Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Chang HY, Hang JF. Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytumorPRNRP.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Clinically indolent papillary renal cell tumor characterized by oncocytic granular tumor cells in papillary or tubulopapillary architecture, apically located nuclei, diffuse and strong GATA3 expression and frequent KRAS mutation
Essential features
- Predominant thin papillary or tubulopapillary growth
- Tumor cells with eosinophilic, finely granular cytoplasm and low grade, apically located nuclei
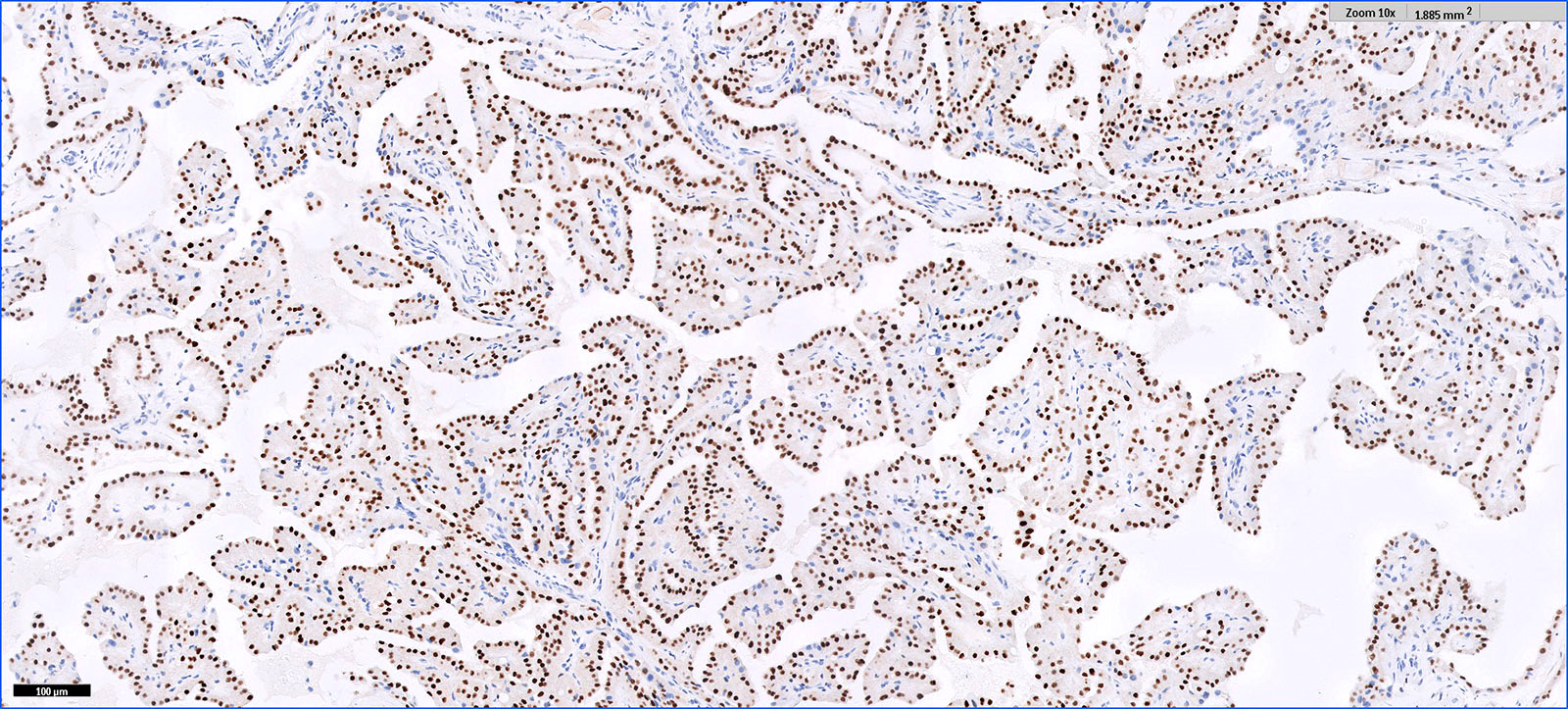
- Diffuse and strong GATA3 nuclear staining
- Recurrent KRAS missense mutation at codon 12
- Indolent, no recurrence or metastasis reported
Terminology
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma with oncocytic cells and nonoverlapping low grade nuclei (Hum Pathol 2008;39:96)
- Oncocytic papillary renal cell carcinoma with inverted nuclear pattern (Pathol Int 2009;59:137)
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma, type 4 (Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1618)
- Oncocytic papillary renal neoplasm with inverted nuclei (Histopathology 2020;76:1070)
- Papillary adenoma, type D (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:277)
Epidemiology
