Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Immunofluorescence description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Ashraf N, Warmke L. Rheumatoid arthritis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/jointsra.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder often characterized by symmetrical and progressive destructive arthritis
- RA can also affect other tissues and organs, such as the skin, eyes, lungs and blood vessels, often resulting in significant disability if not adequately managed (Lancet 2016;388:1984)
Essential features
- Rheumatoid arthritis often affects women and frequently presents with symmetric arthritis, often involving the small bones of the hands and feet
- Patients may have an increase in serum acute phase reactants and positive autoantibodies, including rheumatoid factor and anticitrullinated protein antibodies
- Microscopic findings typically show thickening of the synovial lining, abundant lymphocytes and plasma cells, angiogenesis and erosion of bone and cartilage
- Extra-articular manifestations are common and can include rheumatoid nodules, pleuritis, vasculitis and scleritis
Terminology
- Chronic inflammatory polyarthritis
- 2 types of rheumatoid arthritis: seropositive and seronegative
- Caplan syndrome (rheumatoid pneumoconiosis)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: M06.9 - rheumatoid arthritis, unspecified
Epidemiology
- RA affects about 0.5 - 1.0% of the global population (Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:1316)
- Annual incidence is estimated to be around 20 - 50 cases per 100,000 individuals (Arthritis Rheum 2010;62:1576)
- Twice as common in women than men; M:F between 1:2 and 1:4
- May begin at any age with peak frequency in the fourth and fifth decades
- Higher prevalence rates in Northern Europe and North America
- Lower prevalence rates in Asia and certain Afro-Caribbean groups
Sites
- Affects all joints, predominantly the small joints of the hands and feet
- May also affect larger joints such as knees, hips, elbows and shoulders (Lancet 2016;388:2023)
Pathophysiology
