Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Immunofluorescence description | Positive stains | Electron microscopy description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Breitbarth Borgen A, Andeen NK. Rhabdomyolysis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneyrhabdomyolysis.html. Accessed November 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Acute tubular injury with myoglobin+ tubular casts seen in setting of rhabdomyolysis
Essential features
- Acute tubular injury with myoglobin+ tubular casts
- Seen in setting of rhabdomyolysis; also has elevated serum creatine kinase
Terminology
- Also called pigment nephropathy
ICD coding
- ICD-10: M62.82 - rhabdomyolysis
Epidemiology
- Acute kidney injury develops in 10 - 40% of patients with severe rhabdomyolysis (Am J Kidney Dis 2018;71:A12)
Pathophysiology
- Myoglobin may damage tubules via multiple mechanisms:
- Vasoconstriction with subsequent tubular epithelial ischemia (Free Radic Biol Med 2011;51:1062)
- Direct cytotoxic and oxidative damage (Biochim Biophys Acta 2009;1792:796)
- Tubular obstruction by pigmented casts
Etiology
- Rhabdomyolysis results from muscle injury (Crit Care 2014;18:224):
- Traumatic: crush injury, exercise, seizure
- Drug related: cocaine, heroin, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) inhibitors, rapamycin, oseltamivir (Transplantation 2006;82:645)
- Toxic: clostridial toxin, snake venom
- Malignant hyperthermia
- Electrical current
Clinical features
- Oliguria
- Dark (cola colored) urine
- Muscle swelling, stiffness
- Reference: Crit Care 2014;18:224
Laboratory
- Urinalysis: dipstick positive for heme protein, no erythrocytes, dark pigmented casts on urine microscopy
- Elevated creatine kinase, often > 100,000 U/L
- Elevated creatinine
- Electrolyte abnormalities: hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperuricemia, hypocalcemia
- Reference: Crit Care 2014;18:224
Prognostic factors