- Accounting for 8.6 - 9.1% of previously diagnosed papillary renal cell carcinoma (Histopathology 2021;78:1019, Hum Pathol 2021;112:48)
- Mean age: 63 years (range: 36 - 82 years) (Am J Surg Pathol 2021 Aug 5 [Epub ahead of print])
- M:F = 56:44 (Am J Surg Pathol 2021 Aug 5 [Epub ahead of print])
Sites
- Kidney, renal cortex
Pathophysiology
- Arising from the epithelial cells of the distal renal tubule, especially the cortical collecting duct (Histopathology 2020;76:1070)
- Recurrent KRAS missense mutation at codon 12 (Mod Pathol 2020;33:1157, Mod Pathol 2020;33:690, Histopathology 2020;76:1070, Histopathology 2021;78:1019, Hum Pathol 2021;112:48, Am J Surg Pathol 2021 Aug 5 [Epub ahead of print])
- Type D papillary adenoma represents the precursor or the small sized analogue (Histopathology 2021;78:1019)
Etiology
- No specific risk factors reported
Clinical features
- Usually asymptomatic and incidentally found (Histopathology 2021;78:1019, Hum Pathol 2021;112:48)
- 21 - 25% associated with end stage renal disease and hemodialysis (Histopathology 2021;78:1019, Hum Pathol 2021;112:48)
Diagnosis
- Mostly incidental mass on the radiologic imaging (Histopathology 2021;78:1019, Hum Pathol 2021;112:48)
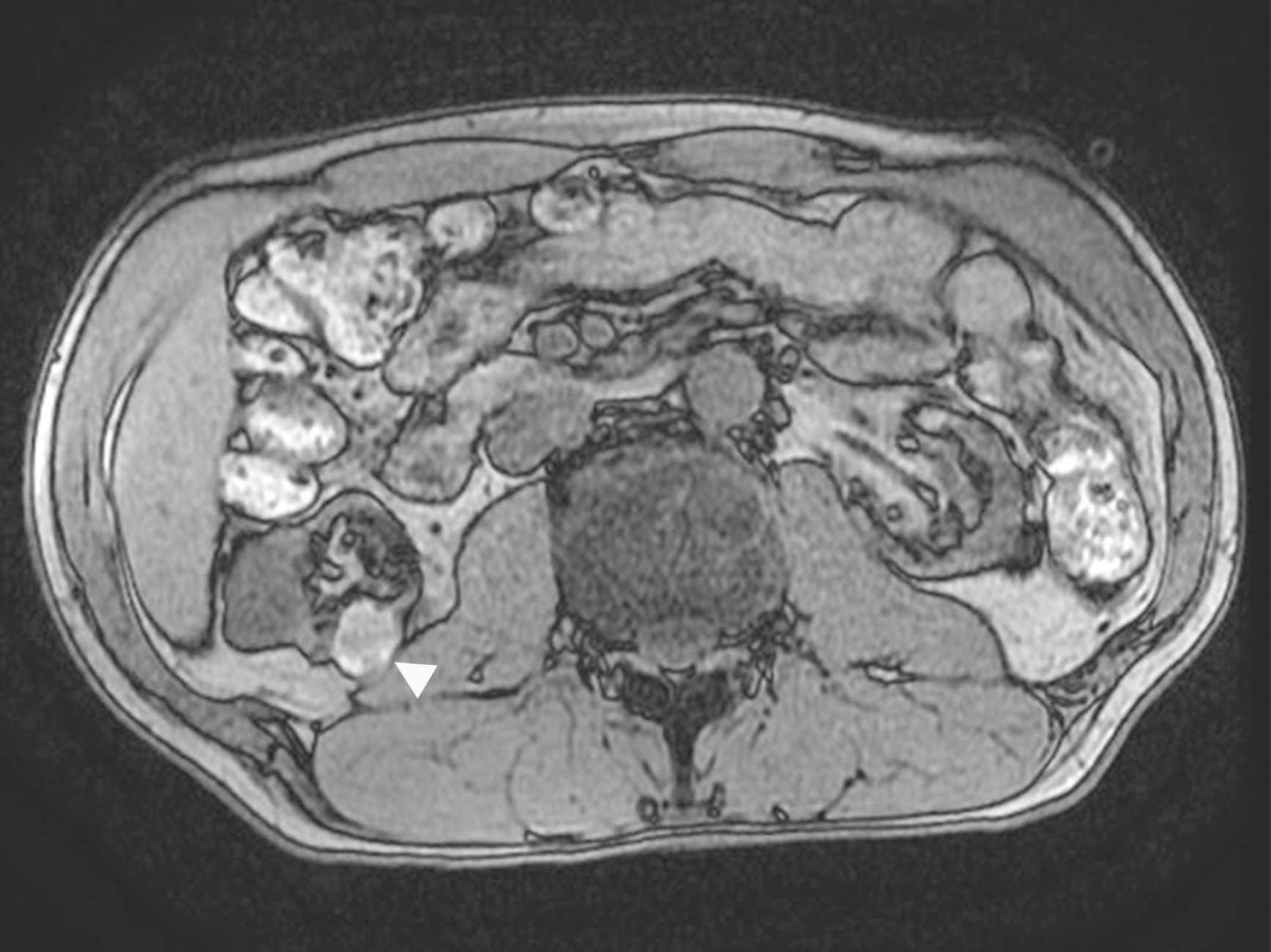
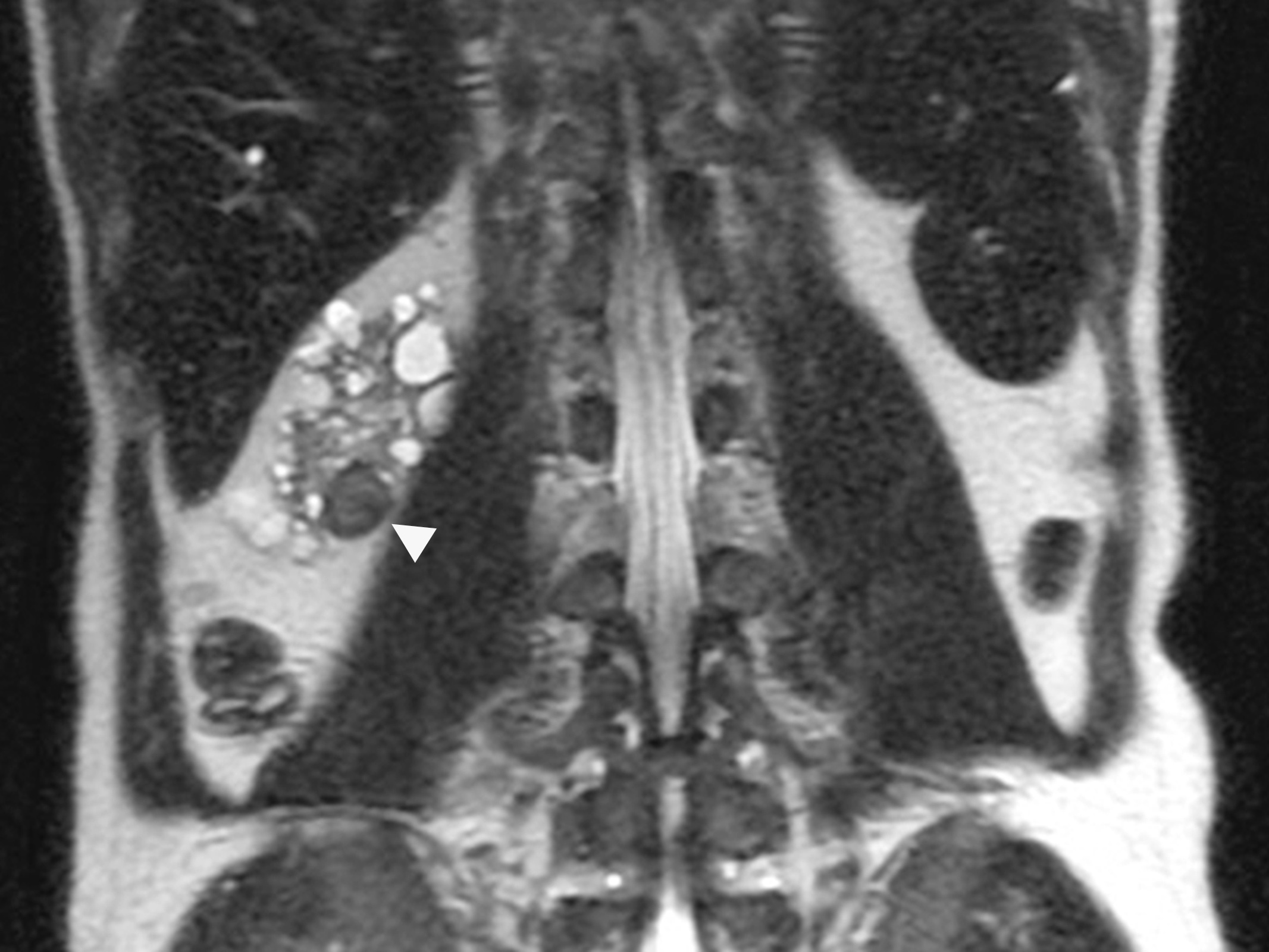
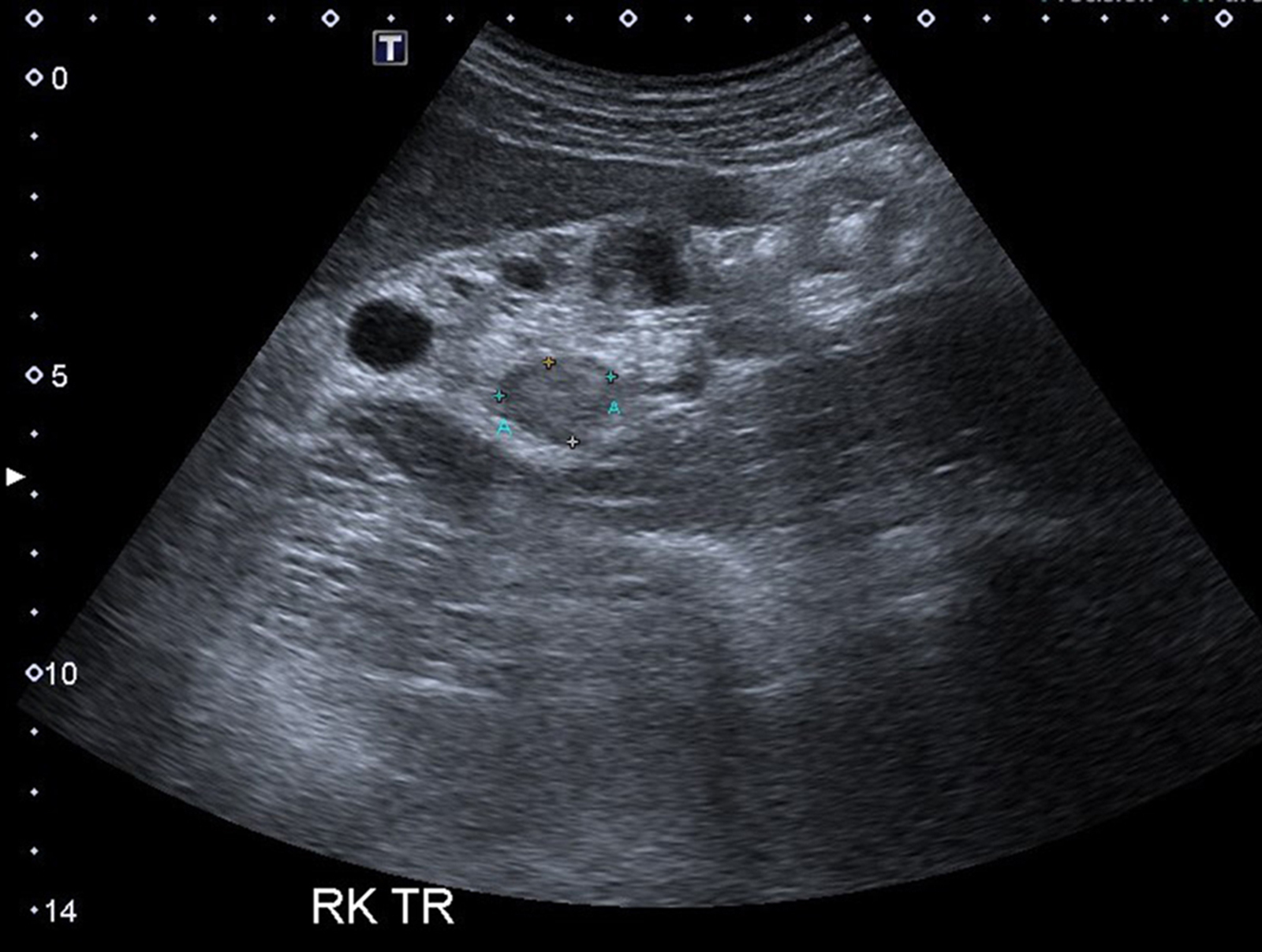
Radiology description