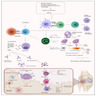
- Disease process begins with activation of immune cells, such as T and B lymphocytes, which infiltrate the synovium, initiating a cascade of inflammatory cytokine release, including TNFα, IL1 and IL6 (Lancet 2001;358:903)
- Inflammatory setting promotes synovial hyperplasia and angiogenesis, leading to pannus formation, cartilage destruction and bone erosion
- Plasma cells manufacture rheumatoid factors, along with other antibodies (e.g., against type II collagen)
- Activation of periosteal osteoclasts leads to periarticular bone erosion
- Damage to articular surfaces is mediated by matrix degrading enzymes (e.g., matrix metalloproteinases)
Etiology
- One or more sporadic conditions of unknown cause
- Autoimmune disorder influenced by genetic and environmental factors
- Genetic association with major histocompatibility complex (MHC), polymorphisms of HLA-DRB1 affect disease severity
- Earlier onset and greater severity with DRB1*0401/*0404 compound genotype
- Environmental factors such as smoking, infections (e.g., Epstein-Barr virus) and hormonal triggers (e.g., estrogen deficiency in postmenopausal women) can act as triggers (Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2020;72:1766)
Clinical features
- Variable clinical course
- Periods of remission and relapse
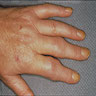
- Symmetrical joint pain, swelling and stiffness, often affecting small joints such as those in the hands, wrists and feet (Ann Rheum Dis 1976;35:357)
- Morning stiffness, often lasting over 30 minutes, which may improve with movement (J Rheumatol 1999;26:1052)
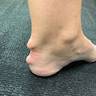
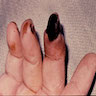
- Joint deformities, such as swan neck deformity, boutonniere deformity and ulnar deviation, due to chronic inflammation and joint damage
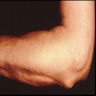
- Rheumatoid nodules commonly found over pressure points or on the extensor surfaces of joints (Am J Med 1984;76:279)
- Rheumatoid nodules present in ~20% of cases (Histopathology 1991;19:193)
