Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Immunofluorescence description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Moeen S, Qureshi MB, Ud Din N. Calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition disease. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/jointspseudogout.html. Accessed January 20th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition (CPPD) is characterized by calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal accumulation in extracellular cartilage matrix, synovium and joints
Essential features
- Most common crystalline arthropathy
- Different clinical presentations in the elderly
- Diagnosis requires demonstration of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in synovial fluid or biopsy material
- Classic rhomboid shaped crystals with positive birefringence under polarized light
Terminology
- Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease
- Pseudogout
- Chondrocalcinosis polyarticularis
- Articular chondrocalcinosis
- Pyrophosphate arthropathy
- Chondrocalsynovitis
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Affects the elderly (Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2017;69:1400)
- Young age presentation in familial and secondary types (Am J Hum Genet 1999;64:136)
- M = F (Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009;48:711)
Sites
- Knee is the most commonly affected site (Ann Rheum Dis 2003;62:513)
- Other sites include hip, shoulder, wrist, hand, ankle, pubic symphysis, intervertebral disc (Pathol Res Pract 2001;197:499)
- Can occur in atypical locations, like temporomandibular joint (Hum Pathol 1995;26:587)
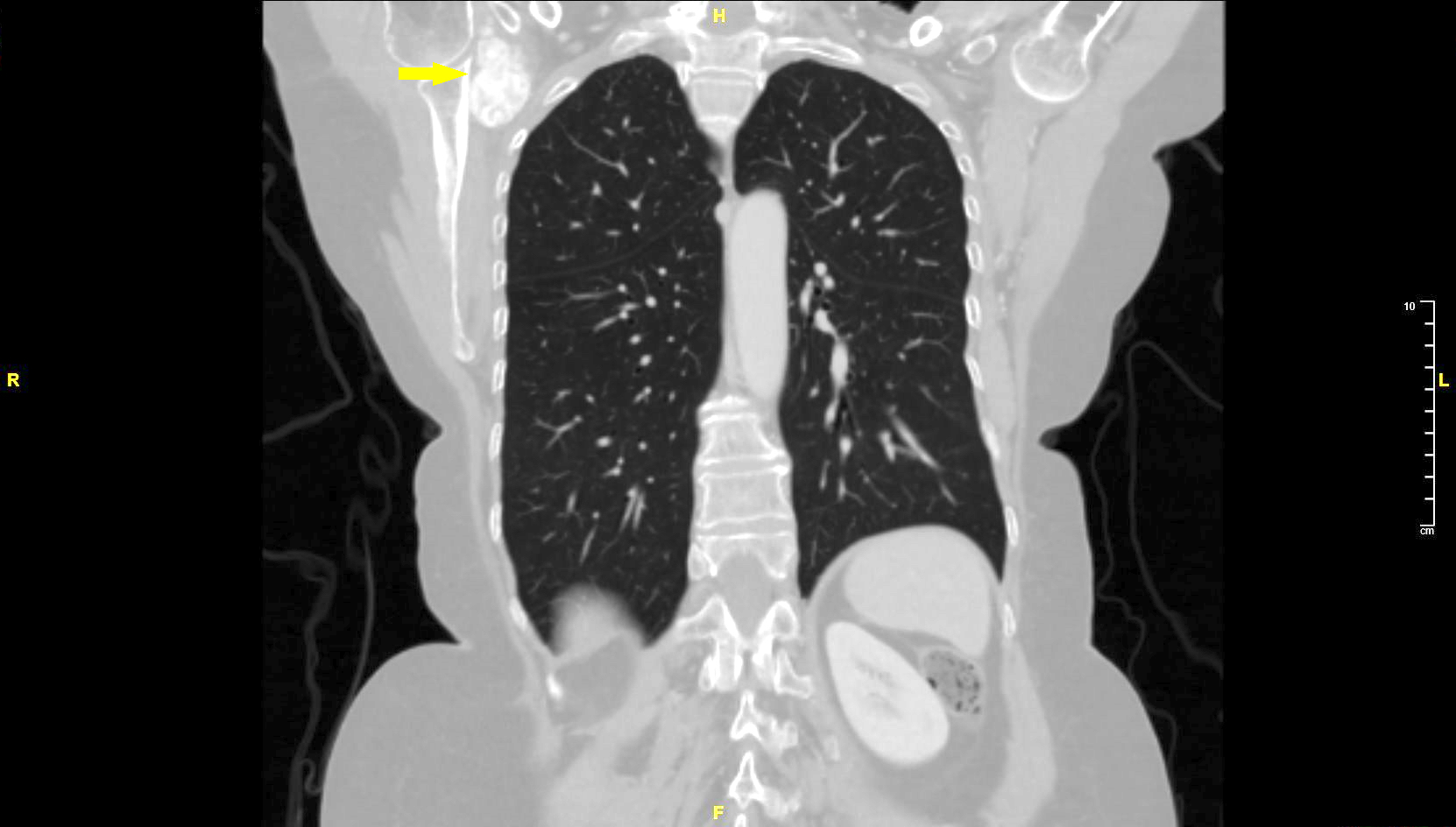
