Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology / etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Cheng L, Tretiakova M. Hemangioblastoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytumormalignanthemangioblastoma.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Very rare, benign tumor in kidney, with fewer than 20 cases reported in English literature (Clin Case Rep 2019;7:2321)
- Renal counterpart of the central nervous system (CNS) hemangioblastoma
Essential features
- Lipoblast-like epithelioid cells with abundant cytoplasmic microvacuoles
- Complex network of thin walled vessels in arborizing or pericytomatous patterns
- Positive for inhibin, S100, neuron specific enolase (NSE) and vimentin
Terminology
- Also known as capillary hemangioblastoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9161/1 - hemangioblastoma
- ICD-10: D30.0 - benign neoplasm of kidney
- ICD-11: 2F98 & XH6810 - neoplasms of unknown behavior of urinary organs & hemangioblastoma
Epidemiology
- M = F (in contrast to CNS hemangioblastoma, which is male predominant)
- Age range: 16 - 71 (Diagn Pathol 2012;7:49, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1545)
- Sporadic, not associated with von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease (different from CNS hemangioblastoma, which is associated with VHL in 25% of cases) (Clin Case Rep 2019;7:2321)
Sites
- Extracranial locations include but are not limited to kidney, intestine, orbit, forearm, peritoneum, periadrenal soft tissue, flank and peripheral nerve (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:119)