- MRI: hyperintense in T1 and hypointense in T2
- Ultrasonography: isoechoic or heterogeneous mass with a sharp margin
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Indolent; no recurrence or metastasis reported (Mod Pathol 2020;33:1157, Mod Pathol 2020;33:690, Histopathology 2020;76:1070, Histopathology 2021;78:1019, Hum Pathol 2021;112:48, Am J Surg Pathol 2021 Aug 5 [Epub ahead of print])
Case reports
- 61 year old man with concurrent clear cell renal cell carcinoma (Diagn Pathol 2020;15:123)
- 80 year old patient with a 2 cm renal mass (NYU Langone Health: Genitourinary Pathology - Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma with Reversed Polarity [Accessed 22 September 2021])
Treatment
- Partial or radical nephrectomy (Histopathology 2021;78:1019, Hum Pathol 2021;112:48, Am J Surg Pathol 2021 Aug 5 [Epub ahead of print])
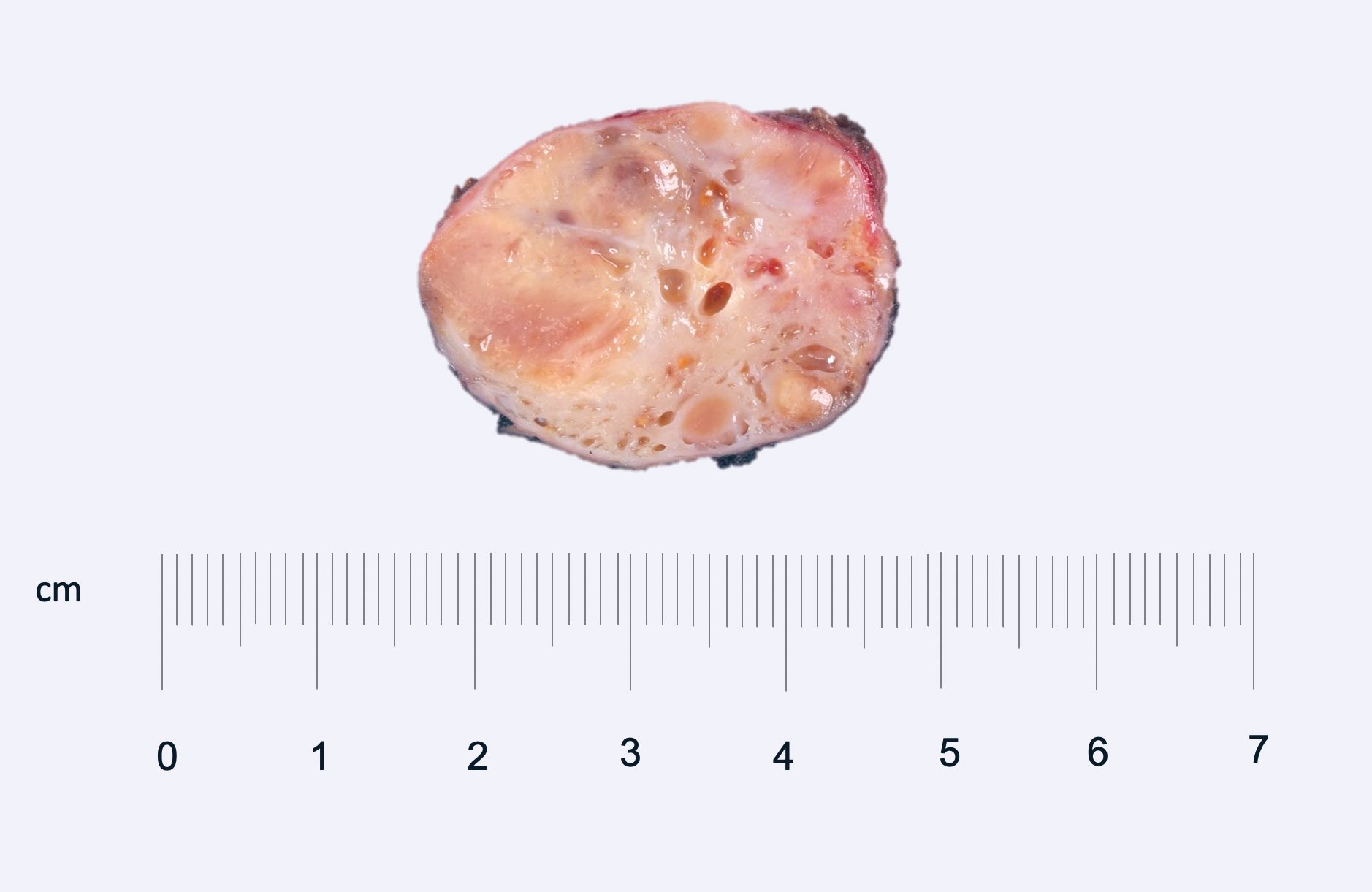
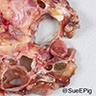
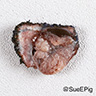
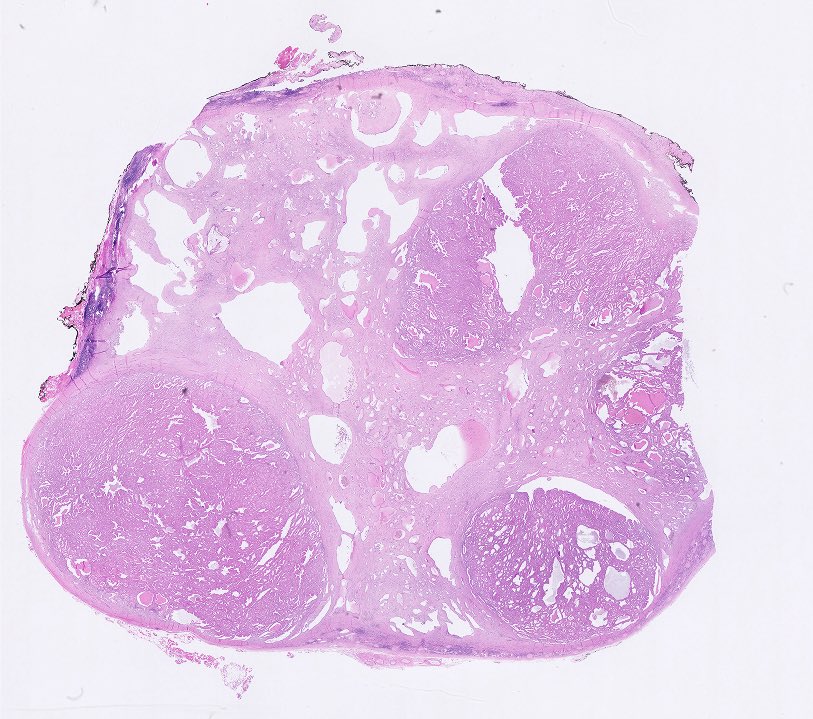
Gross description
- Often circumscribed, soft and brown-tan
- May contain cystic component and hemorrhage
- Mean size: 2.1 cm (median: 1.7 cm; range: 0.8 - 8.5 cm) (Am J Surg Pathol 2021 Aug 5 [Epub ahead of print])
Gross images
Contributed by @katcollmd on Twitter
Images hosted on other servers:
Courtesy of Katrina Collins, M.D.