- Fatigue, malaise, low grade fever and unintentional weight loss may be present
- Extra-articular manifestations include but are not limited to dry eyes, scleritis, vasculitis, pericarditis, pleuritis and peripheral neuropathy (Ann Rheum Dis 2003;62:722)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis of RA is supported by at least 1 swollen joint not otherwise explained and meeting classification criteria of the American College of Rheumatology (Arthritis Rheum 1988;31:315)
- Serologic testing for rheumatoid factor
- Xray to look for bone erosions
Laboratory
- Rheumatoid factor (antibodies to the Fc portion of IgG) is the only established marker, although not specific
- Elevated acute phase reactants, such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C reactive protein (CRP), indicating systemic inflammation
- Presence of autoantibodies, including rheumatoid factor (sensitivity: 60 - 80%, specificity: 70 - 90%) and anticitrullinated protein antibodies (sensitivity: 80%, specificity: 95%) (Ann Intern Med 2007;146:797)
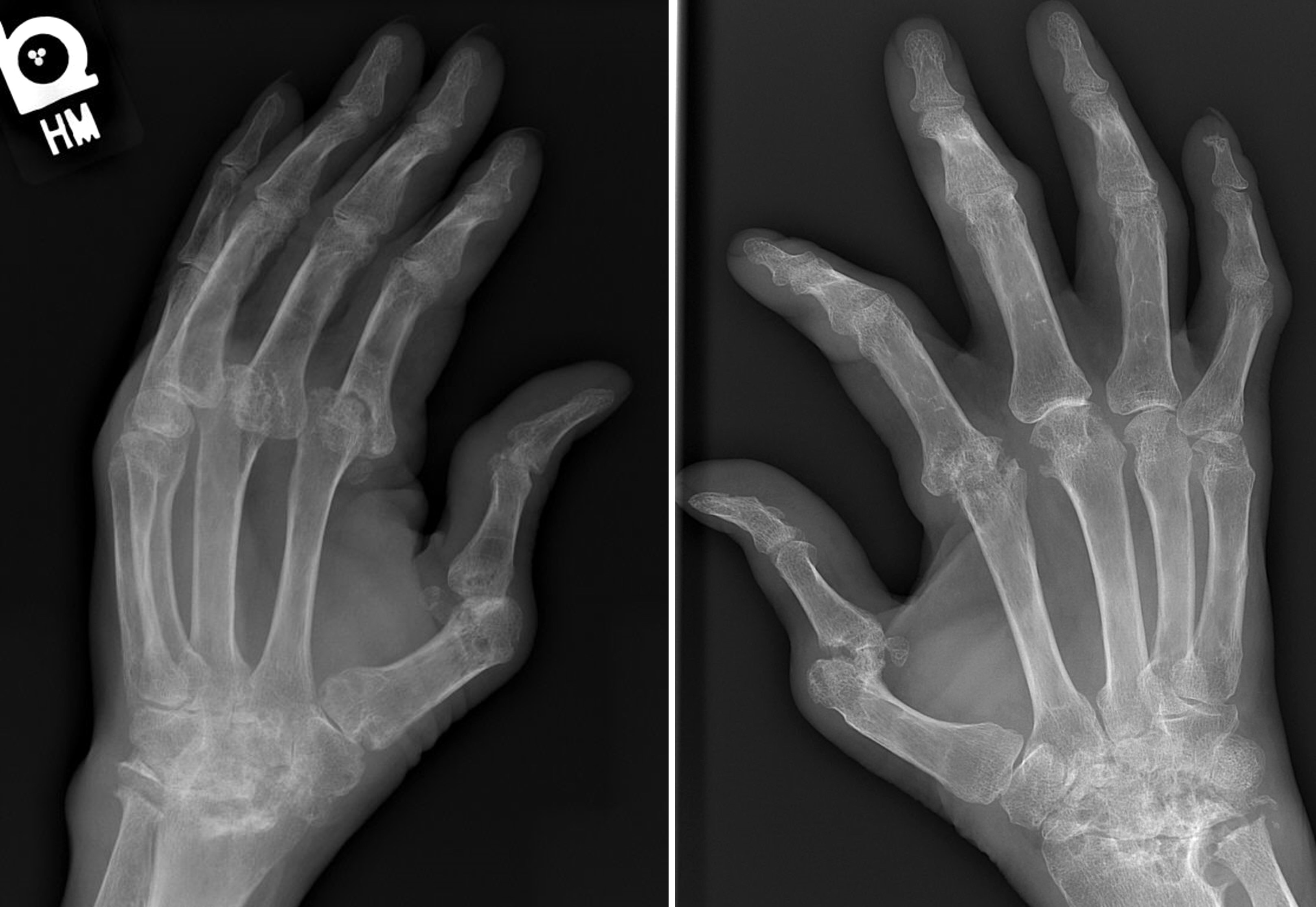
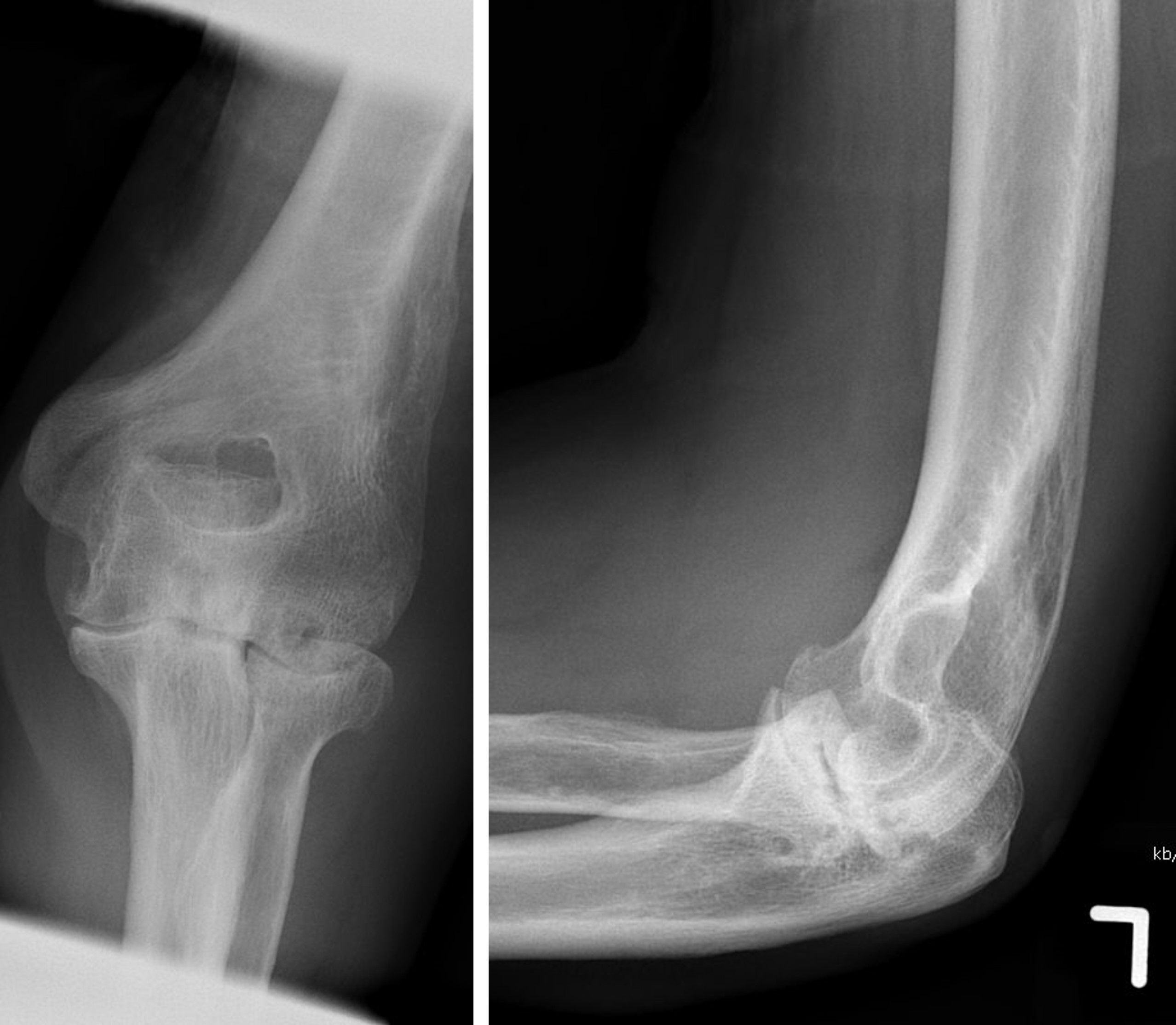
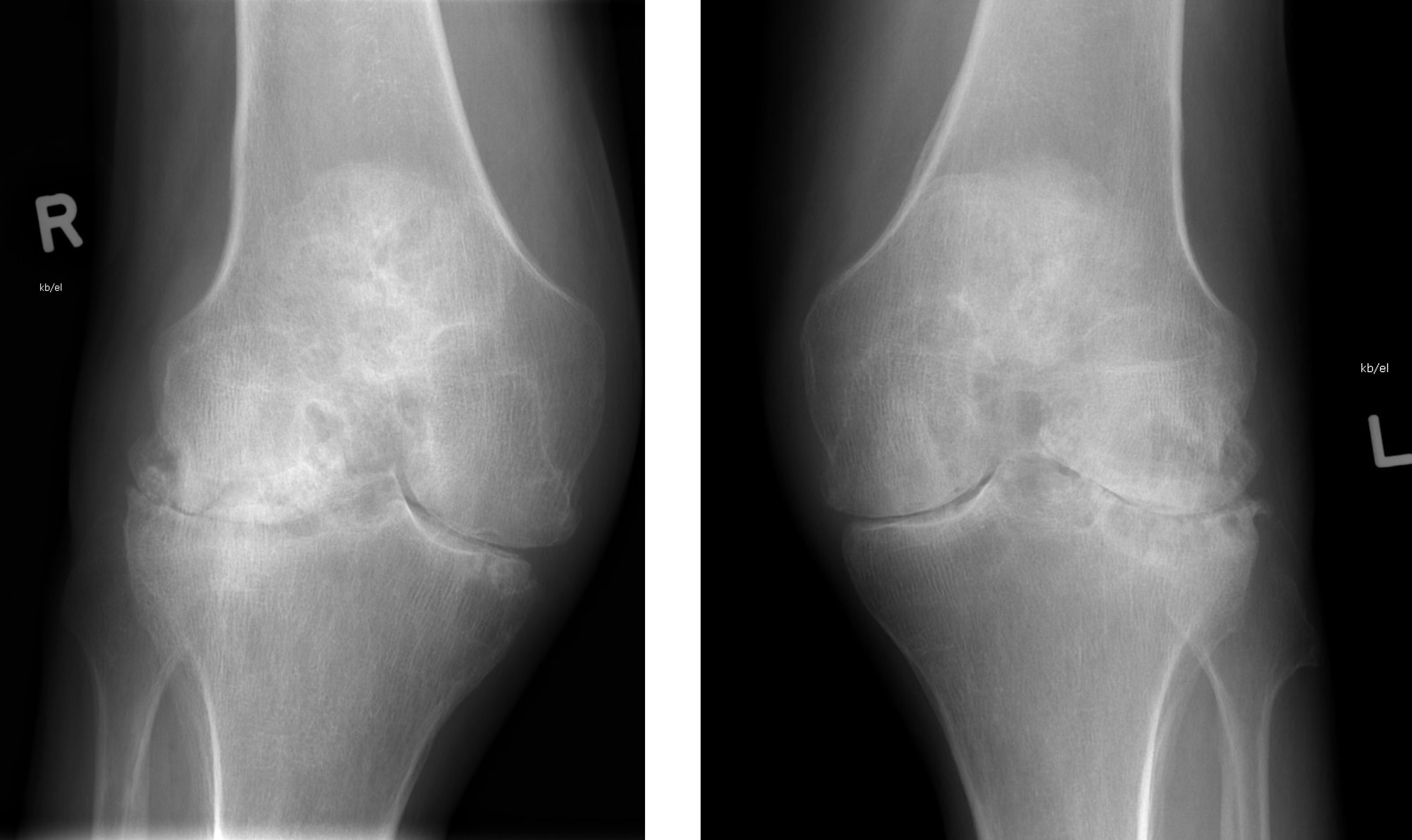
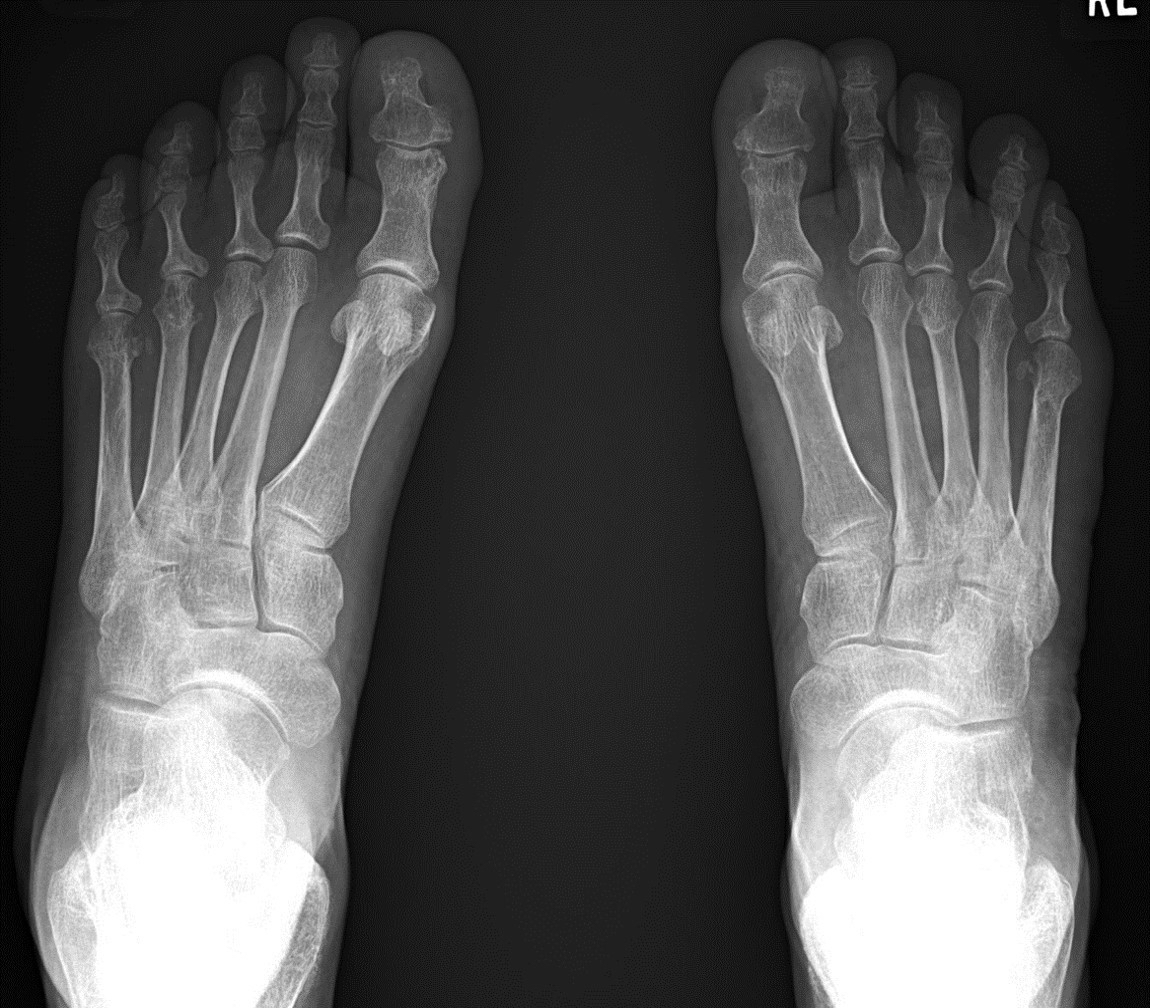
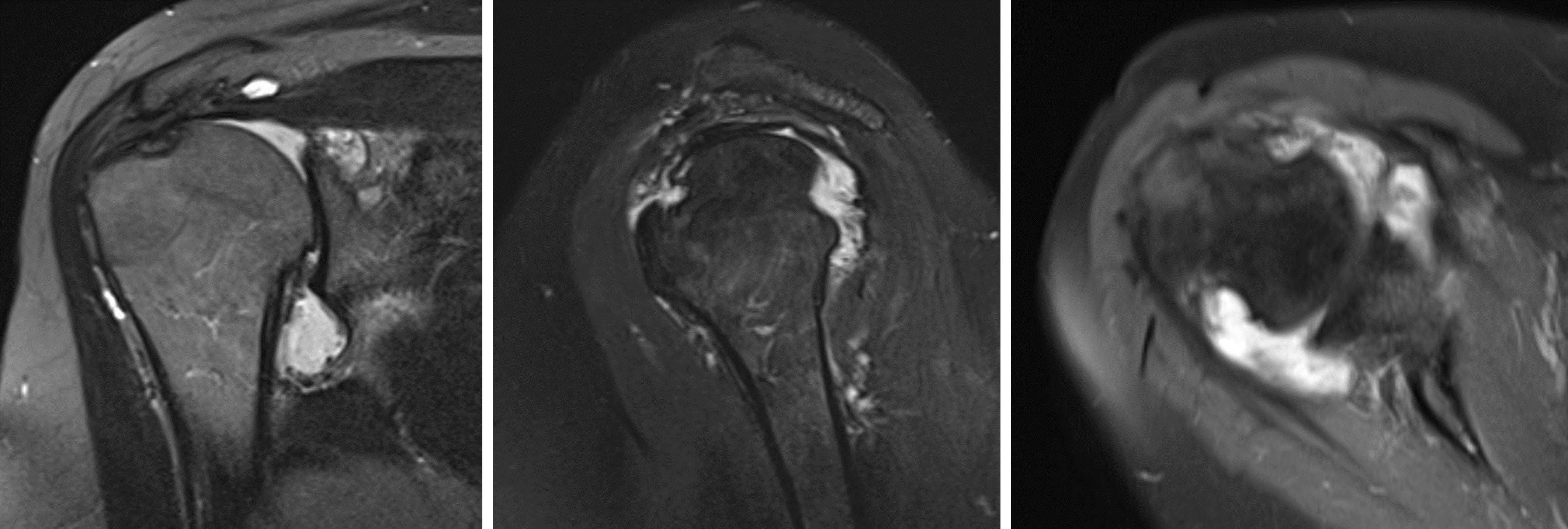
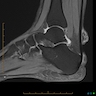
Radiology description
- Radiographic hallmarks are soft tissue swelling, osteoporosis, joint space narrowing and margin erosions (Helms: Fundamentals of Skeletal Radiology, 5th Edition, 2019)
- Progressive loss of joint space due to cartilage destruction
- Erosions appear as well defined areas of bone loss, usually at the joint margins (J Rheumatol 1989;16:585)
- Marked joint space narrowing in the wrist is known as carpal crowding
- Joint deformities include ulnar deviation, swan neck deformity and boutonniere deformity
- On magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), rheumatoid nodules are low to intermediate signal on T1 weighted (T1W) images and isointense to muscle (Clin Imaging 1998;22:216)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- High disease activity score (DAS) is associated with worse outcome (J Rheumatol 2009;36:1873)