- Rarely, extraskeletal sites may be affected (Am J Surg 2010;200:e28, J Hand Surg Am 2008;33:1325, Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc 2019;57:324)
Pathophysiology
- An imbalance between the production of pyrophosphate and the level of pyrophosphatases in diseased cartilage causes high levels of extracellular pyrophosphate, resulting in CPPD
- Pyrophosphate is deposited in the synovium and adjacent tissues and combines with calcium to form calcium pyrophosphate (CPP)
- CPP crystals mediate damage by eliciting inflammation or by inducing the production of destructive matrix metalloproteinases and prostaglandins (Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2021;35:101718, N Engl J Med 2016;374:2575)
- Crystals have a direct catabolic effect on chondrocytes and alter the mechanical properties of cartilage (Curr Rheumatol Rep 2001;3:17)
Etiology
- CPPD can be primary, familial / sporadic, or secondary
- Familial CPPD is caused by mutation in the ankylosis protein homolog (ANKH) gene (Curr Rheumatol Rep 2012;14:155)
- ANKH encodes a putative transmembrane inorganic pyrophosphate transport channel
- Loss of function of ANKH results in increased extracellular pyrophosphate level, thus causing pyrophosphate deposition (Am J Hum Genet 2002;71:985, Am J Hum Genet 1999;64:136)
- Secondary causes include metabolic disorders like hypothyroidism, hypophosphatasia, hyperparathyroidism, hypomagnesemia, hemochromatosis and Wilson disease (Semin Arthritis Rheum 1992;22:188, Eur J Rheumatol 2018;5:53, Curr Rheumatol Rep 2022;24:40)
- Acute pseudogout has been proposed as a possible side effect of bisphosphonate treatment (Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e6177)
Clinical features
- Clinical patterns:
- Chondrocalcinosis:
- Asymptomatic incidental finding in articular tissues