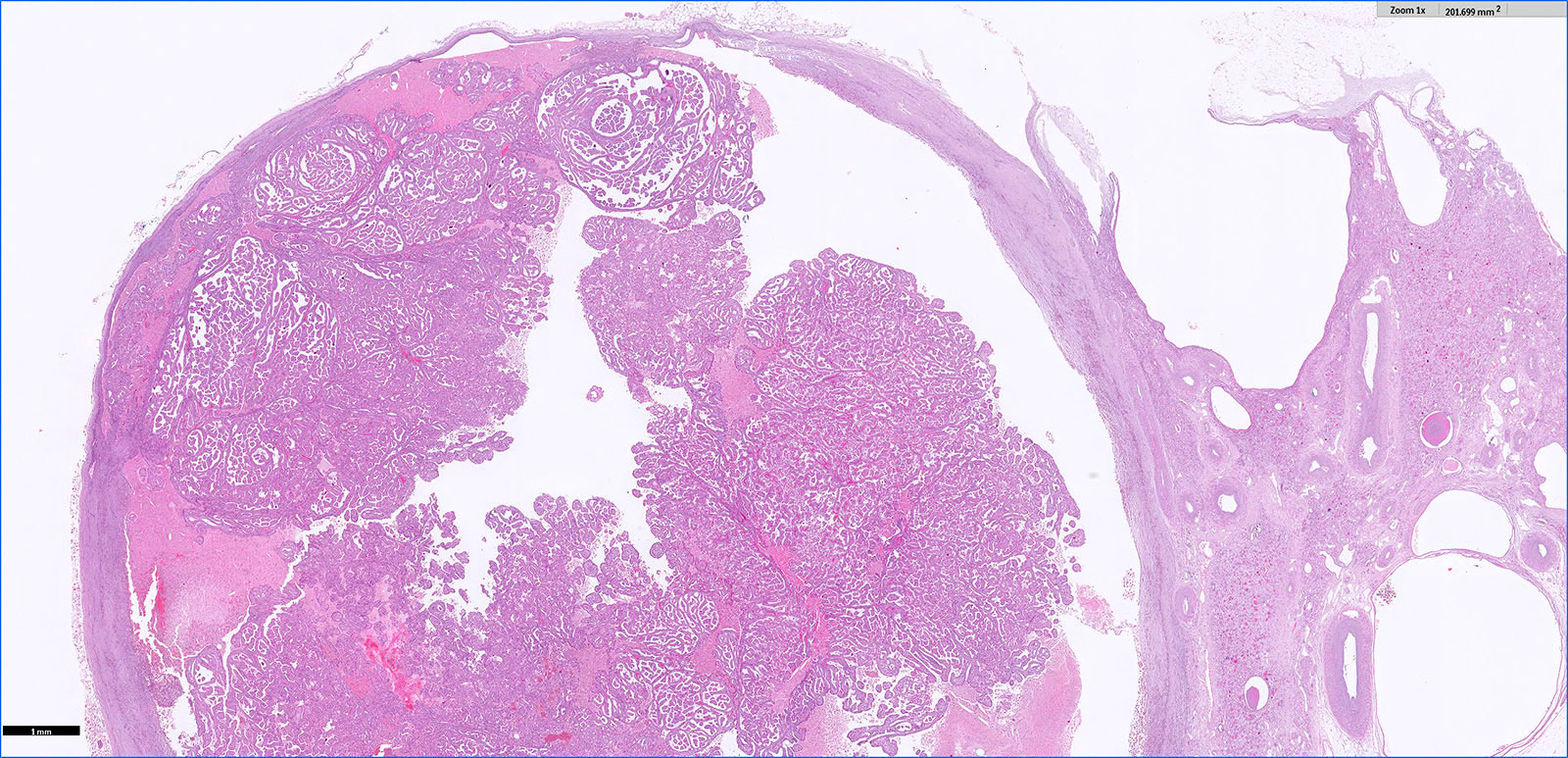
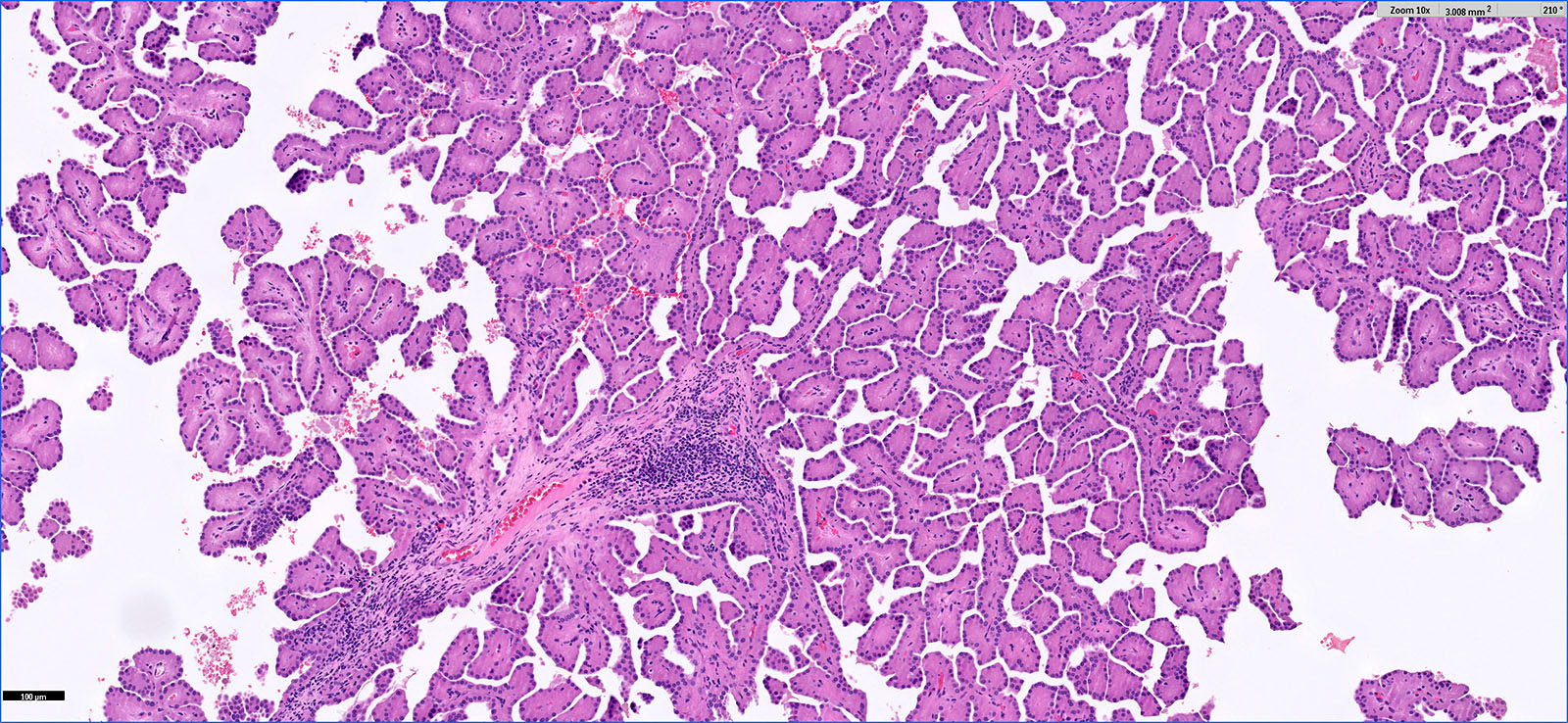
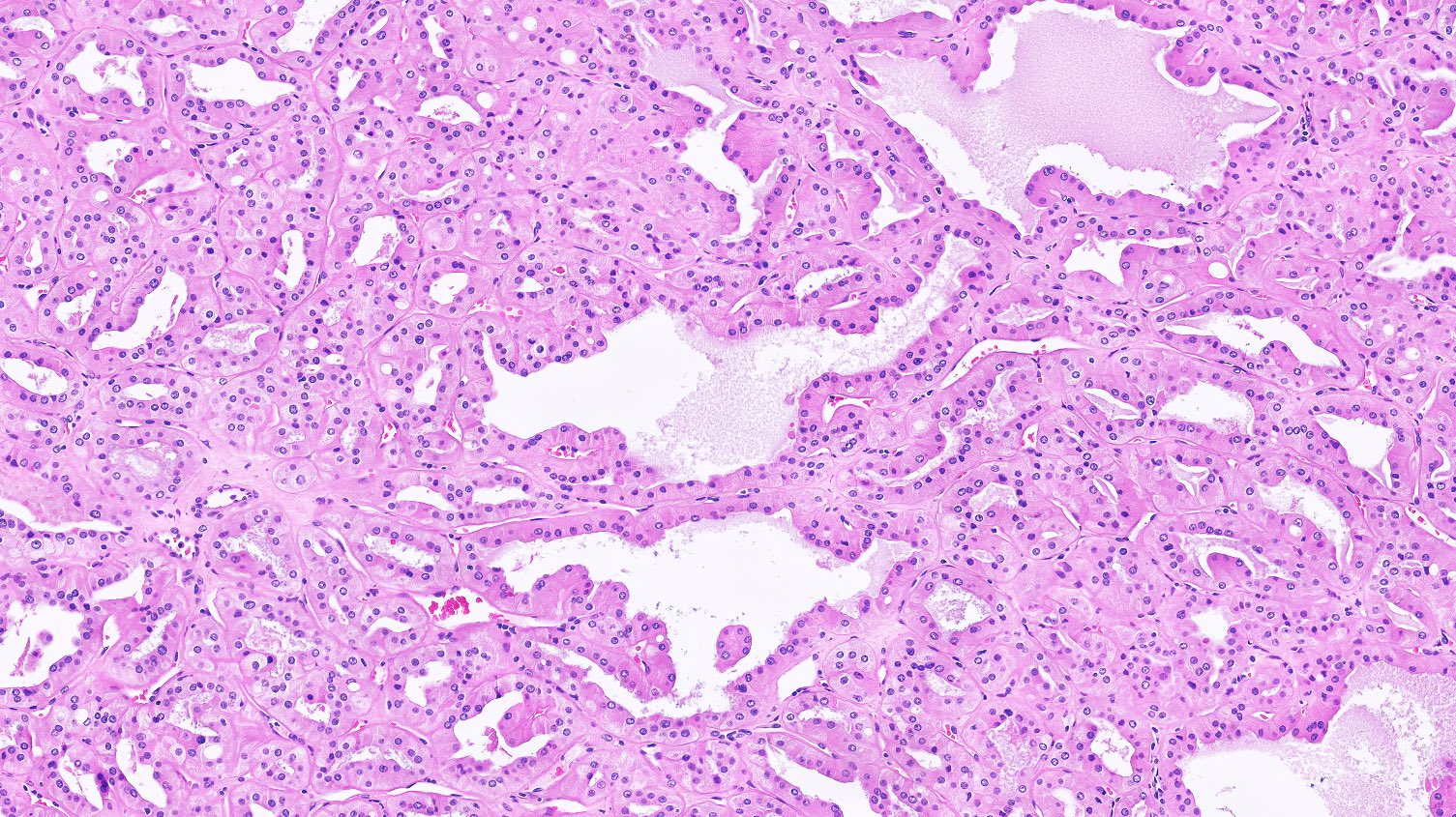
Microscopic (histologic) description
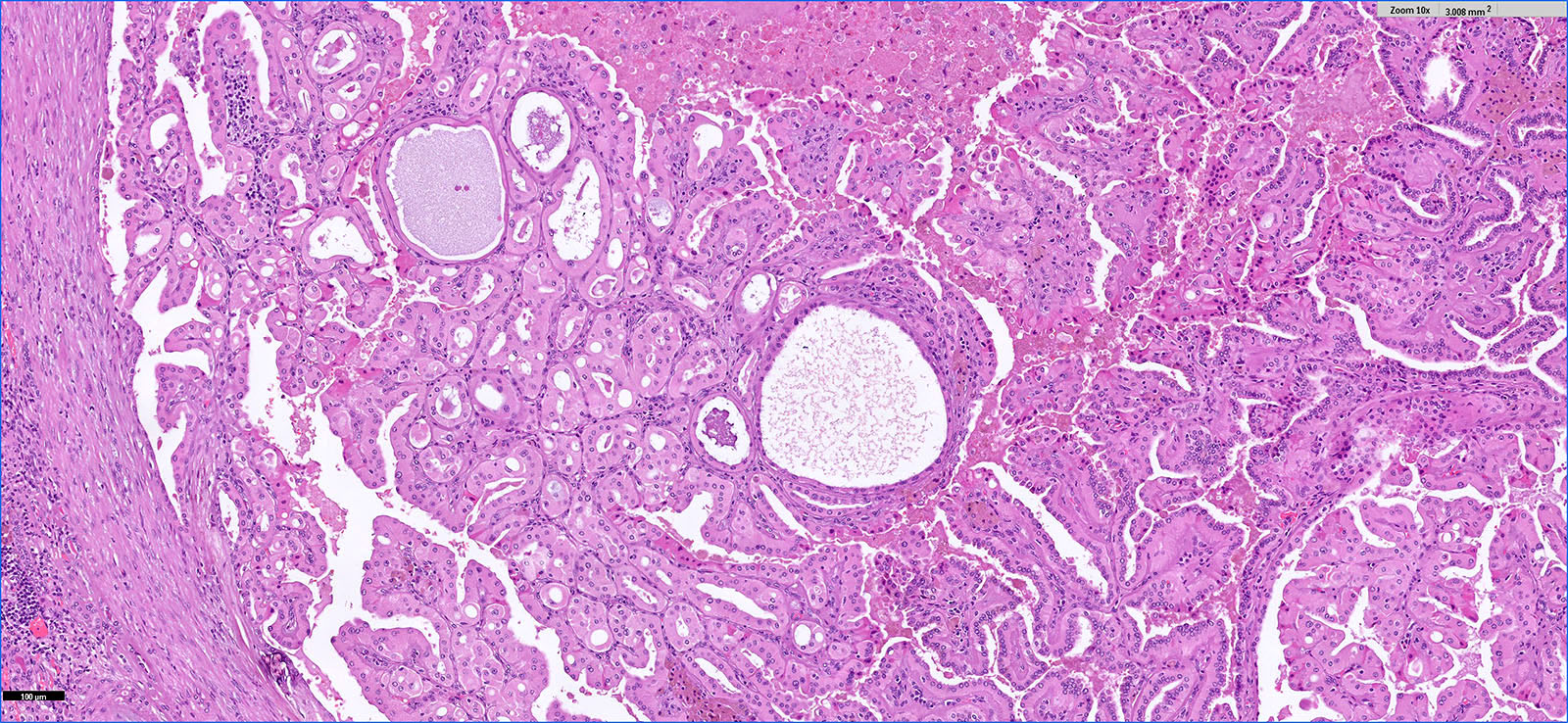
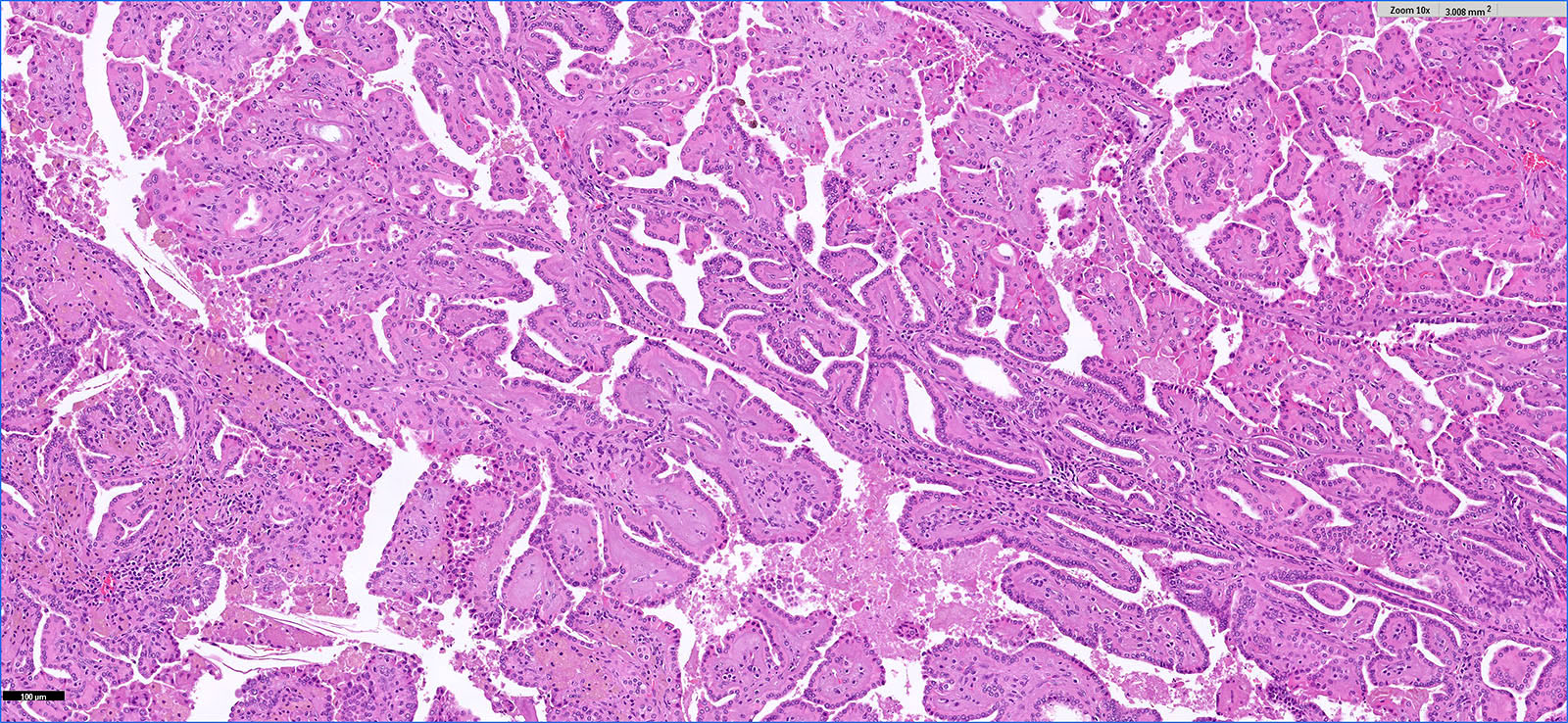
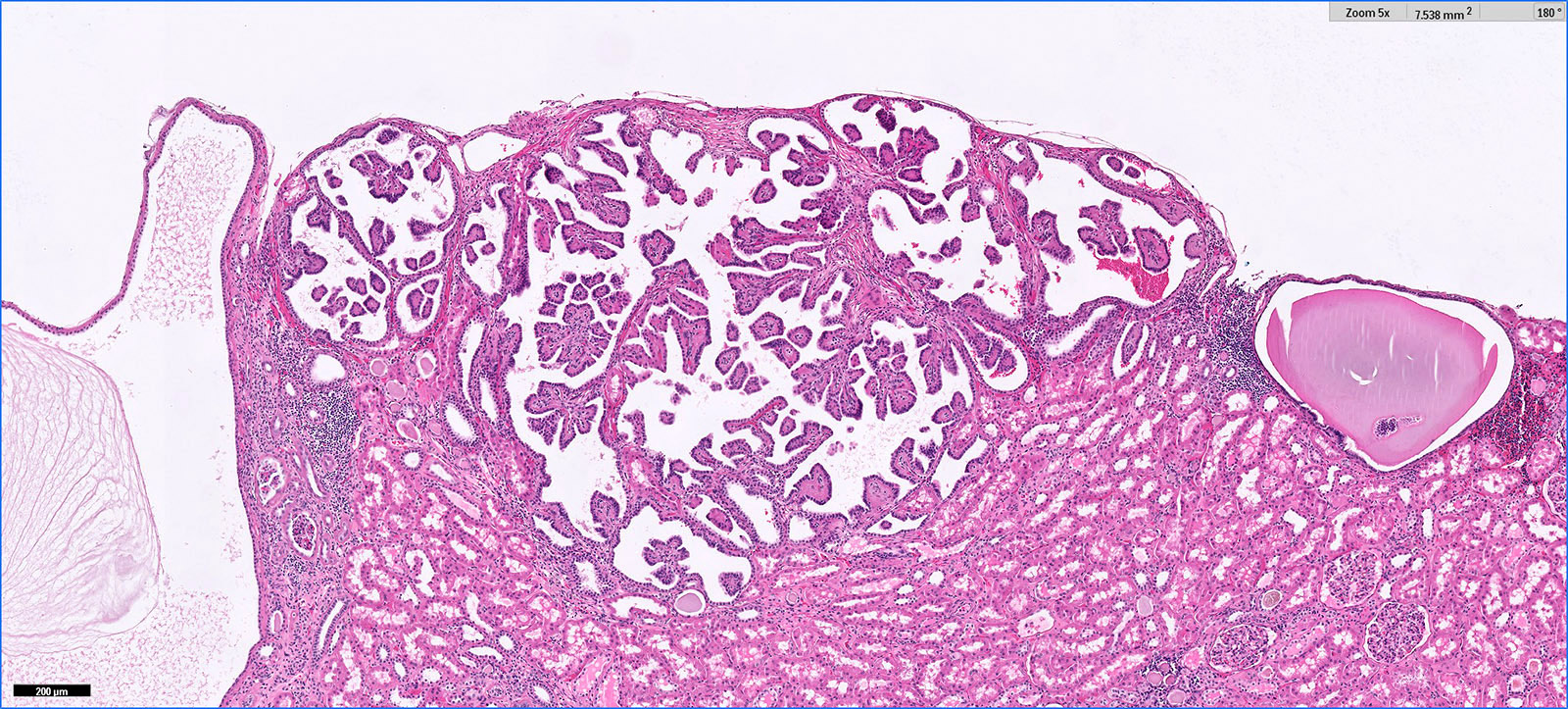
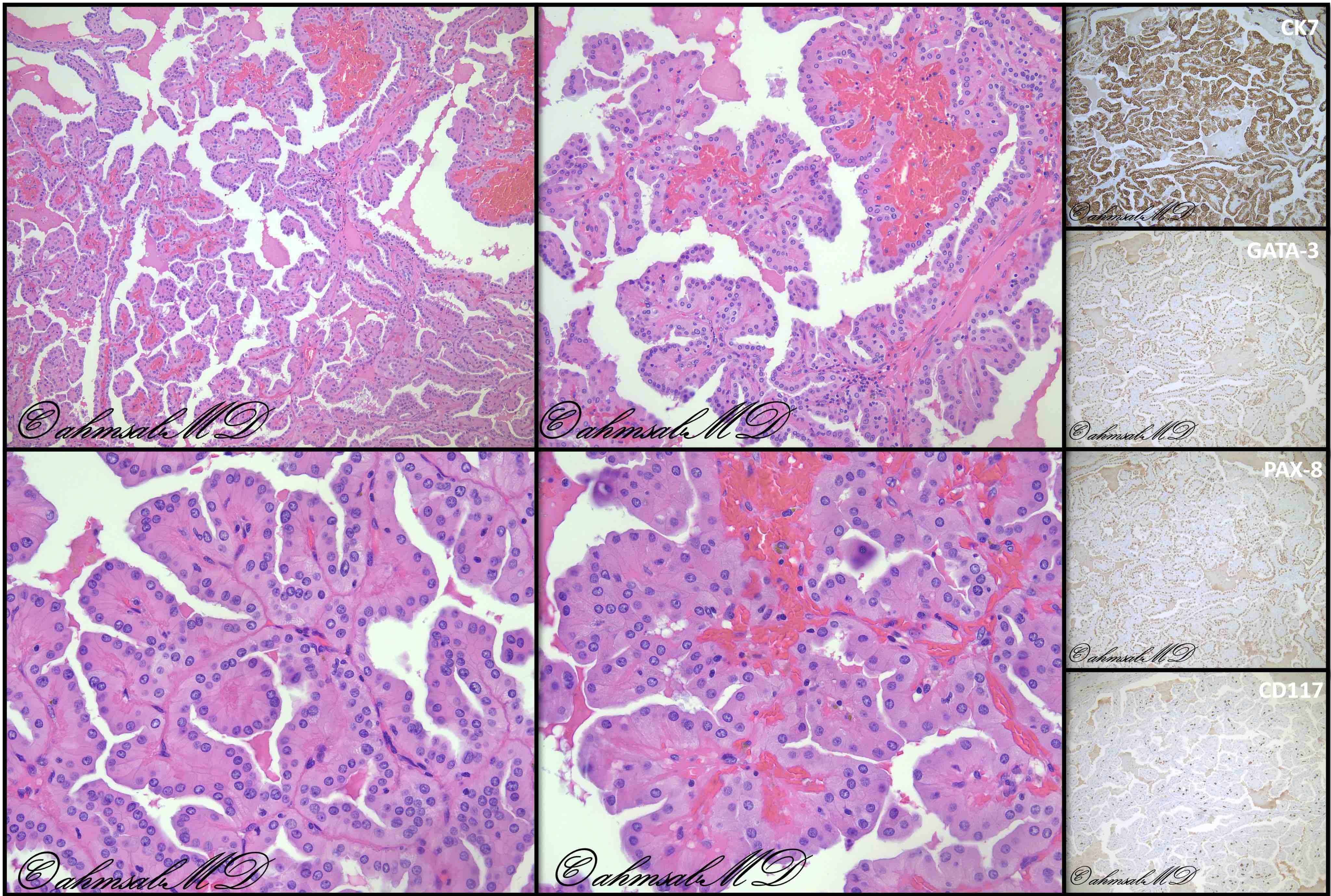
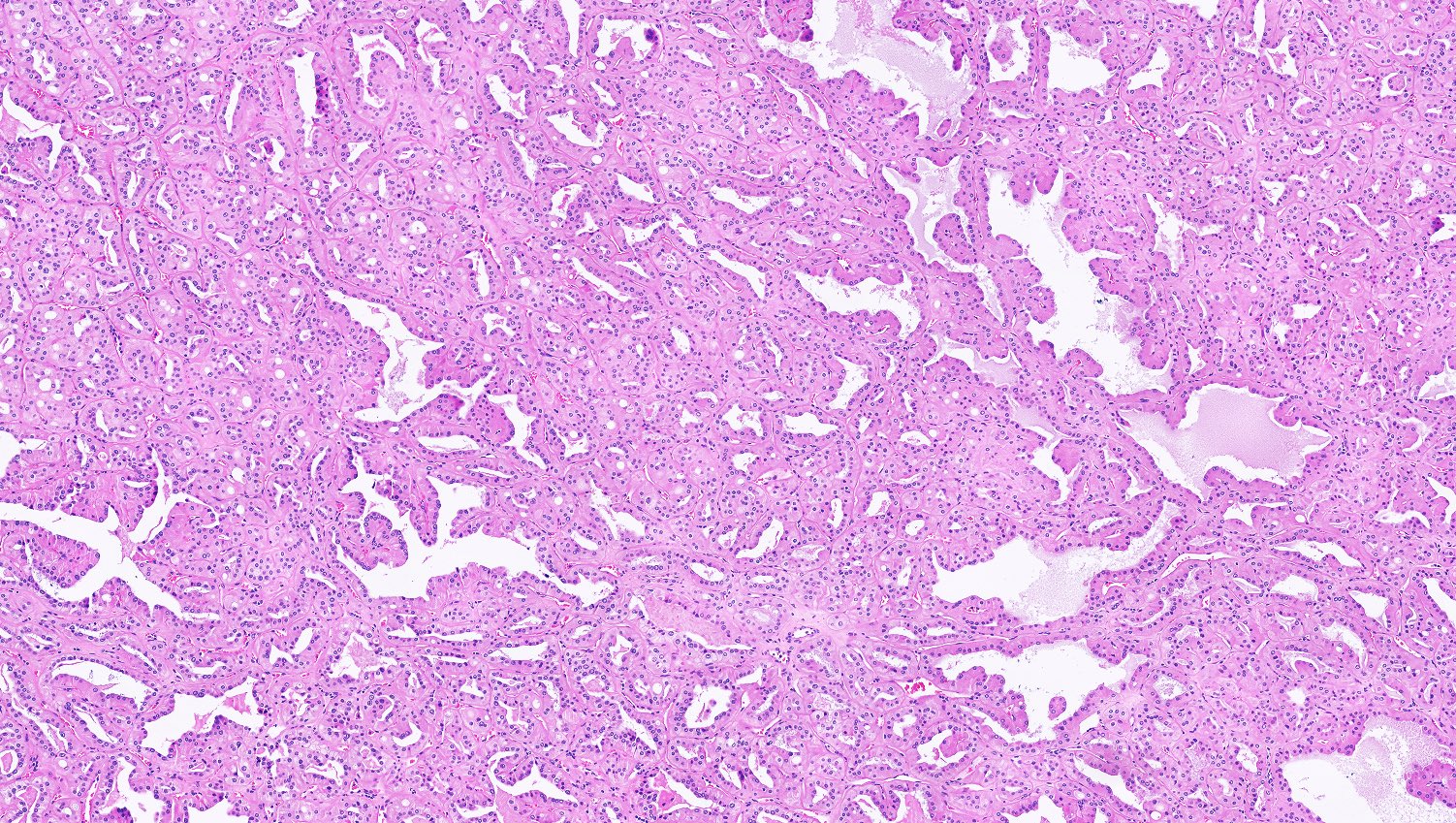
- Major morphologic features (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:277, Hum Pathol 2021;112:48, Am J Surg Pathol 2021 Aug 5 [Epub ahead of print]):
- Predominant thin papillary or tubulopapillary growth
- Focal or diffuse stromal hyalinization
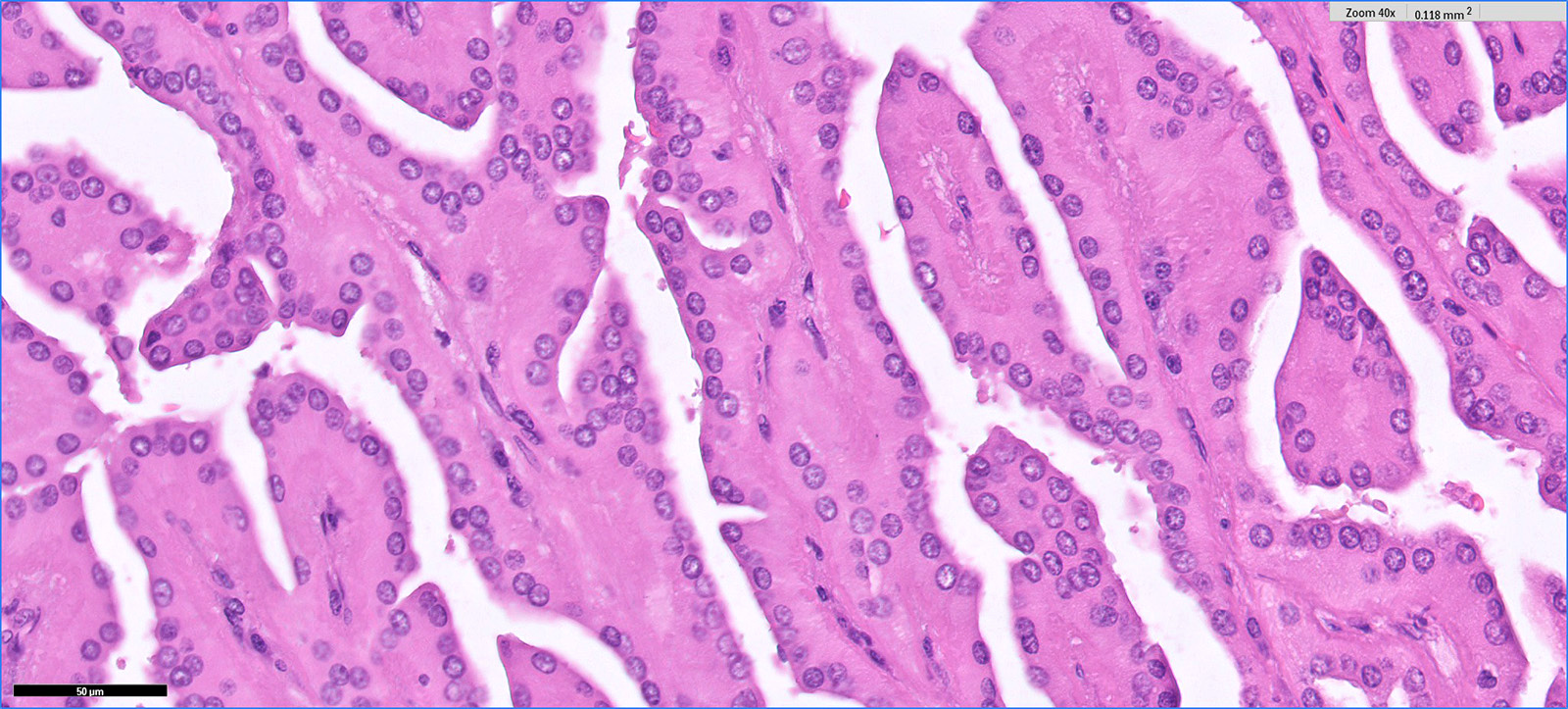
- Eosinophilic, finely granular cytoplasm
- Apically located, low grade (WHO / ISUP grade 1 - 2) nuclei
- Minor morphologic findings: cystic change, edematous papillae, aggregates of foamy histiocytes, mast cell infiltration, hobnail cells, clear cell change, cytoplasmic vacuoles, intracytoplasmic hemosiderin, pseudostratification, multinucleation and metaplastic ossification (Mod Pathol 2020;33:1157, Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1099, Histopathology 2020;76:1070, Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:728, Histopathology 2021;78:1019, Hum Pathol 2021;112:48)
