Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Valencia A, Gordetsky JB, Craig JC. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytumormalignantmucinoustubular.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Distinct polymorphic, malignant renal cell neoplasm composed of bland anastomosing tubules, spindle cell areas and myxoid stroma / extracellular mucin
Essential features
- Compact tubules lined by bland cuboidal or flattened cells merging with low grade spindle cell areas
- Myxoid stroma with basophilic extracellular mucin
- Absence of distinct, well formed papillae
- References: Eur Urol 2022;82:458, Mod Pathol 2021;34:1392, Diagn Pathol 2015;10:168, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2020;144:115
Terminology
- Historic terminology not recommended by WHO 2022
- Low grade tubular mucinous renal neoplasm
- Low grade collecting duct carcinoma
- Low grade myxoid renal epithelial neoplasm with distal nephron differentiation
Epidemiology
- Accounts for < 1% of all renal neoplasms
- Median age: 50 - 60 years
- F > M
- References: Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:767, Clin Genitourin Cancer 2019;17:268, BJU Int 2015;116:85
Sites
- Kidney
Pathophysiology
- These tumors have a phenotypic expression pattern similar to the loop of Henle region of normal nephrons (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1571)
- Hippo pathway dysregulation with increased nuclear YAP1 protein expression (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:767)
- CDKN2A or CDKN2B deletion may be present in high grade tumors (Mod Pathol 2021;34:445)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Most cases are asymptomatic
- Incidental finding on imaging
Diagnosis
- Essential morphologic features include anastomosing tubules lined by low grade cells
- Tubules should merge with areas of bland spindle cells
- Areas of myxoid stroma or extracellular mucin should be present
- References: Eur Urol 2022;82:458, Mod Pathol 2021;34:1392, Diagn Pathol 2015;10:168, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2020;144:115
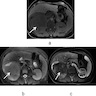
Radiology description
- Majority are homogeneous
- Small subset may show cystic changes, which is more commonly seen in papillary renal cell carcinoma (RCC)
- Typically isodense or hypodense on unweighted CT
- Hyperintense on T2 due to extracellular mucin
- Appears unencapsulated
- References: Br J Radiol 2021;94:20210548, Abdom Radiol 2021;46:5250
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Indolent behavior (Clin Genitourin Cancer 2019;17:268)
