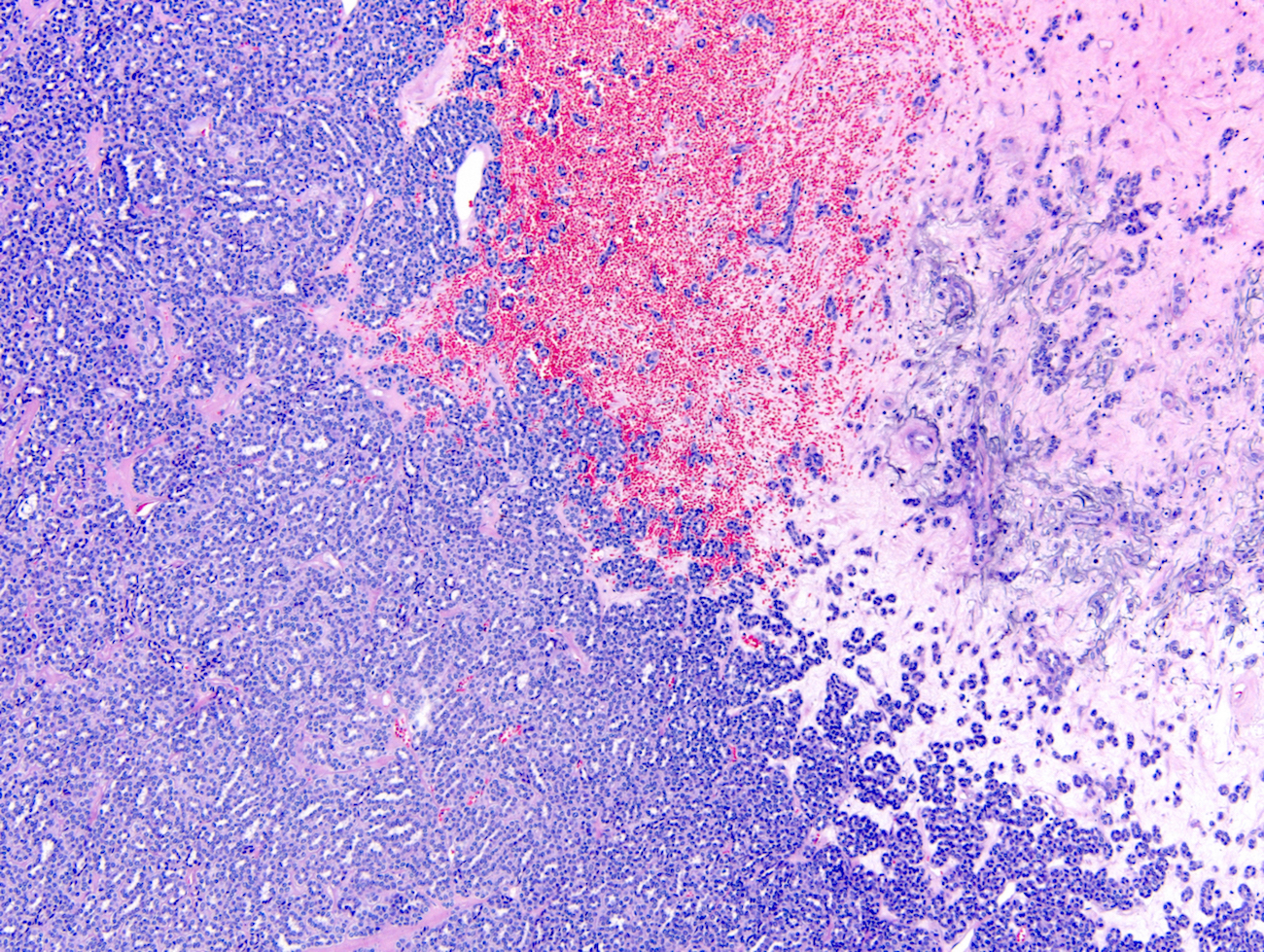
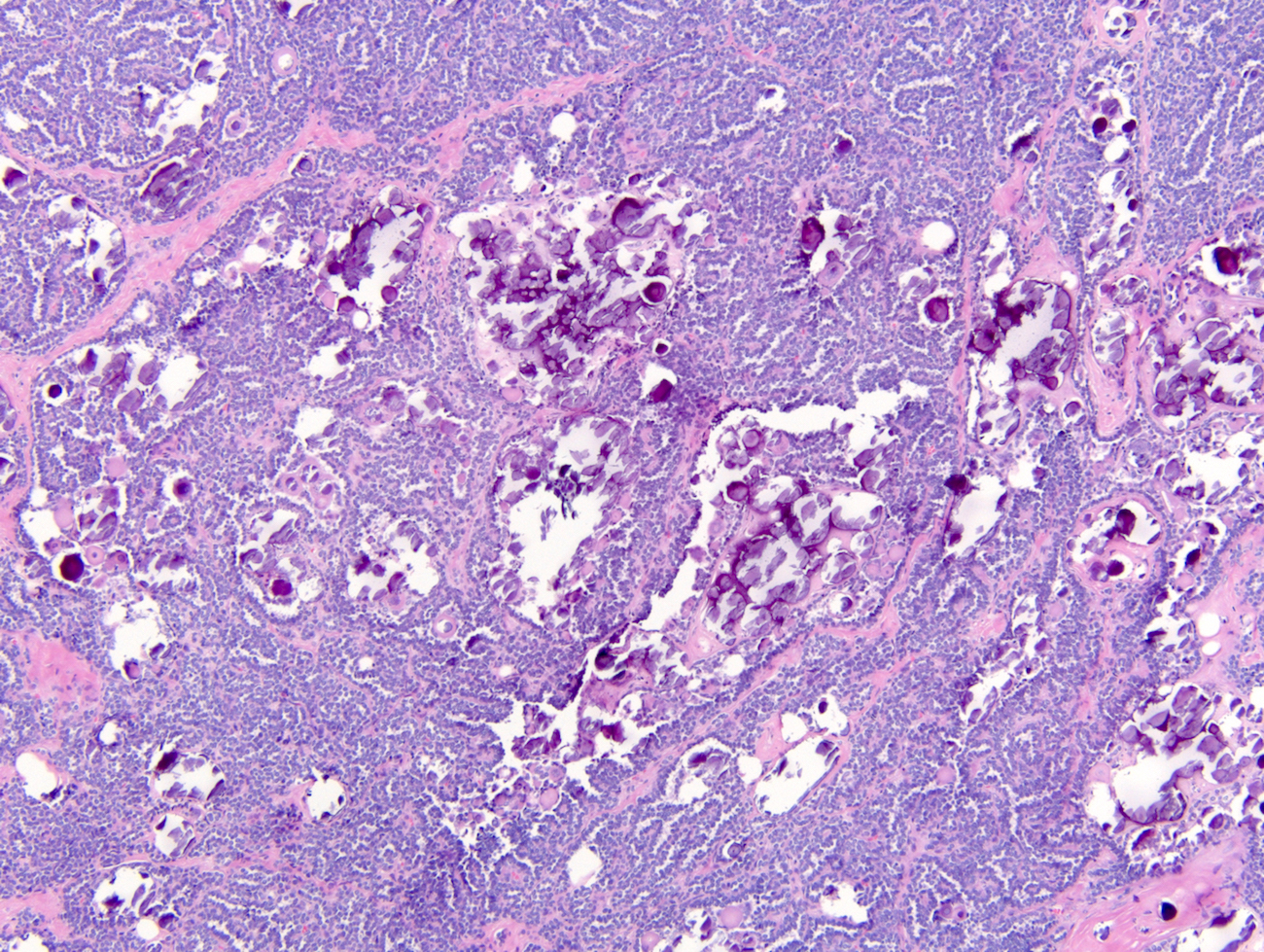
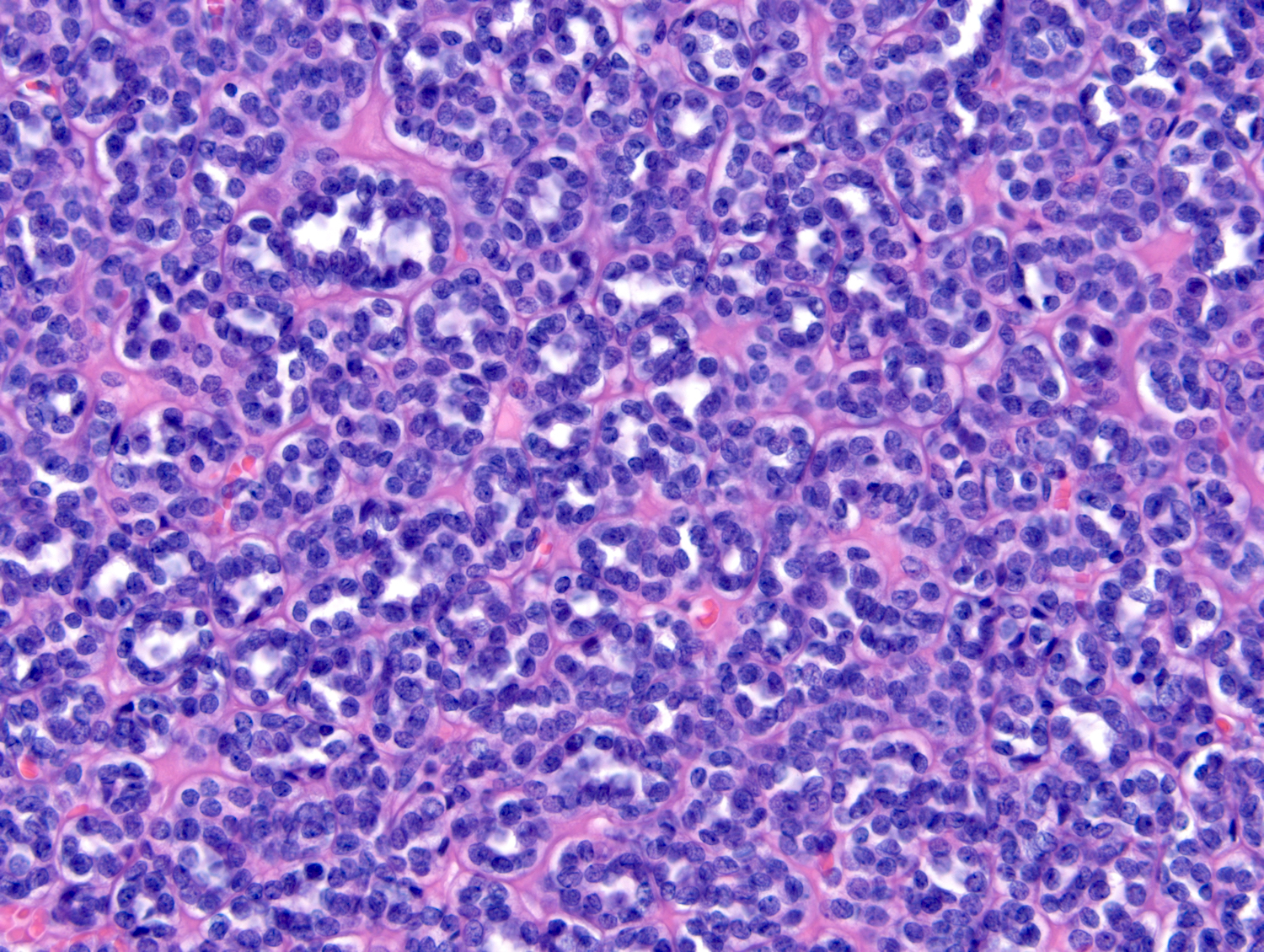
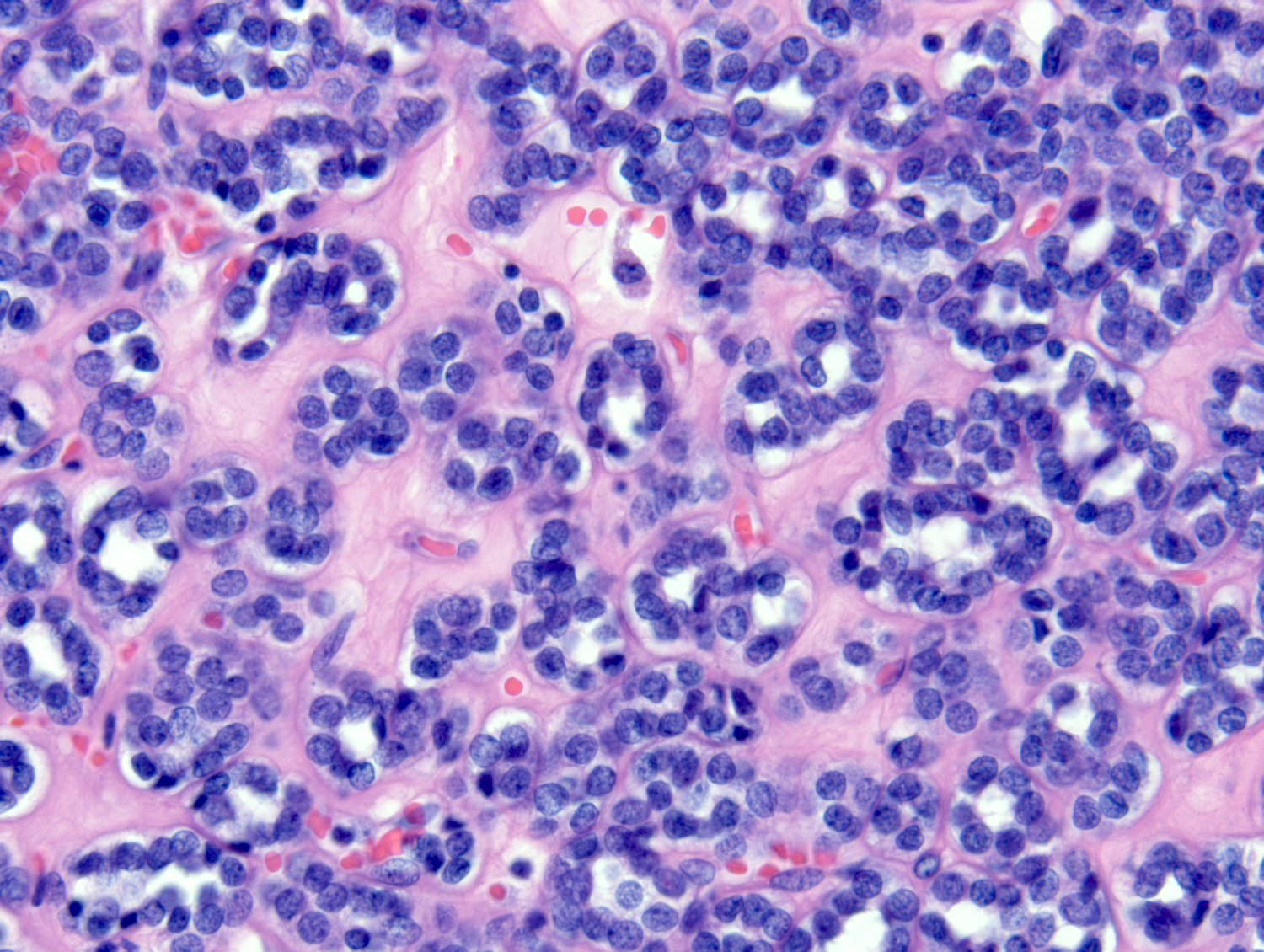
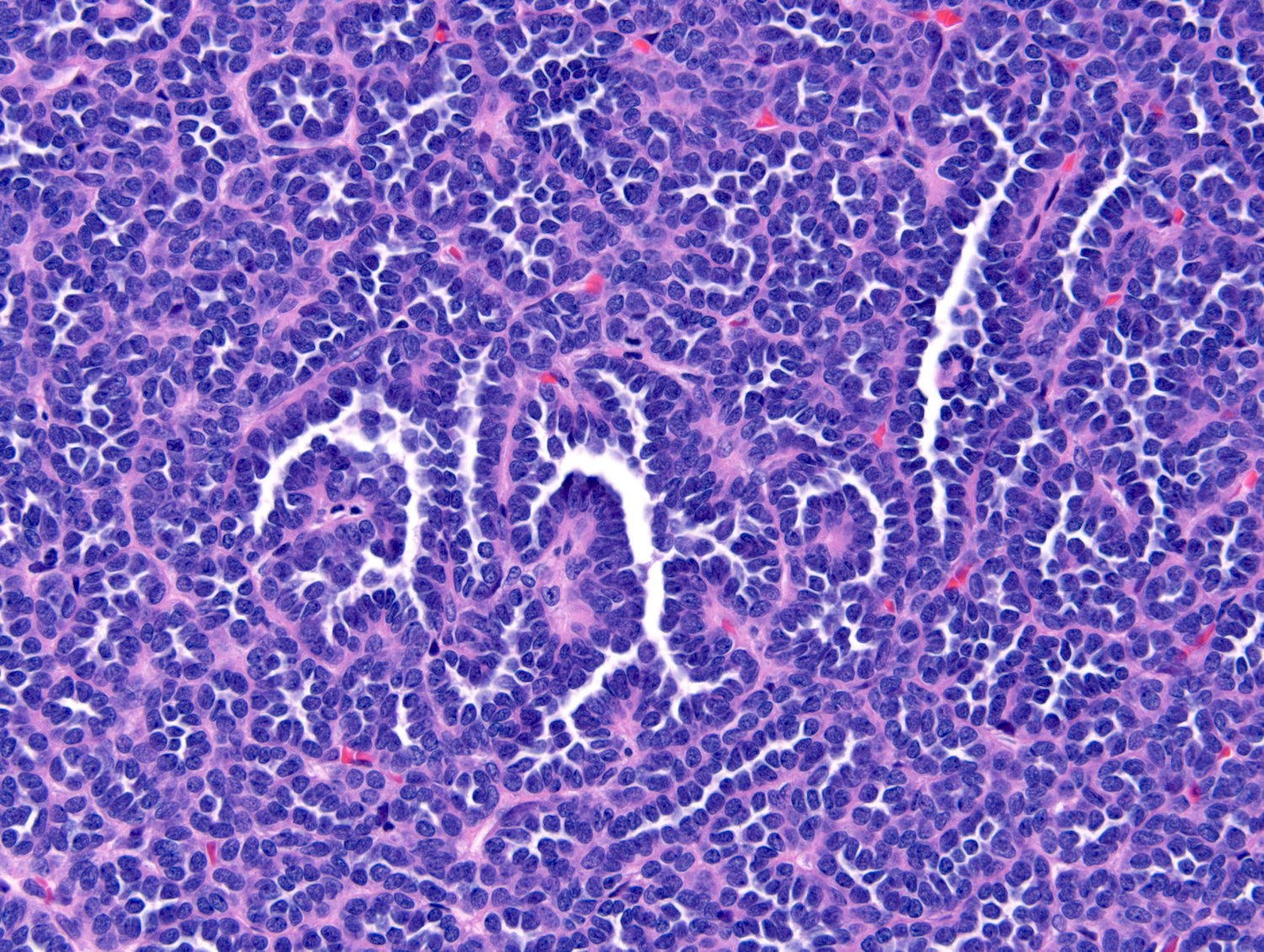
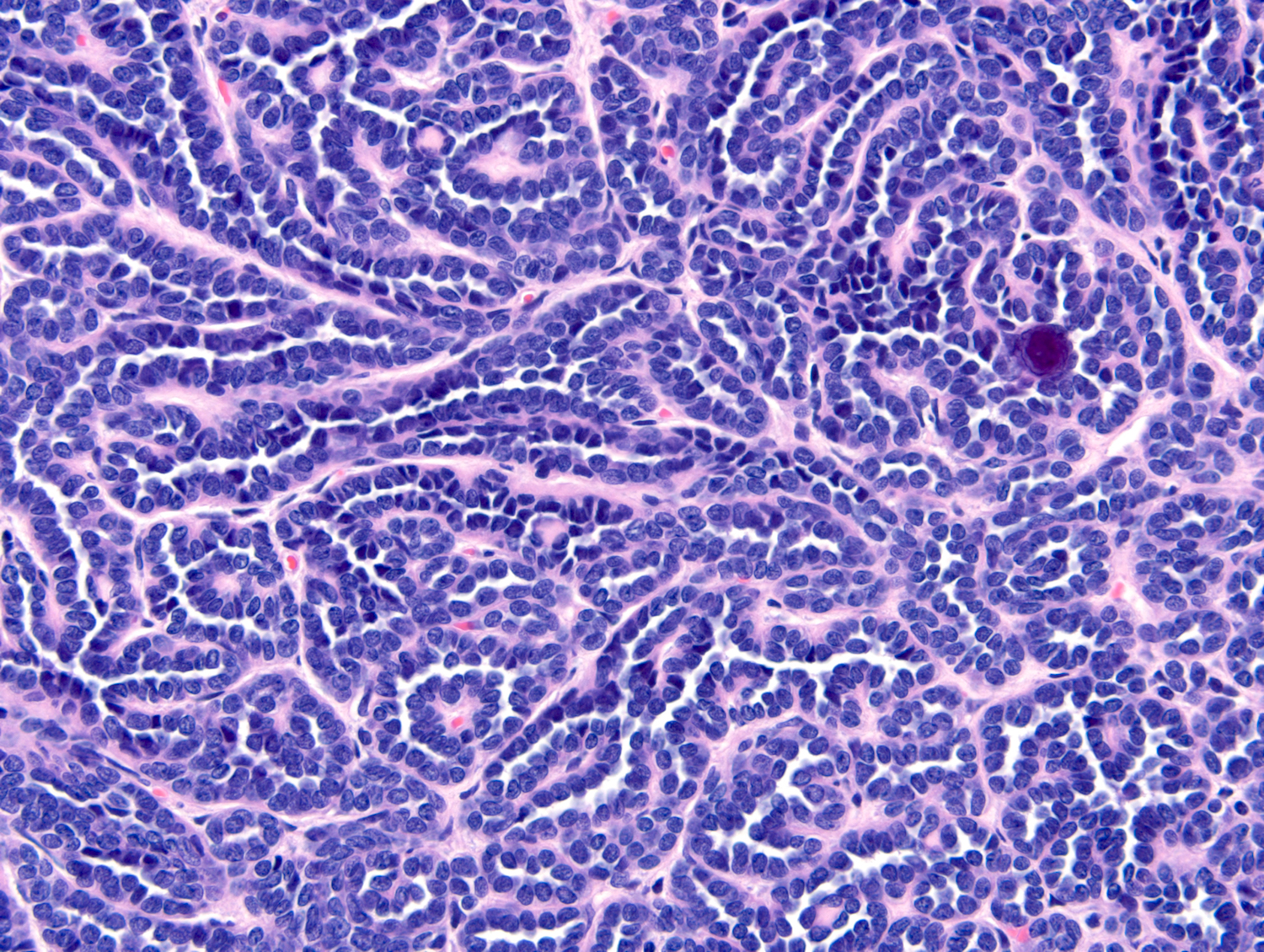
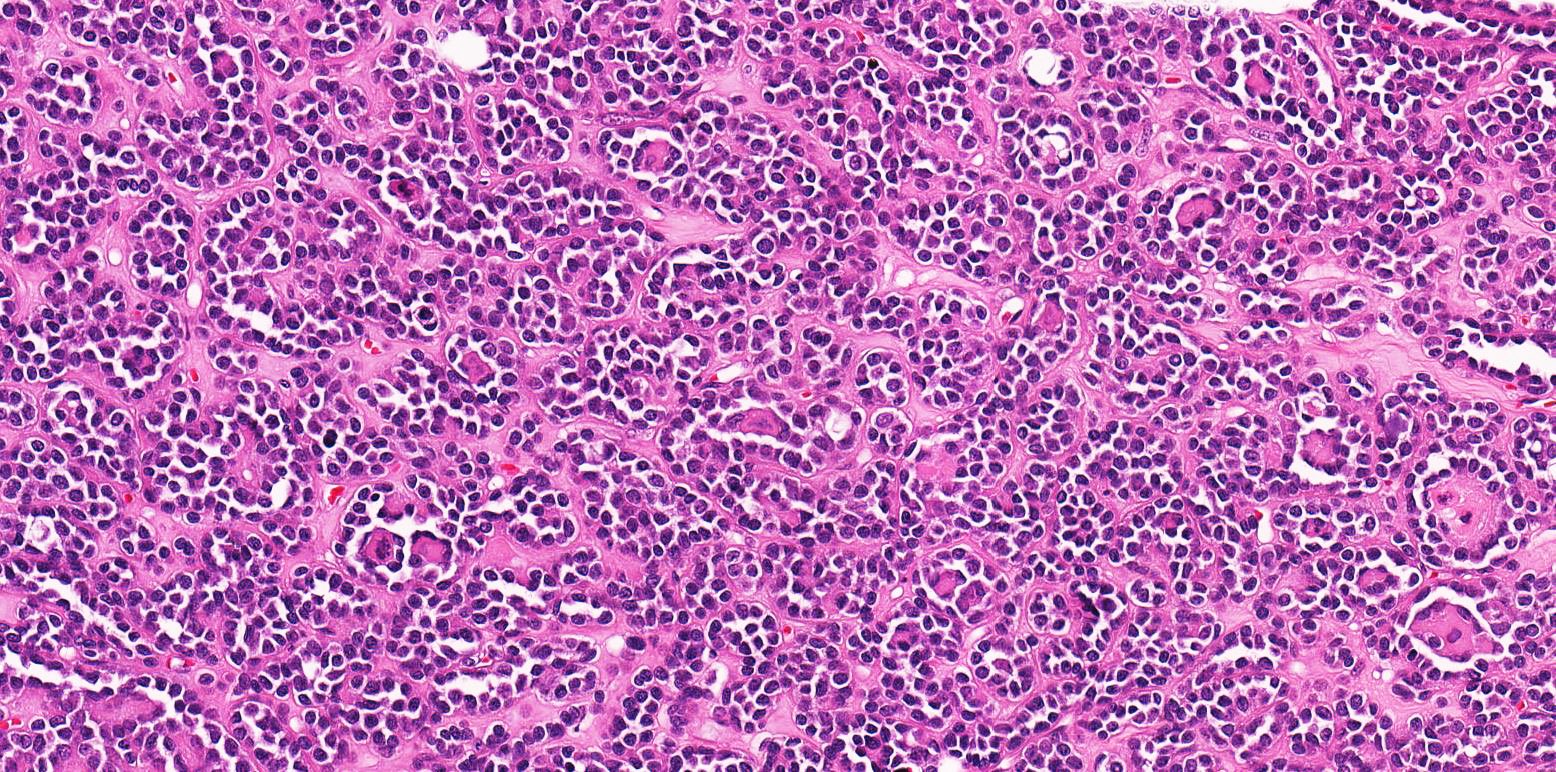
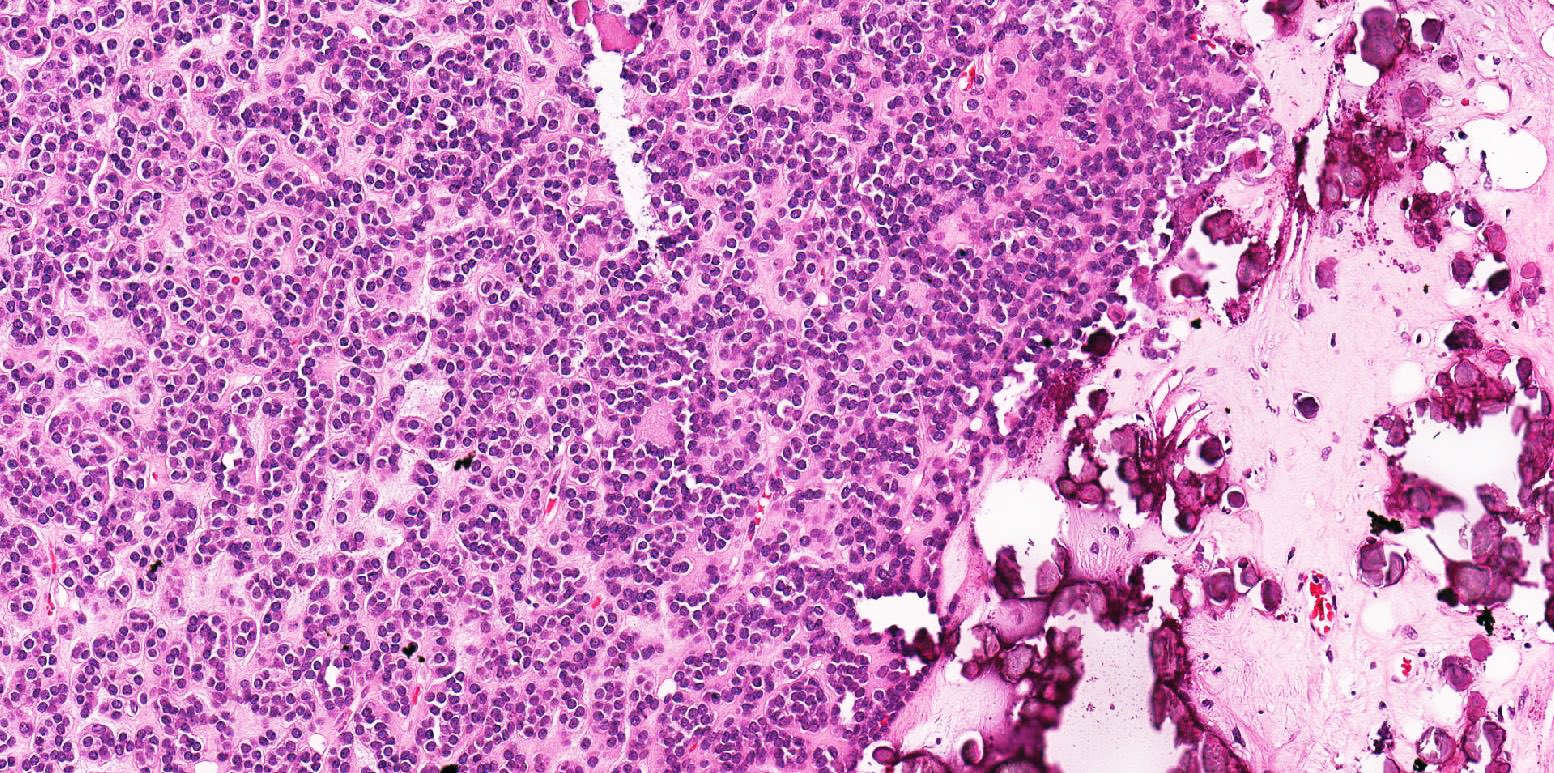
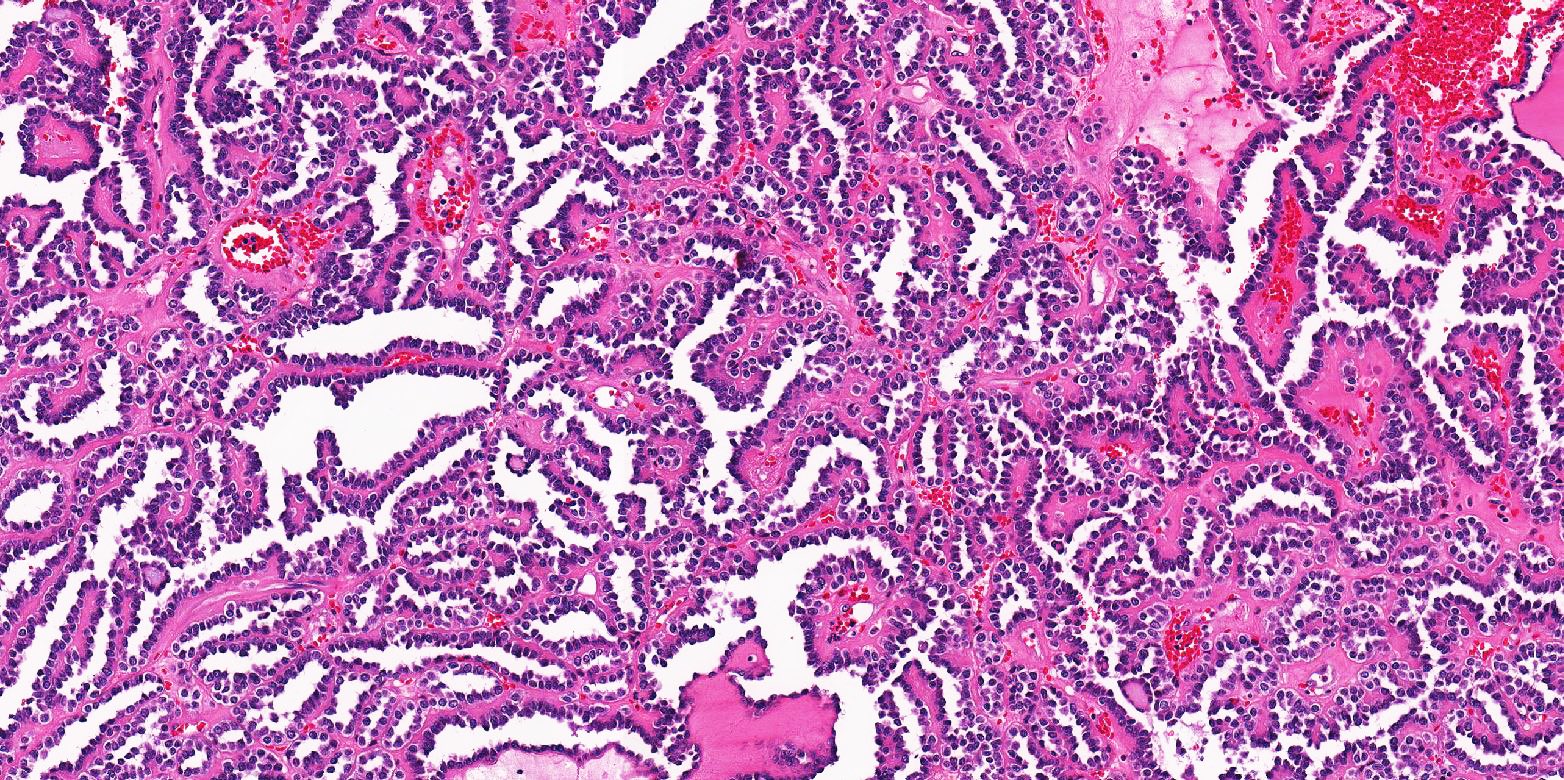
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Classic appearance is a cellular blue tumor composed of tightly packed tubules, long branching and angulated ducts and abortive glomeruli
- Tumor cells have scant cytoplasm and nuclei are small with no nucleoli
- Mitotic figures are very rare or absent
