Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Barcode and RFID technologies | Barcode and RFID scanning data applications in surgical pathology | Potential barriers and limitations | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Absar SF, Prichard JW. Barcoding and tracking. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/informaticsbarcodingtracking.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Barcoding and tracking systems allow surgical pathology practices to be supported by computer readable information
- To achieve maximal laboratory efficiency, they standardize and automate work processes by encoding identification of specimen parts at accession, grossing, histology and pathology sign out areas
- Scanning ensures patient safety by reducing laboratory errors, increasing efficiency and allowing for quality management
- Main technologies involve barcode and radio frequency identification (RFID)
Essential features
- 2 main technologies for scanning and tracking in surgical pathology are barcode and radio frequency identification
- These allow for surgical pathology practices to be supported by computer readable information for laboratories to be efficient, standardized and automated
- Barcodes exist as linear 1 dimensional barcode lines and matrix 2 dimensional barcode dot matrices
- RFID tags can be passive (no internal power source) or active (battery powered)
Terminology
- 1D barcode = linear code
- 2D barcode = data matrix code = QR code
- Radio frequency identification (RFID)
- Laboratory information system (LIS) / laboratory management system (LMS)
- Quality assurance (QA) / quality control (QC)
Barcode and RFID technologies
- Barcodes (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;131:468, Surg Pathol Clin 2015;8:123)
- More accurately read information from small labels than human eye for fewer identification errors
- Can employ quality controls of checksums or check digits and internal control lines to ensure barcode is intact and read correctly or scan fails
- Can scan multiple slide and block labels at a time
- Linear 1D barcode lines: limited information in larger space
- Matrix 2D barcode dot matrix: more information in smaller space
- Hardware
- Scanners
- Each barcode reader is connected to an individual computer at
- Accessioning
- Grossing stations
- Tissue processors
- Microtomy
- Staining
- Slide assembly
- Slide distribution
- Pathologist workstations
- Requires adequate computers and network bandwidth to support laboratory operations
- Includes
- Contact wands
- Laser barcode scanners
- Image based (camera) barcode readers
- Can be wired, wireless or fixed / mounted