Pathophysiology / etiology
- Unknown at this time
Clinical features
- Mostly asymptomatic (Clin Case Rep 2019;7:2321)
- Occasionally hematuria or abdominal pain
Diagnosis
- Radiographic studies showing renal mass
- Histological examination on renal biopsy or resection specimen
Laboratory
- Rare case showing polycythemia (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1695)
- No increase of erythropoietin (EPO)
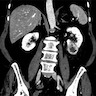
Radiology description
- Usually unilateral solid renal mass
- Rare case showing multiple renal lesions (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:119)
- Rare cases containing cystic spaces (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1545, Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1695)
Prognostic factors
- Benign tumor, no distant metastasis
- Persistent disease after incomplete resection (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:119)
Case reports
- 51 year old woman with right kidney mass (Hum Pathol 2013;44:2247)
- 57 year old woman with right kidney mass (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6:1953)
- 61 year old man with left kidney mass (Diagn Pathol 2022;17:34)
- 72 year old woman with left kidney mass (Clin Case Rep 2019;7:2321)
- 5 cases of renal hemangioblastomas (J Clin Pathol 2015;68:1020)
Treatment
- Surgical resection
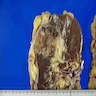
Gross description
- Well circumscribed, lobulated, gray to brown, solid
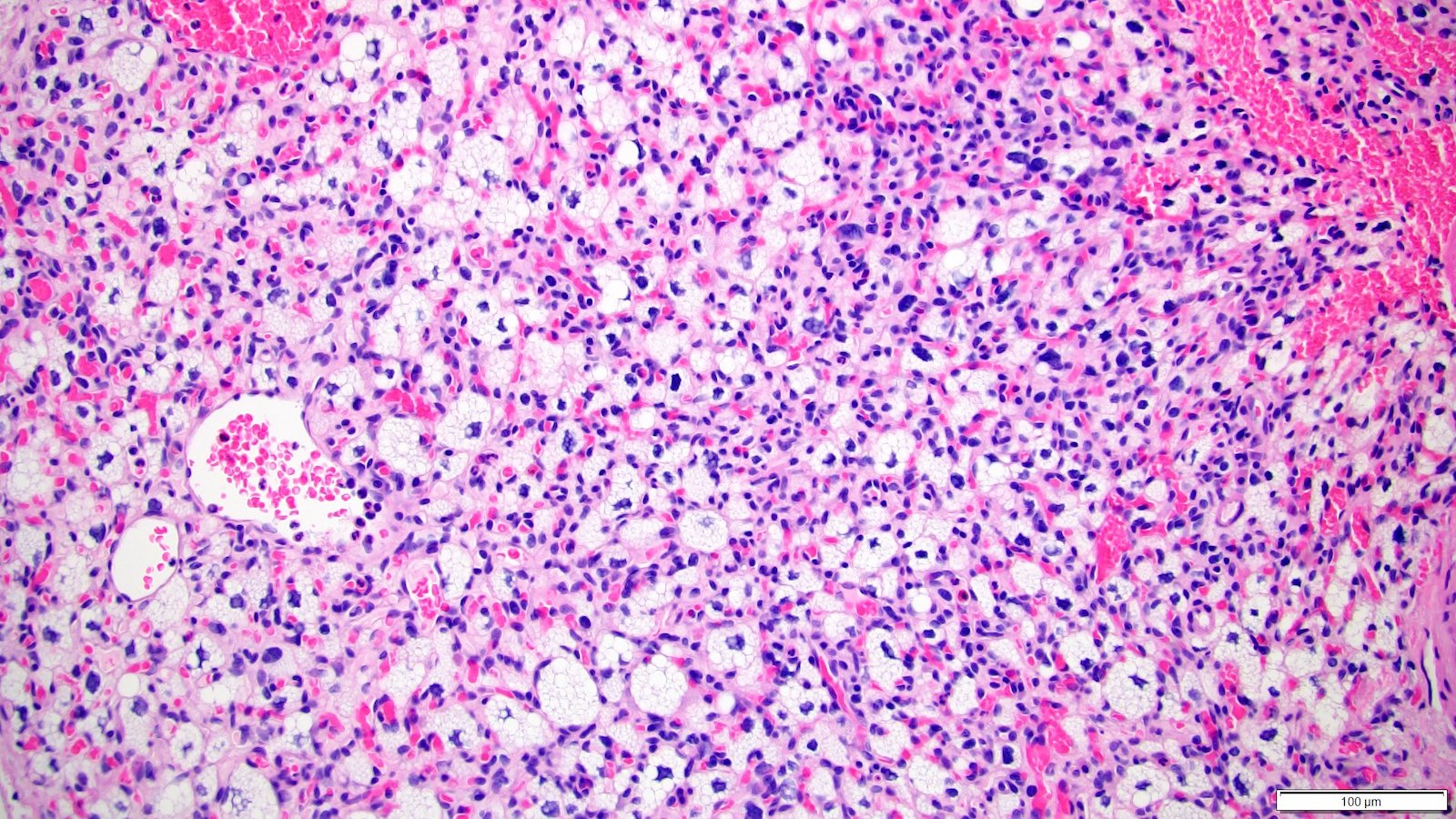
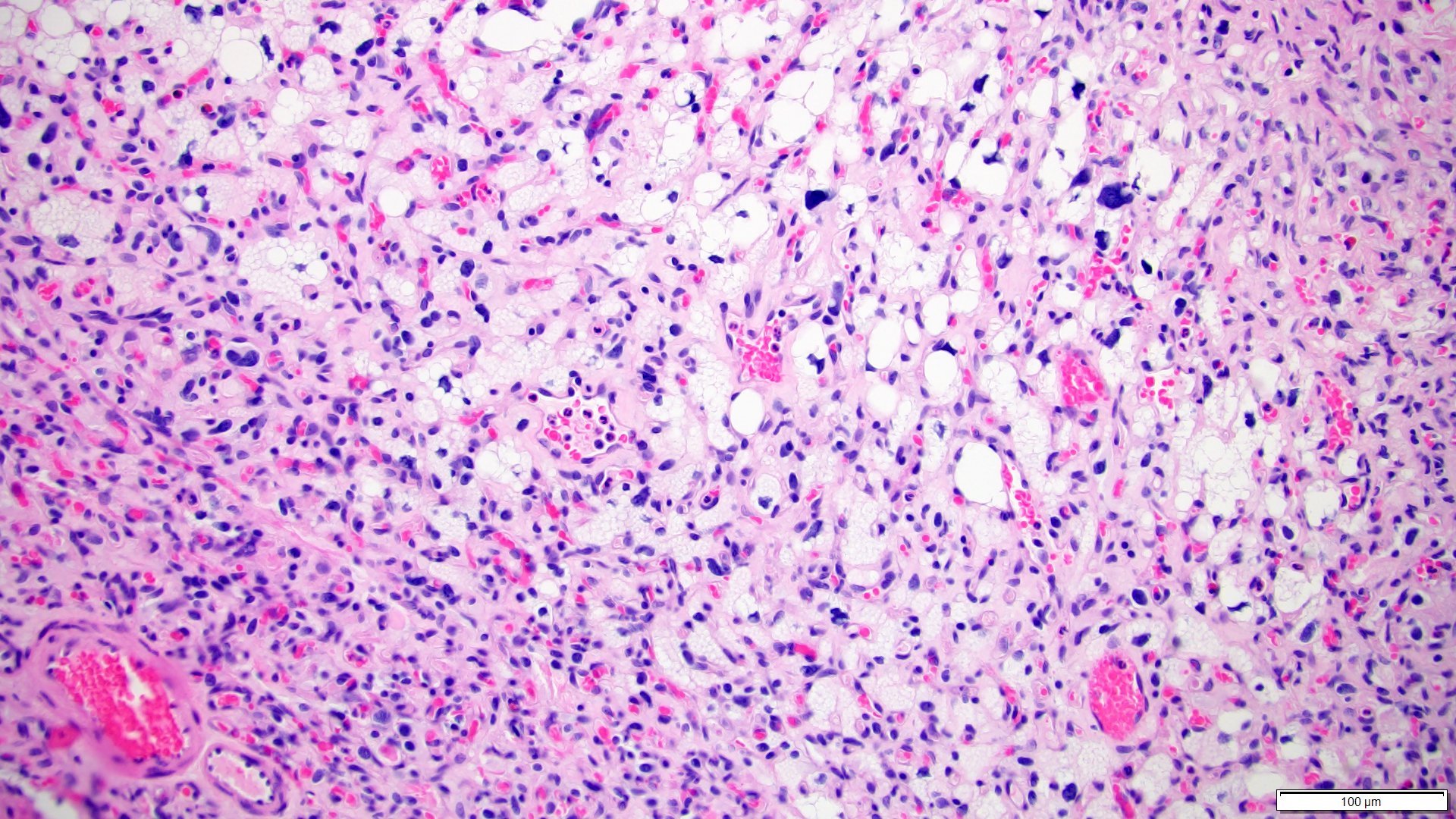
Microscopic (histologic) description
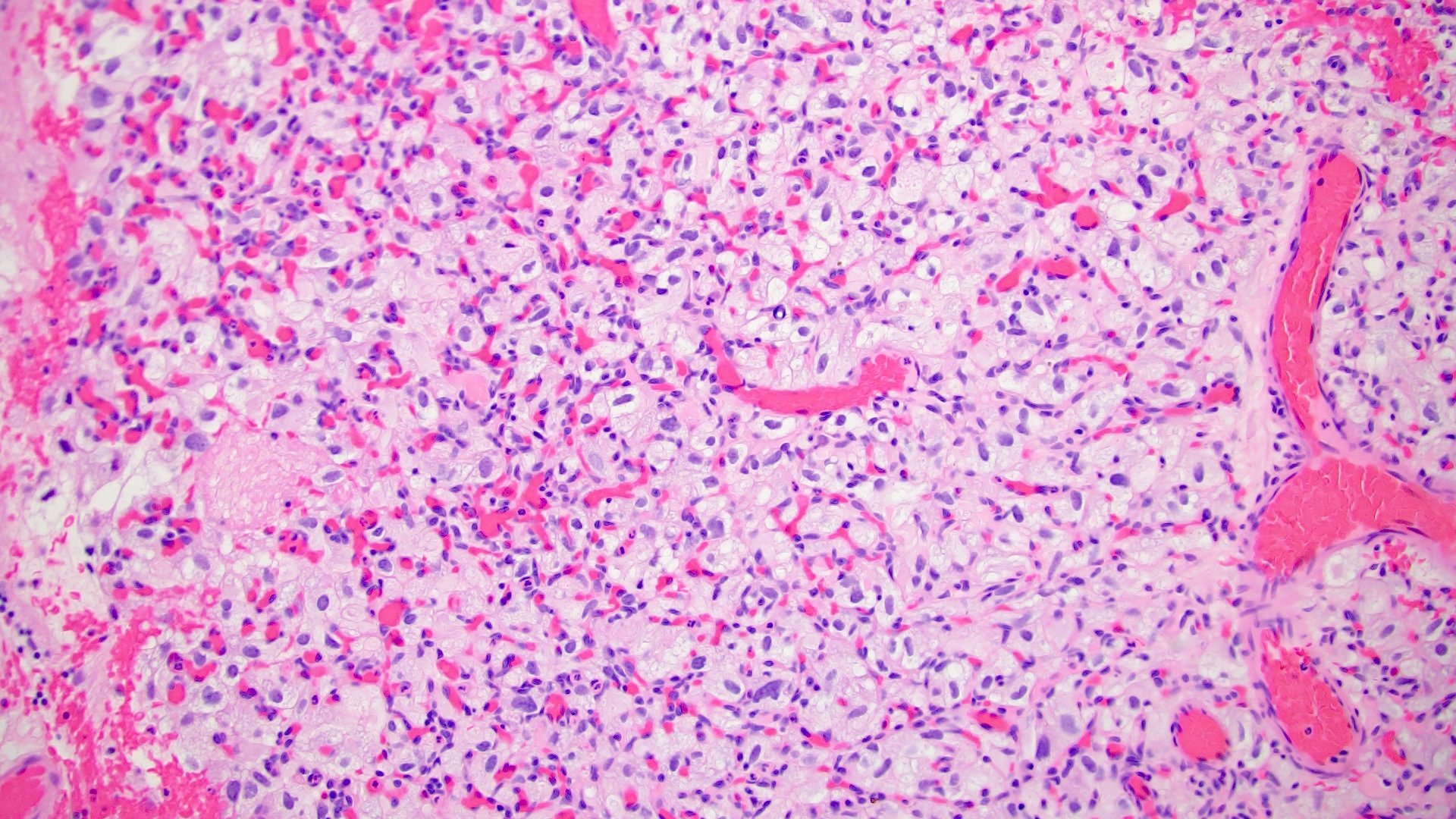
