Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Case reports | Radiology images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Sangle N. Tuberculosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneytb.html. Accessed December 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Each year, 9 million new cases of TB, causing 1.5 million annual deaths (WHO: Global tuberculosis report 2017 [Accessed 19 January 2018])
- GU tract is #2 most common site of infection after lungs
Clinical features
- Renal involvement may be indolent, may not become apparent until 20+ years from detection of primary infection
- Urogenital TB is associated with unilateral nonfunctioning kidney in 27% of cases, with renal failure present in 7% (Int J Urol 2008;15:827)
- In chronic kidney disease of all causes, one study from India demonstrated a 4% incidence of TB, which was usually tuberculin skin test negative (Clin Nephrol 2007;67:217)
- In immunocompromised patients, urogenital TB usually has systemic symptoms, dissemination, multiple renal foci (Int Urol Nephrol 2009;41:327)
Case reports
- 20 year old man with tuberculosis associated chronic kidney disease (Am J Trop Med Hyg 2011;84:843)
- 29 year old man with renal hydronephrosis (Case #128)
- 33 year old man presenting with end stage renal disease secondary to renal TB (Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 2012;54:57)
- 38 year old man with negative PPD and repeatedly negative AFB tests (Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent) 2012;25:236)
Gross description
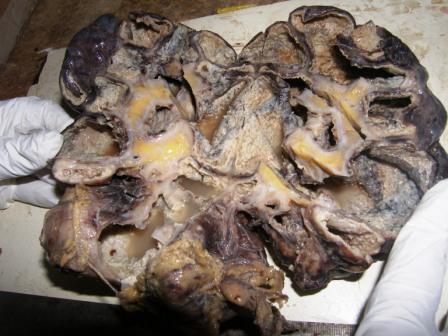
- Multiple cavities filled with yellow friable necrotic material
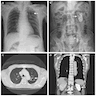
Gross images
Microscopic (histologic) description
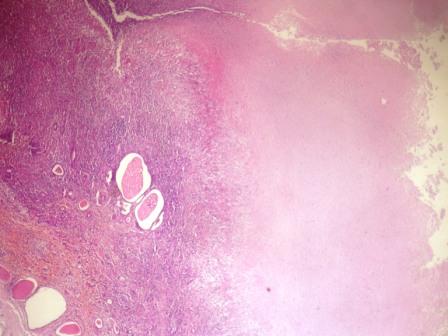
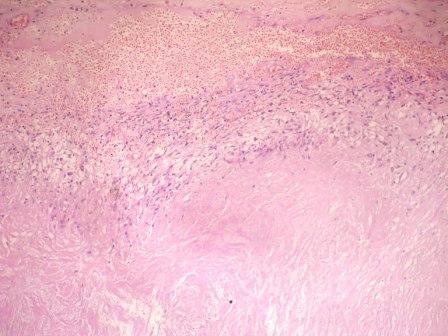
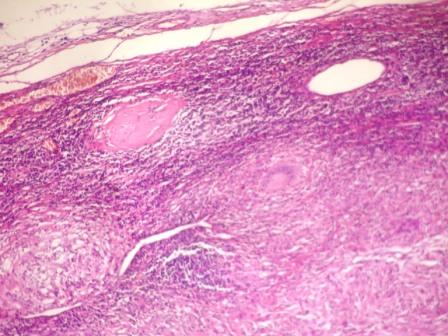
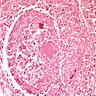
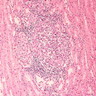
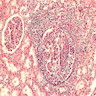
- Extensive caseous necrosis, with occasional granulomas composed of epithelioid cells and Langhans giant cells with surrounding lymphocytes
- Very early granulomas might not show caseation
- The interface of viable cells and caseous necrosis is where acid fast bacilli (AFB) are most found
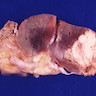
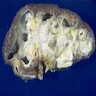
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Occasionally fungal infections and sarcoidosis can cause noncaseating epithelioid cell granulomas
- Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: different clinical picture, AFB negative, although AFB may be difficult to detect even in TB patients; TB PCR and AcuProbe are more sensitive (Int J Urol 2006;13:67)