- Commonly involves knee menisci and intervertebral discs
- Often detected on radiology
- Acute CPP deposition (acute pseudogout):
- Symptomatic, painful swollen joints with warmth and erythema
- Constitutional symptoms include fever, chills and malaise
- Commonly involves knee
- Acute episodes seen in the arms of elderly women
- May last for weeks to months (Clin Exp Rheumatol 2019;37:254)
- CPPD osteoarthritis:
- CPPD crystal deposition frequently occurs in degenerated joints
- Commonly affects the elderly
- Radiology shows features of osteoarthritis, may detect crystals (Curr Opin Rheumatol 2007;19:158)
- Chronic CPP deposition disease (pyrophosphate arthropathy):
- Polyarticular form of arthritis that resembles osteoarthritis
- Commonly affects women
- Involvement of glenohumeral, wrist and metacarpophalanageal joints, in contrast to typical osteoarthritis
- Chondrocalcinosis:
- Tophaceous pseudogout and tumoral CPPD are solitary space occupying lesions, commonly seen in digits
- Associated with crowned dens syndrome (Eur Radiol 2000;10:1003)
- Associated with myelodysplastic syndrome (J Rheumatol 2017;44:1101)
- Can be present as part of true neoplasms, such as calcified chondroid mesenchymal tumors with FN1 fusions (Mod Pathol 2021;34:1373)
Diagnosis
- Arthrocentesis for synovial fluid analysis by light microscopy, compensated polarized light microscopy or phase contrast microscopy (Open Access Rheumatol 2014;6:39)
- Can be identified in biopsy material, even in decalcified tissue
- Radiography of the involved joints is helpful
Laboratory
- Raised serum inflammatory markers like erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C reactive protein (CRP)
- Screening for metabolic causes such as hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, hyperparathyroidism and hypomagnesemia (J Med Assoc Thai 1999;82:569)