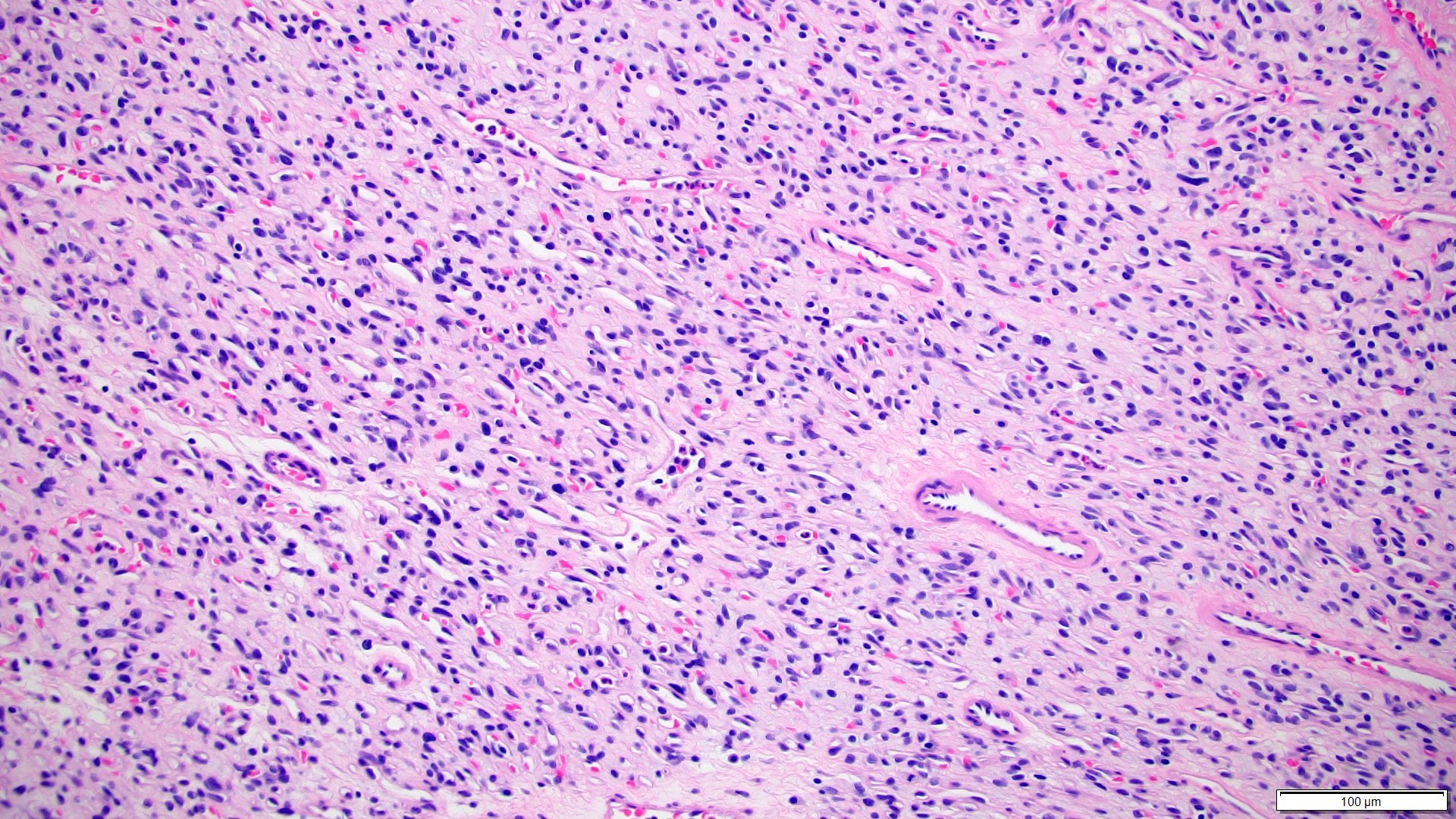
- Sheets, lobulated or nested growth pattern
- Round to oval shaped cells containing microvacuoles in eosinophilic or clear cytoplasm (so called stromal cells), mimicking lipoblasts
- Complex capillary network comprises mainly thin walled vessels
- Some areas show spindle cells surrounding vessels (so called pericytomatous pattern) (Int J Surg Pathol 2012;20:519)
- Focal areas may contain predominant spindle cells with minimal cytoplasm and vague vacuolization (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:119)
- Usually mild pleomorphism; however, occasional marked nuclear pleomorphism, rhabdoid features or pseudointranuclear inclusions can be seen (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:119, Diagn Pathol 2012;7:39)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
