Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Images | Diagrams / tables | Applications | Advantages | Potential limitations | Implementation | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Dietz RL, Pantanowitz L. Intraoperative consultation telepathology. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/informaticsintraoperativeconsult.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Also known as frozen section via telepathology
- Transmission of images to a remotely located pathologist during intraoperative consultation / frozen section
- Broadly classified into static, dynamic, robotic, whole slide imaging and hybrid (J Pathol Inform 2014;5:39, J Pathol Inform 2016;7:26)
Terminology
- Static image telepathology with still photographs (snapshots)
- Advantages: low bandwidth requirement and quick image transmission with small image files, digital cameras (including cell phones) widely available, low cost and no complex software needed (Hum Pathol 2007;38:1330)
- Disadvantages: skilled person is required onsite to take photos, image quality depends on the experience of the photographer and only limited portion of tissue / slide examined (Anal Cell Pathol 2000;21:201)
- Dynamic telepathology with transmission of a video stream
- Advantages: low bandwidth requirement, remote pathologist can view more regions of a slide, overcomes focus issues and relatively low cost (Hum Pathol 2008;39:56)
- Disadvantages: skilled person is required onsite to examine (drive) slide, may have lag in video transmission and video files infrequently archived
- Robotic telepathology with remote pathologist controlling a remote microscope
- Advantages: no dependence on a person with microscopy skills to drive a stage, no delayed scan time, lower bandwidth requirements, access to freely navigate the entire slide, ability to select different magnification, real time control of focus
- Disadvantages: someone still needs to load a slide on the device, high cost, more complex software and IT setup
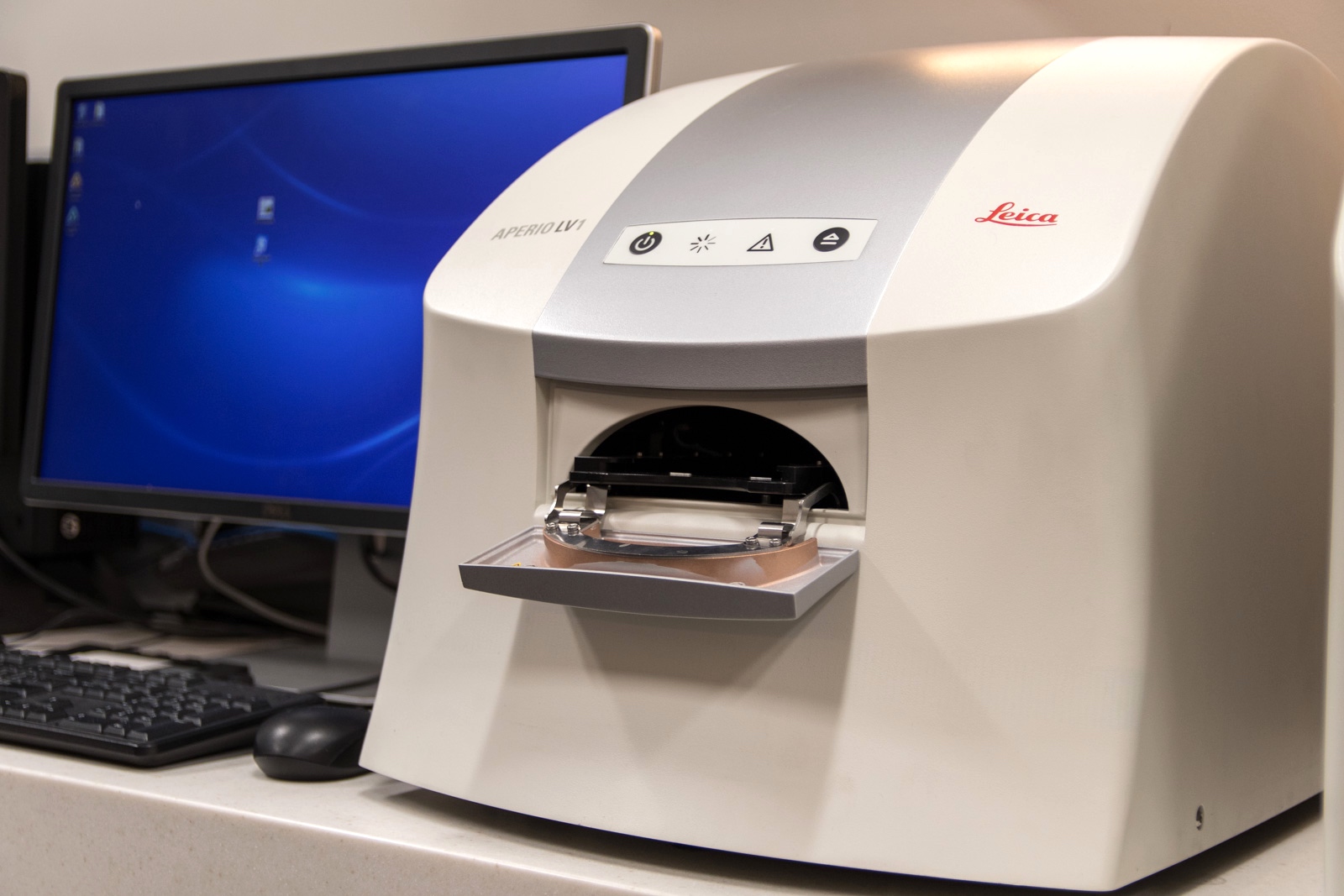
- Whole slide imaging (WSI) involves scanning a glass slide to generate a digital (whole slide) image (J Pathol Inform 2015;6:49)
- Advantages: high resolution image, access to the entire slide and WSI can be archived (Hum Pathol 2009;40:1070)
- Disadvantages: someone still needs to load a slide on the device to be scanned, relatively more expensive, larger footprint of device, high bandwidth requirements, longer time to scan whole slide and transmit large files, small tissue fragments or individual cells may fail to scan, inability to focus in Z axis (unless Z stack scanned) and proprietary file formats may need dedicated image viewers
- Hybrid (multimodal) uses a combination of the other techniques (e.g. WSI and robotic live microscopy) (J Pathol Inform 2016;7:26)
- Panoramic imaging uses a digital camera to stitch together a whole slide image in real time while a user examines slides on a conventional microscope
- Gross telepathology for transmitting images of intraoperatively removed specimens (macroscopy)
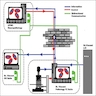
Diagrams / tables
Applications