- Time to diagnosis and treatment
- Age (younger patients have better recovery)
- Reference: Crit Care 2014;18:224
Case reports
- 21 year old man with dengue fever (BMJ Case Rep 2015 Jul 14;2015)
- 53 year old man with suspected influenza and oseltamivir administration (Am J Case Rep 2018;19:673)
- 66 year old man with carnitine palmitoyltransferase II deficiency (Am J Kidney Dis 2018;71:A12)
- 82 year old man taking simvastatin and gemfibrozil, successfully managed with plasmapheresis (Cases J 2009;2:8138)
- 11 patients with indoor cycling (spinning) induced rhabdomyolysis (Electrolyte Blood Press 2015;13:58)
Treatment
- Supportive care
- Correction of inciting factors or disease
- Depends on degree of acute kidney injury (see diagram above, Crit Care 2014;18:224)
- Potentially acetaminophen by decreasing oxidant injury (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010;107:2699)
- Potentially dialysis (Ren Fail 2001;23:183)
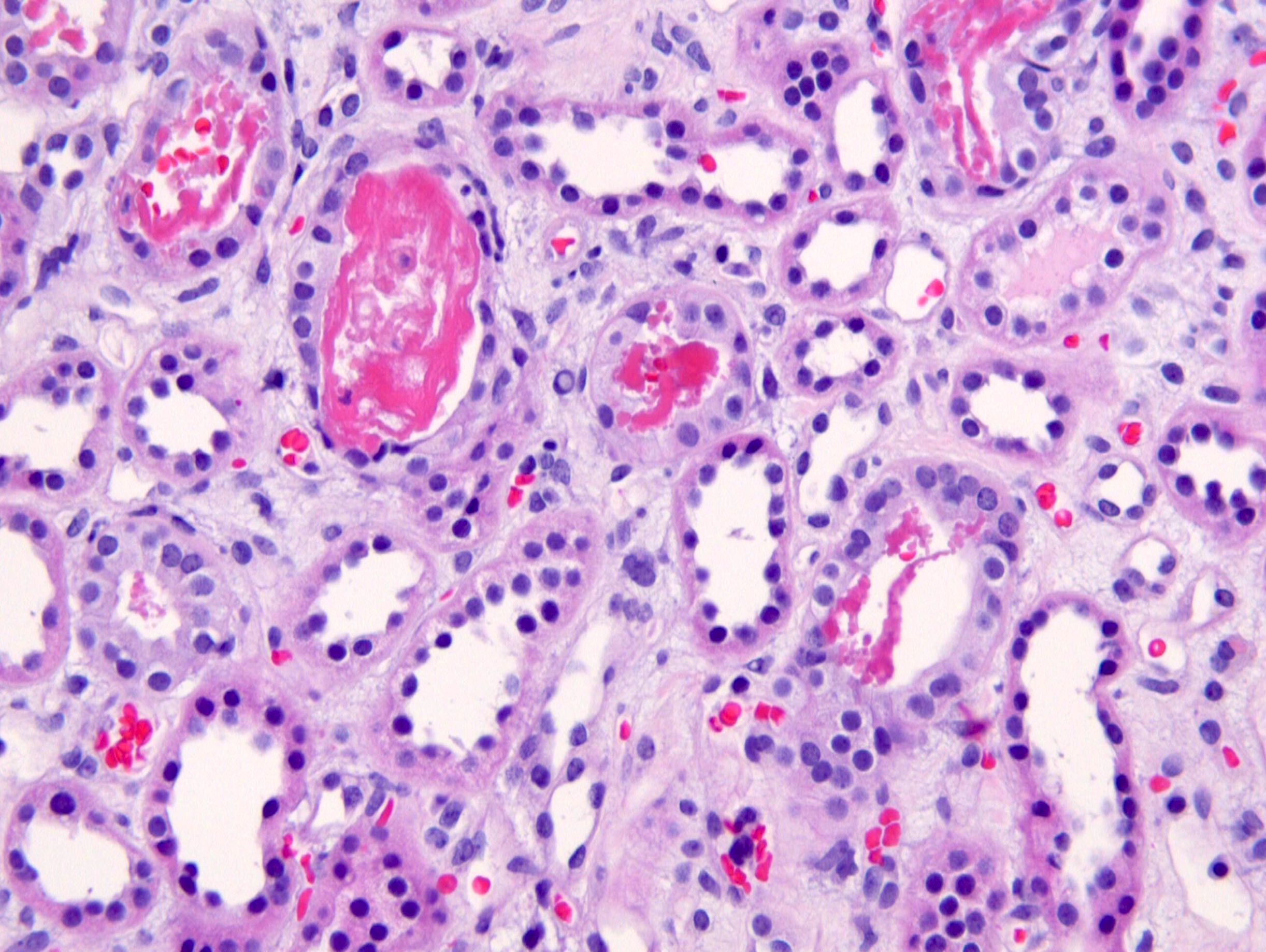