- Greater degree of joint deformity with positive rheumatoid factor, high titers are associated with more severe disease
- Extra-articular manifestations, such as rheumatoid nodules, rheumatoid vasculitis or interstitial lung disease, indicates more aggressive disease
- Increased incidence of comorbidity with septic arthritis and immune system malignancy
- Presence of comorbid conditions, such as cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis or obesity can complicate management
- Rapid and sustained response to disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), particularly within the first few months of treatment initiation, is associated with better long term outcome
Case reports
- 30 year old woman with 7 year history of pain in lumbosacral area and 1 year history of pain in joints of both hands (Chin Med J (Engl) 2011;124:3430)
- 48 year old woman with a nodule in the upper lip (J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2014;72:1532.e1)
- 49 year old woman with chief complaint of restricted mouth opening without pain, lasting ~4 months (Braz Dent J 2012;23:779)
- 52 year old woman had pain in the right wrist joint for 6 months (Case #308)
- 53 year old woman with mass in cubital fossa (J Family Med Prim Care 2020;9:4434)
- 72 year old woman with 6 month history of progressive painful swelling of wrists (Int J Surg Case Rep 2011;2:208)
- Woman with pain and edema in second, third and fourth proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints of hands and wrists (Rev Bras Reumatol 2012;52:648)
Treatment
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), such as methotrexate, TNF inhibitors, IL6 inhibitors and JAK inhibitors among others (Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2022;48:679)
- Joint replacement therapy
Clinical images
Gross description
- Synovium is thickened, swollen and red with villous folds (Klein: Non-Neoplastic Diseases of Bones and Joints, 1st Edition, 2011)
- Hypertrophic synovium grows onto the surface of cartilage and around intra-articular structures, forming an erosive pannus, which destroys the underlying tissue