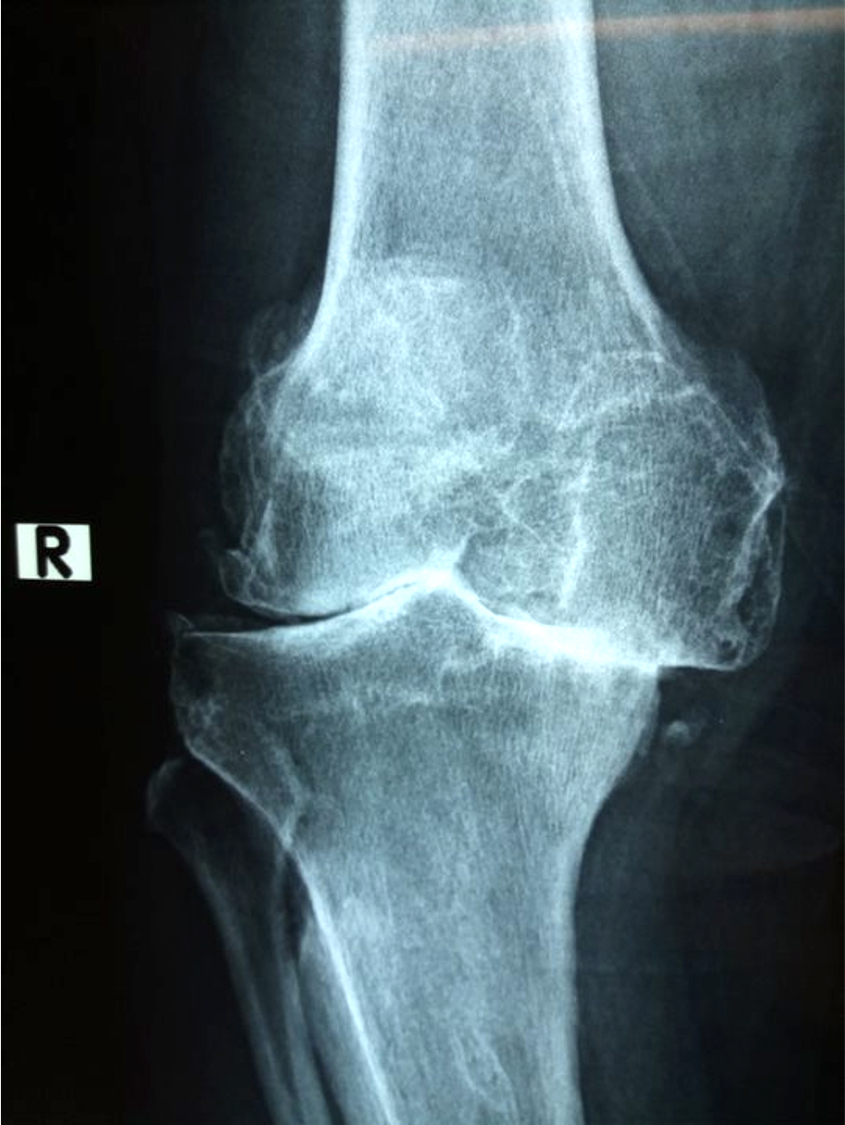
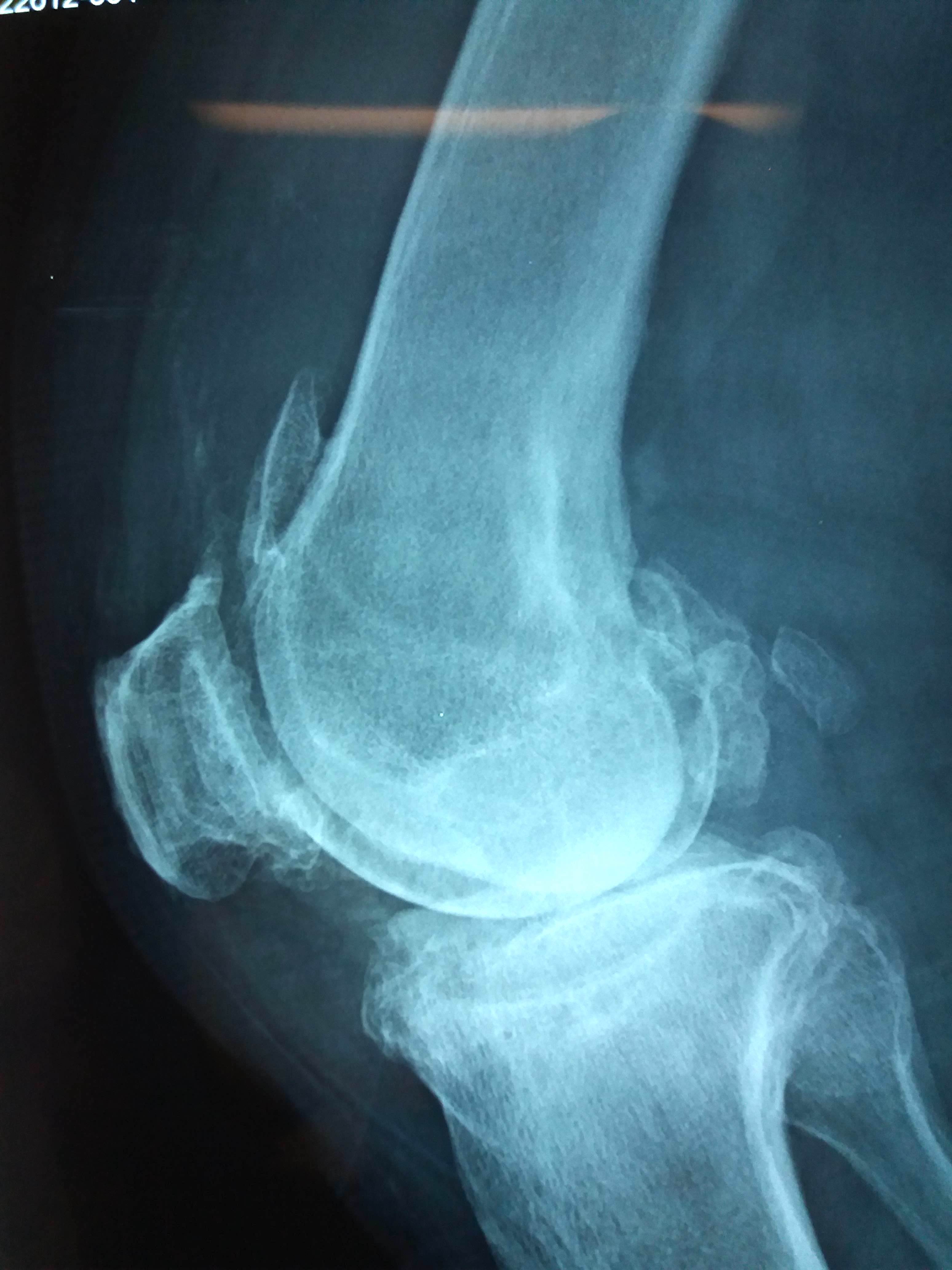
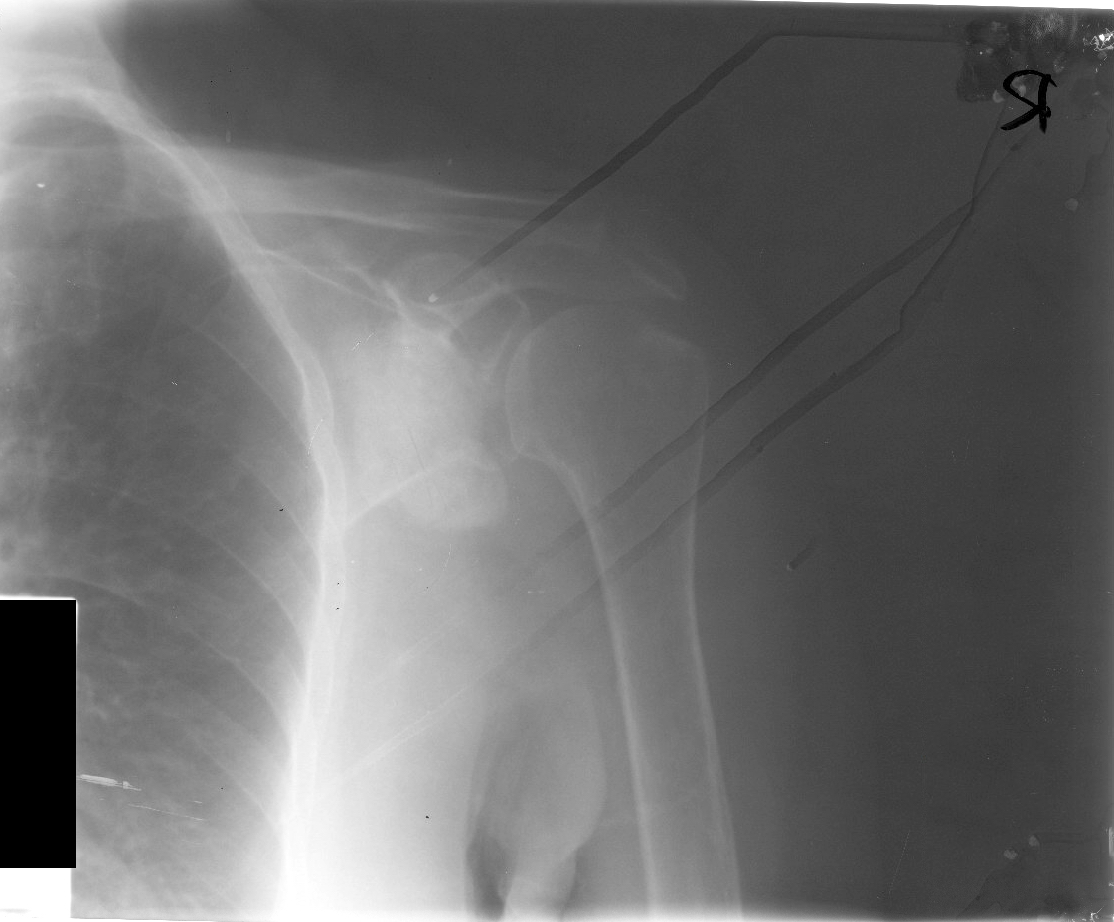
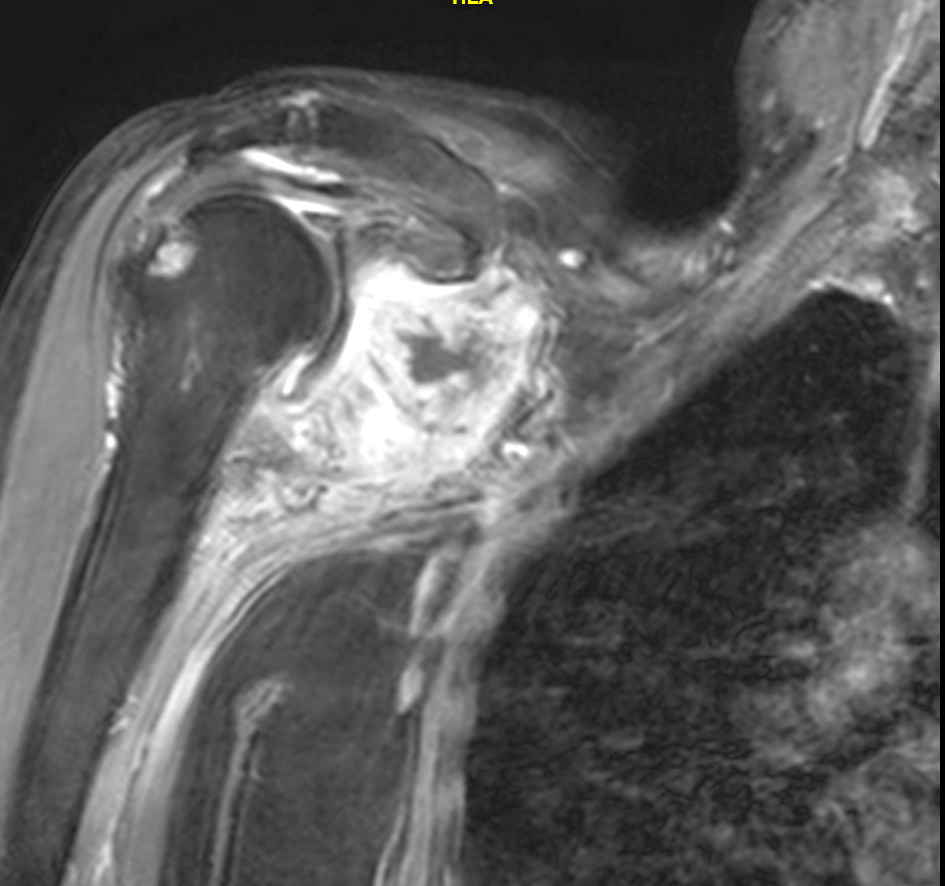
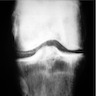
Radiology description
- Polyarticular chondrocalcinosis in fibro and hyaline cartilage (Curr Opin Rheumatol 2020;32:140)
- Joint space narrowing and extensive subchondral sclerosis in pyrophosphate arthropathy
- Knee, when involved, shows cartilage icing, large subchondral cysts, fragmentation of subchondral bone, intra-articular bodies and disproportionate narrowing of patellofemoral joint (PLoS One 2020;15:e0231508)
- Soft tissue tophus-like opacities at the popliteus groove and gastrocnemius tendon calcification can be present
- Hand, when involved, shows subchondral cysts and hook-like projections from second and third metacarpal heads; may show stepladder pattern of joint narrowing
- Scapholunate advanced collapse (SLAC) (Insights Imaging 2014;5:407)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Acute calcium pyrophosphate arthritis is self limited; resolves within days to weeks of treatment
- Chronic CPP arthritis is a waxing and waning disease, lasting for months
- Osteoarthritis is exacerbated by CPPD (Clin Rheumatol 2001;20:428)
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors exacerbate pseudogout (J Immunother Cancer 2019;7:126)
Case reports
- 62 year old woman with left sided upper limb and neck pain (BMJ Case Rep 2019;12:e231508)
- 64 year old man with right shoulder pain radiating to the neck and upper back (Cureus 2019;11:e6239)
- 66 year old woman with multilevel skip lesions involving the cervical and thoracic spine (J Neurosurg Spine 2017;27:145)