- Are preferably omnidirectional, as they read symbologies in any orientation
- Each barcode reader is connected to an individual computer at
- Printers are essential for labeling specimen containers, cassettes and slides
- Labels include barcodes and other patient identification information (case accession number, patient name, slide number, etc.)
- Print on an adhesive label or directly onto the cassette or slide
- Printing technology includes impact (dot matrix) and nonimpact (ink jet, laser and thermal) printing
- Scanners
- Implementation involves
- Planning for which specimens need tracking and what the data will be used for
- Selecting appropriate label
- Determining the space available for hardware
- Developing a plan for IT downtime
- Assessing degree of IT support and finances
- Choosing a vendor whose software maintains interoperability with the laboratory's existing LIS, instruments and computers
- RFID (atlasRFIDstore: Active RFID vs. Passive RFID - What's the Difference? [Accessed 29 June 2021])
- Passive RFID
- Uses tags with no internal power source; instead, these tags are energized by the electromagnetic energy transmitted from an RFID reader
- Used for applications such as access control, specimen tracking, supply chain management and more
- Has lower price point per tag than active RFID tags
- Active RFID
- Uses battery powered RFID tags that broadcast their own signal
- Commonly used as beacons to accurately track the real time location of assets
- Provide much longer read range than passive tags
- Passive RFID
Barcode and RFID scanning data applications in surgical pathology
- Barcode or RFID on badges facilitates identification and login of staff to access rooms, equipment and software
- Barcoded paper requisitions can be scanned to file into document imaging systems
- During case accessioning, scanned requisitions and containers are positively identified and matched to the correct patients in the LIS
- Verification of relationship of requisitions to specimens, blocks and slides
- For accurate and safe handling and transfer between workflow steps
- To prevent mislabeled components and tissues
- Scanning requisitions or specimen containers at grossing bench can trigger tissue cassette engraver labeling on demand
- Only blocks labeled for the specimen being grossed are available
- Only blocks labeled for the specimen being grossed are available
- Scanning cassettes into tissue processing racks records
- Date and time a workflow step occurs
- Grossing staff
- Grossing station location
- Time that the fresh specimen tissue was placed in formalin
- Grouping cassettes in the racks for tracking through tissue processing
- Tissue processors and racks can be barcoded to