- Marginal erosions observed at the periphery of joints, especially interphalangeal joints in the fingers and atlantoaxial joint in cervical spine
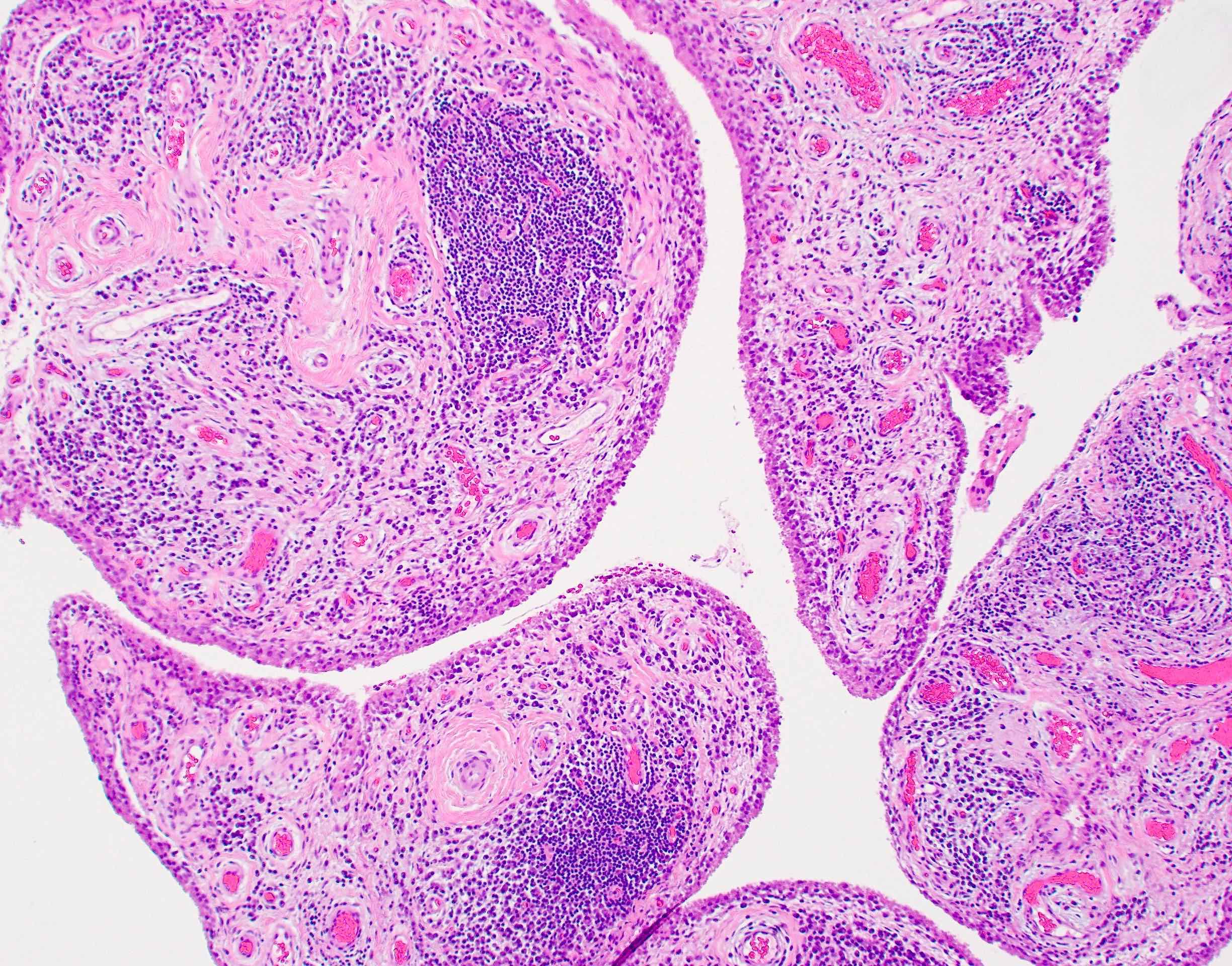
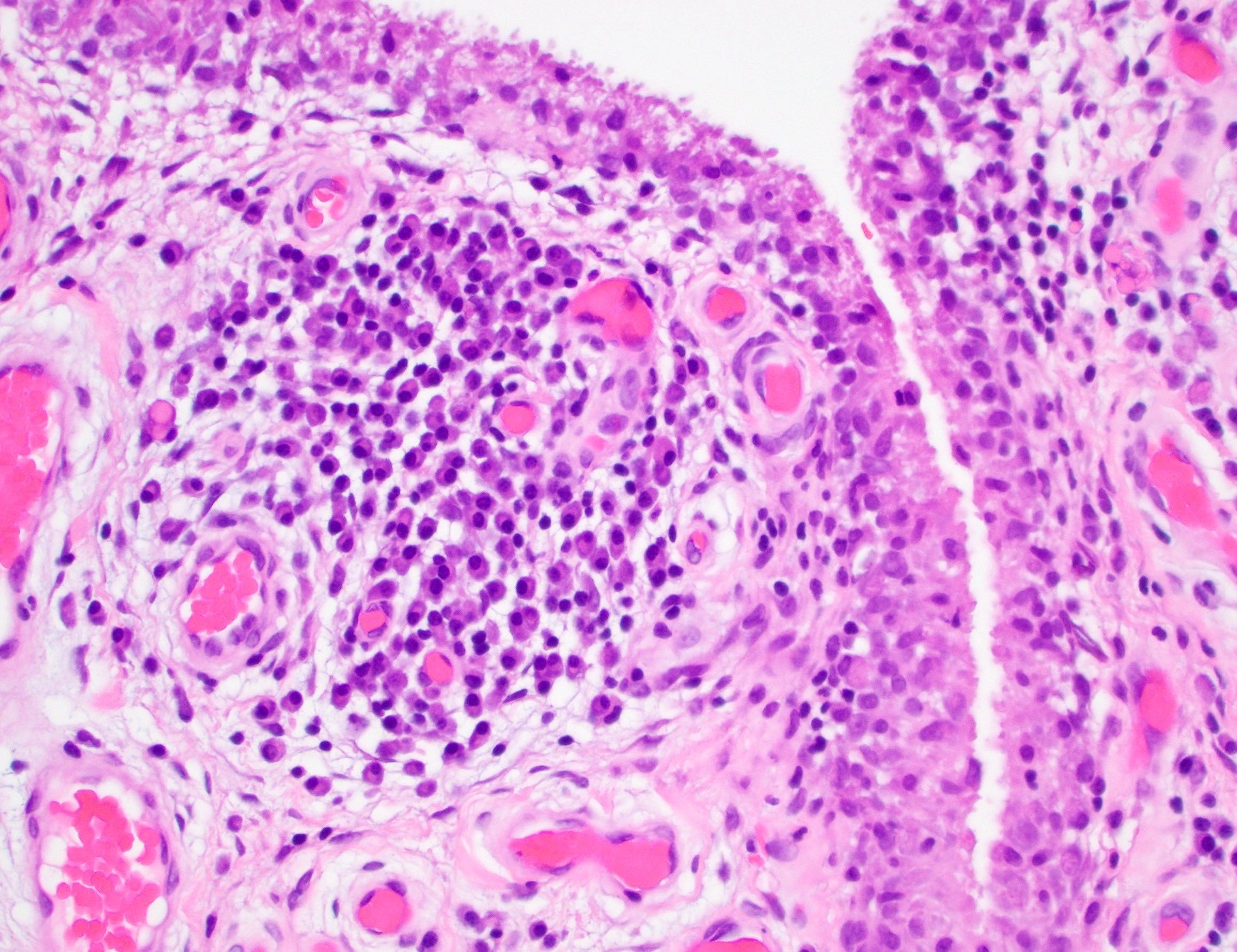
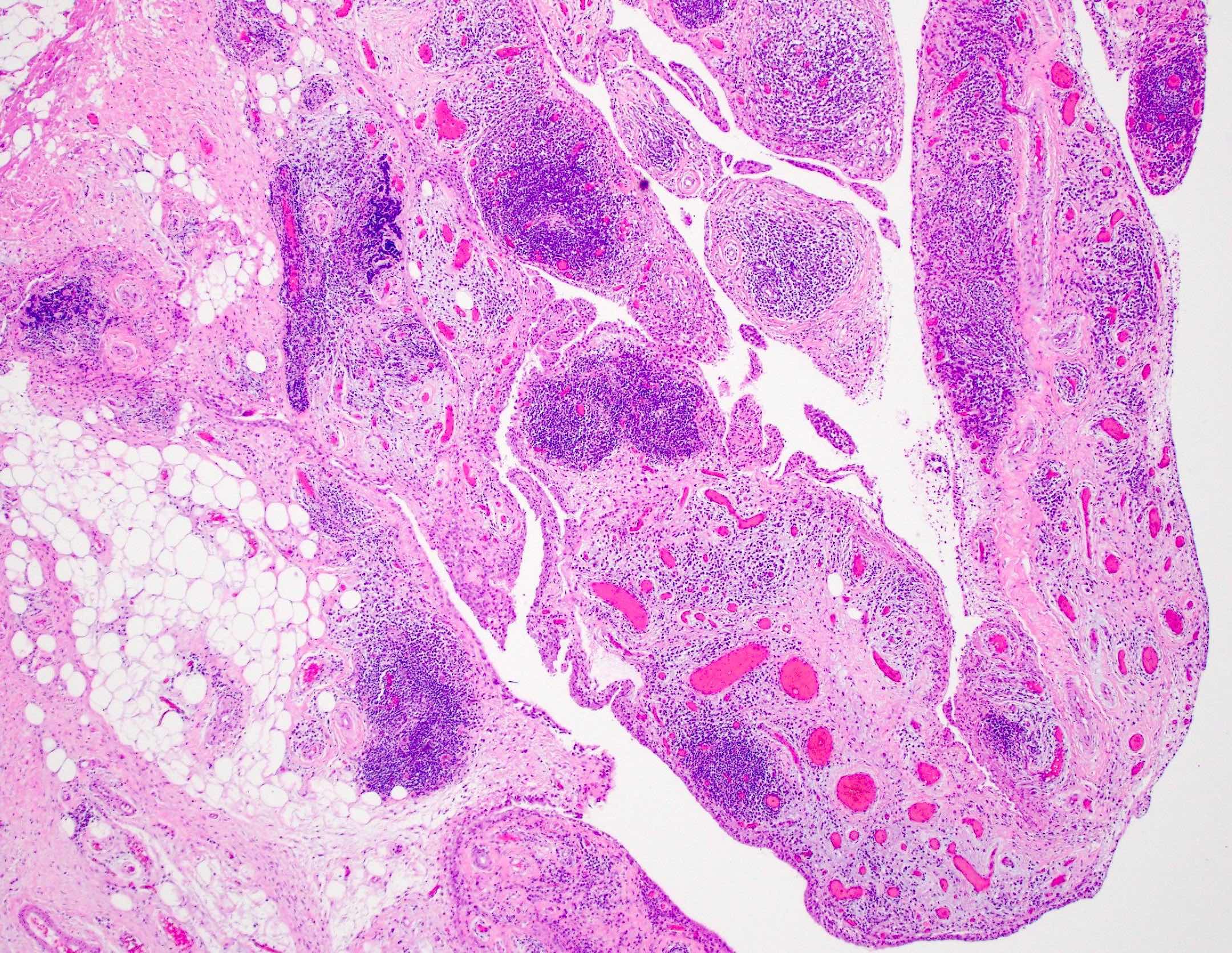
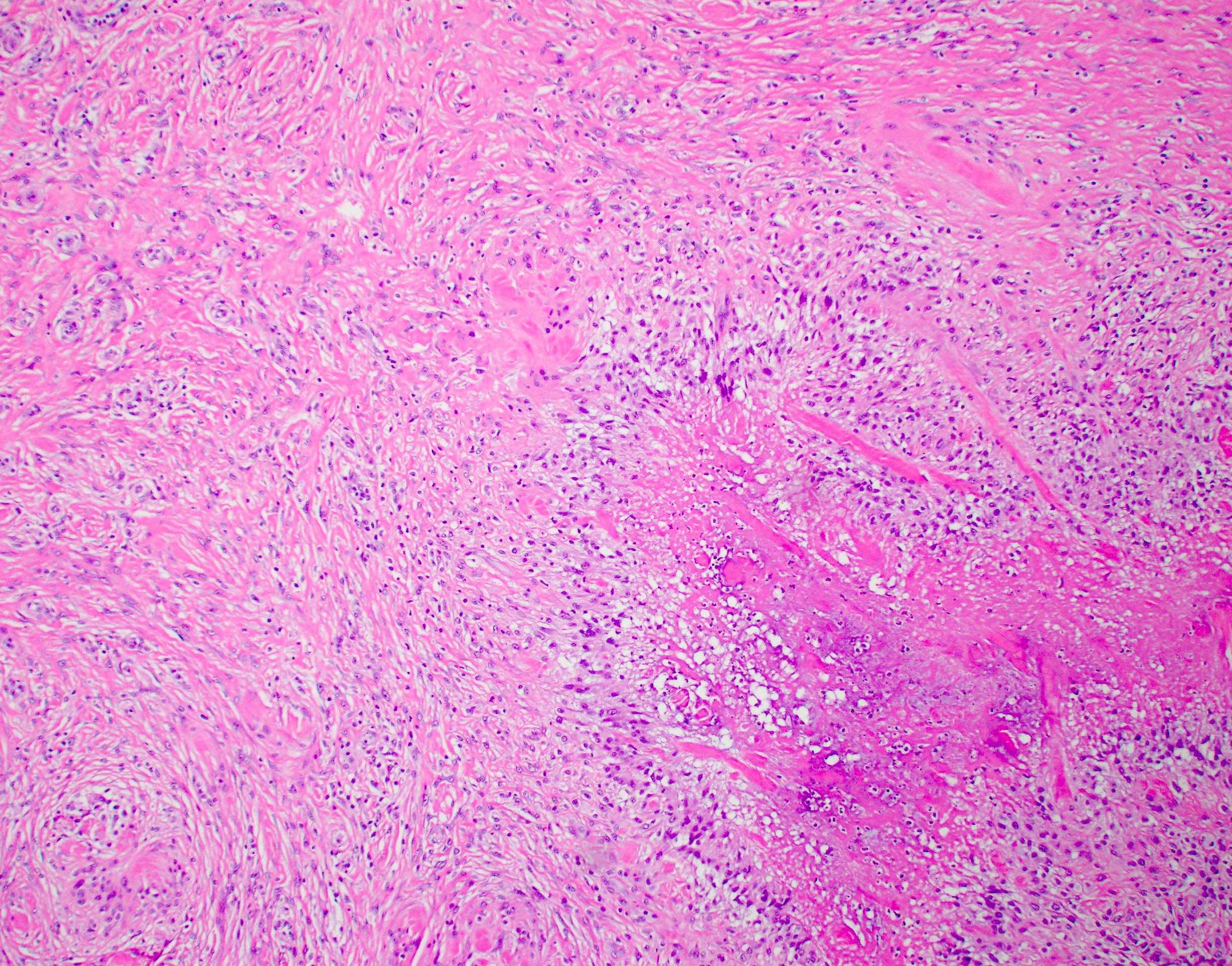
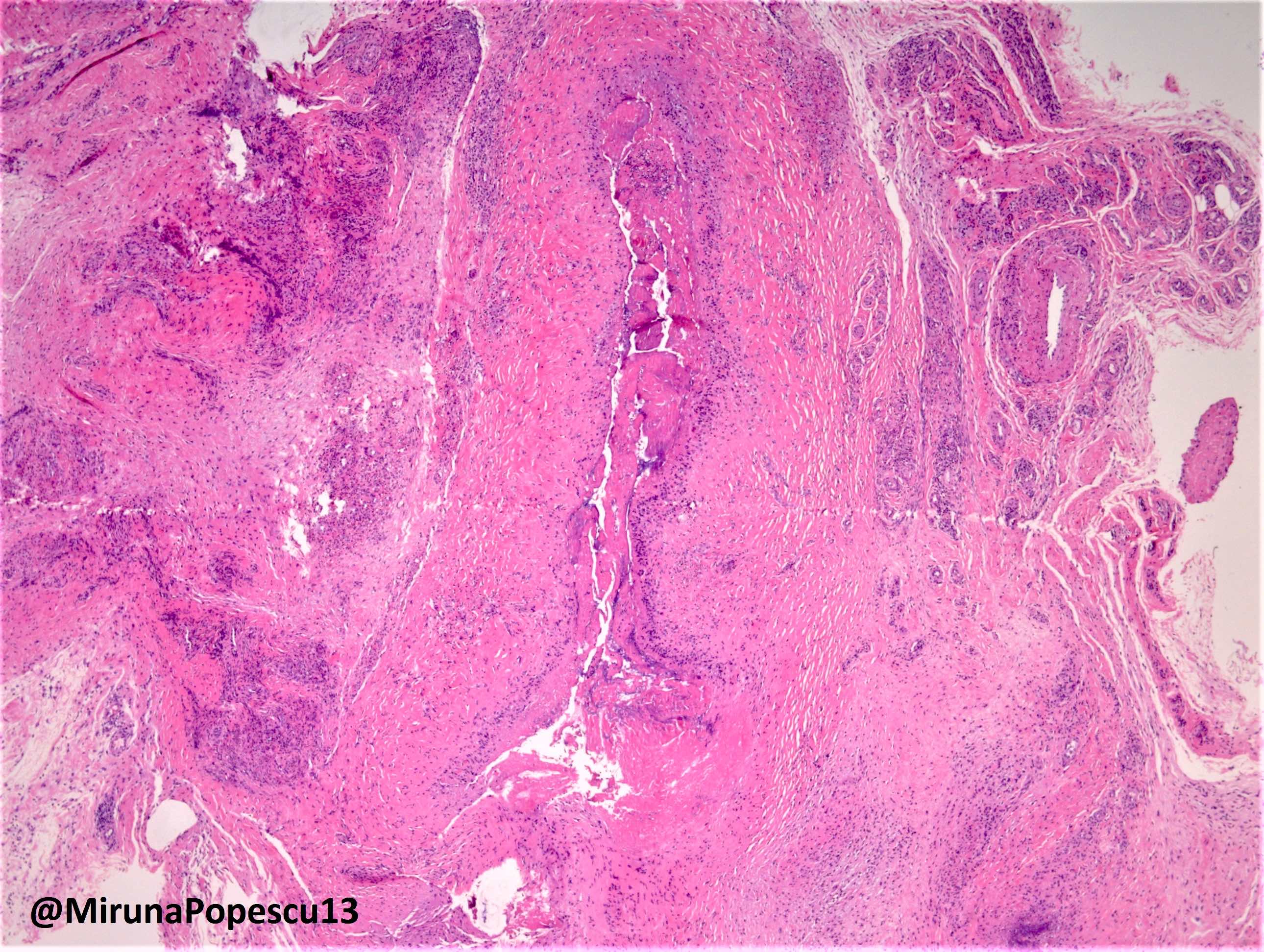
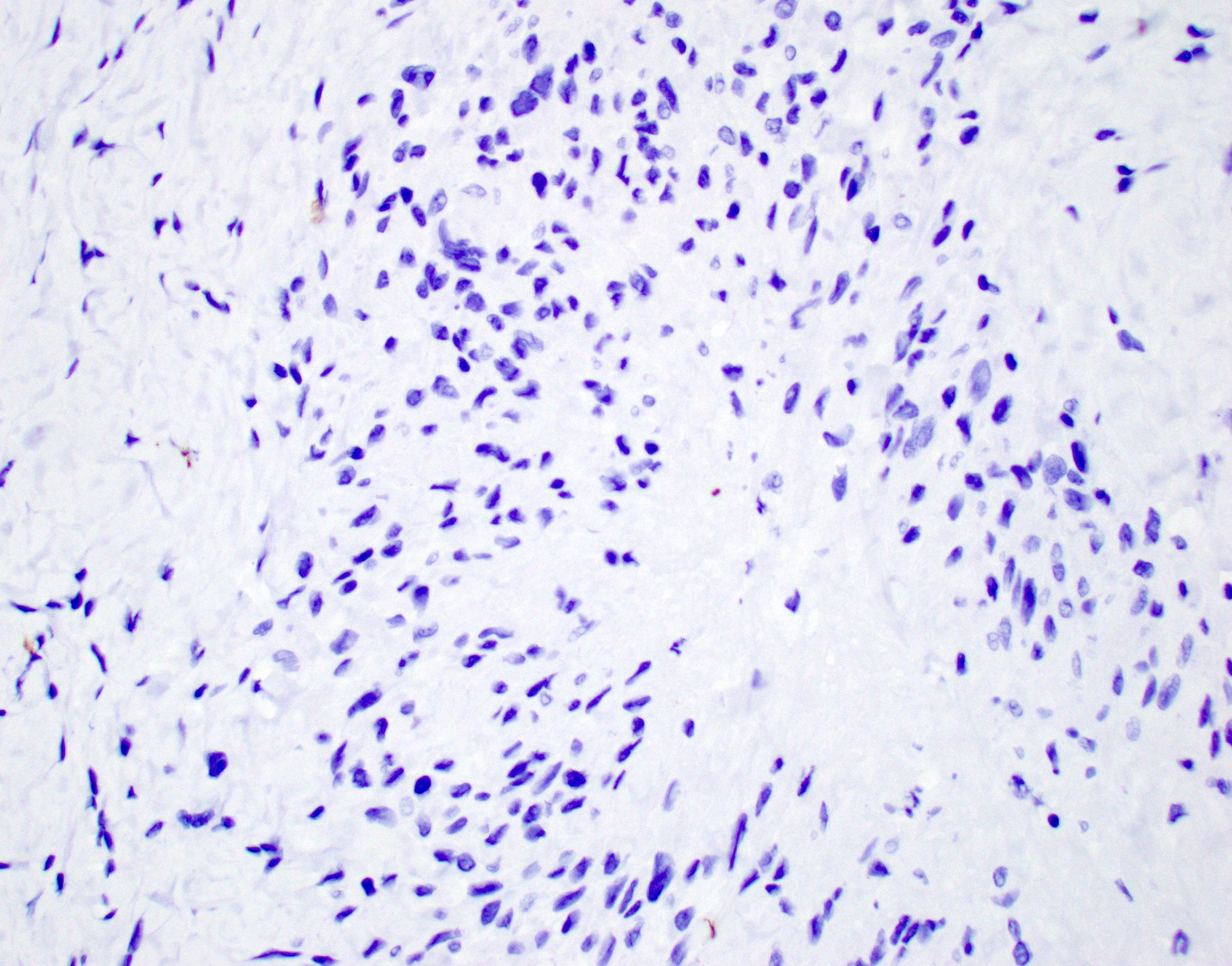
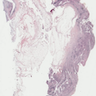
Microscopic (histologic) description
Rheumatoid arthritis (joint involvement)
Rheumatoid nodules
- Synovial hypertrophy and hyperplasia
- Synoviocyte layer can have 5 or more cells in thickness
- Hypertrophic synoviocytes have microvilli protruding from the surface
- Synovium can be replaced by granulation tissue and fibrin with increased blood vessels
- Synovium with prominent lymphocytic and polyclonal plasma cell infiltrate
- Lymphocytes tend to aggregate, forming follicles and occasionally germinal centers
- Mixed inflammatory infiltrate includes T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, macrophages, plasma cells and mast cells
- Neutrophils may be present, especially in an acute flare and early arthritis
- Tendons may have necrosis, myxoid degenerative change and vascular growth
Rheumatoid nodules
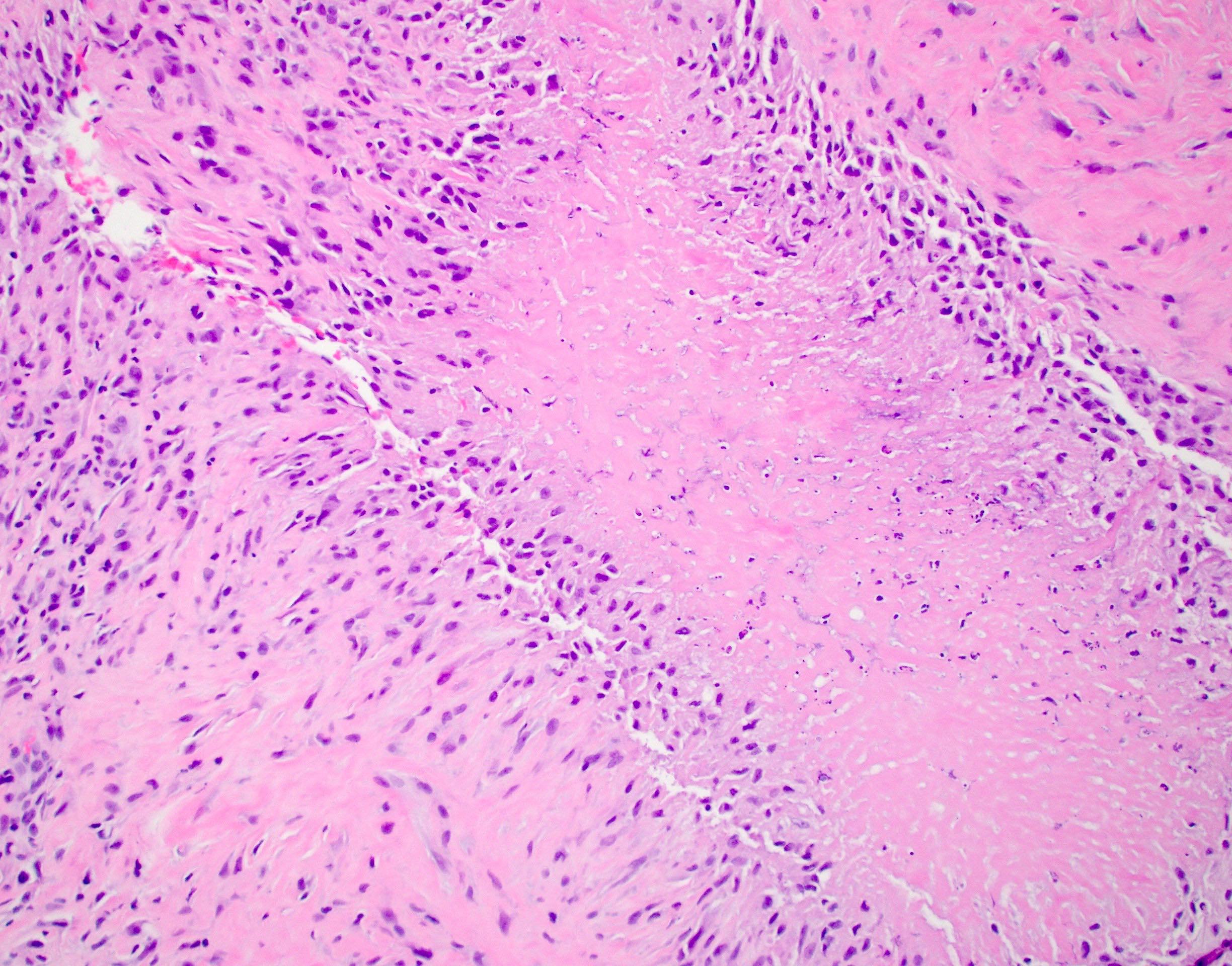
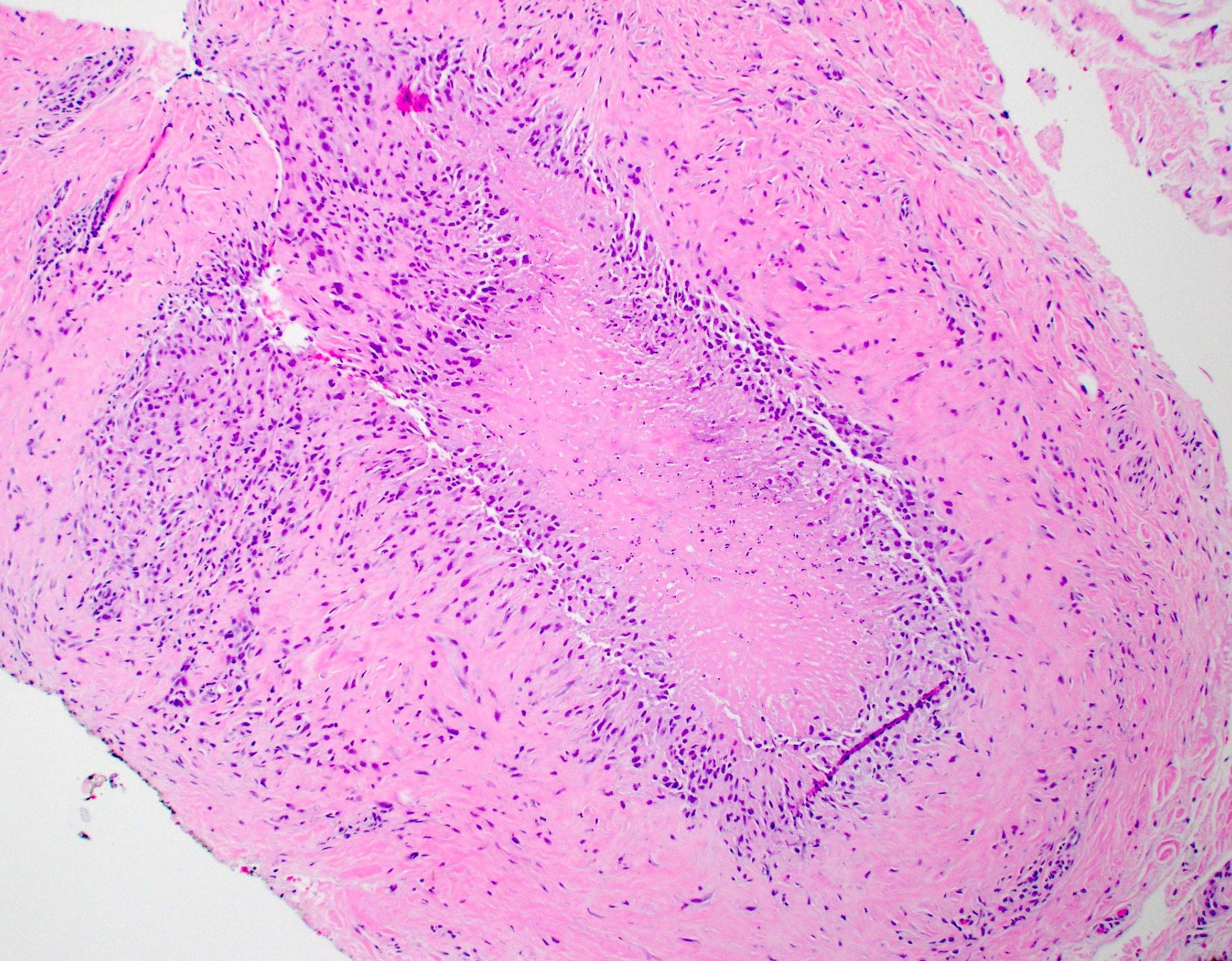
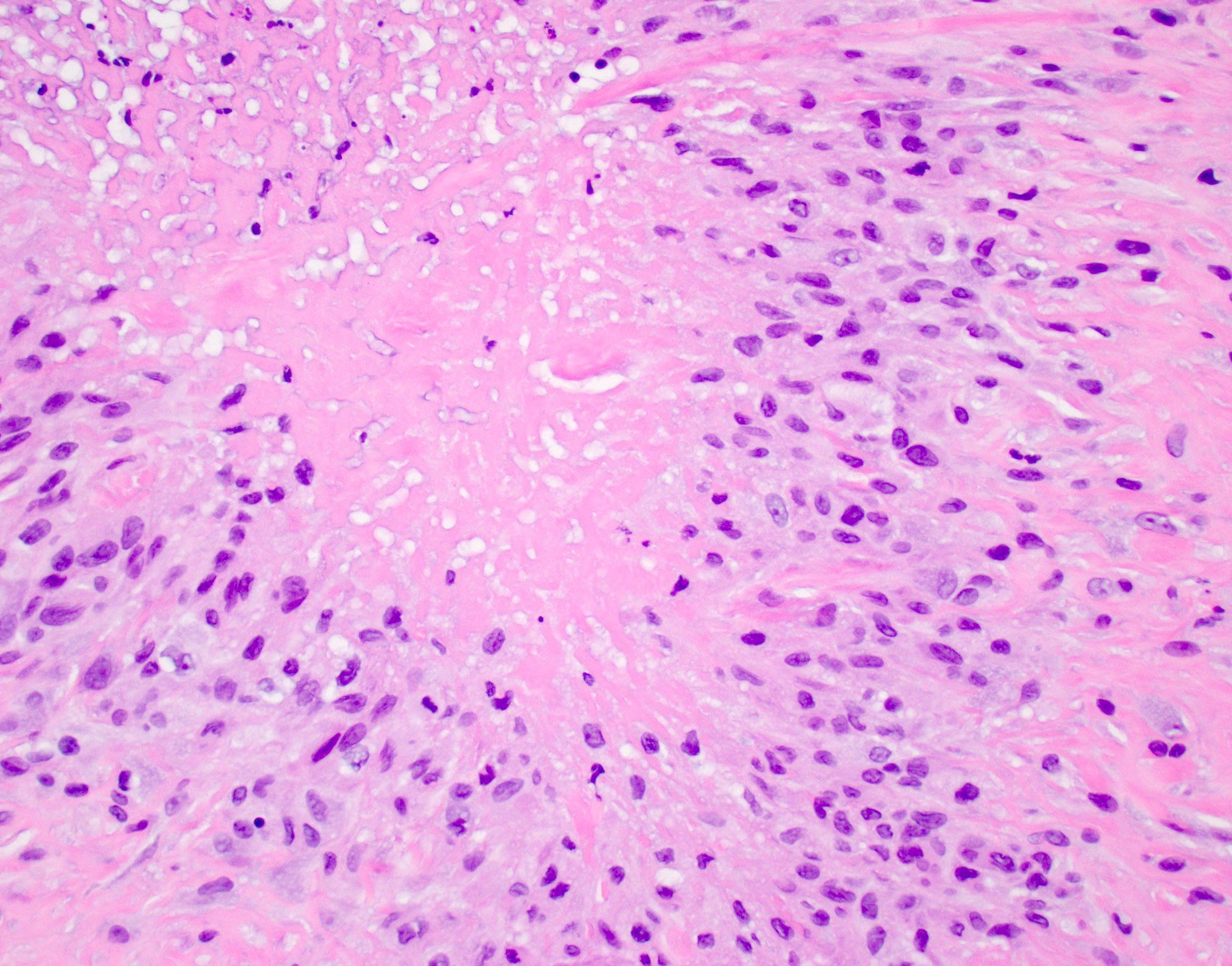
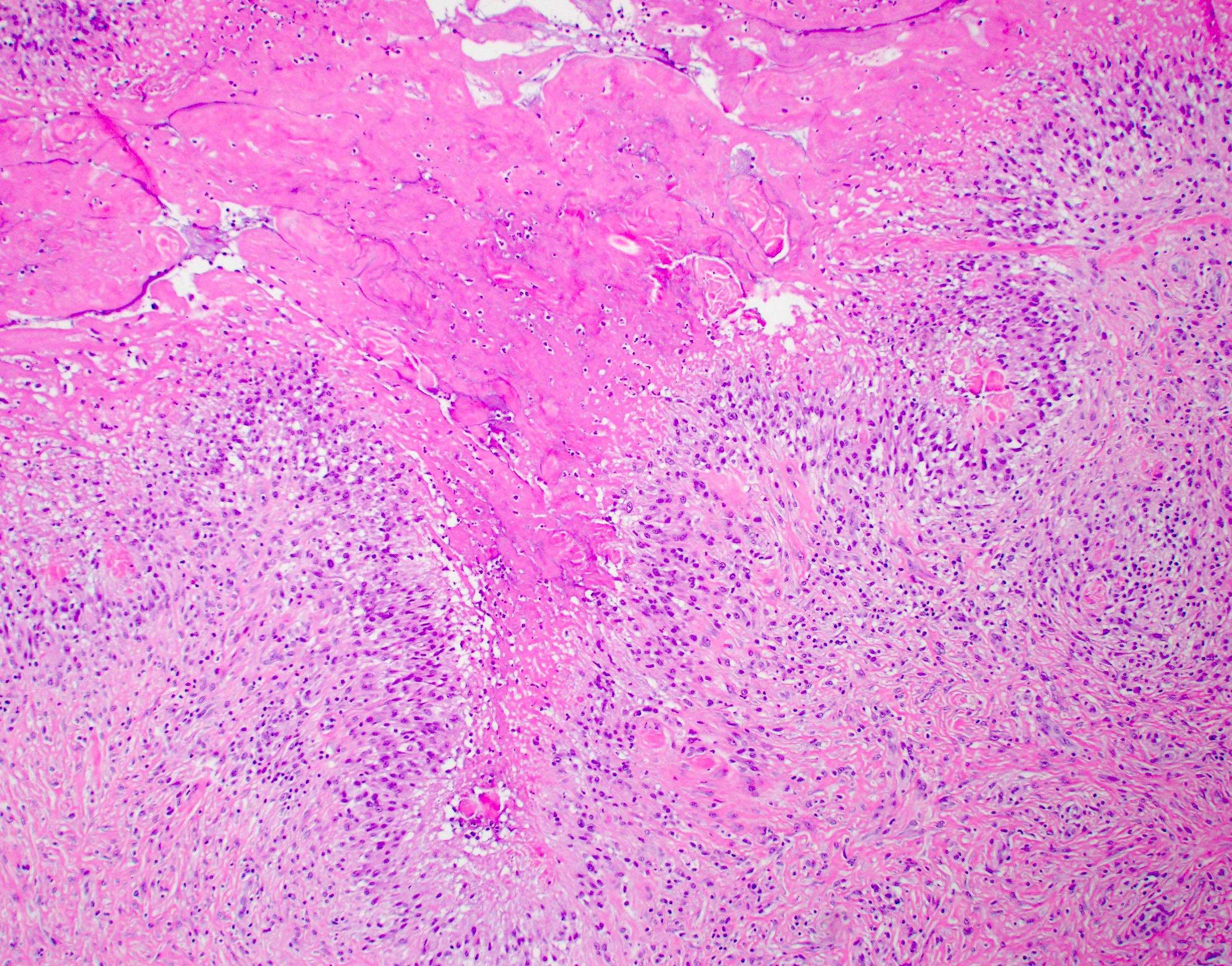
- Rheumatoid nodules have zones of central eosinophilic fibrinoid necrosis surrounded by palisading histiocytes and an outer layer of granulation tissue, chronic inflammation and fibrous tissue
- Rheumatoid nodules become more hyalinized and fibrotic as they mature, extent of necrosis varies with age of the lesion
- Fibrosis may be extensive (Am J Dermatopathol 1988;10:1)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Synovial fluid had fragments of fibrin and ragocytes
- Döhle and Rieder cells may be present
- Fragments of amorphous necrotic debris with metachromasia, better appreciated on Papanicolaou stained smears (Diagn Cytopathol 2003;28:322)
