Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Immunofluorescence description | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Sangle N. Cryoglobulinemia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/kidneycryoglobulinemia.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- See also topic in Bone marrow neoplastic chapter
- Usually systemic disease in which deposits of IgG or IgM immune complexes cause glomerulonephritis (focal, diffuse), cutaneous vasculitis (skin rash) and synovitis (arthritis)
- Defined by presence of serum cryoglobulins, which are immunoglobulin complexes that precipitate at 4°C and become soluble again at 30°C
- Type I: cryoglobulin is single monoclonal immunoglobulin class, usually due to myeloma, Waldenström macroglobulinemia or other lymphoma
- Type II: mixture of 2+ immunoglobulins, one a monoclonal antibody against polyclonal IgG; usually IgG-IgM, in which IgM is monoclonal and has rheumatoid factor activity
- Type III: both immunoglobulin components are usually polyclonal IgG and IgM
Clinical features
- Symptoms of fatigue, purpura over lower extremities, arthralgias, hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, Raynaud phenomenon, glomerulonephritis in 50% with proteinuria and hypertension, progressing to renal failure in 5%
- Usually women ages 30+ years
- Hepatitis C virus is major cause of mixed cryoglobulinemia
- Renal disease unrelated to Hepatitis C is often related to primary Sjögren Syndrome (Medicine (Baltimore) 2009;88:341)
- Cryoglobulinemia found in 83% of chronic hemodialysis patients, although not necessarily symptomatic (Ren Fail 2011;33:801)
- Types II and III associated with B cell lymphoma, chronic infection, chronic liver disease, SLE and hepatitis C
Case reports
- 7 year old boy with glomerular rhomboid inclusions (Am J Kidney Dis 2009;53:866)
- 55 year old man with Hepatitis C (J Med Case Rep 2009;3:91)
- 58 year old woman with ultrastructural diagnosis of cryoglobulinemic glomerulonephritis (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1981;105:474)
- 60 year old man with Hepatitis B virus associated type II cryoglobulinemia and severe multisystem disease, treated with Rituximab (J Med Case Rep 2012;6:39)
- 81 year old man with essential type II cryoglobulinemia unrelated to Hepatitis virus (Geriatr Gerontol Int 2009;9:92)
Treatment
- Double filtration plasmapheresis; cryofiltration (Ther Apher Dial 2012;16:91)
- Possibly interferon for Hepatitis C related cases (Ren Fail 2009;31:149)
- Possibly Rituximab in nonviral patients age 70 years or less (Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2010;62:1787, Autoimmun Rev 2011;11:48)
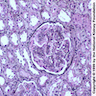
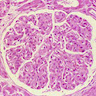
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Expanded mesangium with thickened capillaries
- Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis, often with membranoproliferative pattern
- Also focal and segmental glomerulonephritis and less often crescentic or membranous glomerulonephritis
- Acutely may produce wire loops or thrombi seen in lupus nephritis, vasculitis of interlobular arteries and afferent arterioles
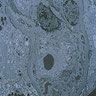
Microscopic (histologic) images
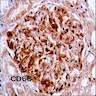
Immunofluorescence description
- Immunoglobulins, strong C3; also C1q and C4
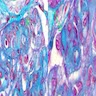
Electron microscopy description
- Large amounts of subendothelial immune complex deposits; lesser amounts of subendothelial deposits
- 50% have glomerular deposits with 25 - 35 nm microtubules forming bundles or arranged in fingerprint-like array
Differential diagnosis
- Fibrillary glomerulonephritis: 15 - 30 nm fibrils
- Immunotactoid glomerulopathy