- Identify groups of blocks
- Specify which processor and which protocol is associated with each tissue block
- Determine appropriate handling of tissue for ancillary tests with special requirements
- Barcoding at embedding can
- Display gross description of tissue count, color and sizes
- Display gross images
- Track work unit processing
- Verify completeness of sets of slides for each case at case assembly before delivery to pathologists
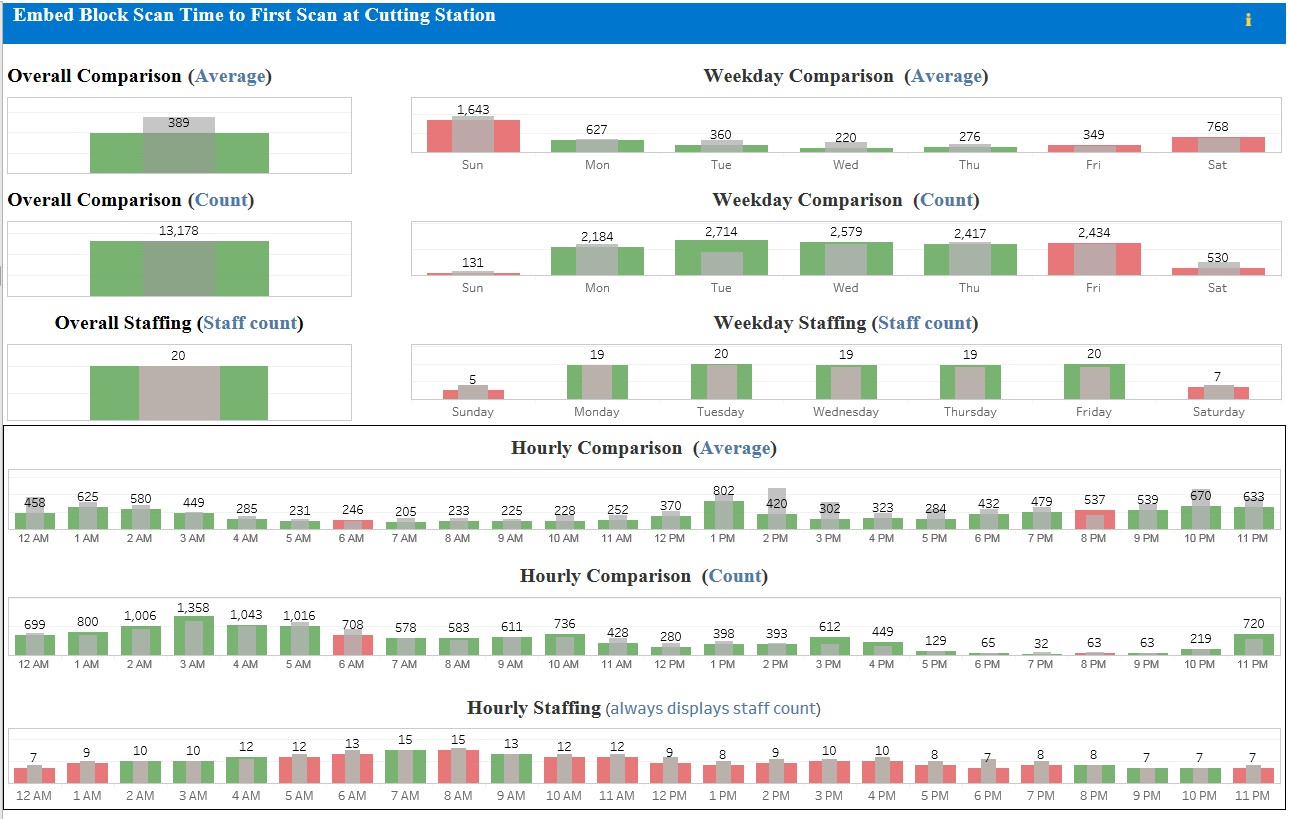
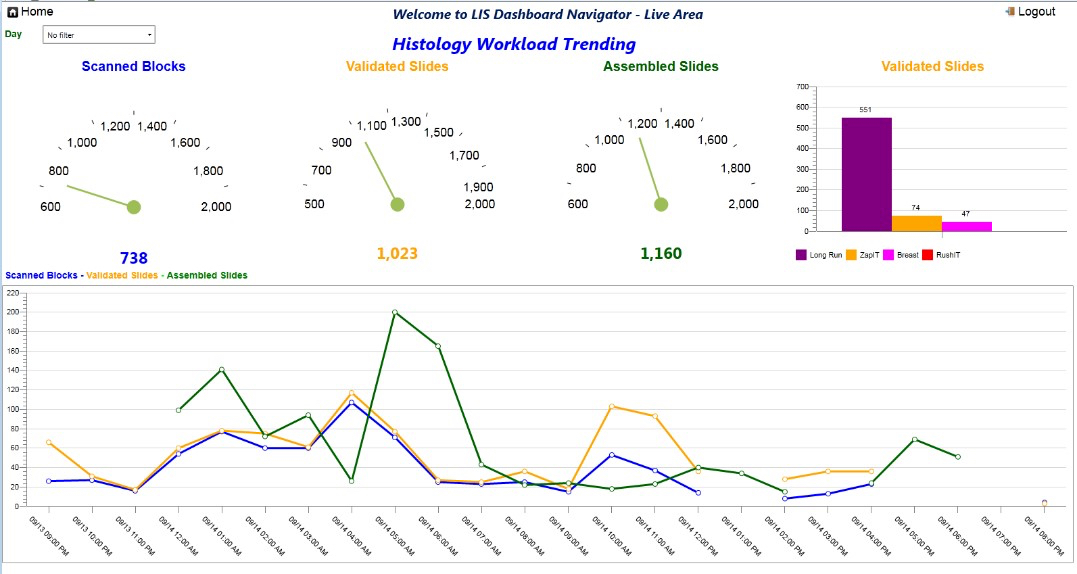
- Record metrics of units worked when requisitions, specimens, blocks and slides are scanned at specific workstations under specific staff logins
- Monitor and trend time between work steps (takt time in Lean language)
- Tablets or wall mounted monitors can facilitate visual presentation of work being done in any work area
- As graphs of barcode or RFID scans
- Visible to all staff
- Available during walkthrough by management
- Remotely accessible
- As graphs of barcode or RFID scans
- Track location for storage, retrieval and purging of specimens, blocks and slides
- Automate identification of slides for
- Assignment to pathologist
- Whole slide imaging and analysis
- Scanning a tag to open a case rather than manually typing can assure synchrony between the scanned object and the LIS context
- Reference: Clin Lab Med 2008;28:207
Potential barriers and limitations
- Cost consideration for low volume practices
- Implementation requirements include workflow process development and modification, training, education and testing
- IT expertise for initial implementation and support
- Interoperability of the instrumentation within the AP laboratory and with the other laboratories in the same institution
- Operator error, for example, tissue mixup during grossing or embedding or slide labeling error
- Mechanical delays from poor quality label printing and label printer maintenance issues
- References: Clin Biochem 2012;45:988, Diagnostics (Basel) 2021;11:2167
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is true about the use of RFID scanning in surgical pathology?
- Passive RFID tags are commonly used as beacons to accurately track the real time location of assets
- Passive RFID tags are more expensive than active ones
- Passive RFID tags are used for applications such as access control, specimen tracking and supply chain management
- Passive RFID tags use battery powered RFID tags that broadcast their own signal
Board review style answer #2
C. Passive RFID tags are used for applications such as access control, specimen tracking and supply chain management
Comment Here
Reference: Barcoding and tracking
Comment Here
Reference: Barcoding and tracking