Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Augmented reality | Background | Design (technology) | Images | Advantages | Applications | System requirements | Videos | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Satturwar S, Pantanowitz L. Augmented reality microscopy (ARM). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/informaticsaugmentedrealitymic.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Modified (smart) microscope with an added / attached accessory augmented reality unit / device that enables real time annotation / image analysis / artificial intelligence to be superimposed on a glass slide
Essential features
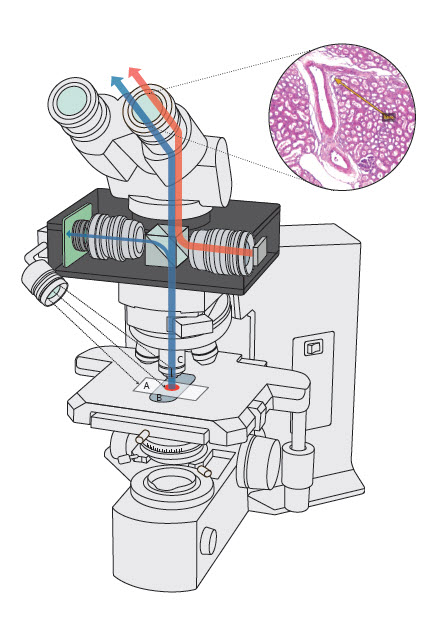
- Requires an accessory augmented reality device to be attached to a conventional microscope, which converts this setup into a smart microscope
- Unit acquires images of a glass slide on the microscope stage in real time, which allows annotations to be superimposed in the microscope's ocular eyepiece or displayed on an attached computer monitor
- This avoids having to first photograph or scan slides in order to perform measurements, image analysis or run artificial intelligence (AI) based algorithms
Terminology
- Augmented reality microscopy (ARM)
- Smart microscope
Augmented reality
- Augmented reality (AR) technology combines reality with digital information by superimposing a computer generated digital image onto an object or user's view of the real world; this differs from virtual reality (VR), where a complete digital or computer generated environment gets generated (Med Ref Serv Q 2012;31:212)
- Examples of nonmicroscope wearable devices: AR (e.g. Google Glass, Microsoft HoloLens), VR (e.g. Oculus Rift, Samsung Gear VR) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018;142:638)
Background
- Introduced into the literature by Chen et al. (Nat Med 2019;25:1453)
- A smart microscope with an attached AR device can augment additional computer generated digital information / analysis that gets overlain on the original microscopic field of view (FOV) in real time, without having to first digitize a glass slide or majorly alter traditional manual pathology workflow
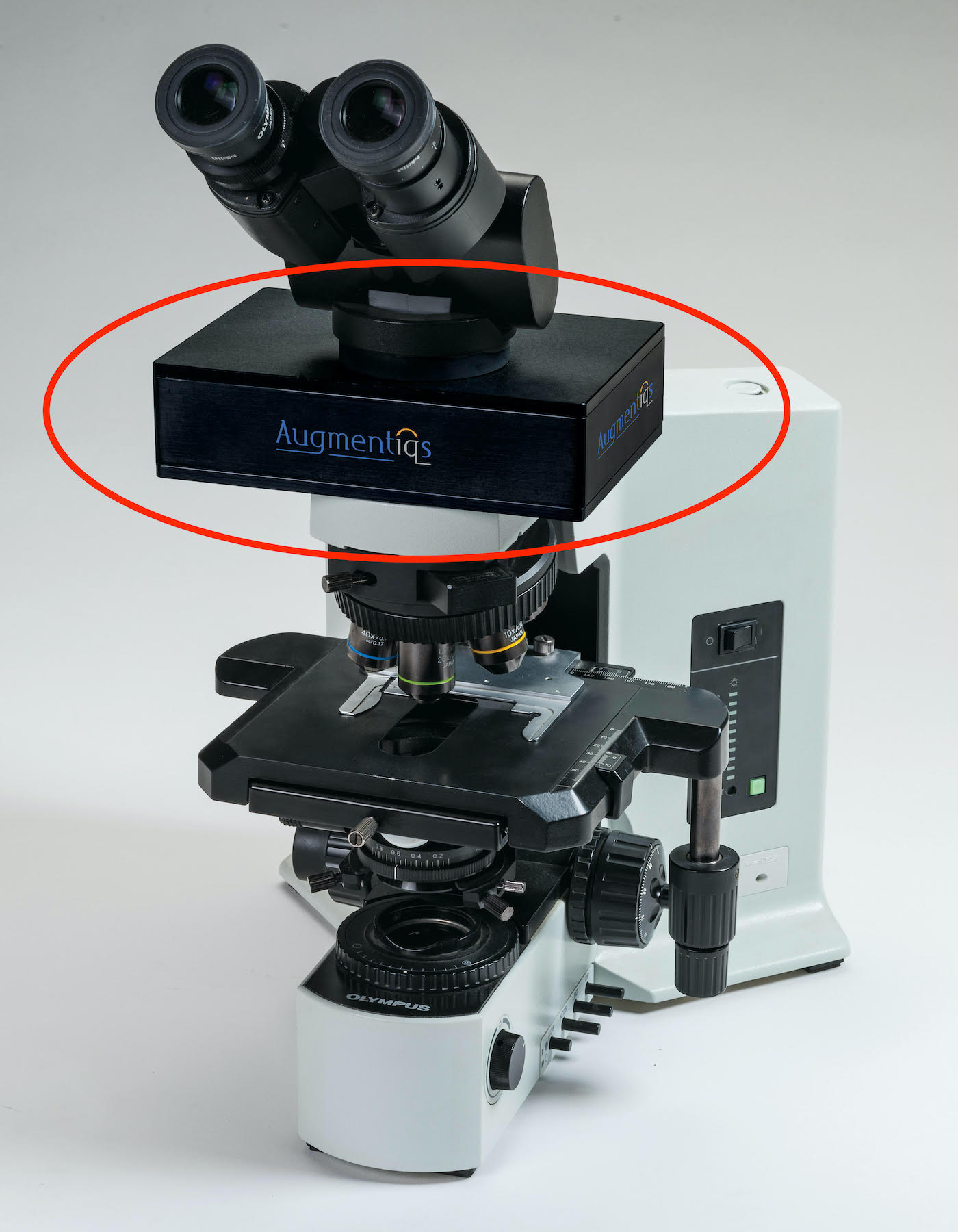
- ARM devices are commercially available from companies such as Augmentiqs and Evidence
Design (technology)
- An ARM unit can be attached to any light microscope where it is inserted between the microscope's objectives and eyepiece unit
