Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Immunofluorescence description | Immunofluorescence images | Electron microscopy descriptionCite this page: Sangle N. Henoch-Schonlein purpura (HSP) / IgA vasculitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneyhsp.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Need clinical history to distinguish between renal limited IgA nephropathy and systemic HSP
- Purpuric skin lesions on extensor arms and legs and buttocks
- Also abdominal pain, vomiting, GI bleeding, arthralgias, hematuria, proteinuria and nephrotic syndrome
- Due to systemic small vessel leukocytoclastic vasculitis
- Most common systemic vasculitis in children
- Also called anaphylactoid purpura
Clinical features
- Significant clinicopathological differences with IgA nephropathy (Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2012;14:506)
- Renal symptoms in 30 - 70%; some adults develop rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis
- 70% are ages 2 - 11 years; rare in adults or infants 1 year or less
- Higher rate of renal involvement in children ages 10 - 18 (Iran J Kidney Dis 2012;6:269)
- Associated with atopy in 1/3; may follow respiratory infection
- Related to IgA nephropathy, due to elevated serum IgA, circulating immune complexes with IgA, similar kidney lesions (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1982;106:192), high serum galactose deficient immunoglobulin A1 levels (Kidney Int 2011;80:79)
- Hypertension, serum creatinine, proteinuria, cellular crescents, glomerular necrotizing lesions and chronic renal lesions are associated with renal failure (Mod Pathol 2001;14:635)
- Variable recurrence rates (12 - 69%) after renal transplant, but usually not clinically important (Transplantation 2011;92:907, Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2011;6:1768, Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2011;6:2034)
- Prognosis: excellent in children (50% have spontaneous remission); poorer in adults (Clin Nephrol 2011;76:49) or with nephrotic syndrome; often difficult to predict (Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2011;6:679)
Case reports
- 15 year old girl with prior onset of IgA nephropathy (Fukushima J Med Sci 2010;56:157)
- 72 year old man with coexisting IgG4 related tubulointerstitial nephritis (Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol 2011;7:5)
- 75 year old man with rectal bleeding and acute renal injury (J Med Case Rep 2011;5:364)
Treatment
- Recommended to administer intensive therapy initially (Indian J Pediatr 2012;79:207)
- Corticosteroids, cytotoxic drugs
- Mycophenolate mofetil for children with nephrotic-range proteinuria (Pediatr Nephrol 2012;27:765)
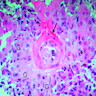
Microscopic (histologic) description
-
Acute:
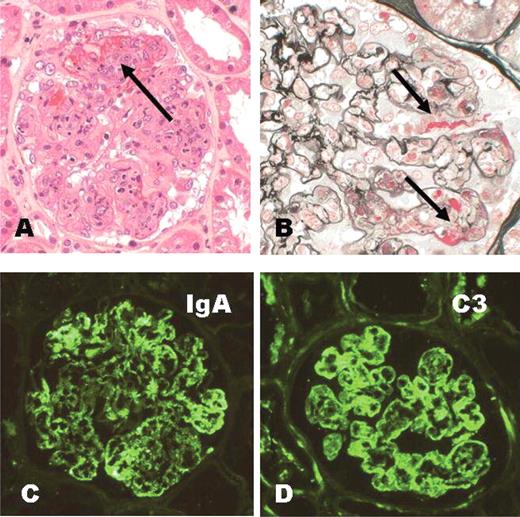
- Leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels due to deposition of IgA immune complexes
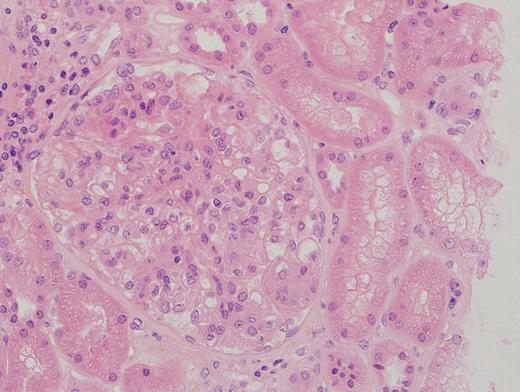
- Diffuse proliferation of mesangial cells and matrix without significant involvement of capillary walls or lumina
- Also segmental necrotizing lesions (50%), endocapillary proliferation (13%), cellular crescents, glomerular acute and chronic inflammatory infiltrate
-
Chronic:
- Glomerular sclerosis, tubular loss, interstitial fibrosis and hyaline arteriolosclerosis
-
Skin:
- Hemorrhage and necrotizing vasculitis in dermal small vessels, which contain IgA
- Vasculitis is present in other organs but usually NOT kidney
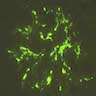
Immunofluorescence description
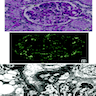
- IgA deposition in mesangium, resembling IgA nephropathy
- Variable IgG, IgM, C3 and properdin
Electron microscopy description
- Mesangial deposits, may extend into subendothelial areas
- May have subepithelial deposits