- Stroma is scant; it can be edematous and occasionally appear scar-like
- Psammomatous calcifications can be abundant (Oncol Lett 2015;10:1816)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Basophilic cells with cytologically bland nuclei and scant cytoplasm forming tightly packed tubules and occasional psammoma bodies (Diagn Cytopathol 2016;44:263, Acta Cytol 2007;51:468)
Positive stains
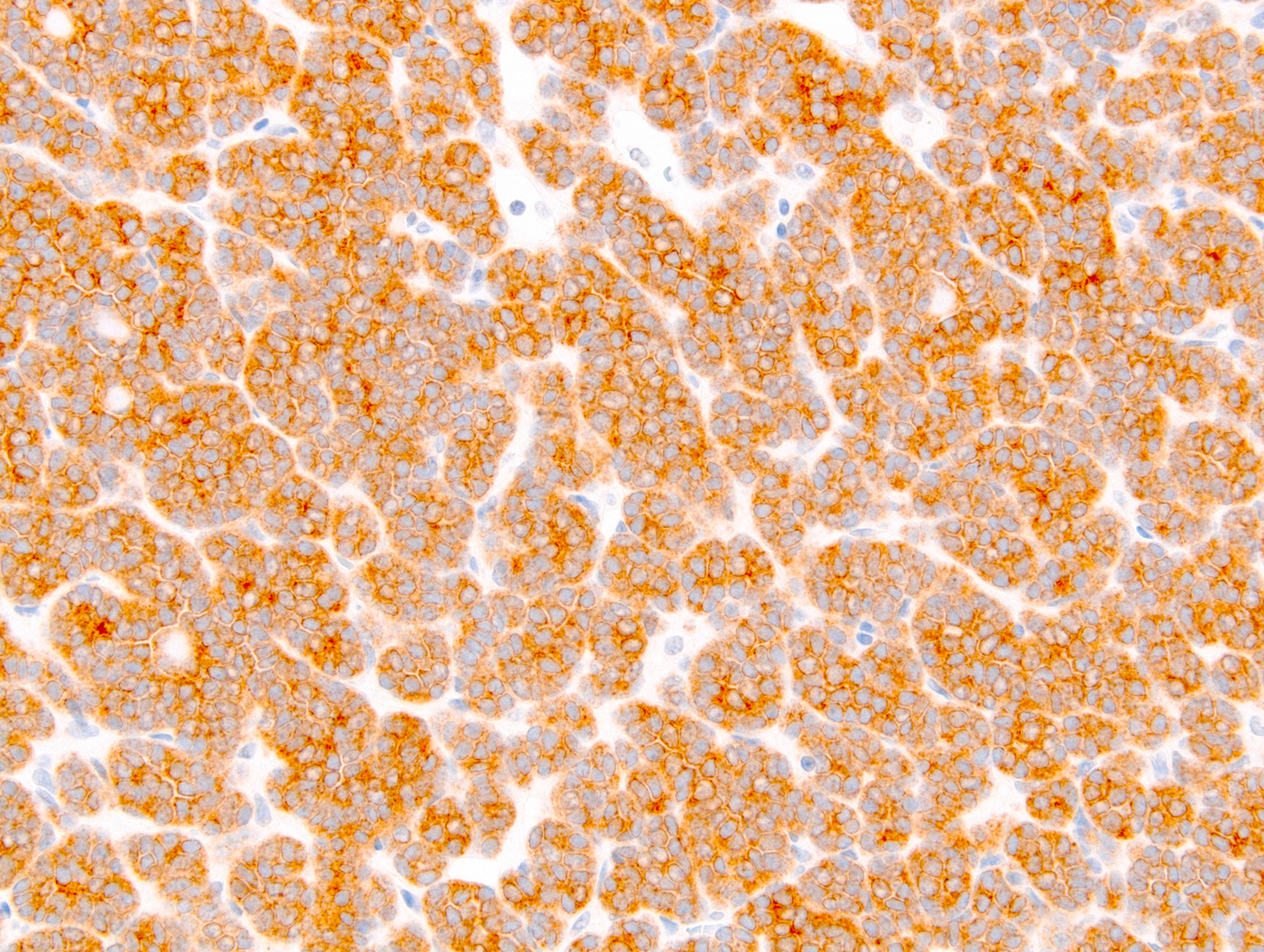
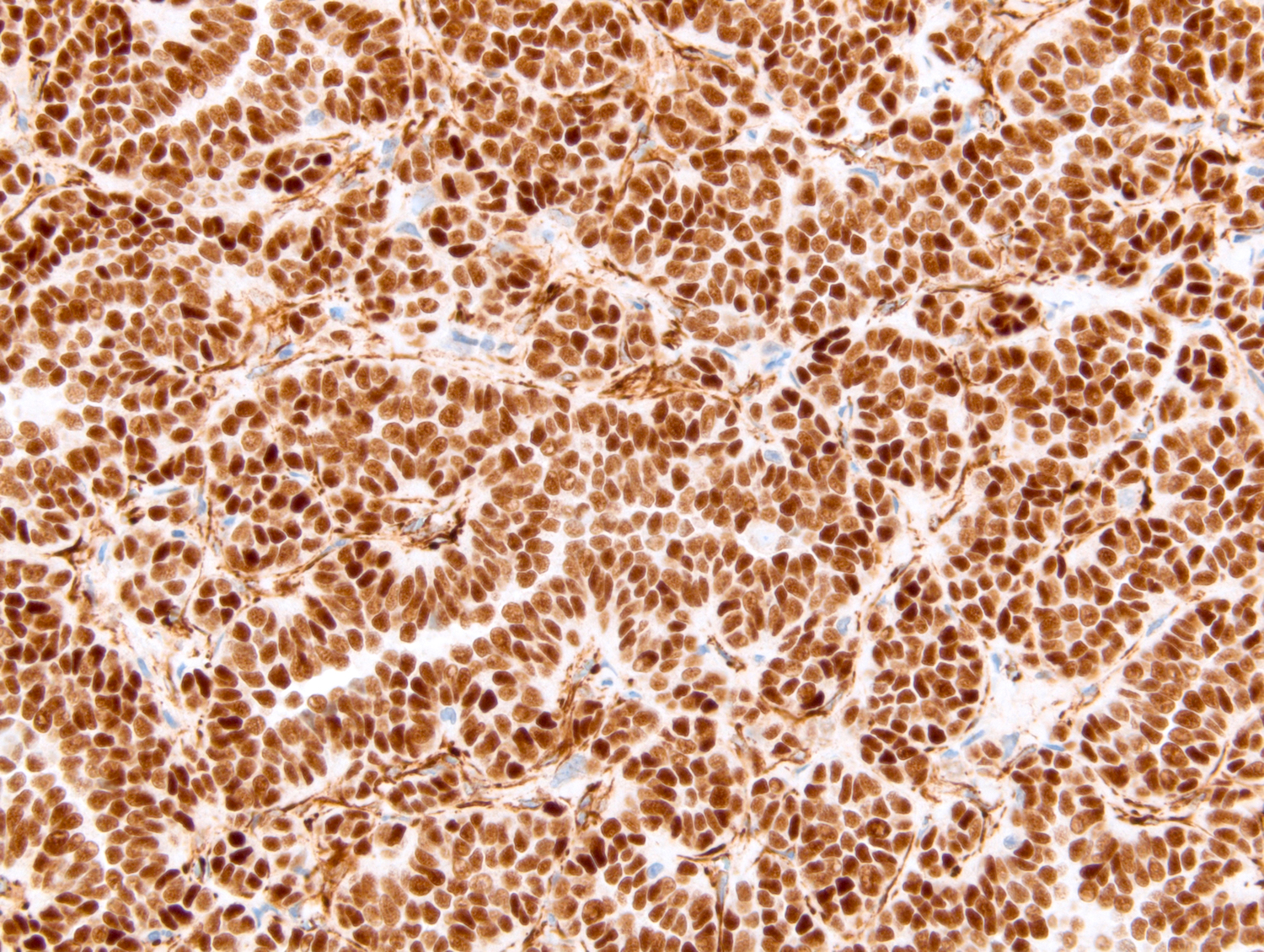
- WT1 and CD57 coexpression is a usual finding (Mod Pathol 2015;28:1236)
- BRAF is highly sensitive (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:549, Histopathology 2015;66:901)
- PAX8
- Cadherin 17 (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:549)