- Computer generated images or annotations from the device get superimposed on the microscope's image visible through the ocular lens or can be displayed on an attached computer monitor
- Any compatible software application can be used to perform real time image analysis or run an AI based algorithm
Advantages
- AR device can be attached to and enhance almost any conventional light microscope
- No change to the regular function or optical quality of the microscope
- No need to digitize / photograph glass slides prior to image analysis
- Less disruption to routine workflow in a busy pathology practice
- Permits real time annotation, image analysis and AI based algorithm use
- Image overlay with AR is an advantage over conventional digital modalities
- Requires minimal technical skills to operate
- No associated simulator sickness that may occur with wearable AR / VR devices
- Possibly quicker and cheaper than a conventional whole slide scanner
Applications
- Permits real time sophisticated annotations to be superimposed on microscopic images (e.g., detection of lymph node metastases of breast carcinoma and prostate cancer detection in prostate specimens) (Nat Med 2019;25:1334)
- Enables real time image analysis and running of AI based algorithms on glass slides (e.g., Ki67 proliferation index quantification) (J Toxicol Pathol 2018;31:315, Cancer Cytopathol 2020;128:535)
- Like other traditional digital cameras attached to a microscope, the AR device can be used to acquire digital photos and transmit images (telepathology, teleconsultation, remote frozen section peer review, tumor board presentations)
- Research and teaching / education
System requirements
- ARM device by Augmentiqs requires PC Windows 7 or higher and Augmentiqs software installed
- Currently, there are no standardized guidelines on validation or licensing requirements for use of ARM
Videos
Google and ARM
Augmentiqs and ARM
Board review style question #1
Which of the following imaging steps is involved in augmented reality microscopy?
- Image archiving and retrieval
- Image compression
- Rapid slide scanning
- Superimposed annotation
- Z stacking
Board review style answer #1
D. Superimposed annotation. ARM superimposes computer generated digital annotations / images over the real world view visible in a microscope's eyepiece or on an attached computer monitor. No glass slides are scanned and therefore ARM does not require subsequent image compression and storage.
Comment Here
Reference: Augmented reality microscopy (ARM)
Comment Here
Reference: Augmented reality microscopy (ARM)