- 77 year old woman with severe chondrocalcinosis of metacarpophalangeal joints (BMJ Case Rep 2018;2018:bcr2018226132)
- 80 year old woman with left lower extremity weakness and fall (Case Rep Rheumatol 2020;2020:3218350)
Treatment
- Based on symptoms, acute / chronic disease, or specific therapy for underlying metabolic cause
- Aimed at decreasing inflammation and limiting pain
- Options include joint aspiration, NSAIDs, colchicine, intra-articular and systemic glucocorticoid administration, IL1 receptor antagonists, excision and reconstruction (Open Access Rheumatol 2014;6:39, Arthritis Rheum 2008;58:631, Oral Maxillofac Surg 2021 Oct 1 [Epub ahead of print])
- Ice packs and joint rest with restriction of weight bearing
Clinical images
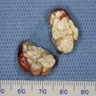
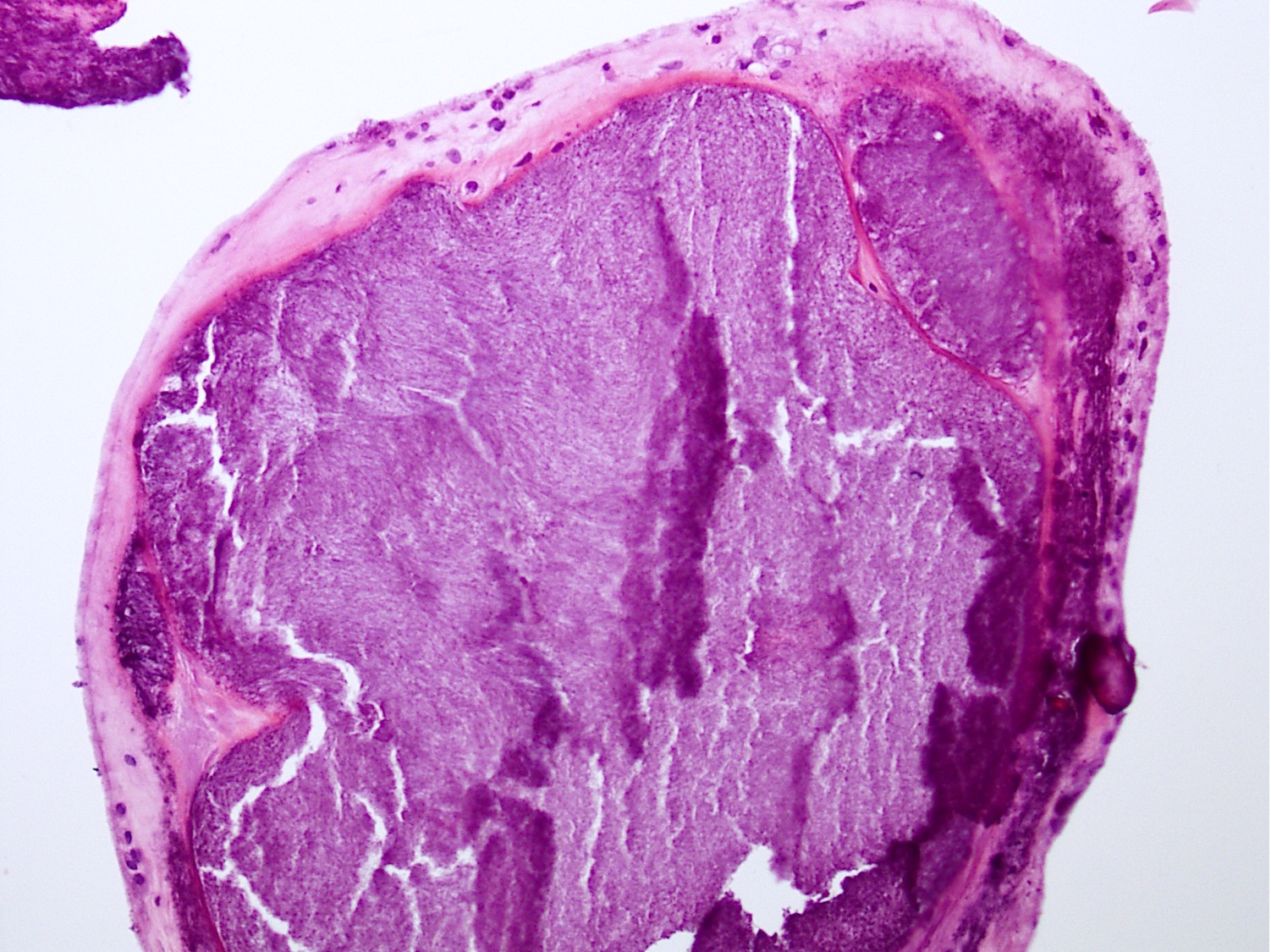
Gross description
- Gray to chalky white deposits in tissue
Frozen section description
- Frozen material shows crystalline material within the stroma (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2004;25:876)
- May show macrophages and histiocytes
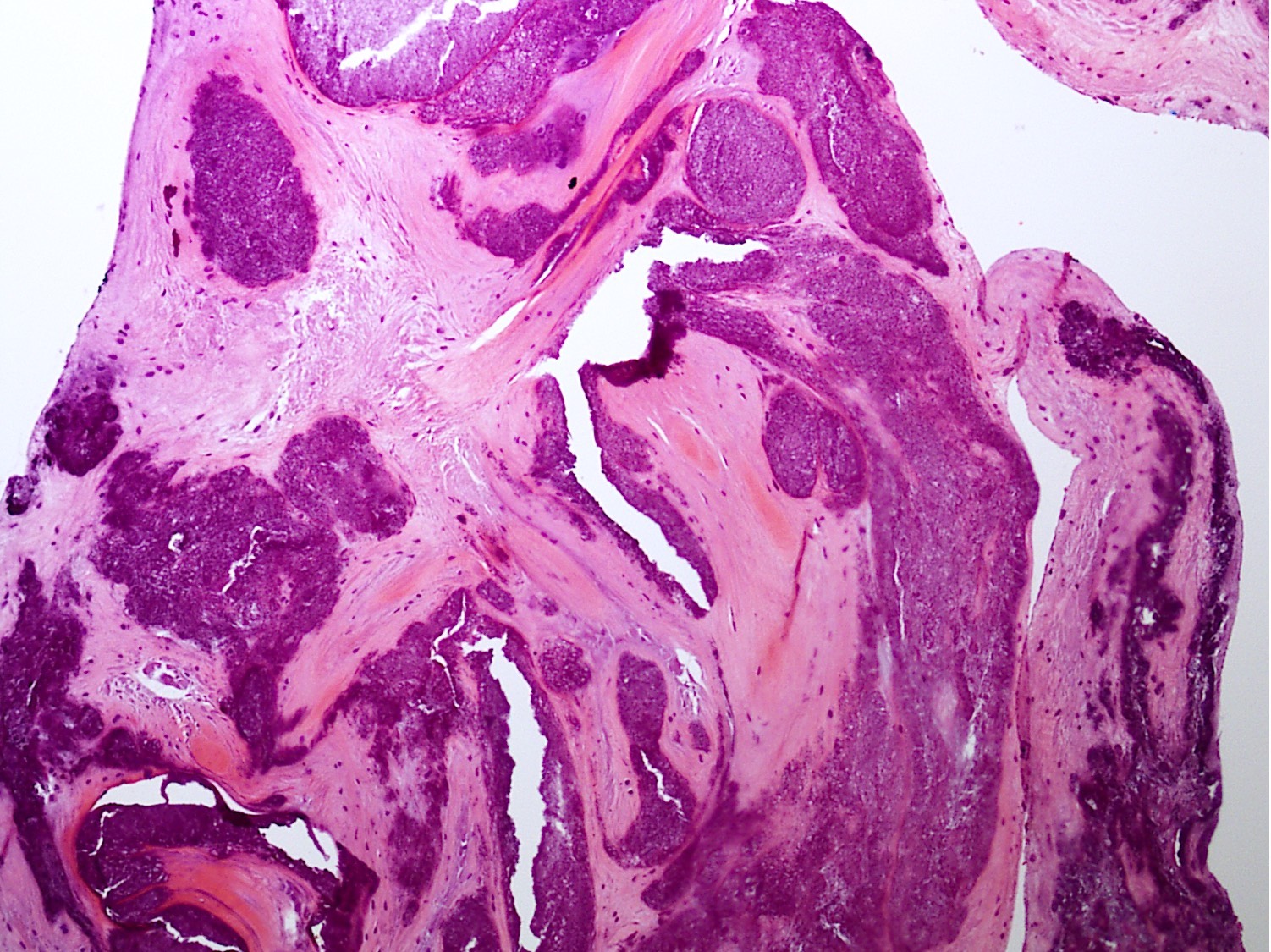
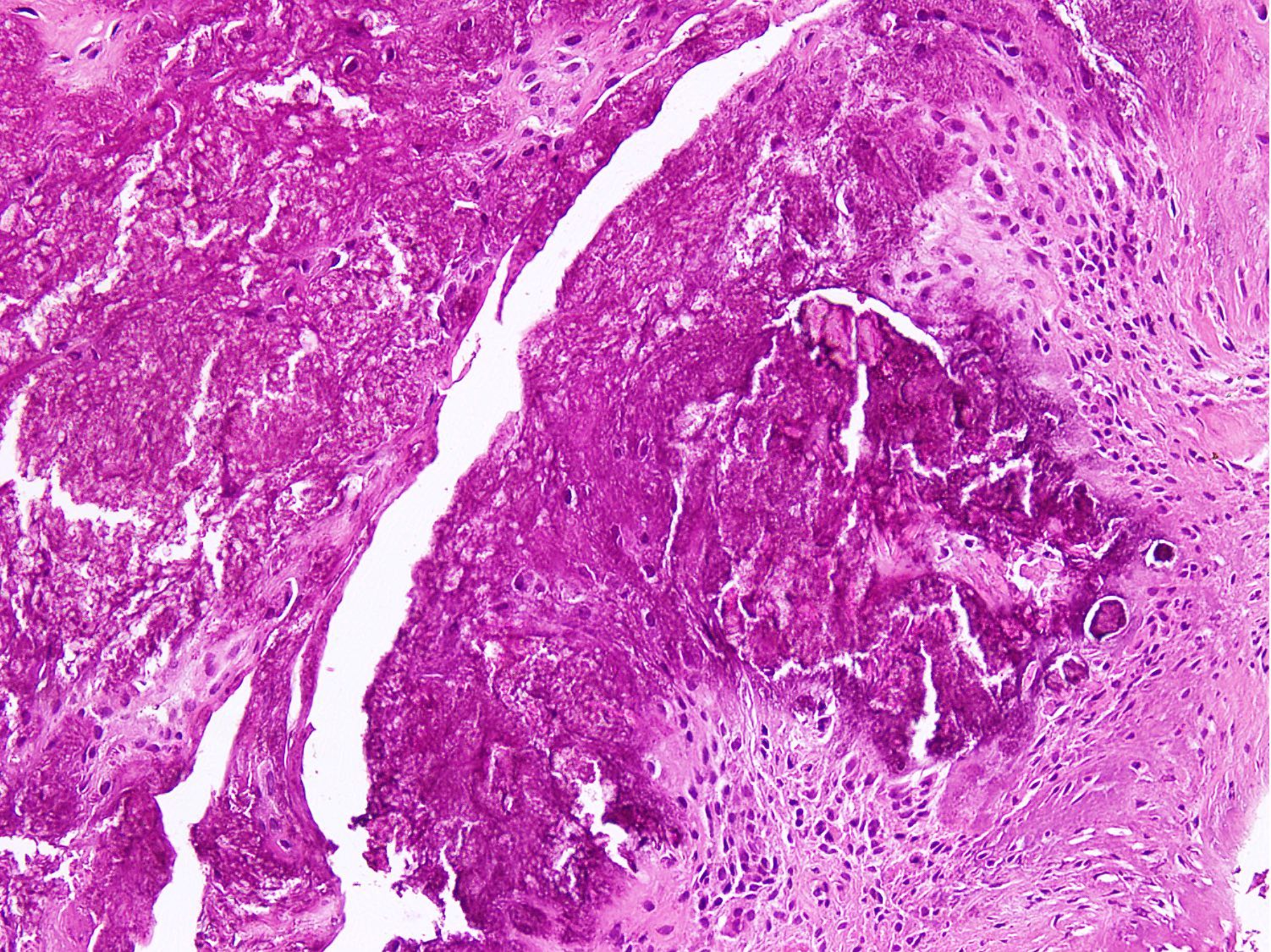
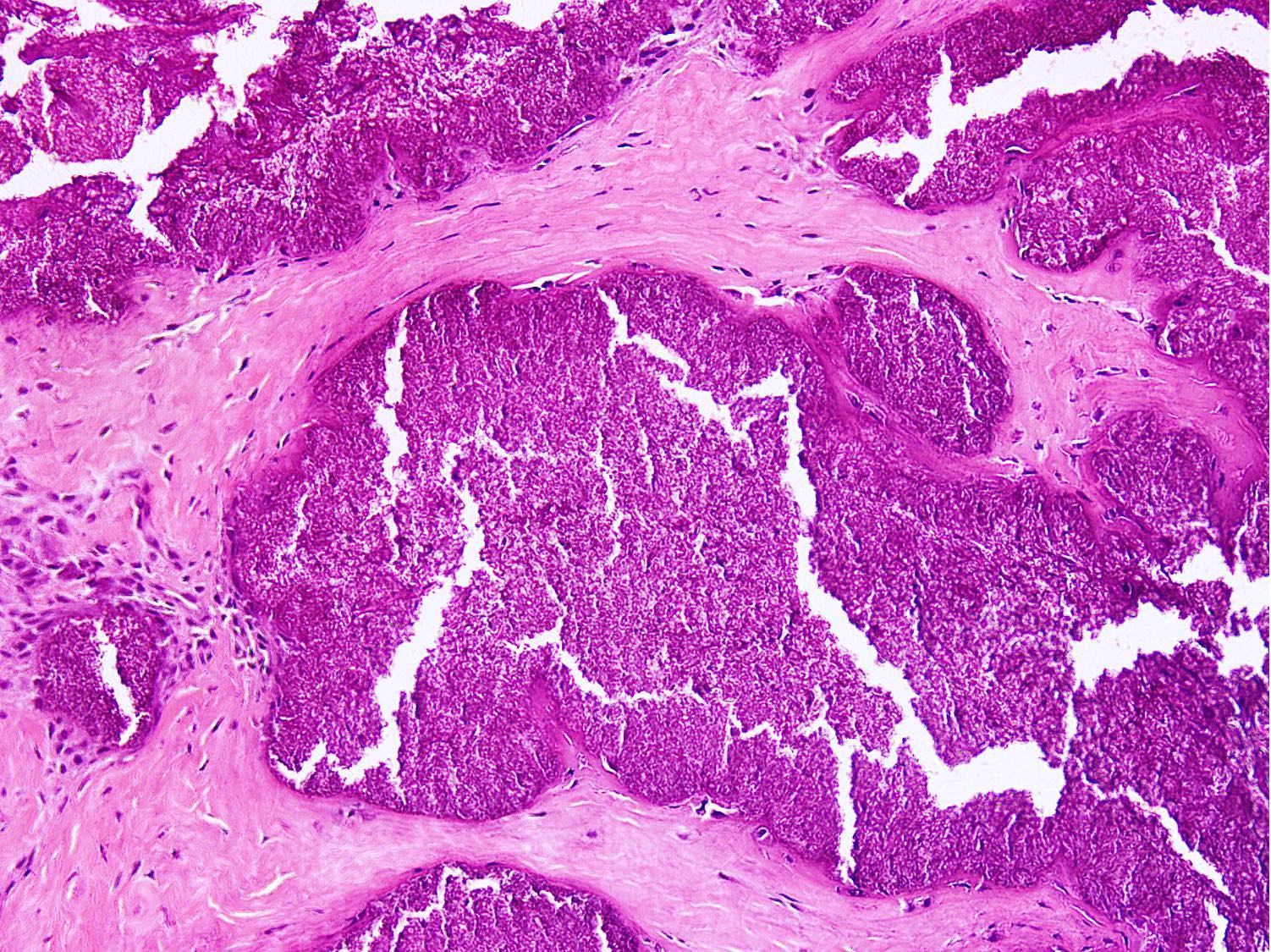
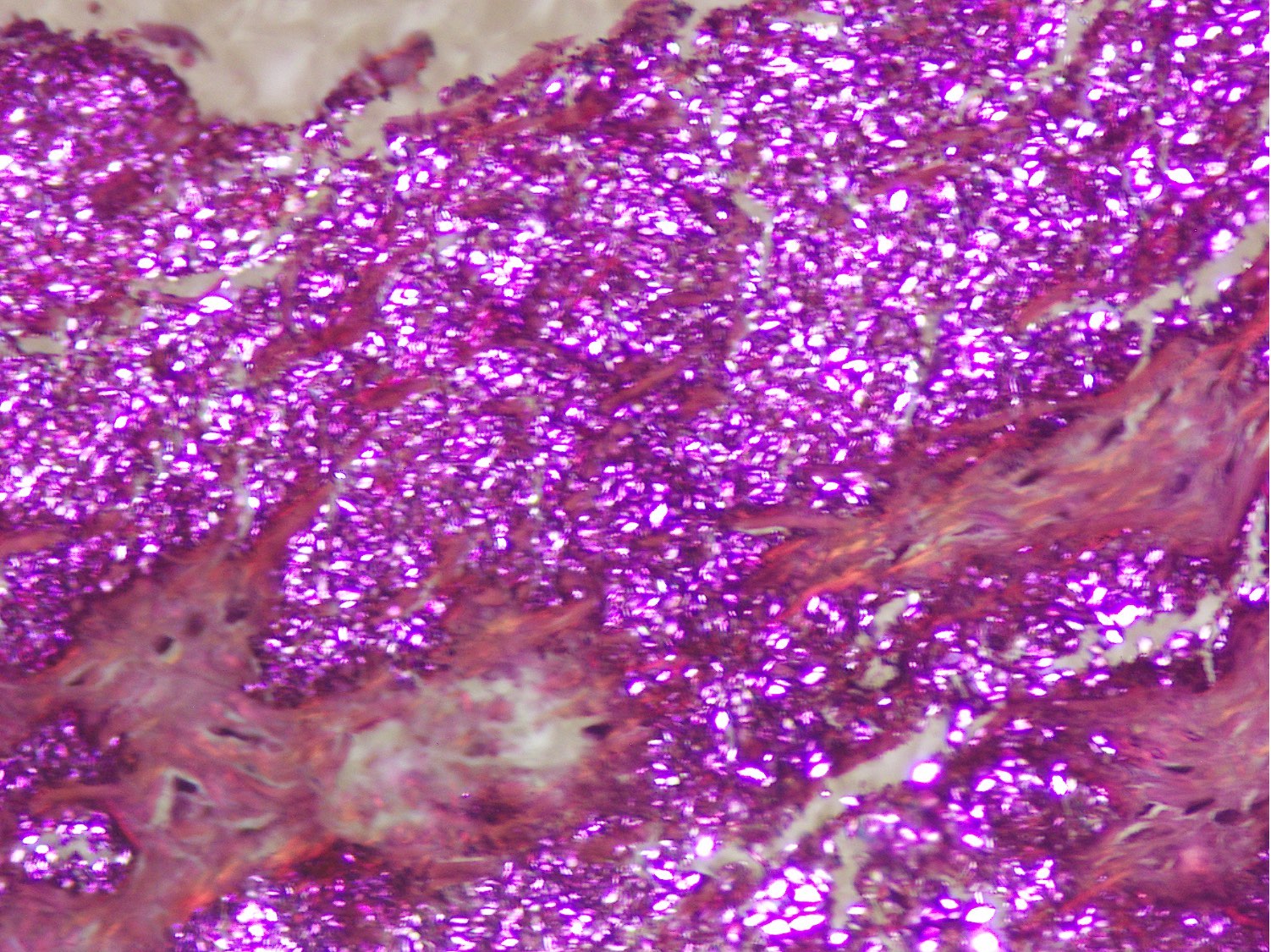
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Distinct aggregates of basophilic to gray-brown material within tissue
- Weakly anisotropic rhomboid to rod shaped crystals demonstrating positive birefringence under polarized light (Pathol Res Pract 2001;197:499)
- Smaller and dimmer than gout crystals
- Can be present within mononuclear cells as well
- Surrounding tissue shows chronic inflammation and histiocytic reaction
- Tophaceous pseudogout shows larger aggregates with granulomatous reaction