Negative stains
- AMACR (Diagn Pathol 2018;13:54, Mod Pathol 2006;19:218)
- CK7 (can be focal) (Diagn Pathol 2018;13:54)
- CD56, EMA
Electron microscopy description
- Cilia on the luminal side resting on abundant basement membrane (Mod Pathol 1996;9:329)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- BRAF V600E gene mutation is a common finding (Eur Urol 2012;62:917)
- Rare cases with BRAF pV600D or BRAF pK601L gene mutations (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:549)
- 1 case of BRAF gene fusions has been reported (Diagn Pathol 2018;13:54)
- 2 cases without BRAF mutations have a t(9;15)(p24;q24) translocation, resulting in a KANK1::NTRK3 gene fusion (Cancer Genet 2017;214:9)
Sample pathology report
- Right kidney, partial nephrectomy:
- Metanephric adenoma, 3.5 cm in greatest dimension (see comment)
- Surgical margins, negative for tumor
- Comment: The sections show well circumscribed tumor composed of tightly packed tubules. The nuclei are small and devoid of nucleoli. No mitotic activity or necrosis is present. The cytoplasm is scant. Numerous psammomatous calcifications are present. Immunohistochemical stains for WT1 and BRAF are positive.
Differential diagnosis
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma, particularly solid variant:
- Metanephric-like ALK rearranged renal cell carcinoma:
- Morphology is similar to metanephric adenoma with small tubules, some of which are elongated
- Metanephric adenoma-like morphology seen in 1 case only at the periphery, with the rest of the tumor being morphologically heterogeneous
- Vimentin+, PAX8+, CK7+, ALK+, AMACR+, BRAF-, CD57-, WT1- (Mod Pathol 2020;33:2564, Virchows Arch 2020;476:921)
- Nephroblastoma:
- Metastatic thyroid carcinoma, particularly poorly differentiated:
Board review style question #1
- A 66 year old woman with flank pain is found to have polycythemia. The CT scan shows a 3.8 cm solid, circumscribed and hypovascular renal cortical tumor. Which of the following renal tumors is likely to be associated with this clinical presentation, imaging study and the histomorphology shown above?
- Angiomyolipoma, triphasic
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Metanephric adenoma
- Nephroblastoma
- Urothelial carcinoma
Board review style answer #1
C. Metanephric adenoma is associated with polycythemia and a hypovascular renal mass on imaging. The section shows a well circumscribed renal tumor composed of tightly packed tubules. Answer A is incorrect because angiomyolipoma contains adipose tissue, which is easily seen on CT scan. Answer D is incorrect because the patient’s age argues against the diagnosis of nephroblastoma. Answer E is incorrect because urothelial carcinoma is neither a cortical tumor nor is it circumscribed. Answer B is incorrect