- Pathognomonic triad of rheumatoid arthritis includes elongated macrophages, multinucleated macrophages and necrotic background material (Acta Cytol 1990;34:465)
- Presence of long fibrin strands in necrotic background occasionally with epithelioid histiocytes arranged in a loose granulomatous pattern may be a clue
Immunofluorescence description
- Direct immunofluorescence shows immunoglobulin and complement deposition in vessel walls (Clin Exp Immunol 1971;8:249)
Positive stains
- IgM occasionally positive in vessel walls (Am J Dermatopathol 1988;10:1)
Negative stains
- Cytokeratin
- INI1 (demonstrates normal retained expression)
- AFB (no acid fast bacilli)
- GMS (no fungal organisms)
- Gram stain (no microorganisms)
- Alcian blue (negative in necrobiosis) (Am J Dermatopathol 1988;10:1)
- Colloidal iron (negative for mucin in necrobiosis)
Videos
Rheumatoid nodule - palisaded necrobiotic granuloma
Rheumatoid nodule & granuloma annulare
Sample pathology report
- Soft tissue, forearm mass, excision:
- Palisading granulomatous inflammation with fibrinoid necrosis (see comment)
- Comment: Excision of the forearm mass shows central fibrinoid necrosis surrounded by palisading granulomatous inflammation and fibrosis. An immunohistochemical stain for cytokeratin is negative. Special stains for microorganisms (AFB, GMS and Gram stain) are negative. All control slides stained appropriately. Taken together, the findings are suggestive of a rheumatoid nodule with the differential diagnosis including a deep granuloma annulare. Clinical and serologic correlation is recommended to assess for the possibility of rheumatoid arthritis.
Differential diagnosis
- Infectious granulomas:
- Suture granulomas:
- Palisading granulomas have been described
- Fragments of birefringent suture material present (Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17:920)
- Chronic osteomyelitis:
- Clinical presentation is different, often with history of known infection
- Cultures might grow microorganisms
- Plasma cell infiltrate can be present in joints adjacent to areas of chronic osteomyelitis