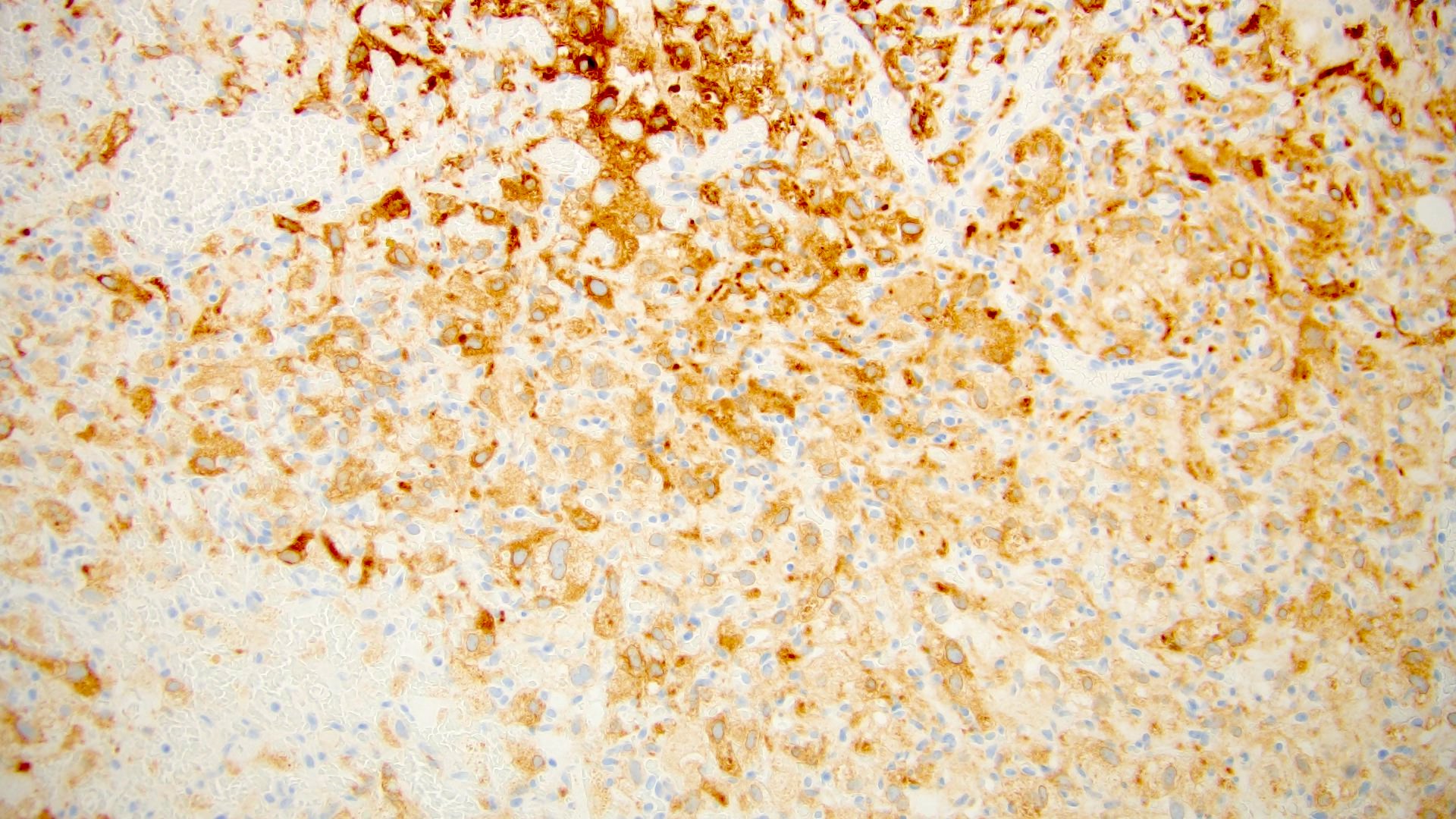
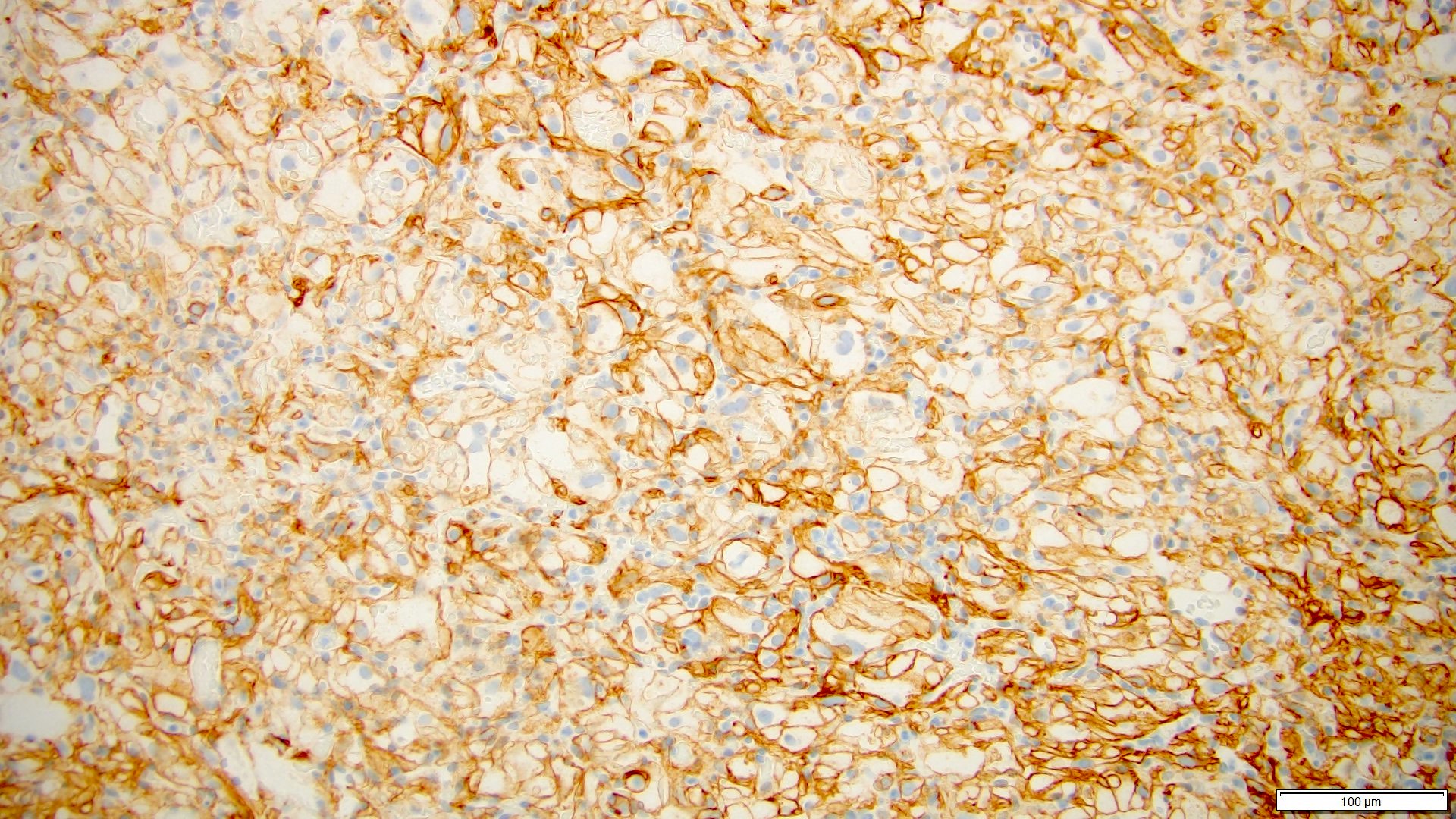
- Inhibin
- Vimentin
- S100
- Neuron specific enolase (NSE)
- PAX8: 100% positive (4 out of 4 cases) (Clin Case Rep 2019;7:2321)
- CD10: 67% positive (4 out of 6 cases) (Clin Case Rep 2019;7:2321)
- GLUT1: positive in 70% of extracranial hemangioblastomas (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:119)
- CAIX (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8:2131)
Negative stains
- AE1 / AE3: focal staining (Hum Pathol 2013;44:2247)
- EMA: focal weak staining in about 25% cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:119)
- Brachyury: positive in CNS hemangioblastoma (cytoplasmic) but not in extracranial tumors
- CD34: highlights the capillary network but negative in the stromal cells
- HMB45
- MelanA
- GFAP
- Myogenin
- Desmin
Sample pathology report
- Left kidney, partial nephrectomy:
- Hemangioblastoma (see comment)
- Surgical margins negative for tumor
- Comment: Clinically, this patient presented with incidental finding of left kidney mass. No other lesions or history of any malignancies are identified. The histological sections of the renal mass show sheets of round to oval atypical cells with complex capillary network. Some of the atypical cells show abundant microvacuoles within clear cytoplasm. Immunohistochemistry studies show that the atypical cells are positive for inhibin, PAX8, S100 and vimentin and negative for CK8 / 18, HMB45 and MDM2. The overall findings are suggestive of a hemangioblastoma, likely renal primary. Clinical correlation is recommended.