- Foreign body giant cell reaction, chondroid metaplasia, hypertrophy of chondrocytes and myxoid degeneration may be seen
- Focal amyloid deposition and lipid can be seen (Arthritis Rheum 1988;31:1057)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Can be diagnosed on cytology
- Smears appear mildly cellular exhibiting histiocytes with intracellular and extracellular crystals (Pathology 2002;34:336)
- Crystals appear colorless to yellow-orange, short, rhomboid shaped (Diagn Cytopathol 2010;38:47)
- Display positive birefringence (Diagn Cytopathol 1996;15:349)
- Foreign body giant cells can be present (Diagn Cytopathol 2018;46:748)
Immunofluorescence description
- Not required for diagnosis (J Immunol 2013;190:6488)
Positive stains
- VEGF and TGF beta (positive in hypertrophic chondrocytes), CD68 (in histiocytes) and CD34 (in vessels), although not required for diagnosis (Clin Rheumatol 2008;27:597)
Negative stains
- SOX9 negative in hypertrophic chondrocytes; can be positive in metaplastic chondrocytes (Clin Exp Rheumatol 2009;27:430)
- Not required for diagnosis
Electron microscopy description
- Helpful when the usual diagnostic methods fail
- Microcrystals are present in the degenerating matrix encasing hypertrophic chondrocytes (Pathol Int 2008;58:723)
- Matrix shows electron dense amorphous material, comprised of proteoglycans and debris of cellular constituents
- Microcrystals are present in close proximity to degenerating collagen fibers (J Bone Joint Surg Am 1989;71:875, Am J Med 1977;63:161, J Neurosurg 1988;68:613)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Genetic sequencing in families has revealed various genetic mutations
- Linkage to short arm of chromosome 5 (Am J Hum Genet 1999;64:136, Arthritis Rheum 2003;48:2627)