- Rarely metastatic (e.g., with epithelial anaplasia or sarcomatoid differentiation)
Case reports
- 39 year old man with right lower back pain and 8 cm kidney mass (Urol Case Rep 2021:40:101889)
- 40 year old woman with incidental kidney mass (J Kidney Cancer VHL 2022;9:10)
- 45 year old man with incidental kidney mass (Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e12933)
- 69 year old man with kidney mass and osseous lesions (IJU Case Rep 2021;4:333)
Treatment
- Surgical excision is the mainstay of treatment
- Selected cases received adjuvant therapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors and PD-1 inhibitors (Clin Genitourin Cancer 2019;17:268)
Gross description
- Well circumscribed, solid, homogenous (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2020;144:115)
- Capsule may be present (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2020;144:115)
- Tan, gray-pink or pale yellow cut surface (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2020;144:115)
- Typically intraparenchymal or partially exophytic mass (BMC Cancer 2023;23:815)
- Most masses are small (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2020;144:115)
- Areas of hemorrhage and necrosis are rare (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2020;144:115)
Frozen section description
- Elongated tubules with low grade epithelial lining merging with areas of low grade spindled cells in a myxoid background
- Extracellular mucin may be present
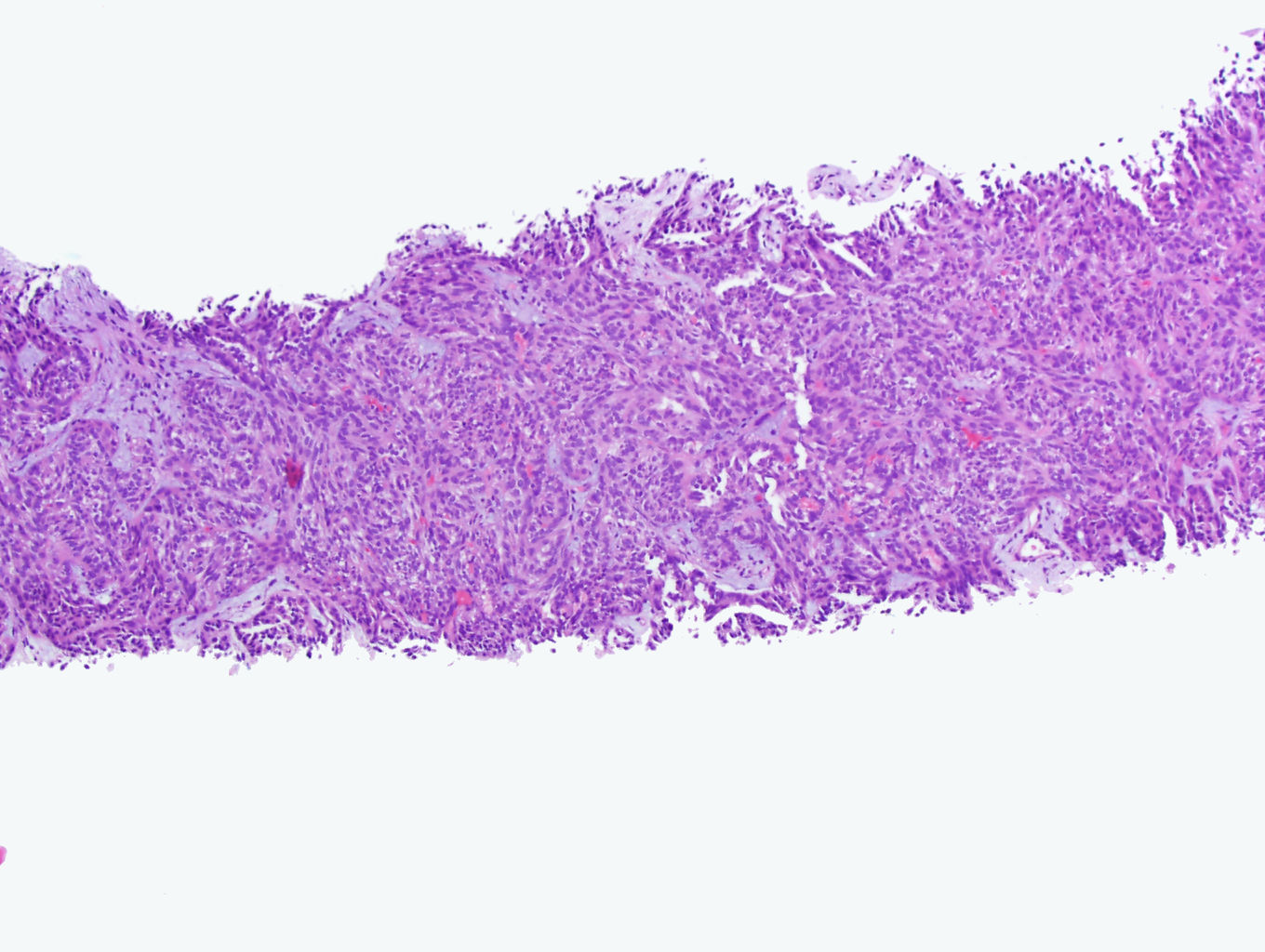
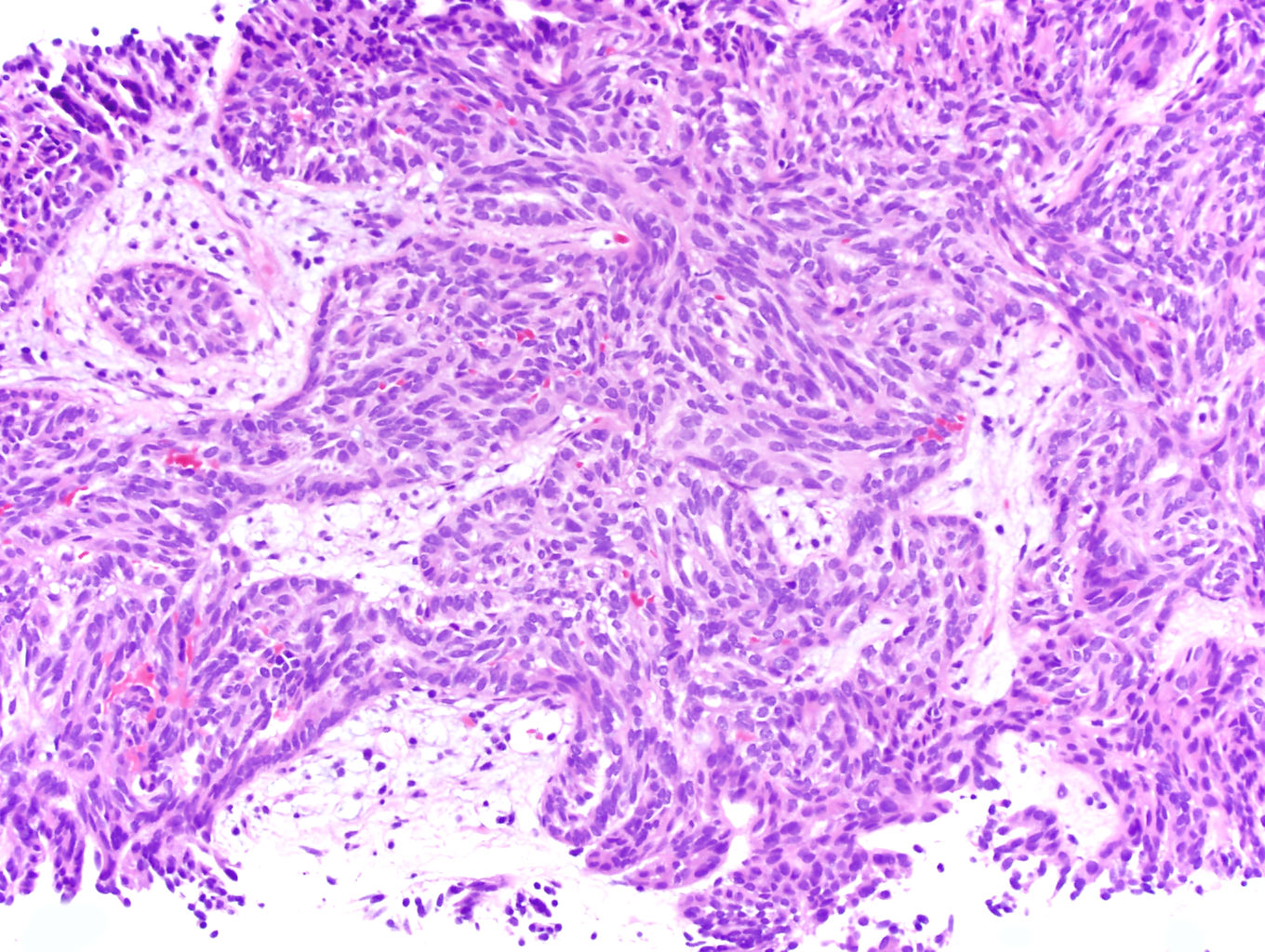
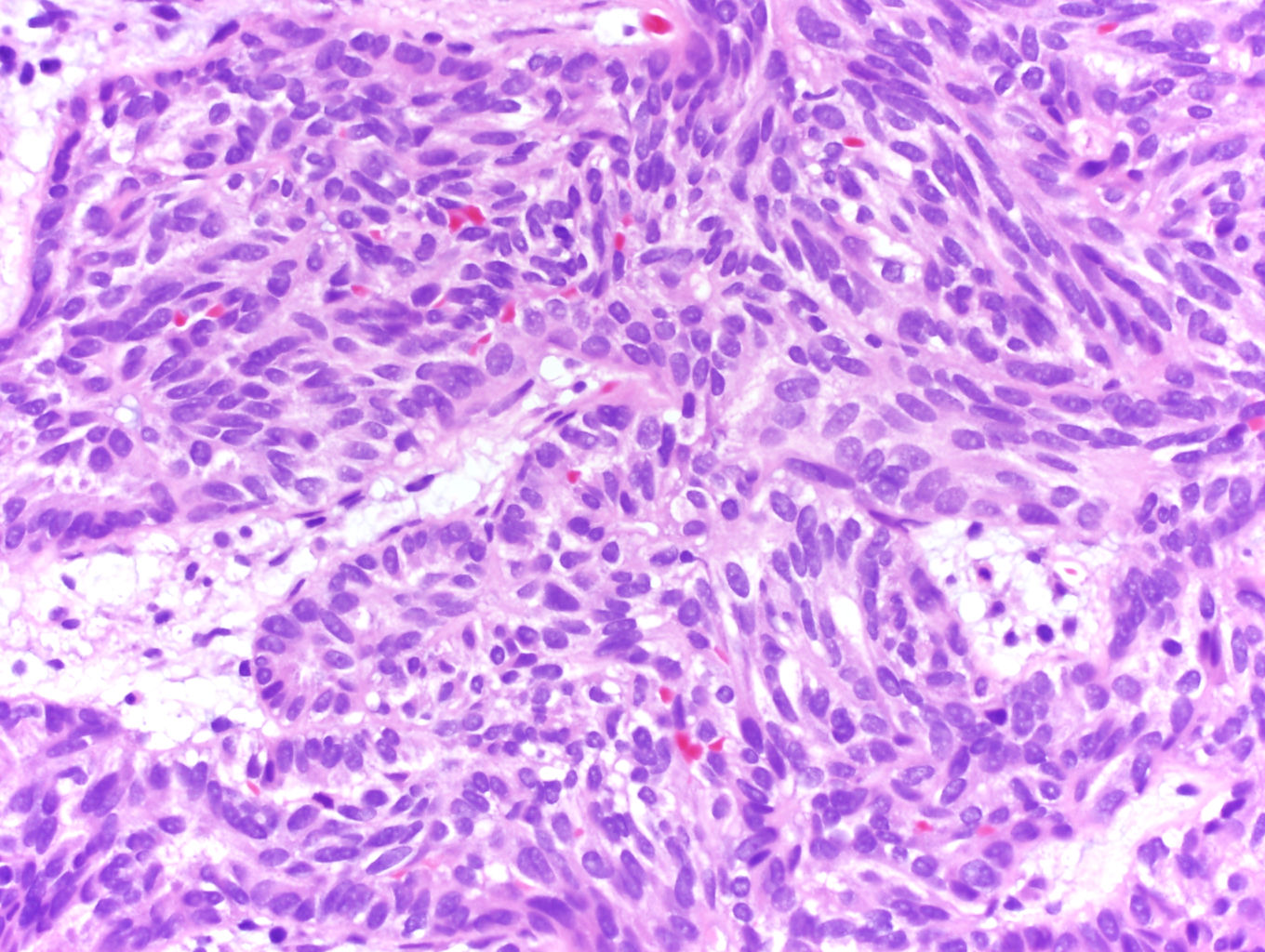
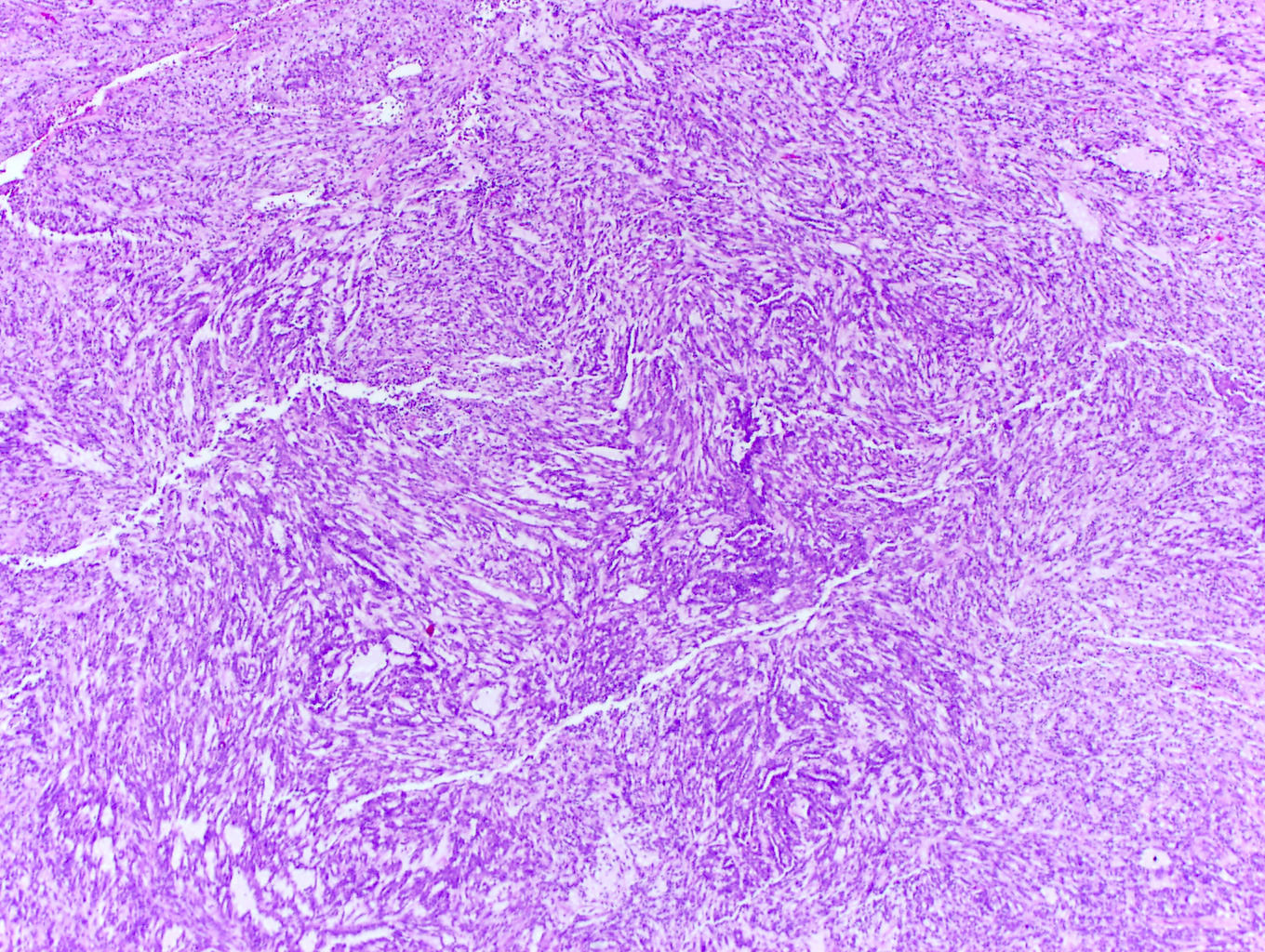
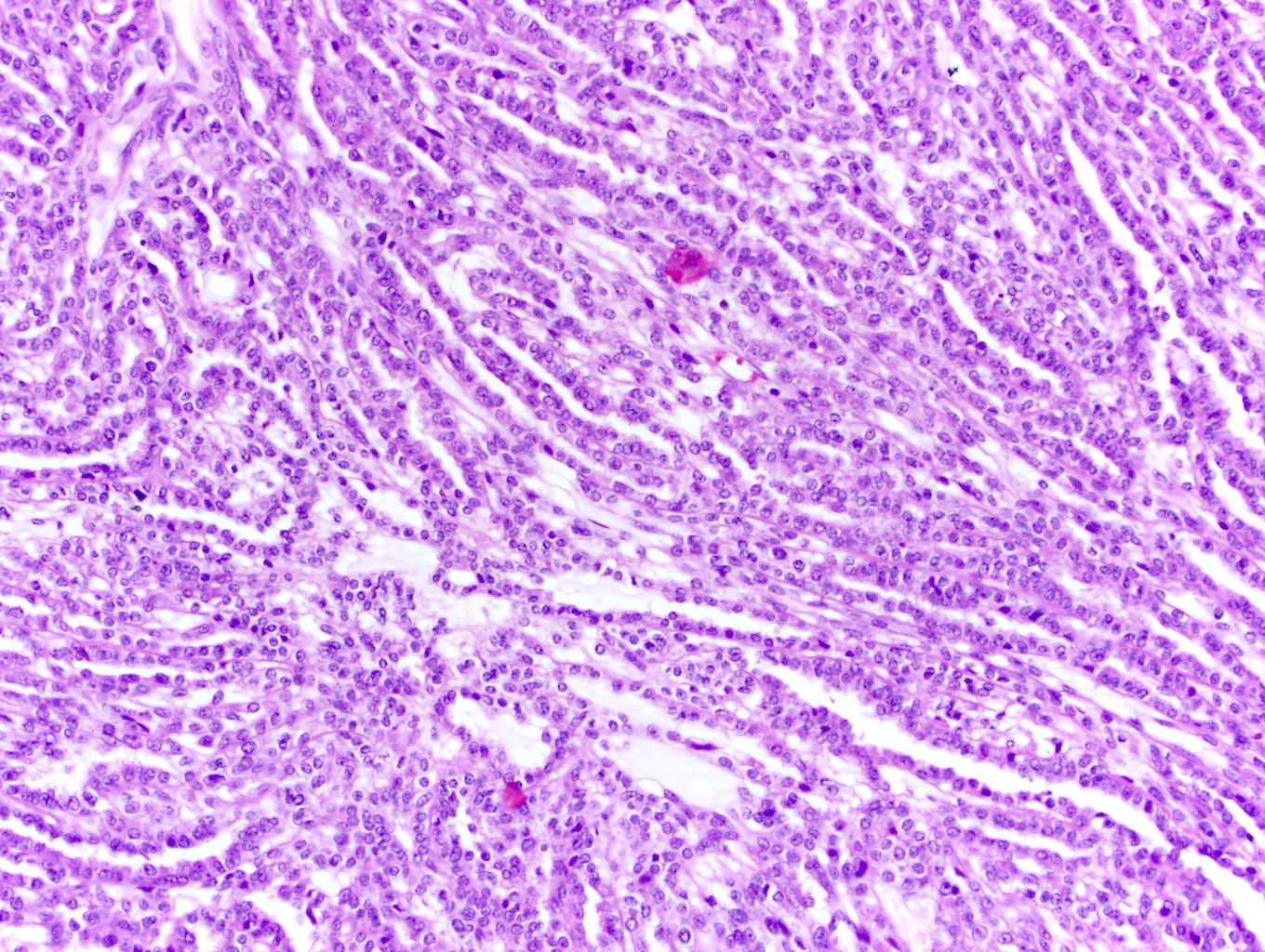
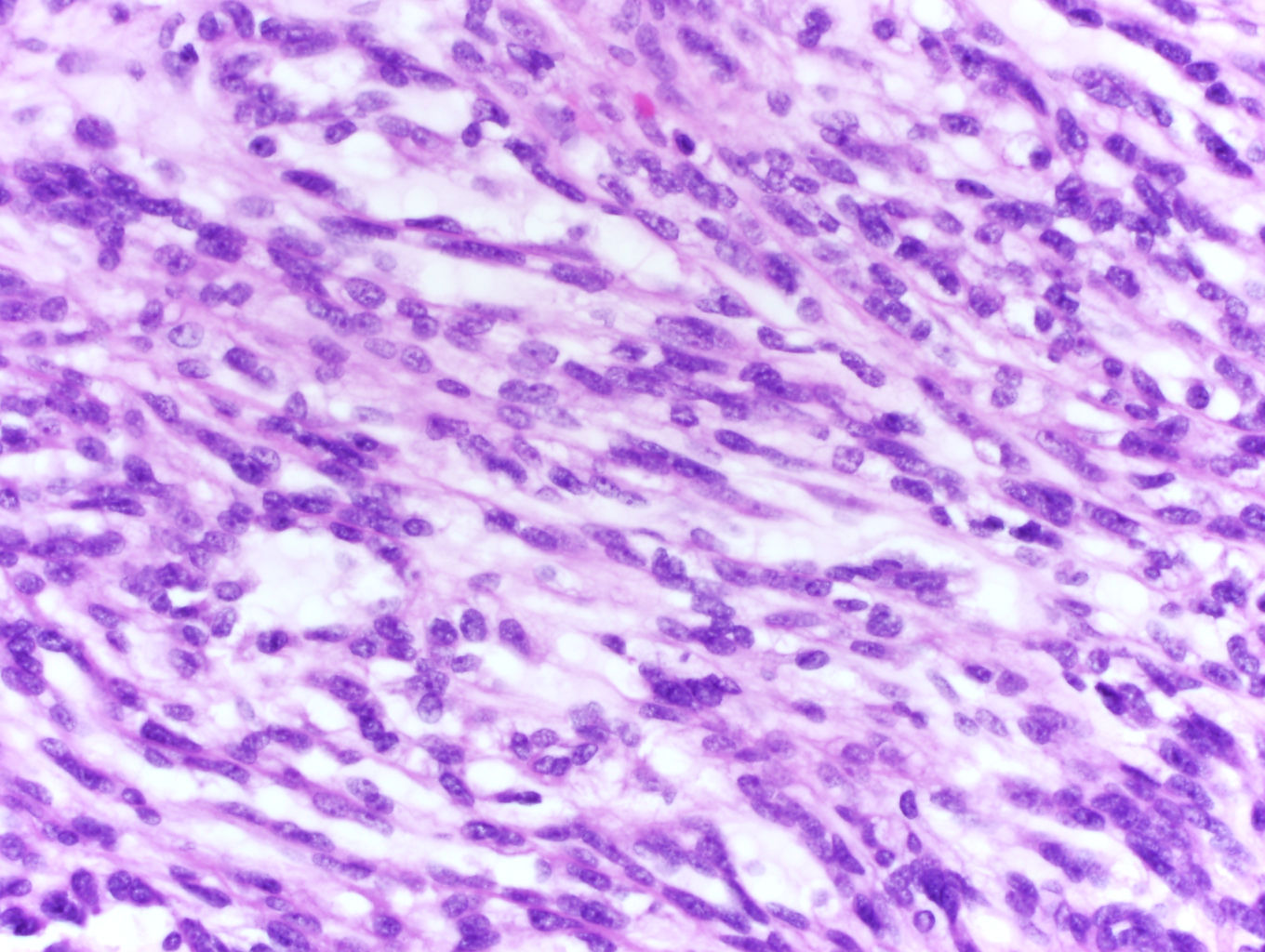
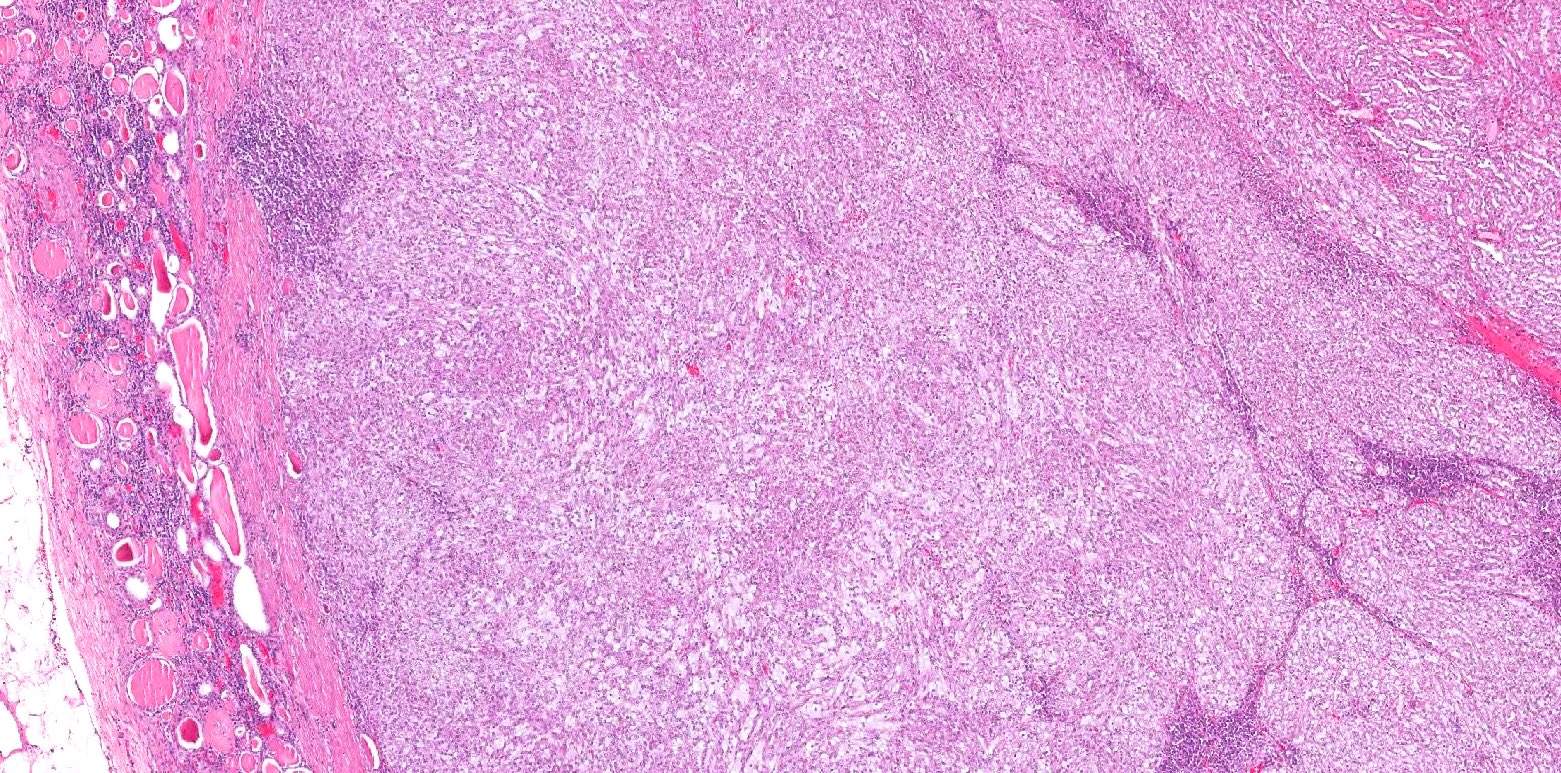
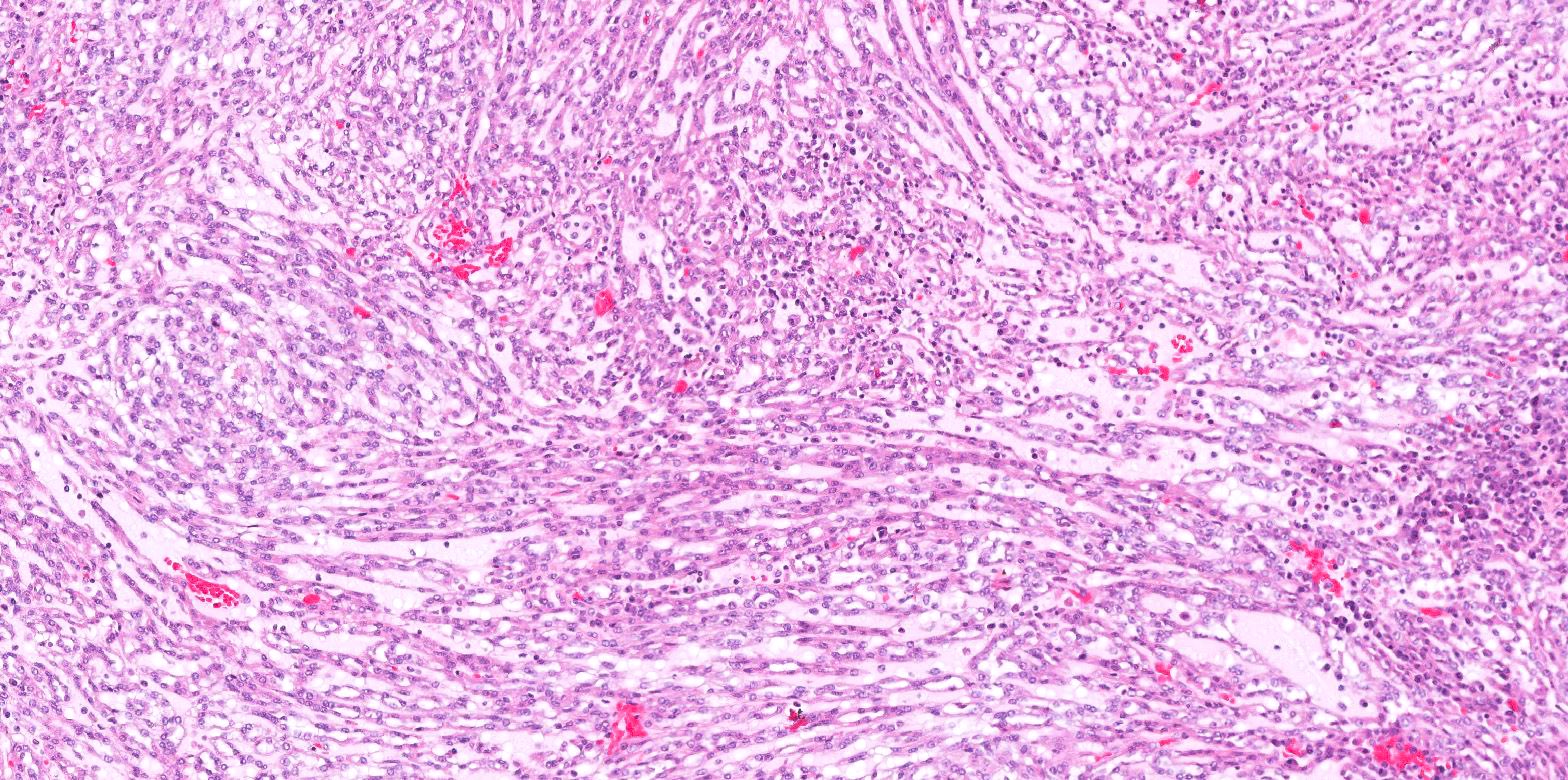
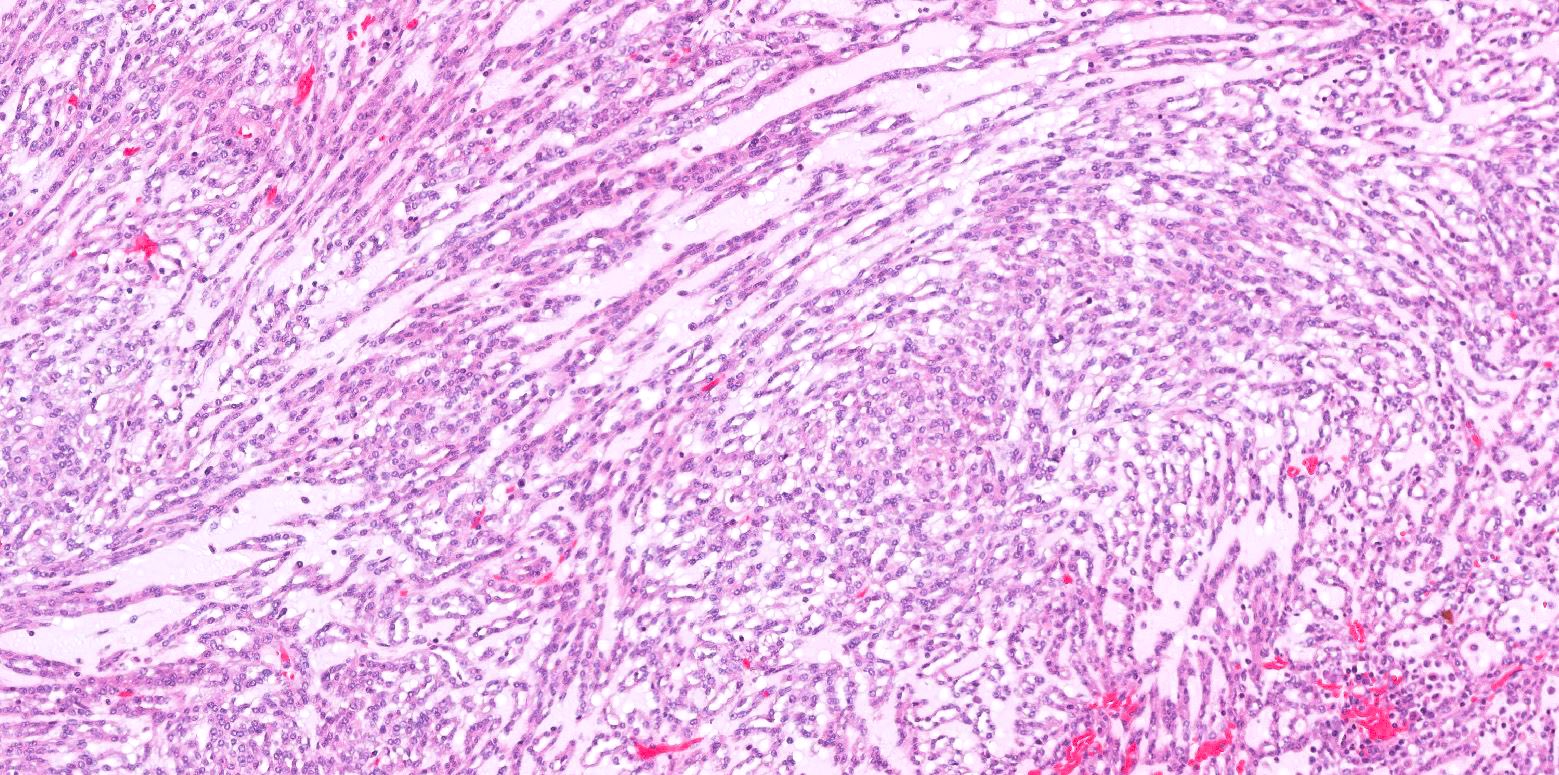
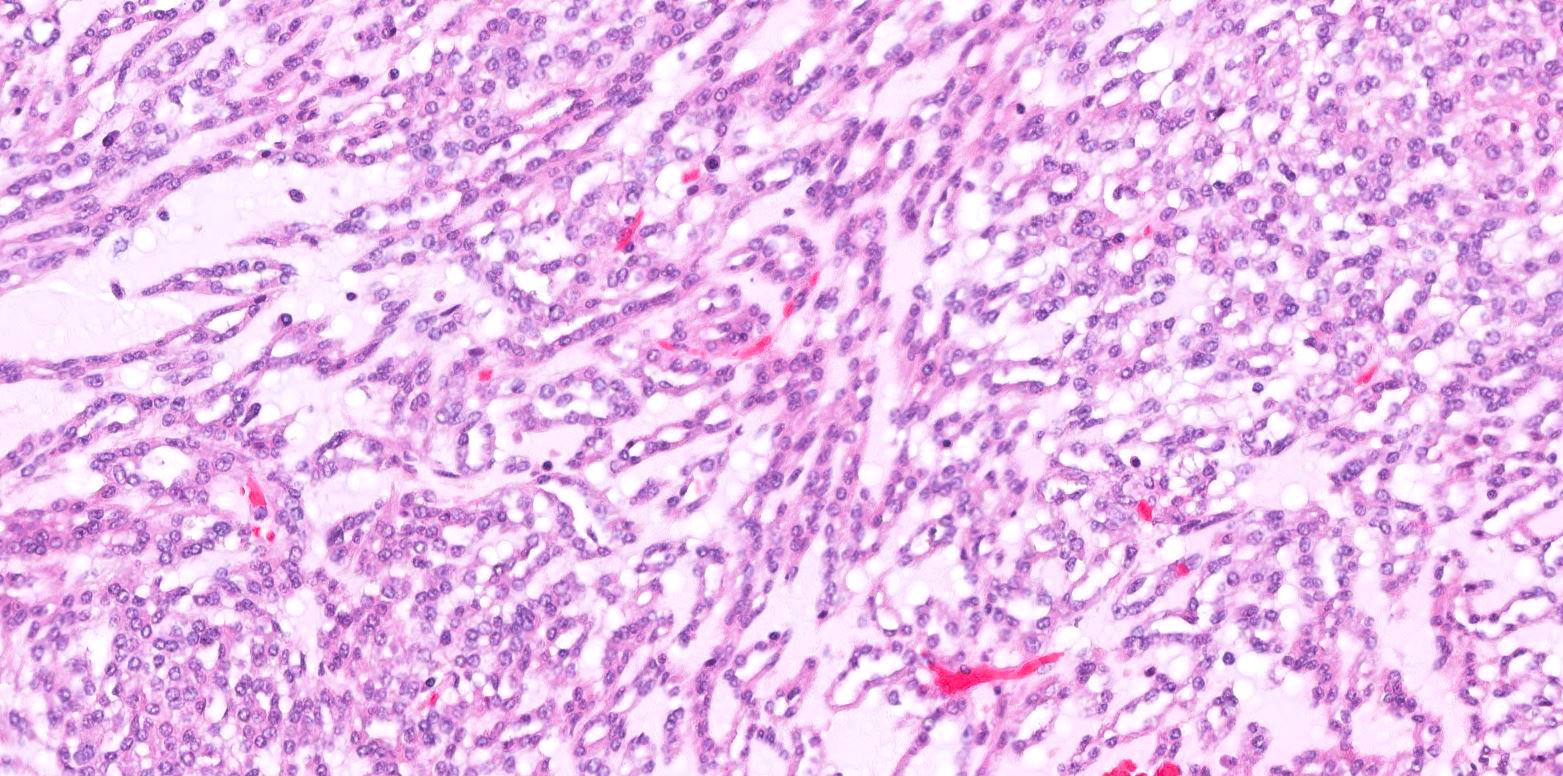
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Bland tubules merging with bland spindle cells in a myxoid stroma
- Absence of distinct, well formed papillae
- Tightly packed tubules and spindle cell areas with smooth lumina
- Compact arrangements of whorled tubules
- Areas of myxoid stroma
- Presence of a capsule or foamy macrophages may be present
- High nucleolar grade or extensive necrosis have been described as occurring in rare cases (Histopathology 2017;71:719)
- References: Eur Urol 2022;82:458, Mod Pathol 2021;34:1392, Diagn Pathol 2015;10:168, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2020;144:115