- No mitosis or necrosis
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Hsin-Yi Chang, M.D., Jen-Fan Hang, M.D., @ahmsab_MD on Twitter and @katcollmd on Twitter
Positive stains
- GATA3, CK7, PAX8: diffuse and strong
- EMA: apical membranous
- L1CAM (CD171): basolateral membranous
- Fumarate hydratase: retained cytoplasmic expression
- Variable: AMACR, CD10, RCC, E-cadherin
- References: Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1618, Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1099, Mod Pathol 2020;33:1157, Mod Pathol 2020;33:690, Histopathology 2020;76:1070, Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:728, Hum Pathol 2021;112:48
Negative stains
- CD117, vimentin, except rare cases with weak, focal expression (Am J Surg Pathol 2021 Aug 5 [Epub ahead of print])
- CK20, CAIX, TFE3 (Pathol Int 2009;59:137, Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:728)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Recurrent KRAS missense mutation at codon 12 in 75 - 93.3% of cases (Mod Pathol 2020;33:1157, Mod Pathol 2020;33:690, Histopathology 2020;76:1070, Histopathology 2021;78:1019, Hum Pathol 2021;112:48, Am J Surg Pathol 2021 Aug 5 [Epub ahead of print])
- Gain of chromosomes 7 and 17 and loss of chromosome Y noted in some cases by fluorescence in situ hybridization (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:1099, Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:728)
- No copy number abnormalities in chromosomes 7, 17 and Y by whole exome sequencing or microarray analysis (Hum Pathol 2021;112:48, Am J Surg Pathol 2021 Aug 5 [Epub ahead of print])
Sample pathology report
- Kidney, right, partial nephrectomy:
- Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity (see comment)
- Comment: Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity is currently considered to be a histologic variant of papillary renal cell carcinoma; however, recent studies suggest that it has a very indolent clinical behavior. No recurrence or metastasis has been reported.
Differential diagnosis
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma, type 2:
- Nuclear stratification without reverse polarity
- Frequent high grade nuclei (WHO / ISUP grade 3)
- GATA3 negative
- No KRAS mutation
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma, oncocytic variant:
- Centrally located nuclei without reverse polarity