because clear cell renal cell carcinoma is a hypervascular tumor, although it can cause polycythemia and is not basophilic.
Comment Here
Reference: Metanephric adenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Metanephric adenoma
Board review style question #2
- A renal mass from a 43 year old woman shows a tumor composed of tightly packed basophilic tubules. The cell nuclei are cytologically bland and cytoplasm is scant. Numerous psammomatous calcifications are present. No mitotic activity or necrosis is present. Which of the following is the immunohistochemical profile that should be seen in this tumor?
- PAX8+, WT1+, CK7-, CD57+, BRAF+
- PAX8-, WT1+, CK7-, CD57+, BRAF-
- PAX8+, WT1+, CK7-, CD57+, BRAF-
- PAX8+, WT1-, CK7-, CD57+, BRAF+
- PAX8+, WT1-, CK7+, CD57+, BRAF+
Board review style answer #2
A. PAX8+, WT1+, CK7-, CD57+, BRAF+. This is a metanephric adenoma. The differential diagnoses include papillary renal cell carcinoma, type 1, solid variant and adult epithelial predominant nephroblastoma. Papillary renal cell carcinoma, type 1 is a PAX8+, vimentin+, CK7+, AMACR+, WT1-, CD57-, BRAF- tumor, as opposed to metanephric adenoma, which is positive for WT1, CD57 and BRAF and negative for CK7. Adult nephroblastoma is positive for WT1 but negative for CD57 and BRAF.
Comment Here
Reference: Metanephric adenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Metanephric adenoma