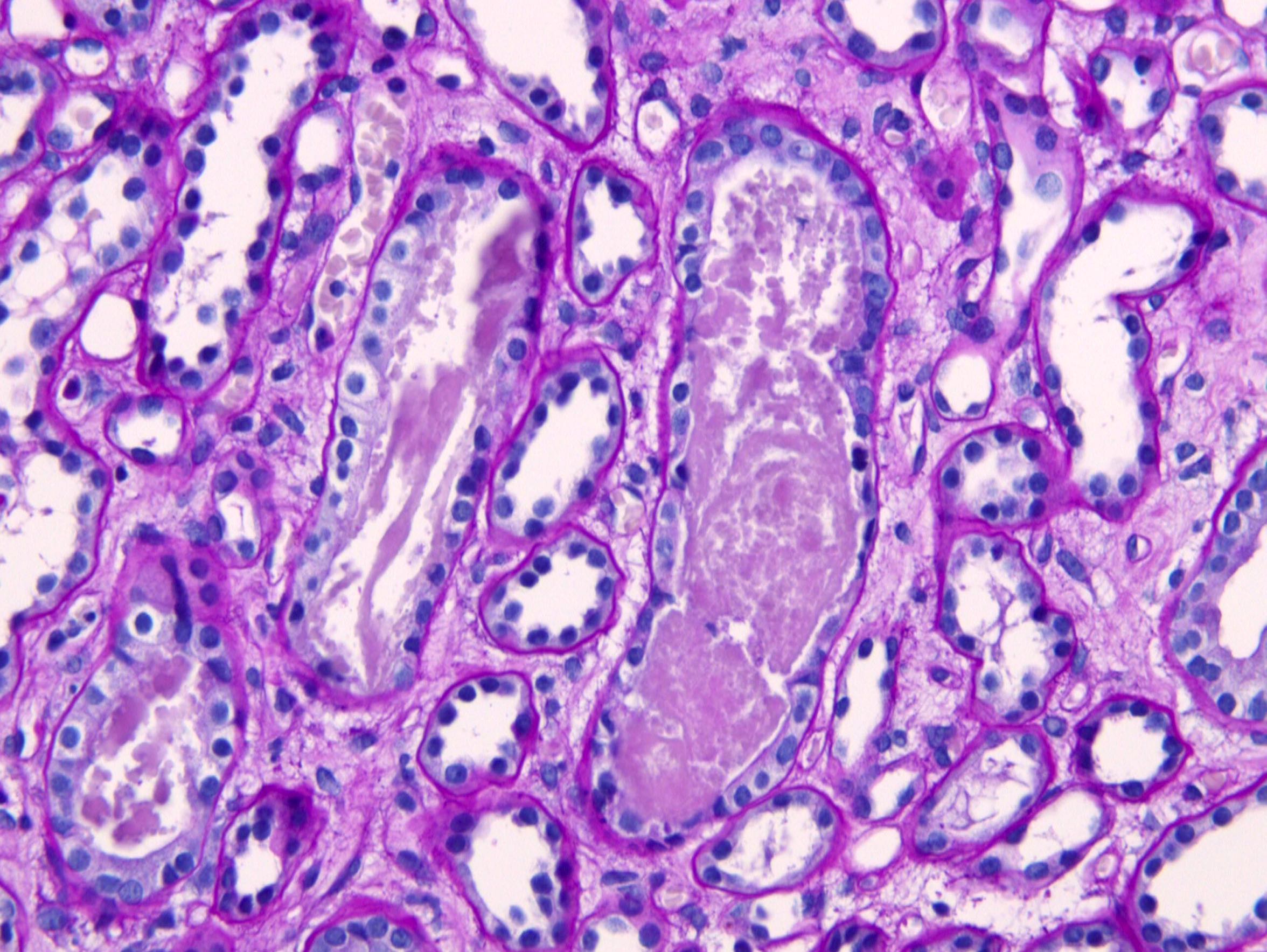
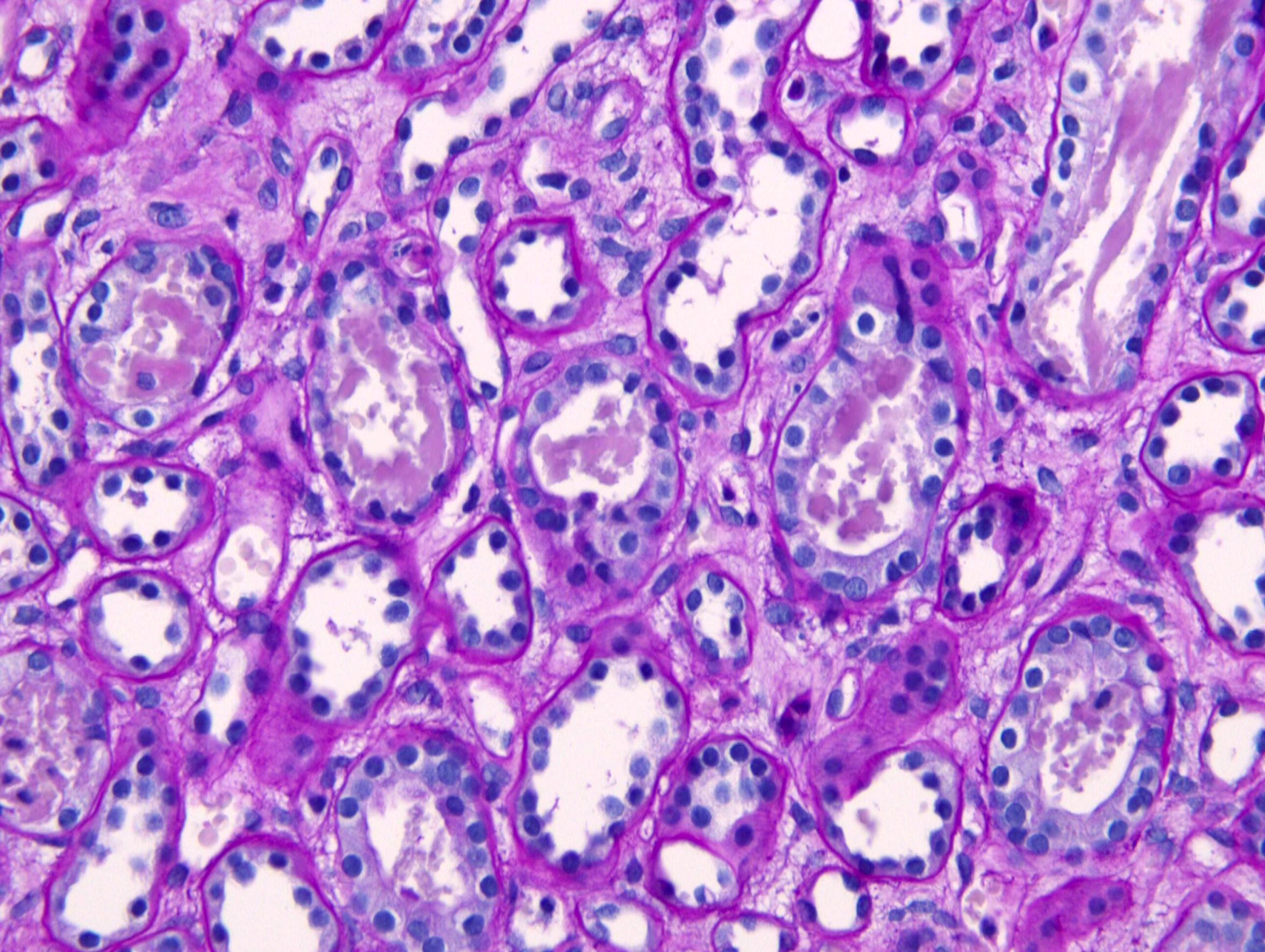
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Acute tubular injury: loss of brush borders, attenuation and sloughing of epithelium
- Granular or pigmented casts in tubules
- Interstitial edema
- Glomeruli spared
Microscopic (histologic) images
Immunofluorescence description
- Negative immunofluorescence
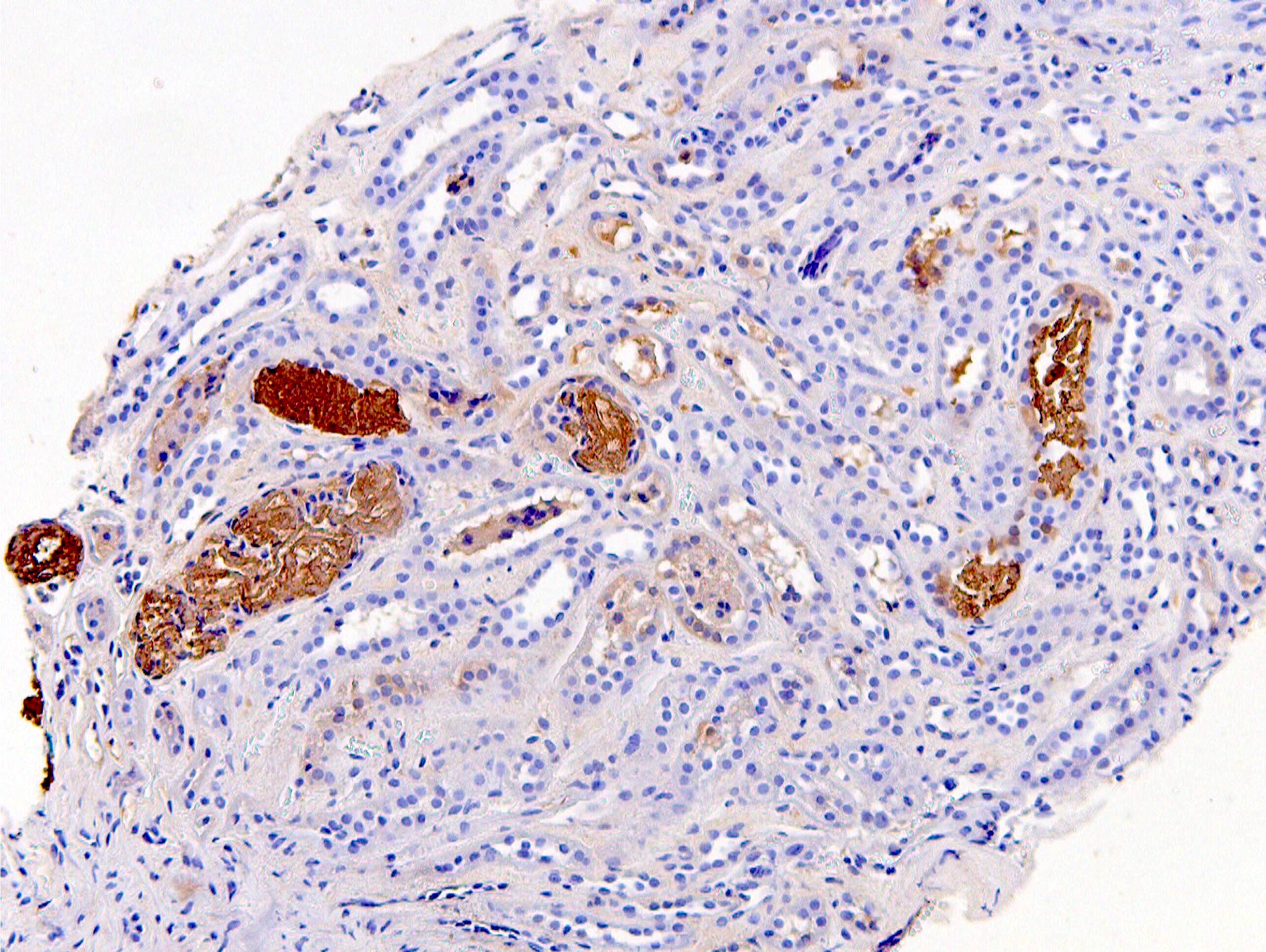
Positive stains
- Myoglobin immunohistochemistry highlights casts
Electron microscopy description
- Casts have electron dense granules
Sample pathology report
- Native kidney biopsy:
- Myoglobin cast nephropathy
- Comment: consistent with the clinical history of acute kidney injury and rhabdomyolysis in this patient, kidney biopsy demonstrates acute tubular injury / acute tubular necrosis with associated myoglobin positive casts, characteristic of myoglobin cast nephropathy
Differential diagnosis
- Hemoglobinuria:
- May have similar appearing pigmented casts
- Casts are negative for myoglobin and positive for hemoglobin by IHC
- Light chain cast nephropathy:
- Other acute tubular injury, including toxic or ischemic:
- Also has acute tubular injury with granular debris in tubular lumen
- Normal serum creatine kinase
- Casts are negative for myoglobin by IHC
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A patient presents with acute kidney injury and renal biopsy demonstrates acute tubular injury. Tubular casts stain with myoglobin by immunohistochemistry. What plasma enzyme will be elevated and what is the correct clinical diagnosis?
- Creatine kinase; rhabdomyolysis
- Creatinine; multiple myeloma
- Lactate dehydrogenase; paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
- Troponin; myocardial infarction
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
D. Trauma, extreme physical exercise or prolonged immobilization
Comment Here
Reference: Rhabdomyolysis
Comment Here
Reference: Rhabdomyolysis