- WHO / ISUP grade ranging from 2 to 3
- GATA3 negative
- No KRAS mutation
- Fumarate hydratase deficient renal cell carcinoma:
- Mixed architectural patterns of papillary, solid, tubulocystic, cribriform, etc. (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:865)
- High grade nuclei with prominent eosinophilic nucleoli and perinucleolar halo (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1578)
- Fumarate hydratase loss of expression; 2SC overexpression
- GATA3 negative
- No KRAS mutation
- Acquired cystic disease associated renal cell carcinoma:
- Mixed architectural patterns of papillary, solid, tubulocystic, cribriform, etc.
- Presence of oxalate crystals
- Frequent high grade nuclei (WHO / ISUP grade 3) without reverse polarity
- GATA3 negative
- No KRAS mutation
- Papillary adenoma:
- Size ≤ 1.5 cm
- Type D papillary adenoma is the smaller sized equivalent tumor
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
D. GATA3. In renal cell carcinomas (RCCs) with eosinophilic cytoplasm, GATA3 positivity is only seen in papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity (PRNRP). Interestingly, GATA3 positivity is reported in another indolent neoplasm with reverse polarity but optically clear cytoplasm, namely clear cell papillary RCC. CK7 is expressed in PRNRP but also in type 1 papillary RCC and chromophobe RCC. Though CD117 is positive in chromophobe RCC and oncocytoma, positive weak staining for PRNRP is also reported in a small percentage of cases. CD10 shows variable expression in papillary RCC, chromophobe RCC, oncocytoma and PRNRP (Hum Pathol 2017;66:152, Mod Pathol 2005;18:535, Pathol Int 2009;59:137, Mod Pathol 2020;33:690, Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:728, Am J Surg Pathol 2021 Aug 5 [Epub ahead of print]).
Comment Here
Reference: Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity
Comment Here
Reference: Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
B. KRAS. Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity is characterized by KRAS hotspot mutation at codon 12. Loss of function mutation of VHL gene is the molecular hallmark of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC). MET alterations are frequently found in papillary RCC. FH mutations are diagnostic for FH deficient RCC.
Comment Here
Reference: Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity
Comment Here
Reference: Papillary renal neoplasm with reverse polarity