- Telepathology during intraoperative consultation (remote frozen section reads), especially for access to expert subspecialists (e.g. neuropathologists) and during nonbusiness hours (e.g. on call at night and weekends) with comparable accuracy to glass slides (J Pathol Inform 2015;6:55, Am J Clin Pathol 2020;153:198)
- Teleconsultation for a second opinion among pathologists
- Nonclinical use cases (e.g. education, proficiency testing, quality assurance, archiving)
Advantages
- Decreased travel time for pathologists covering multiple locations and taking call at home (Hum Pathol 1991;22:514, Stud Health Technol Inform 2000;77:1127)
- Comparable accuracy to glass slides (Am J Clin Pathol 2020;153:198)
- General pathologists can have backup from off site pathologists for difficult frozen sections (J Clin Pathol 1999;52:761)
- Fewer subspecialized pathologists are needed at each location (J Pathol Inform 2015;6:55, Histopathology 2019;74:902)
Potential limitations
- Preanalytical factors:
- Improper tissue sampling (Pathol Int 1996;46:436)
- Slide artifacts (tissue folds, air bubbles, excess mounting medium) (Anal Cell Pathol 2000;21:201, J Pathol Inform 2016;7:26)
- No access to view gross specimens (Anal Cell Pathol 2000;21:201, Mod Pathol 2002;15:1197)
- Handling multiple frozen sections and multiple specimens simultaneously
- Depending on the mode of technology, limited access to examine the entire slide (Gen Diagn Pathol 1995;141:105, Hum Pathol 1997;28:30)
- Image related problems: poor focus, limited resolution, color discrepancy and corrupt image file (Anal Cell Pathol 2000;21:169)
- End user unfamiliarity with the telepathology system (Zentralbl Pathol 1992;138:413)
- Difficult / borderline pathology cases (e.g. dysplasia, screening for microorganisms)
- Higher deferral rate (Pathol Oncol Res 2000;6:197, Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:744)
- Potential delayed turnaround times (Anal Cell Pathol 2000;21:169, Diagn Pathol 2016;2:1)
- Downtime (e.g. telepathology system failure) (Histopathology 2019;74:902)
- Pathologist mindset (technophobia, reluctance, fear of making an error)
Implementation
- System selection to match telepathology system with clinical need and available resources
- Deployment with appropriate IT infrastructure (sufficient network bandwidth, HIPAA security)
- Validation according to CAP guidelines (e.g. 60 cases for glass versus digital with 2 week washout)
- Downtime policy and procedure
- Documentation (e.g. state that telepathology was performed in the pathology report)
- Maintenance (regular IT checks that the system is online and operational)
- Quality assurance program (monitor frozen final discrepancy and deferral rates)
- Business operations (hospital privileges, malpractice coverage, avoid Stark law antikickback violations)
Board review style question #1
What is the telepathology modality where a remote pathologist can control the microscope stage and objectives at the location where a frozen section slide was prepared?
- Dynamic
- Panoramic
- Robotic
- Static
- Whole slide imaging
Board review style answer #1
C. Robotic telepathology. The ability to remotely control the microscopic stage and objectives is a feature of robotic telepathology systems.
Comment Here
Reference: Intraoperative consultation telepathology
Comment Here
Reference: Intraoperative consultation telepathology