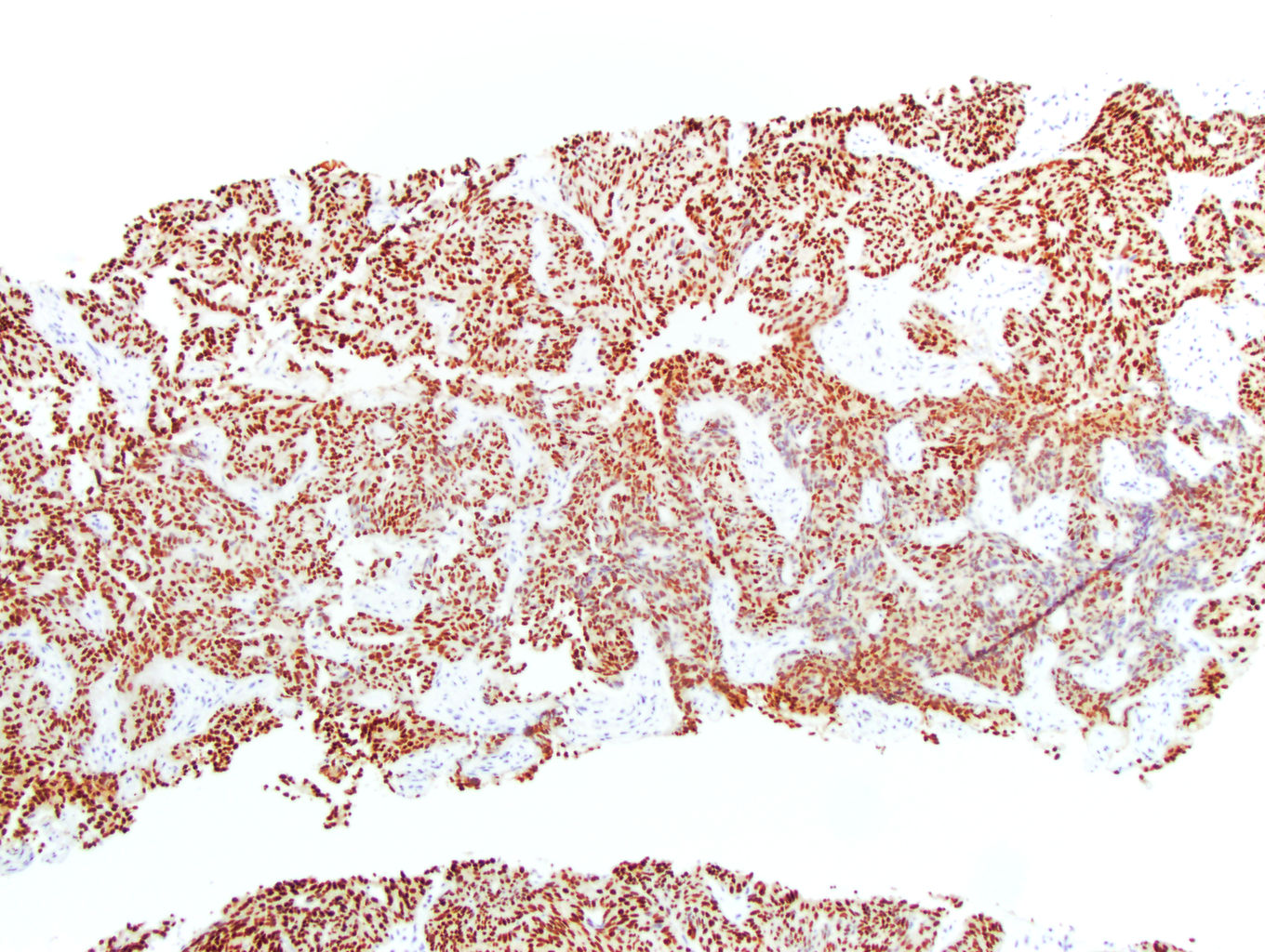
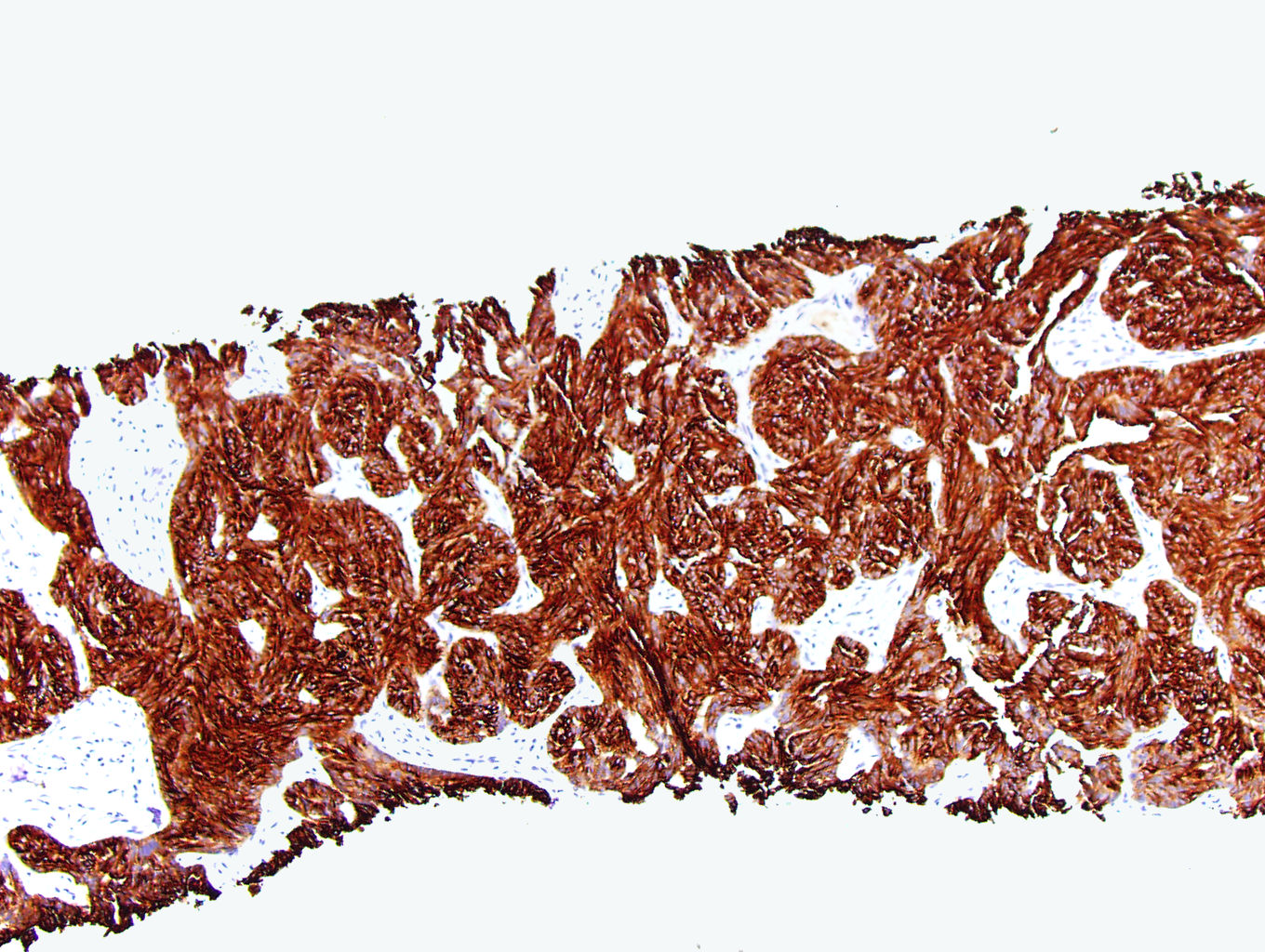
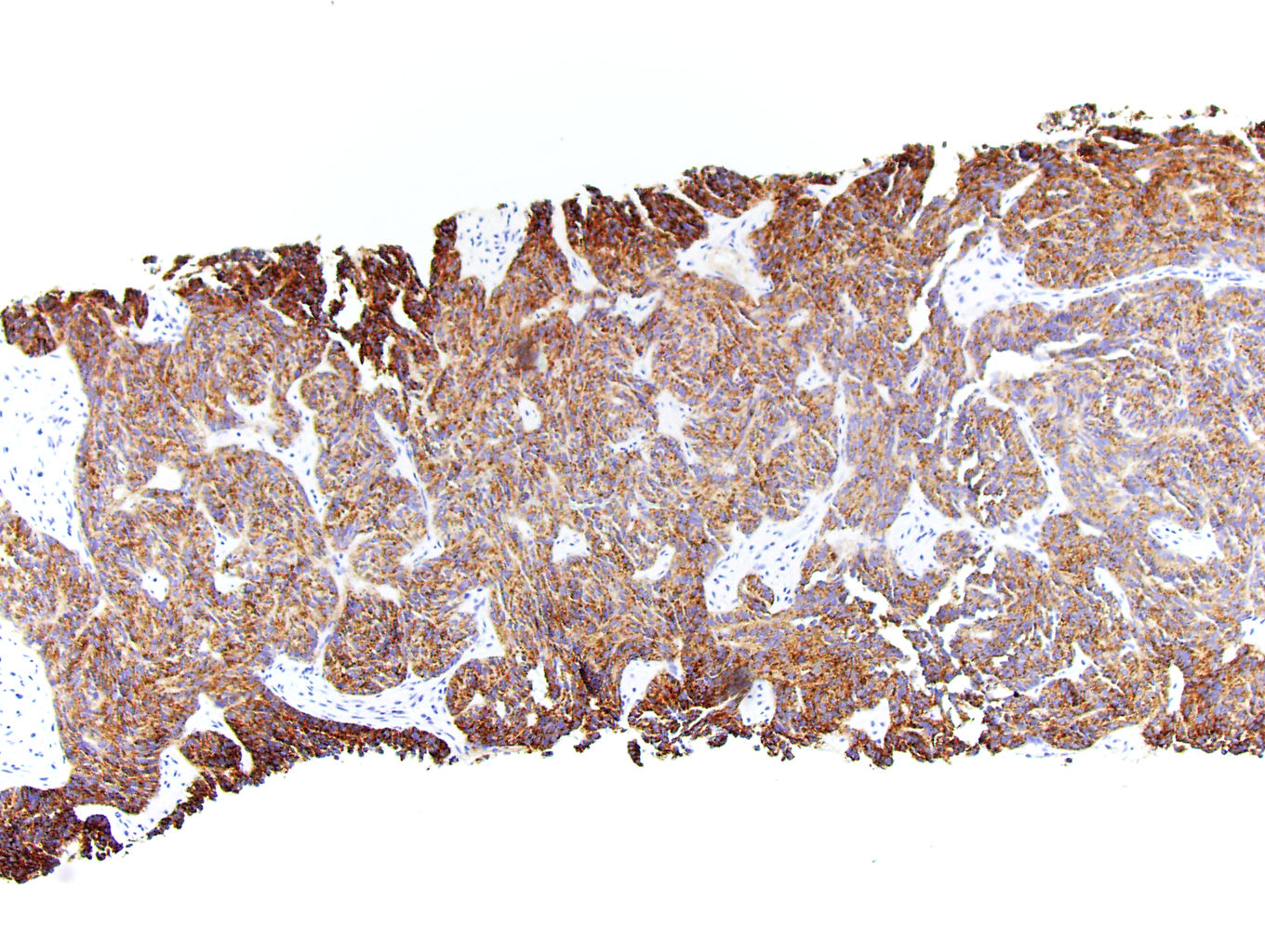
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by J. Cody Craig, M.D., Aida Valencia, M.D., Jennifer B. Gordetsky, M.D. and @katcollmd on Twitter
Positive stains
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Tightly packed, often elongated tubules composed of slender attenuated cells, similar to those found in the normal loop of Henle (Int Braz J Urol 2002;28:477)
- Discontinuation of the tubular basement membranes (Int Braz J Urol 2002;28:477)
- Low columnar, cuboidal and spindle cells with a low nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio (Pathol Res Pract 2014;210:454)
- Small nuclei with small nucleoli, dispersed chromatin and smooth nuclear membranes (Pathol Res Pract 2014;210:454)
- Scant cytoplasmic organelles and intermediate filaments (Pathol Res Pract 2014;210:454)
- Short apical microvilli and well developed desmosomes at the site of attachment between the apposing cell membranes (Pathol Res Pract 2014;210:454)
- Foamy macrophages may be present (Pathol Res Pract 2014;210:454)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Monosomy of chromosomes 1, 6, 9, 14, 15 and 22 (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:767)
