Table of Contents
Definition / general | Case reports | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Immunofluorescence description | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Sangle N. Hyperacute rejection. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneyhyperacuterejection.html. Accessed December 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Occurs within minutes to hours after revascularization, causing abrupt cessation of urine production
- Due to preformed circulating antibodies in recipient to donor endothelial cells, caused by prior pregnancies, blood transfusions or transplants
- Can perform ABO incompatible transplants if low titers (Nephrol Dial Transplant 2010;25:3794)
- Rare currently due to routine screening and cross matches
Case reports
- With negative pretransplantation T and B cell flow cytometric crossmatches and blood group identity (Transplant Proc 2008;40:2422)
Gross description
- Mottled cyanosis and diminished turgor in renal graft
Microscopic (histologic) description
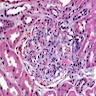
- Fibrin thrombi in glomerular capillaries, peritubular venules and other vessels leading to infarction and tubular necrosis
- Variable white blood cells within glomeruli, peritubular capillaries and interstitium
Immunofluorescence description
- Linear staining of IgM or IgG, as well as C3 and C4d along glomerular and peritubular capillaries
- At later stages Ig may not be detectable
Electron microscopy description
- Capillary occlusion by degranulated platelets and endothelial denudation of glomerular basement membrane
- Also fibrin, sludged red blood cells
Differential diagnosis
-
Other conditions that can cause primary graft failure include:
- Acute tubular necrosis
- Major vascular occlusion
- Perfusion injury