- TNFRSF11B gene: gain of function mutation (Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2018;26:797)
- CYP24A1 gene mutations (Joint Bone Spine 2017;84:349)
Videos
Pseudogout
Sample pathology report
- Finger, incisional biopsy:
- Histologic features are consistent with calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition disease (see comment)
- Comment: Calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition disease (CPPD) is a benign condition exhibiting aggregates of basophilic to gray-brown deposits of rhomboid crystals. These crystals show positive birefringence under polarized light. It can be primary (idiopathic or familial) or secondary due to metabolic disorders like hypothyroidism, hypophosphatasia, hyperparathyroidism, hypomagnesemia, hemochromatosis, Wilson disease and trauma. Clinical and serological correlation is recommended.
Differential diagnosis
- Gout:
- Early onset < 40 years, late onset disease > 40 years
- M > F
- Ultrasound examination: echogenic monosodium urate crystals line the surface of articular cartilage, in contrast to echogenic CPPD calcifications, located within the cartilage
- Polarizable needle shaped urate crystals show negative birefringence (Arthritis Rheumatol 2020;72:1408)
- May have hyperuricemia
- Bone erosion may be seen
- Rheumatoid arthritis:
- Presence of skeletal erosive changes on radiology indicates a true rheumatoid arthritis process rather than CPPD (Radiology 1981;140:615)
- Affects small bones of adult women
- Proliferative synovitis with dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate
- Necrobiotic nodules, fibrosis and organizing fibrin
- Septic arthritis:
- Usually affects young age adults and children
- Involves single joint
- Increased neutrophils and neutrophilic collections within tissue