- Multiple loss of chromosomes 1, 4, 6, 8, 9, 13, 14, 15 and 22 (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:767)
- FISH shows no VHL deletions (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:767, Int Braz J Urol 2002;28:477)
- Recurrent chromosomal losses and somatic mutations of genes in the Hippo pathway (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1571)
- Moderate to high expression of VSTM2A via RNA in situ hybridization (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1571)
- Biallelic loss of Hippo pathway tumor suppressor genes (PTPN14, NF2, SAV1) (Cancer Discov 2016;6:1258)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Kidney, right, radical nephrectomy:
- Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma, 3 cm (see comment)
- Organ confined
- Margins negative for tumor
- No tumor necrosis identified
- No sarcomatoid or rhabdoid features identified
- No metatasis to lymph nodes
- Pathologic stage: pT1a pN0 pMx
- Comment: The specimen shows a kidney composed of low grade tubules merging with areas of spindled cells in a myxoid stroma. No well formed papillary areas are present. Immunohistochemical stains show positivity for PAX8, CK7, racemase and vimentin.
Differential diagnosis
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1353):
- Papillary architecture
- May have necrosis
- Papillary cores show psammoma bodies or foamy macrophages
- Lack of spindled stroma and mucin
- There is no difference in the nuclear expression of YAP / TAZ between mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma and papillary renal cell carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:767)
- Frequently positive for CD10
- Renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation (Mod Pathol 2021;34:1392):
- High grade cytologic atypia in spindle cells
- Abrupt transition from epithelial to spindle cell component
- Presence of distinct alternative histologic subtype (clear cell, papillary, etc.)
- ALK rearrangement associated renal cell carcinoma (Diagn Pathol 2022;17:52):
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
C. PAX8+, CK7+, vimentin+, racemase+. The images show a mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma, which should show positive staining for PAX8, CK7, racemase and vimentin. Answer D is incorrect because this immunophenotype is more consistent with metastatic thyroid cancer. Answer B is incorrect because this immunophenotype is more consistent with a clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Answer A is incorrect because this immunophenotype is more consistent with mesothelioma.
Comment Here
Reference: Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma
Board review style question #2
Which of the following features would be most helpful in distinguishing a mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma from a renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid features?
- PAX8+, CK7+, vimentin+, racemase+
- Presence of foamy macrophages
- Retained FH and SDHB expression on IHC
- VHL mutation on molecular studies
Board review style answer #2
D. VHL mutation on molecular studies. VHL mutations are not found in mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinomas. This would be more consistent with a clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Answer A is incorrect because this immunophenotype can be found in papillary renal cell carcinoma. Answer C is incorrect because this immunophenotype excludes an SDHB deficient or an FH deficient RCC but many other renal cell neoplasms can have this finding. Answer B is incorrect because mesothelial tumors will express both CK5/6 and D2-40.
Comment Here
Reference: Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma