Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Immunofluorescence description | Immunofluorescence images | Positive stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Genetics | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Larqué AB. Membranous nephropathy. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneymemgn.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Autoimmune glomerular disease characterized by diffuse subepithelial immune complex deposition with nephrotic range proteinuria, without known systemic cause (Colvin: Diagnostic Pathology - Kidney Diseases, 2nd Edition, 2015)
Essential features
- Idiopathic autoimmune glomerular disease
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Thickening of glomerular basement membrane and subepithelial deposition of immune complexes (silver stain, spike)
- Anti-PLA2R autoantibodies
Terminology
- Membranous glomerulopathy
- Membranous glomerulonephritis
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in nondiabetic adults
- Incidence: ~8 - 10 cases per 1 million
- Mean age: 50 - 60 years; rare in children (Nephrology (Carlton) 2015;20:572)
- Caucasian predilection (Postgrad Med J 2019;95:23, Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2017;12:983)
Sites
- Kidney (glomerular disease)
Pathophysiology
- Circulating autoantibodies bind to an autoantigen on the surface of the podocytes resulting in in situ immune complex formation that activates the lectin complement pathway and causes podocyte injury and proteinuria
- 2 major target antigens are now firmly recognized: the M type phospholipase A2 receptor 1 (PLA2R) (~70%) and the thrombospondin type 1 domain containing 7A (THSD7A) (2 - 5%) (J Am Soc Nephrol 2017;28:421)
Etiology
- Idiopathic autoimmune disease with a predisposition to autoimmunity conferred by HLA genes and an environmental trigger (J Am Soc Nephrol 2013;24:525)
Clinical features
- Nephrotic syndrome
- 20% with nonnephrotic proteinuria
- Less frequent: hematuria (usually microscopic), hypertension, thrombotic and thromboembolic events (Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2017;12:983)
Diagnosis
- Nephrotic syndrome with serum anti-PLA2R antibody (Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2017;12:983)
- Demonstration of subepithelial deposition of immune complexes by renal biopsy and immunofluorescence
- Positive PLA2R staining in glomeruli by immunohistochemistry
Laboratory
- Positive serum anti-PLA2R antibody
- High antibody levels (before and after treatment) correlate with proteinuria, response to therapy and (after therapy) long term outcomes (Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2017;12:983)
Prognostic factors
- 33% spontaneously remit
- 33% remain stable with proteinuria and little progression
- 33% progress to end stage renal disease (ESRD)
- 10 - 30% recur after kidney transplantation
- Adverse clinical prognostic features: high PLA2R antibody titer, nephrotic syndrome, higher levels of proteinuria, persistence of proteinuria, renal insuffiency, male sex and advanced age (J Am Soc Nephrol 2017;28:421, Colvin: Diagnostic Pathology - Kidney Diseases, 2nd Edition, 2015)
Case reports
- 38 year old man with nephrotic syndrome (Nephrology (Carlton) 2018;23:94)
- 39 year old woman with severe nephrotic syndrome (Am J Kidney Dis 2016;67:775)
- 50 year old woman with heavy proteinuria (Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 2019;30:531)
- 63 year old man with PLAR2 positive membranous nephropathy whose kidney was donated after cardiac death (Am J Transplant 2022;22:299)
Treatment
- Supportive care with or without immunosuppressive therapy (Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2017;12:983)
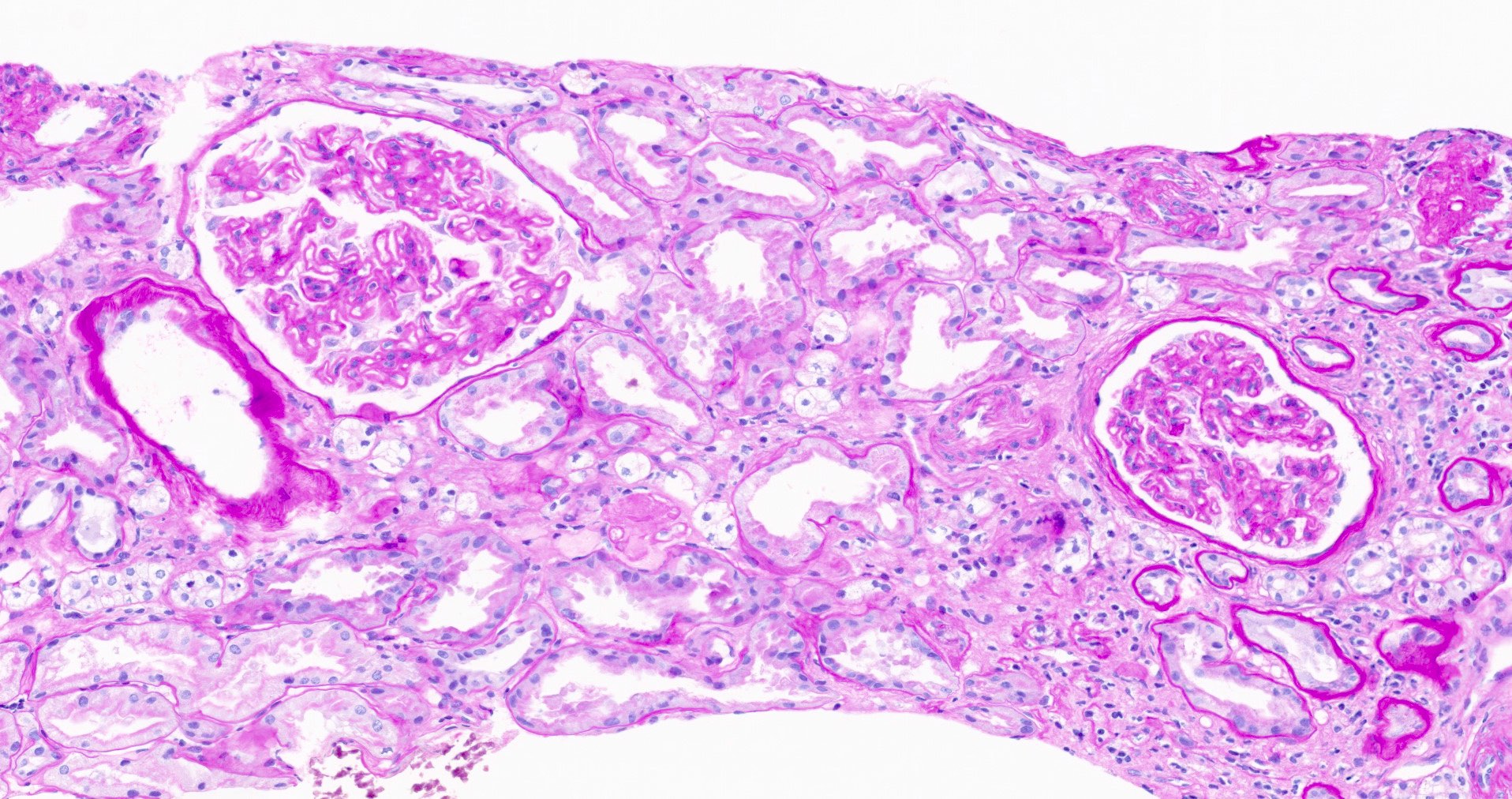
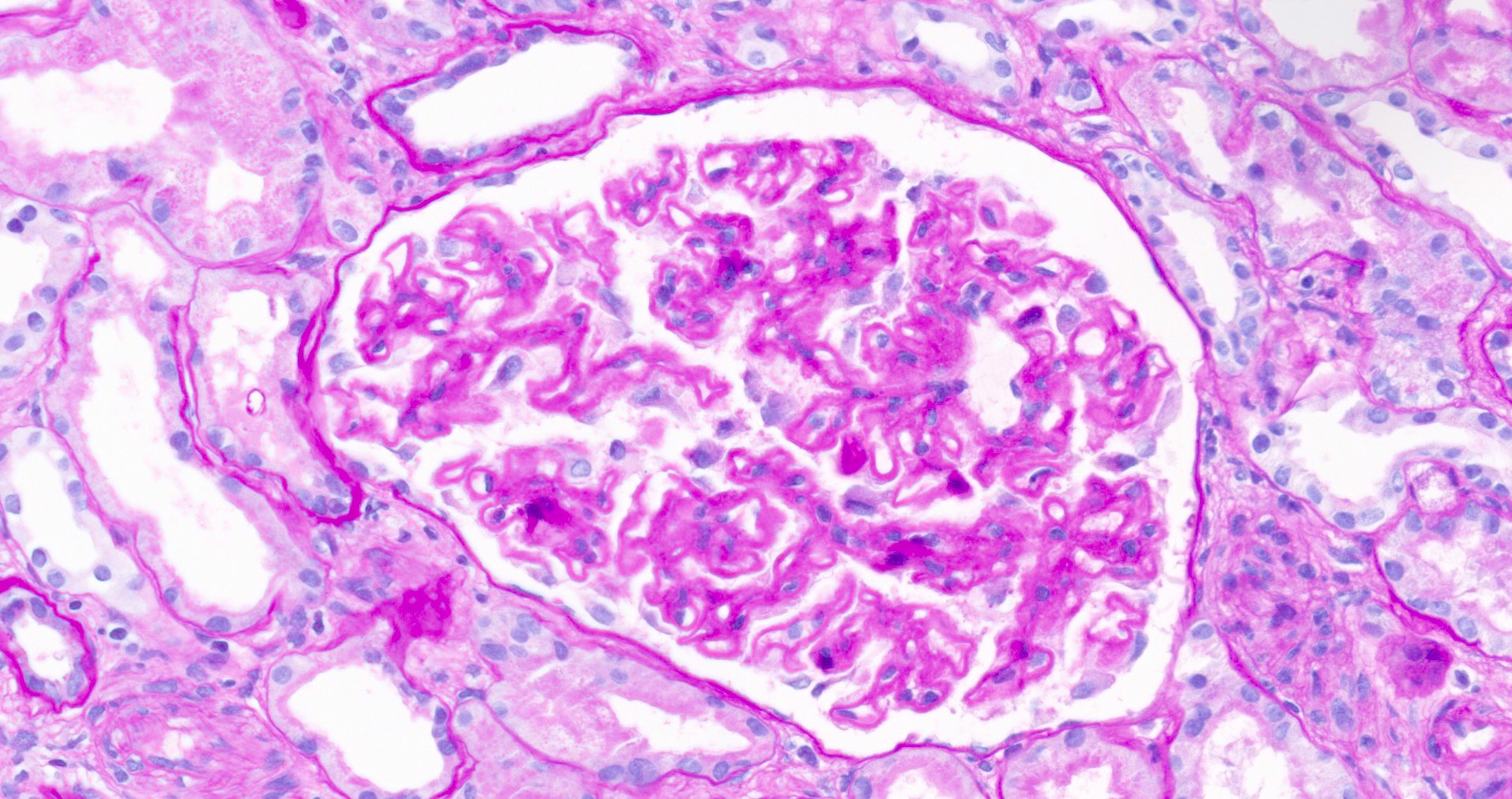
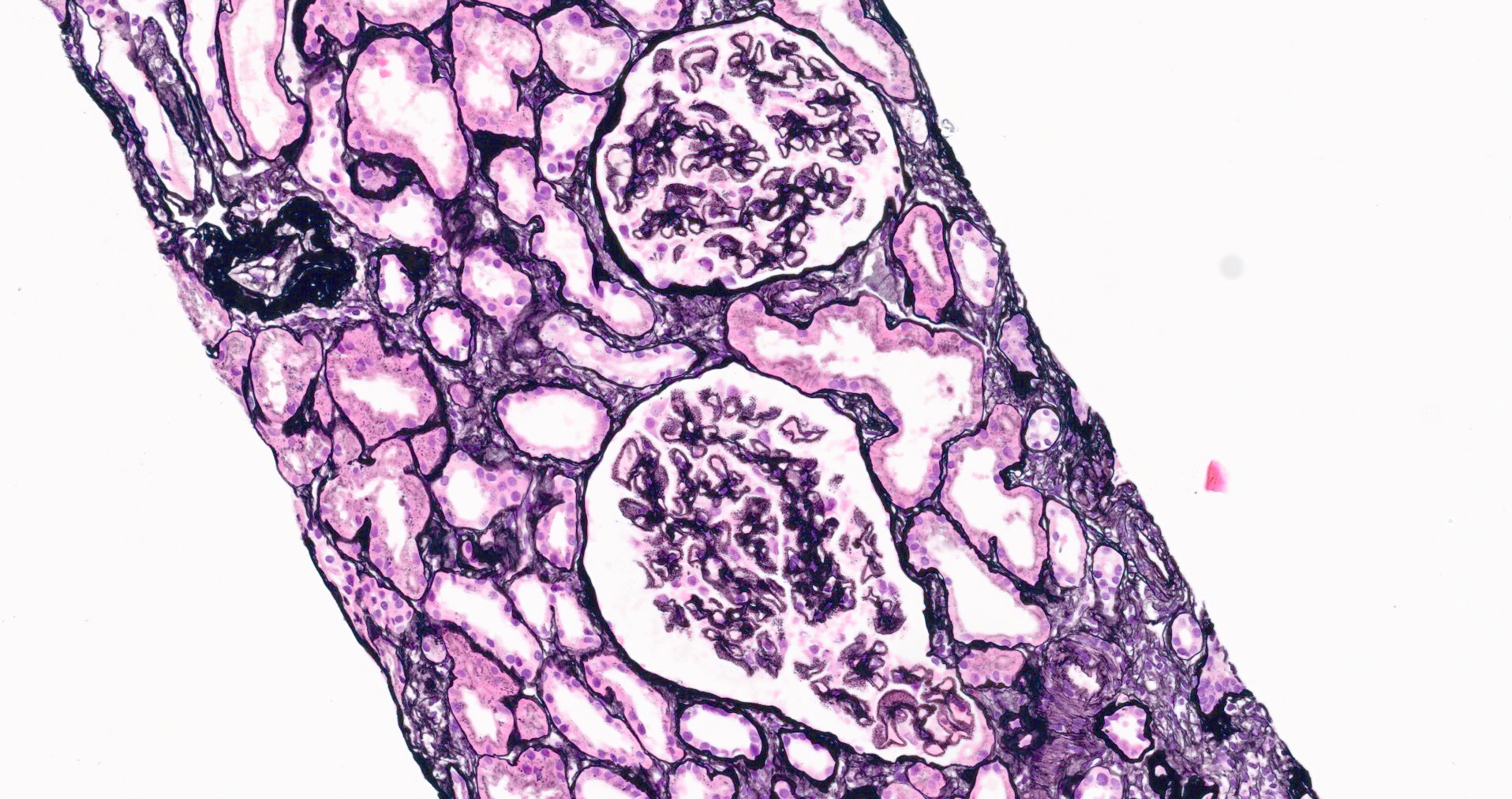
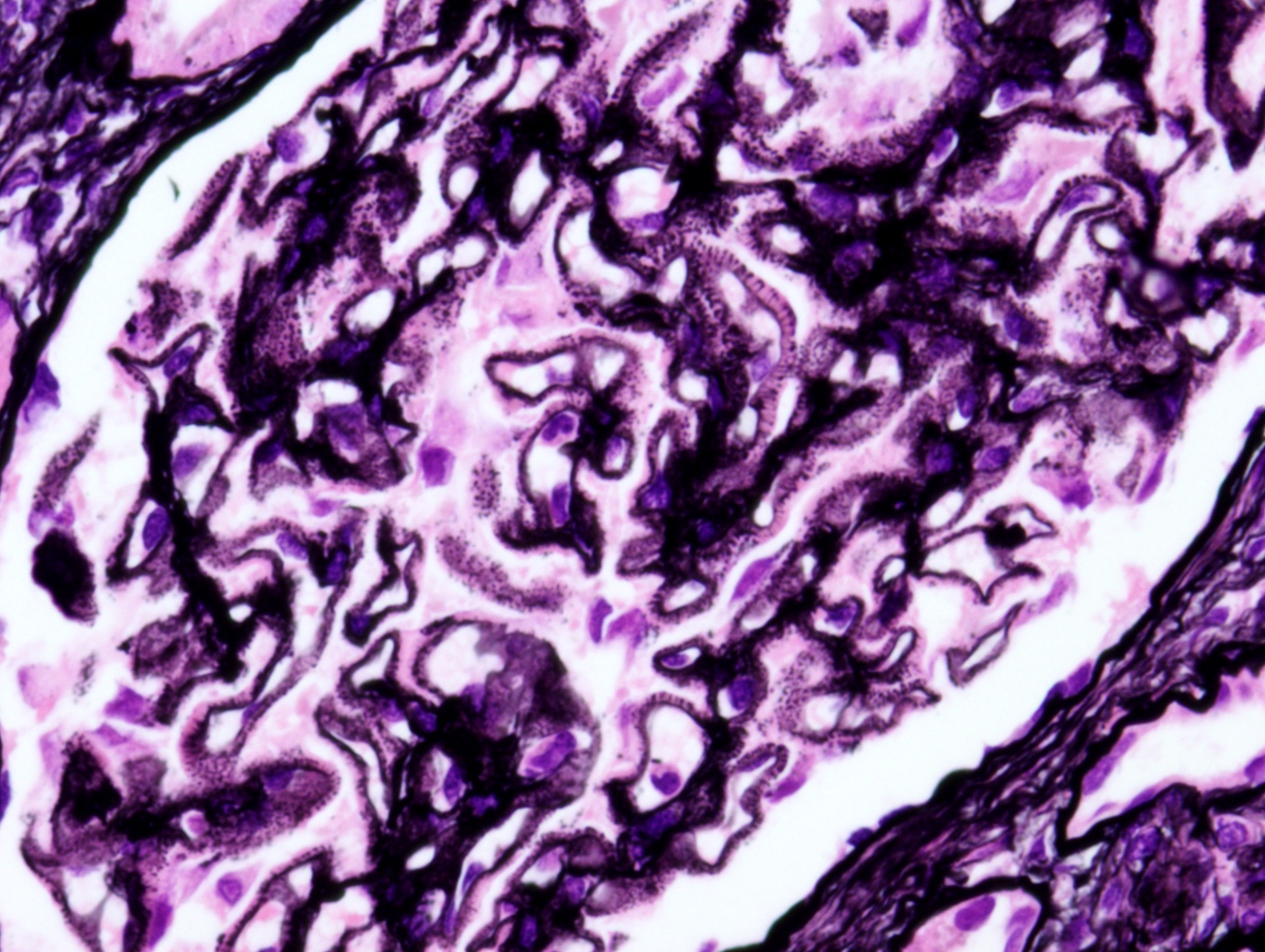
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Glomeruli may appear entirely normal in early disease (stage 1)
- Thickening of glomerular basement membrane
- Subepithelial spike formation or vacuolated appearance on PAS or Jones silver stain (Colvin: Diagnostic Pathology - Kidney Diseases, 2nd Edition, 2015, Zhou: Silva's Diagnostic Renal Pathology, 2nd Edition, 2017)
Microscopic (histologic) images
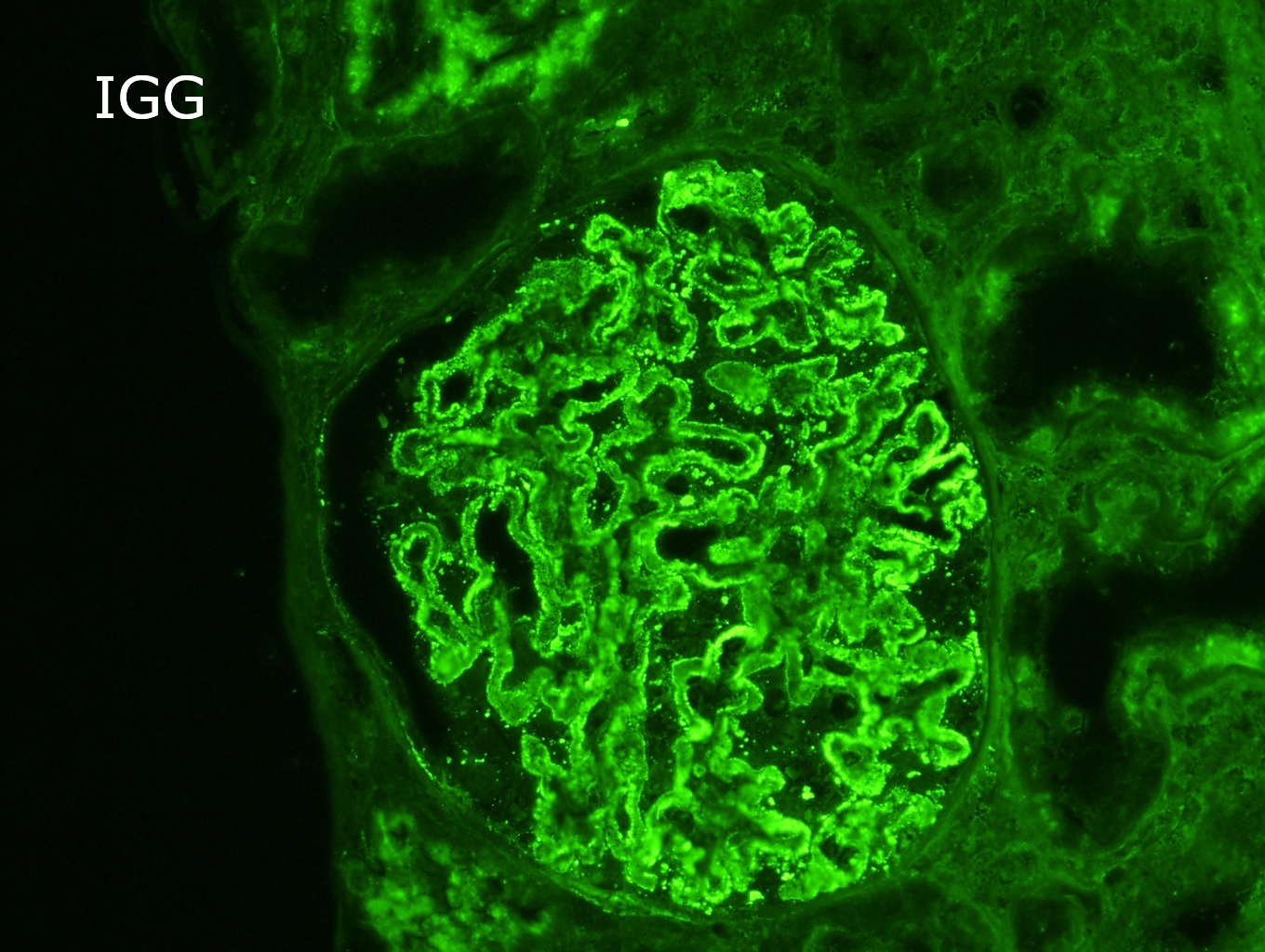
Immunofluorescence description
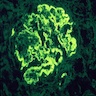
- Finely granular staining for IgG, predominately IgG4, presents uniformly in a subepithelial distribution in all glomeruli (Colvin: Diagnostic Pathology - Kidney Diseases, 2nd Edition, 2015, Zhou: Silva's Diagnostic Renal Pathology, 2nd Edition, 2017)
Immunofluorescence images
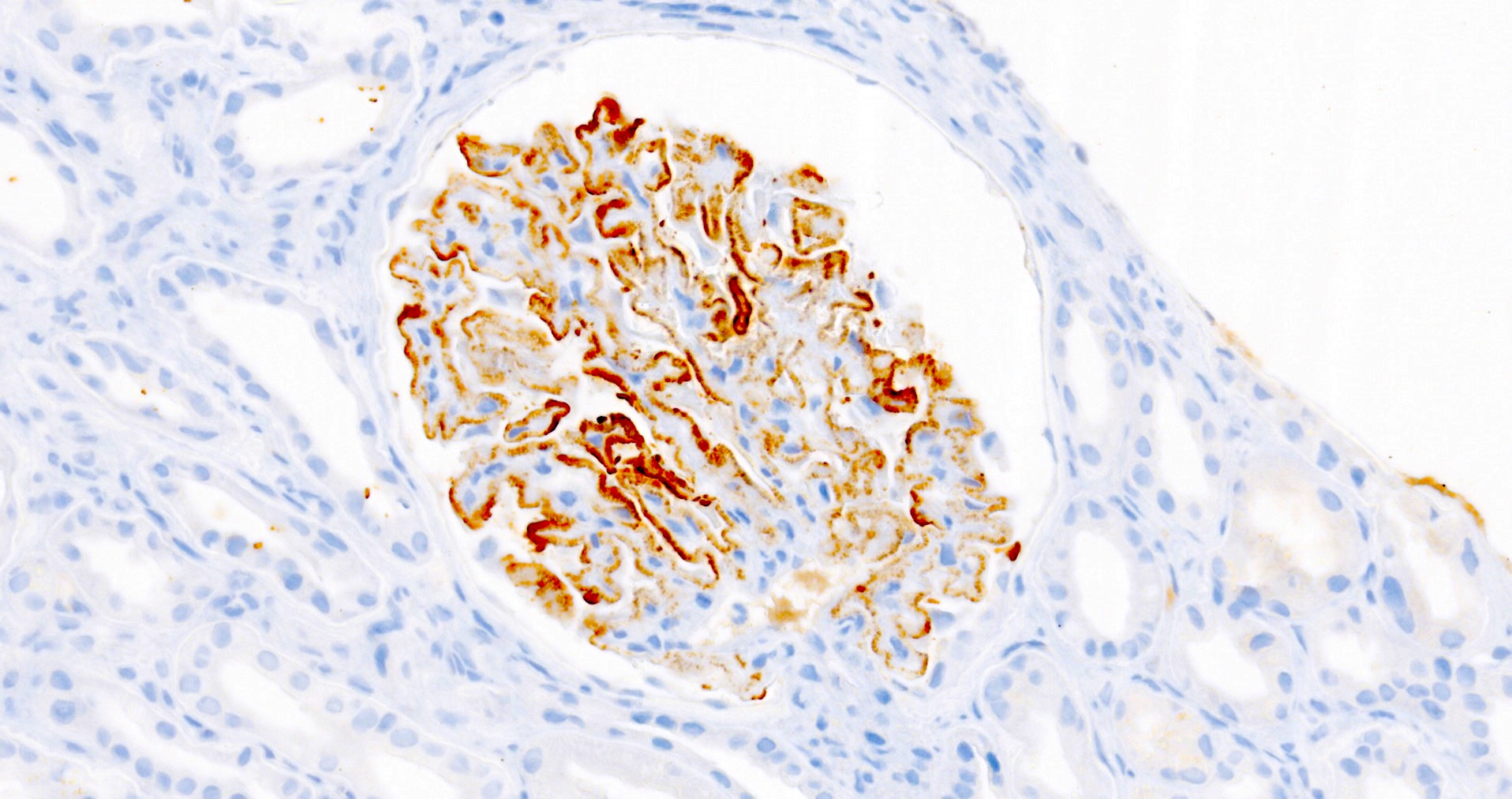
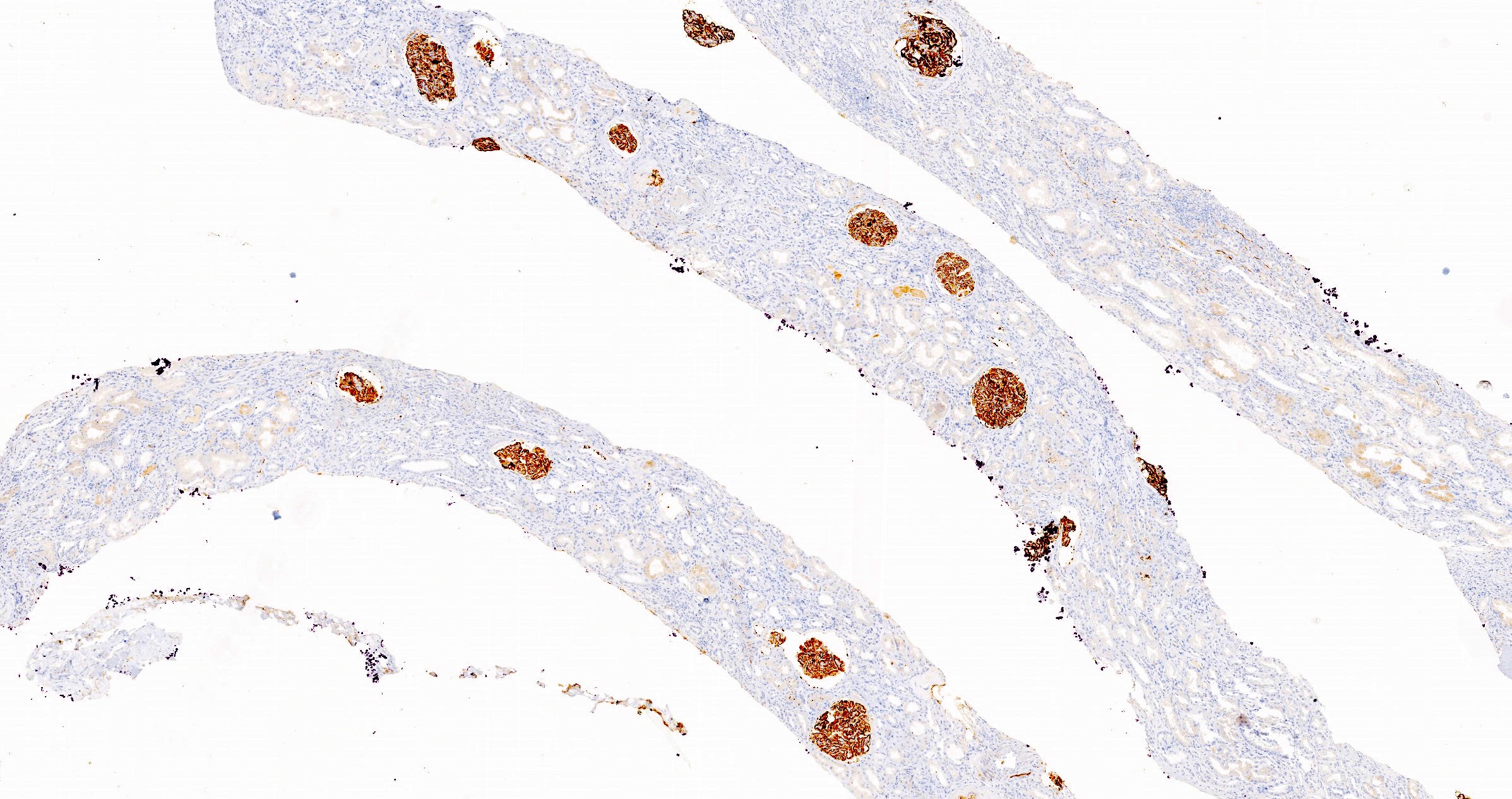
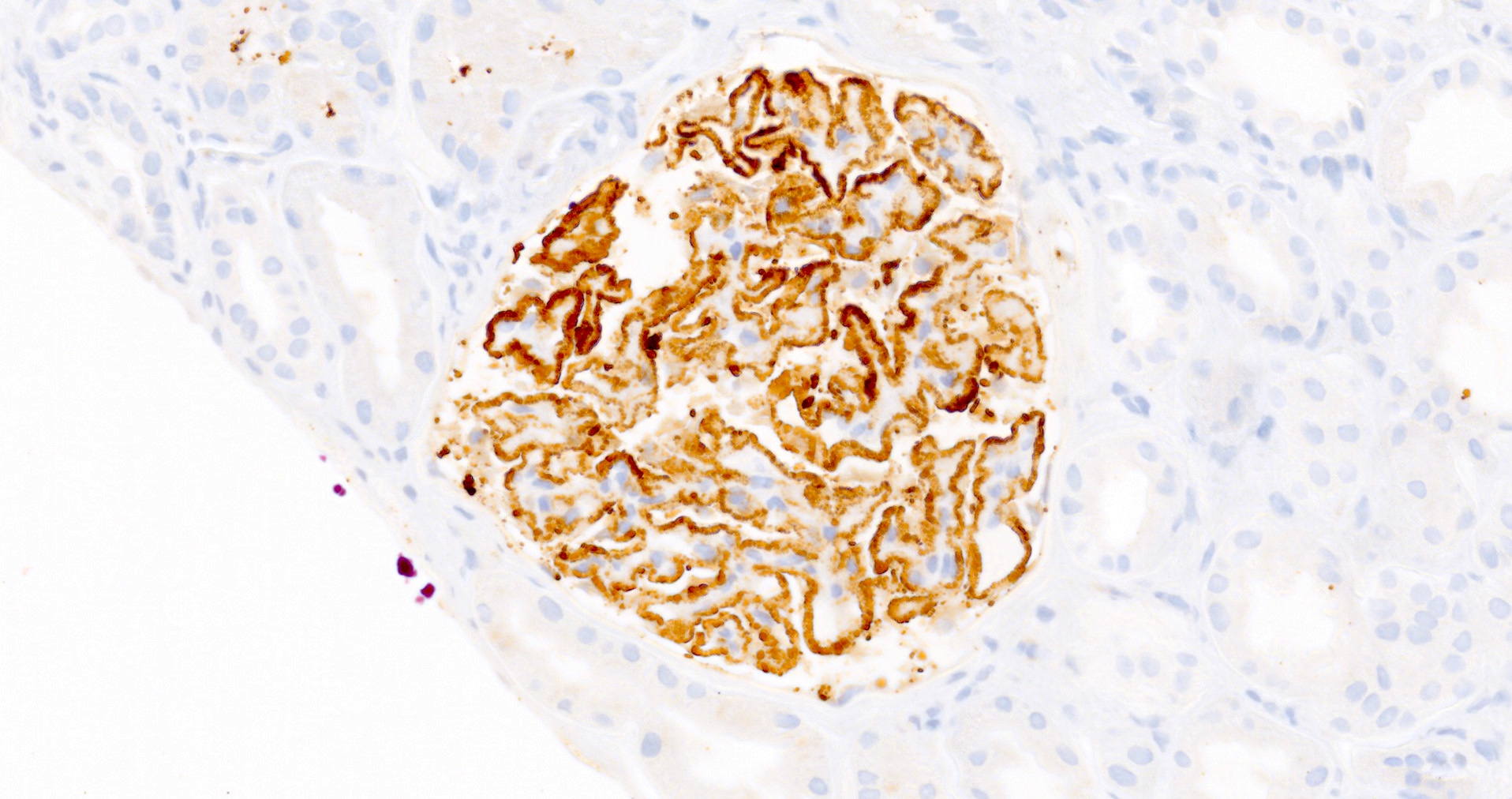
Positive stains
- PLA2R and IgG4: intense global and granular staining of glomerular basement membrane (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2021;29:414)
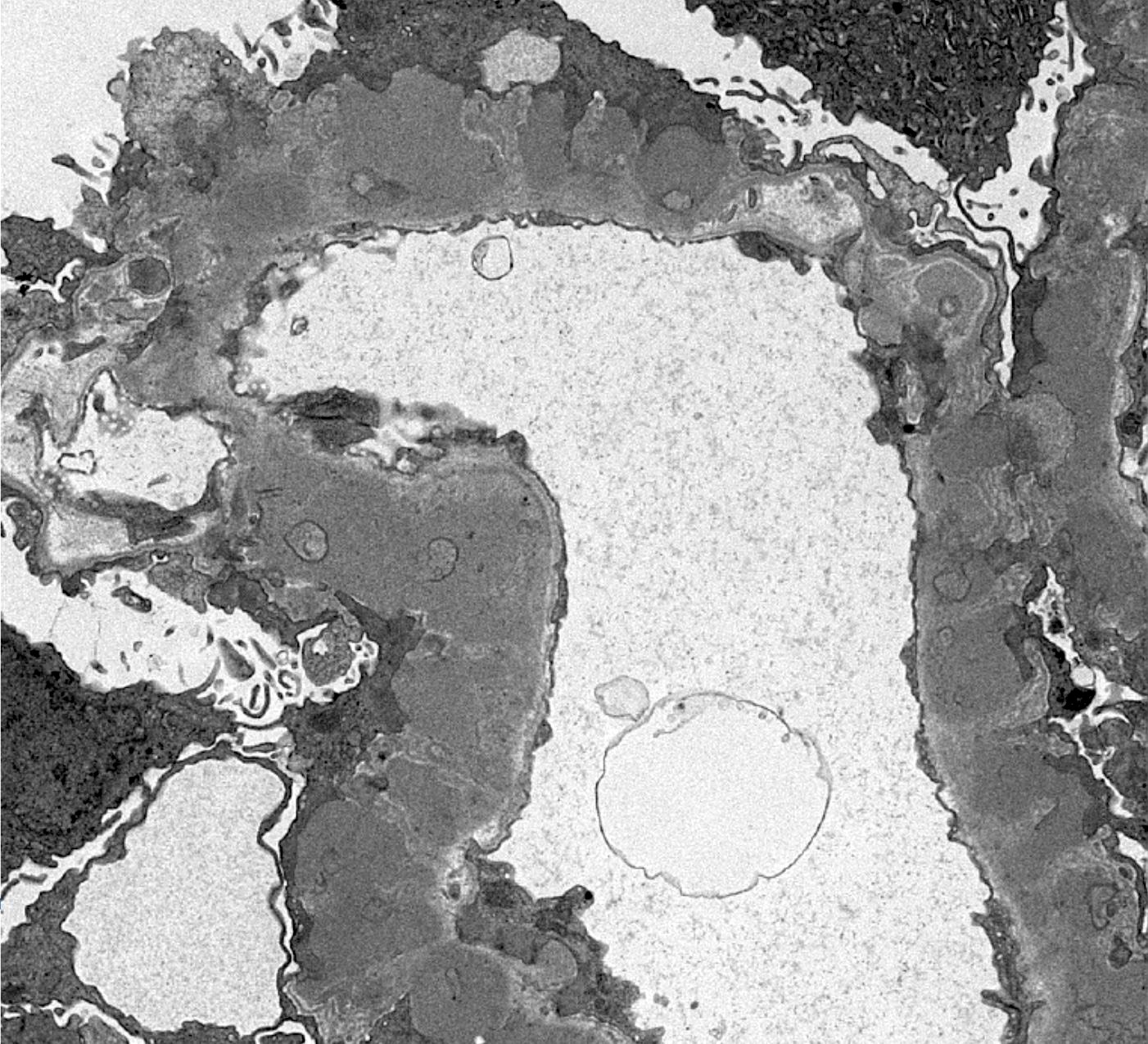
Electron microscopy description
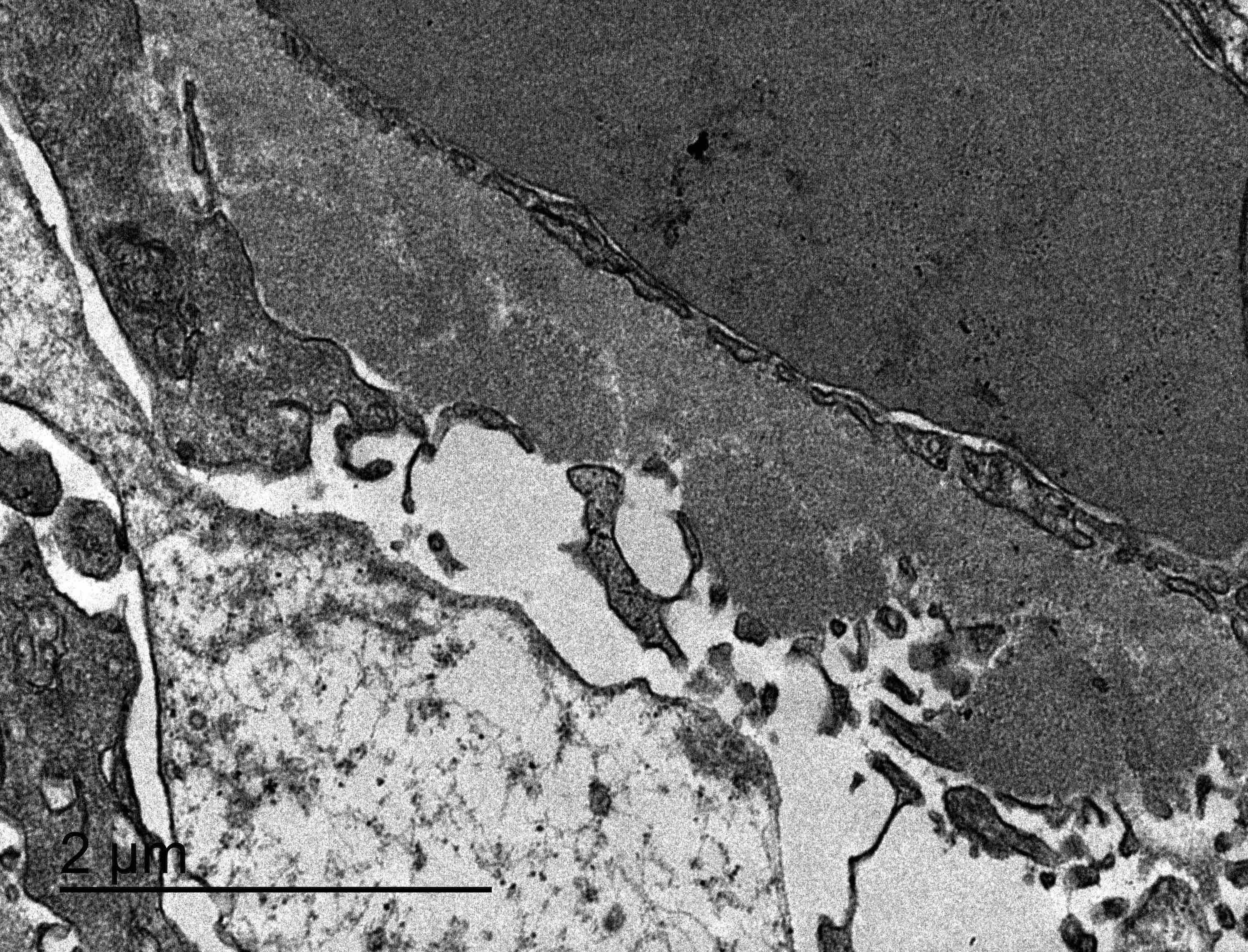
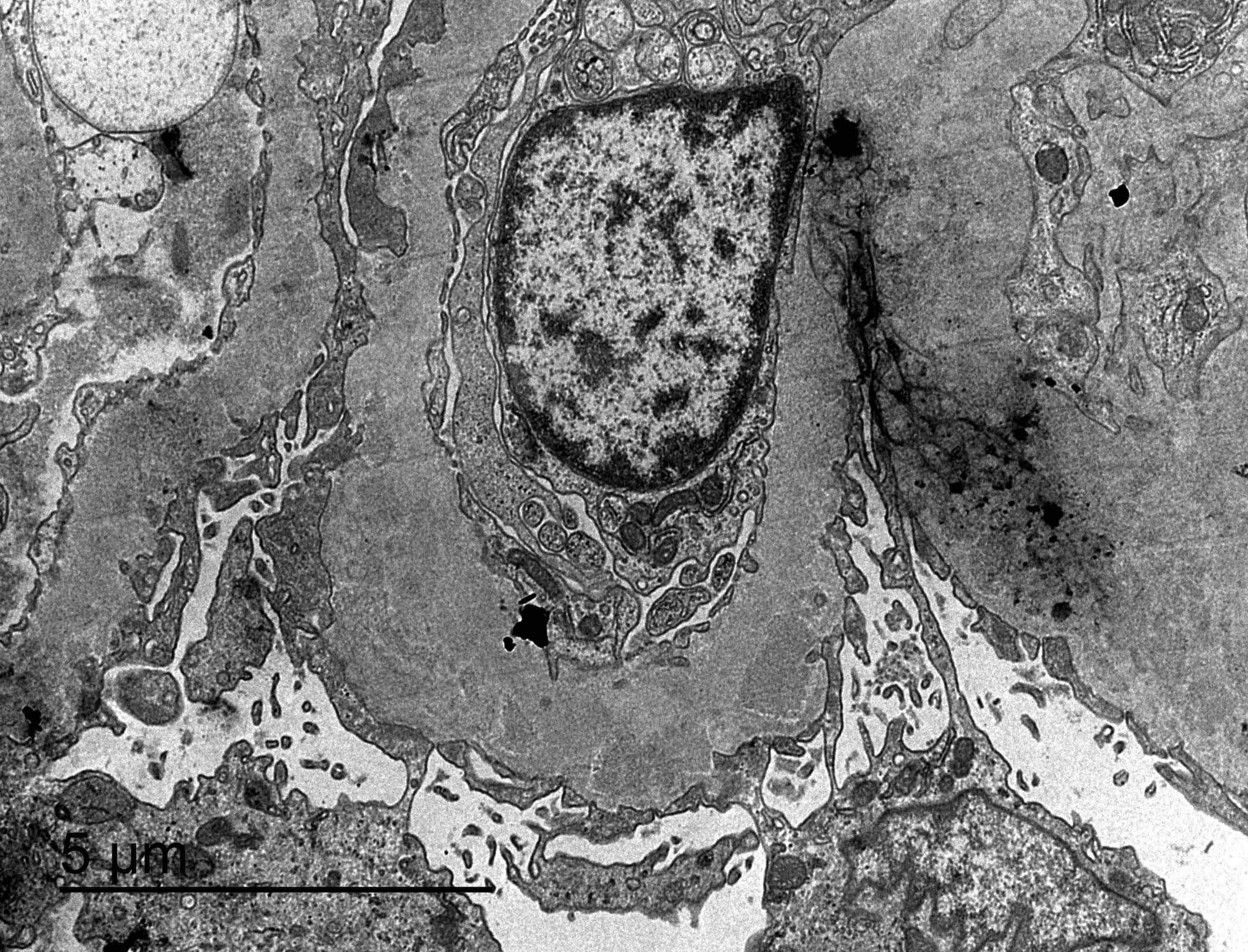
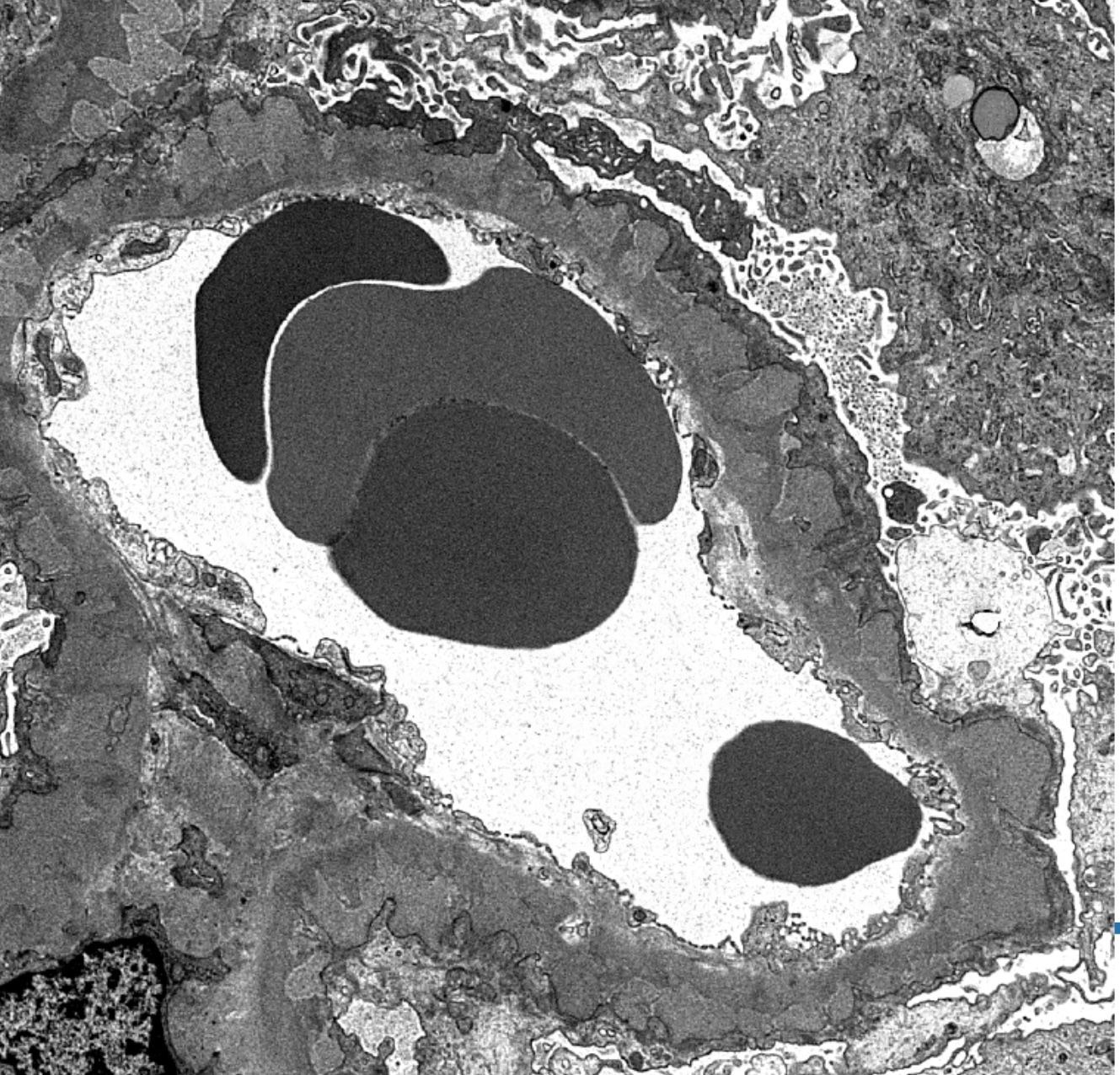
- Electron microscopy confirms the subepithelial localization of electron dense deposits
- 4 stages:
- Scattered electron dense deposits on the epithelial side of the glomerular basement membrane
- Subepithelial deposits with basement membrane material (spikes) between deposits
- Subepithelial (or intramembranous) deposits with basement membrane material between and surrounding deposits
- Electron lucent areas represent probable resorption of prior subepithelial immune complexes
- References: Colvin: Diagnostic Pathology - Kidney Diseases, 2nd Edition, 2015, Zhou: Silva's Diagnostic Renal Pathology, 2nd Edition, 2017
Electron microscopy images
Contributed by Ana Belén Larqué, M.D., Ph.D. and Jonathan E. Zuckerman, M.D., Ph.D.
Images hosted on other servers:
Genetics
- 2 strongly linked loci in genome wide association studies: HLA DQA1 allele and PLA2R allele (Colvin: Diagnostic Pathology - Kidney Diseases, 2nd Edition, 2015)
Sample pathology report
- Right kidney, biopsy:
- Membranous nephropathy; minimal chronic changes (see comment)
- Adequacy: adequate (cortex 85%, medulla 15%)
- Microscopic description: 18 glomeruli, 1 of these with global sclerosis. Thickening of the glomerular capillary wall. Presence of spikes and internal vacuolizations of the glomerular basement membrane evaluated by silver stain. No evidence of hypercellularity, crescent or necrosis. Fibrosis occupying < 10% of the interstitium.
- Immunofluorescence microscopy:
- Number of glomeruli: 4
- Diffuse granular staining of the glomerular basement membrane for IgG (+++) and C3 (++); there were no deposits of IgA, IgM, C1q or fibrin.
- Immunohistochemistry: diffuse and strong granular positivity of glomerular basement membrane for PLA2R and IgG4
- Comment: positivity for anti-PLA2R and IgG4 favor the diagnosis of primary membranous glomerulopathy
- Membranous nephropathy; minimal chronic changes (see comment)
Differential diagnosis
- Secondary form of membranous nephropathy:
- Requires clinical correlation
- Mesangial or endocapillary hypercellularity
- Mesangial or subendothelial deposits
- PLA2R+ deposits in < 10% (depends on cause)
- Staining for all subclasses of IgG
- Membranous lupus nephritis:
- Postinfectious glomerulonephritis:
- Generally has a history of hypocomplementemia and presents with nephritic features
- Subepithelial deposits have segmental distribution, a hump-like configuration, lack of spikes around humps and stain predominantly for C3
- Deposits in mesangium and subendothelial space
- Intraglomerular inflammation and hypercellularity
- Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis:
- Presence of mesangial and subendothelial deposits in addition to intramembranous deposits (Colvin: Diagnostic Pathology - Kidney Diseases, 2nd Edition, 2015, Zhou: Silva's Diagnostic Renal Pathology, 2nd Edition, 2017)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true about primary membranous nephropathy?
- Active periglomerular inflammation and rupture of Bowman capsule
- Little or no immunoglobulin or complement deposits by immunofluorescence
- Most common cause of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in nondiabetic adults worldwide
- Significant mesangial or endocapillary hypercellularity
Board review style answer #1
C. Most common cause of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in nondiabetic adults worldwide
Comment Here
Reference: Primary membranous nephropathy
Comment Here
Reference: Primary membranous nephropathy
Board review style question #2
Which of the following findings favors primary membranous nephropathy over secondary forms?
- Glomerular basement membrane spikes by PAS and silver stains
- Intense global and granular PLA2R and IgG4 staining of glomerular basement membrane
- Nephrotic range proteinuria
- Thickening of the glomerular capillary wall
Board review style answer #2
B. Intense global and granular PLA2R and IgG4 staining of glomerular basement membrane
Comment Here
Reference: Primary membranous nephropathy
Comment Here
Reference: Primary membranous nephropathy