- Osteoarthritis:
- Usually affects joints of weight bearing distribution
- Manifests after 50
- Necrotic chondrocytes with thinned and fragmented cartilage
- Soft tissue chondroma:
- Involves distal extremities including digits, hands and feet
- Adults are commonly affected
- Discrete lobulated mass in soft tissue
- Hyaline cartilage is present with secondary dystrophic calcification
- Ankylosing spondylitis:
- Considered in differential when intervertebral discs are involved
- Affects lumbar and thoracic spine
- Mostly caused by pyogenic organisms
- Necrosis of disc with acute or chronic osteomyelitis, can be granulomatous
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 60 year old woman presented with painful knee swelling. Biopsy showed fibroadipose and fibrocollagenous tissue with a chalky white, firm lesion. Histology showed basophilic aggregates and clumps surrounded by macrophages. Chondroid metaplasia was also seen. The aggregates contained rhomboid shaped crystals with positive birefringence under polarization. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition disease
- Chondroma
- Gout
- Synovial chondromatosis
- Tumoral calcinosis
Board review style answer #1
A. Calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition disease
Comment Here
Reference: Calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition disease
Comment Here
Reference: Calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition disease
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is a cause of secondary calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition disease?
- ABCG2 gene mutation
- ANKH gene mutation
- FGF23 gene mutation
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Idiopathic
Board review style answer #2