Differential diagnosis
- Renal cell carcinoma, clear cell type:
- Angiomyolipoma / PEComa:
- Atypical lipomatous tumor / well differentiated liposarcoma:
- Adrenal cortical carcinoma:
- Presence of adrenal lesion, involving kidney by direct extension or metastasis
- Lipid microvacuoles in cytoplasm
- Positive for inhibin, MelanA, synaptophysin and calretinin
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is the most common histological feature of hemangioblastoma?
- Admixture of adipose tissue, smooth muscle and thick walled vessels
- Lobules of mature adipocytes
- Spindle cells with cytoplasmic microvacuoles and complex capillary network
- Storiform fibrosis
- Sustentacular cells wrapped around chief cells, forming zellballen pattern
Board review style answer #1
C. Spindle cells with cytoplasmic microvacuoles and complex capillary network. Hemangioblastoma commonly shows spindle cells with cytoplasmic microvacuoles mimicking lipoblasts and a complex capillary network comprising mainly thin walled vessels. Answer A is incorrect because an admixture of adipose tissue, smooth muscle and thick walled vessels is a feature of angiomyolipoma. Answer B is incorrect because presence of lobules of mature adipocytes is a feature of lipoma. Answer D is incorrect because storiform fibrosis is seen in IgG4 related diseases. Answer E is incorrect because sustentacular cells wrapped around chief cells, forming zellballen pattern, is a feature of paraganglioma.
Comment Here
Reference: Hemangioblastoma
Comment Here
Reference: Hemangioblastoma
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is the most likely immunophenotype of kidney primary hemangioblastoma?
- PAX8+, AE1 / AE3+, inhibin-, HMB45-, S100-
- PAX8+, AE1 / AE3-, inhibin+, HMB45-, S100+
- PAX8-, AE1 / AE3-, inhibin-, HMB45+, S100+
- PAX8-, AE1 / AE3+, inhibin-, HMB45-, S100-
- PAX8-, AE1 / AE3-, inhibin-, HMB45-, S100-
Board review style answer #2
B. PAX8+, AE1 / AE3-, inhibin+, HMB45-, S100+. Most of the kidney primary hemangioblastomas are positive for PAX8, inhibin and S100. They are AE1 / AE3 negative and HMB45-, which can differentiate them from renal carcinomas and angiomyolipomas.
Answer A is incorrect because hemangioblastomas should be negative for AE1 / AE3. This immunophenotype can be seen in renal cell carcinomas.
Answer C is incorrect because kidney primary hemangioblastomas are commonly PAX8 positive. This immunophenotype can be seen in angiomyolipomas.
Answer D is incorrect because hemangioblastomas are negative for AE1 / AE3. This immunophenotype can be seen in epithelial neoplasms.
Answer E is incorrect because kidney primary hemangioblastomas are commonly positive for PAX8, inhibin and S100.
Comment Here
Reference: Hemangioblastoma
Comment Here
Reference: Hemangioblastoma