- Subcutaneous granuloma annulare:
- Absence of arthritis and constitutional symptoms
- Lesions often in pretibial region, dorsum of hand and occipital scalp (N Engl J Med 2006;354:2697)
- Pale, edematous necrobiosis with bluish hue suggestive of extracellular mucin
- Multinucleated giant cells are not observed
- Lesser degree of fibrosis
- Alcian blue stains necrobiosis (Am J Dermatopathol 1988;10:1)
- Colloidal iron shows mucin deposition in necrobiosis
- Negative for IgM
- Epithelioid sarcoma:
- Predilections for deep soft tissue of extremities in young adults
- Tumor cells epithelioid to spindled with at least mild nuclear atypia
- True tumor necrosis is present
- Tumor cells positive for cytokeratin, EMA and occasionally CD34
- Loss of INI1 expression is characteristic
- Osteoarthritis:
- Eburnation, subchondral sclerosis and osteophyte formation
- Typically shows less intense inflammation
- Patients do not have increased systemic inflammatory markers
- Gout:
- Acute inflammation with neutrophils and needle shaped monosodium urate crystals
- Tophus formation
- Patients may have hyperuricemia (Ther Umsch 2016;73:137)
- Necrobiotic xanthogranuloma:
- Classically presents as erythematous plaque in periorbital area
- Patients with a history of monoclonal gammopathy
- Necrosis, granulomatous inflammation and several giant cells, including Touton giant cells
- Cholesterol clefts frequently encountered
- Necrobiosis lipoidica:
- Commonly presents as atrophic yellowish plaques on the shins
- Alternating layers of granulomatous inflammation and necrobiosis
- Plasma cells are frequently present
- Often occurs in patients with diabetes
Board review style question #1
A 45 year old woman presents with a 6 month history of joint pain, swelling and morning stiffness lasting more than 1 hour. Physical examination reveals symmetrical swelling of the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints. Laboratory testing reveals a positive rheumatoid factor (RF). A synovial biopsy is performed. Which of the following histologic findings is most characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis?
