Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stainsCite this page: Lynch D. Crystal storing histiocytosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/hematologycsh.html. Accessed January 4th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare; crystalline material accumulates in cytoplasm of histiocytes; usually kappa light chain origin (Histopathology 2016;68:482)
- Adults are affected with a wide age range; men and women affected nearly equally
- Most commonly affects the head and neck, lung, kidney, bone marrow and lymph nodes, although nearly any site may be involved (Head Neck Pathol 2012;6:111)
- Strongly associated with underlying plasma cell neoplasm or lymphoma with plasma cell differentiation
- A minority of cases are associated with nonneoplastic causes such as infections and autoimmune disease
Essential features
- Rare disease with crystalline material in cytoplasm of histiocytes
- May affect any organ system
- Strongly associated with underlying lymphoid or plasma cell neoplasm
Case reports
- 38 year old woman with seizures (Clin Neuropathol 2014;33:23)
- 50 year old woman with lung mass and rheumatoid arthritis (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:1159)
- 51 year old woman with upper lip and cheek tumor (Head Neck Pathol 2012;6:111)
- 73 year old man with ascites, weight loss and fatigue (Blood 2002;100:1817)
Microscopic (histologic) description
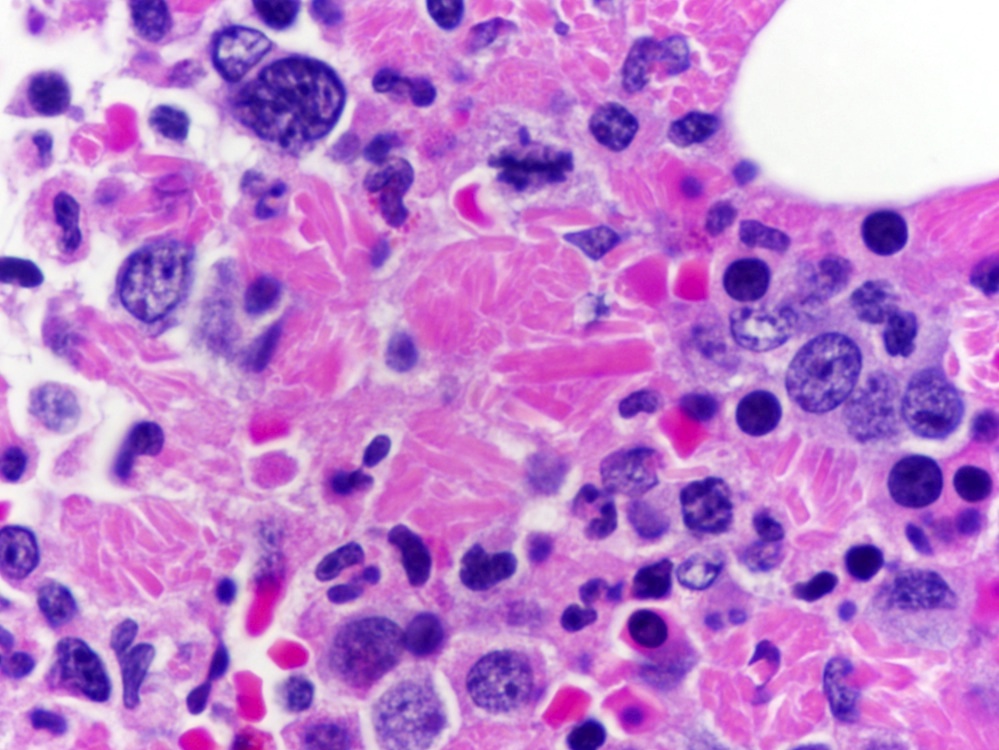
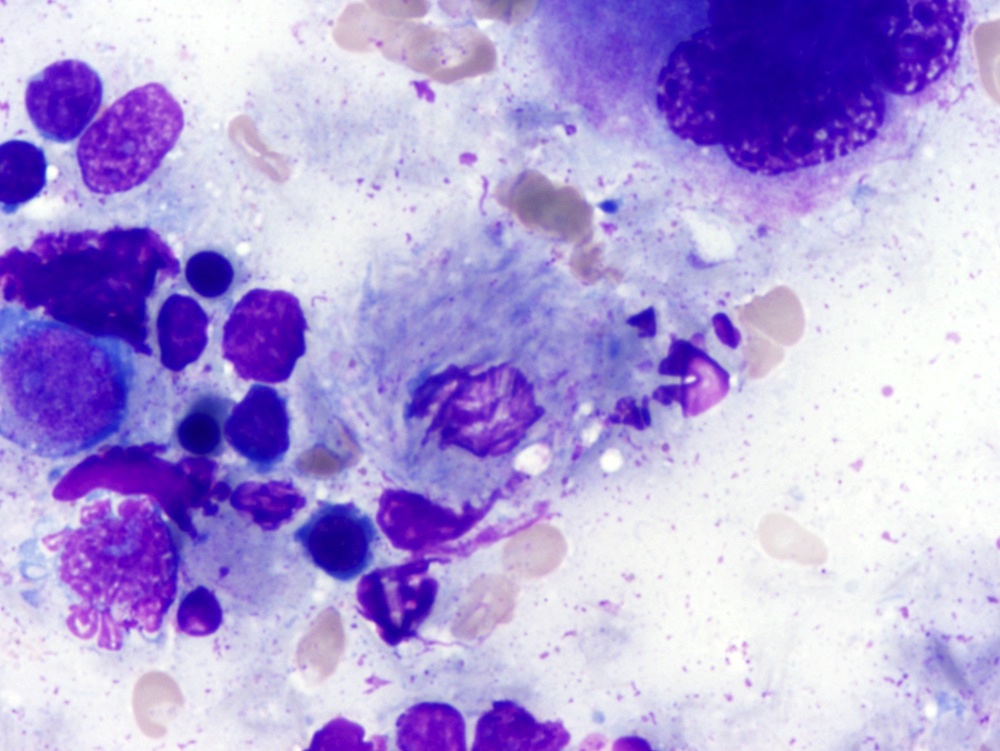
- Cytologically benign histiocytes with abundant cytoplasm filled with many refractile eosinophilic crystals which may be needle-like or rhomboid in shape
- Neoplastic lymphocytes and plasma cells may be present
- Histiocytes often compose the majority of cellular elements, potentially obscuring an underlying neoplasm
Microscopic (histologic) images
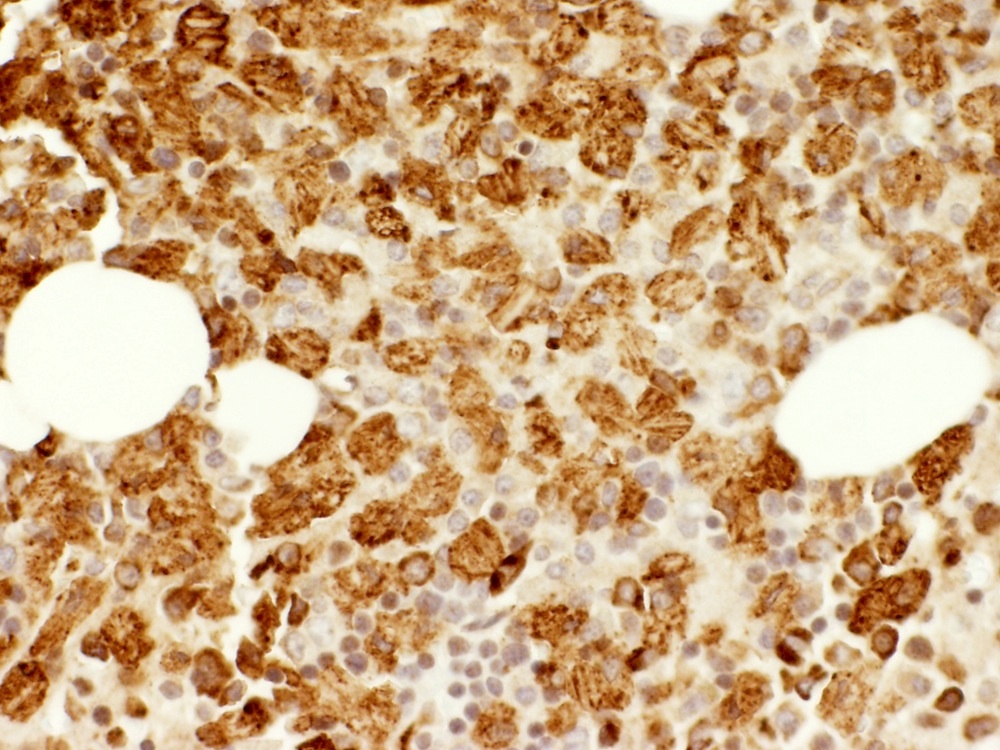
Positive stains
Negative stains