- Dense infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells in the synovium with formation of lymphoid follicles
- Deposition of monosodium urate crystals in the synovial fluid
- Formation of osteophytes in the joint margin
- Presence of noncaseating granulomas in the synovium
Board review style answer #1
A. Dense infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells in the synovium with formation of lymphoid follicles.
In rheumatoid arthritis, the synovium typically shows dense infiltration of inflammatory cells, including plasma cells and lymphocytes, often forming lymphoid follicles. This chronic inflammatory process leads to synovial hyperplasia and pannus formation, which invades and erodes cartilage and bone. Answer D is incorrect because noncaseating granulomas are characteristic of sarcoidosis. Answer B is incorrect because monosodium urate crystals are associated with gout. Answer C is incorrect because osteophyte formation is a feature of osteoarthritis.
Comment Here
Reference: Rheumatoid arthritis
Comment Here
Reference: Rheumatoid arthritis
Board review style question #2
If a subcutaneous soft tissue nodule is excised and shows palisading granulomatous inflammation, which of the following findings is most supportive of a rheumatoid nodule?
- Fibrinoid necrosis without mucin
- Immunohistochemical expression of cytokeratin
- Polarizable foreign material compatible with sutures
- Presence of fungal organisms
Board review style answer #2
A. Fibrinoid necrosis without mucin. A rheumatoid nodule characteristically has palisading granulomatous inflammation with fibrinoid necrosis. Extracellular mucin is more commonly seen in the necrobiosis associated with subcutaneous granuloma annulare. Answer D is incorrect because it is most consistent with a fungal infection. Answer C is incorrect because it describes a suture granuloma. Answer B is incorrect because it would be concerning for the possibility of an epithelioid sarcoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Rheumatoid arthritis
Comment Here
Reference: Rheumatoid arthritis