Table of Contents
Definition / general | Case reports | Radiology images | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Pernick N. Cystic tumor of the atrioventricular node. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/hearttumormesotheliomaofAVnode.html. Accessed December 2nd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Also called cystic tumor of AV node or mesothelioma of AV node but does not appear to have mesothelial origin
- Rare; usually identified at autopsy
- May be congenital rests of endodermal origin (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1990;114:1057) or ultimobranchial heterotopia identical to solid cell nests of thyroid (Am J Clin Pathol 2005;123:369)
- Associated with other congenital anomalies
- Often causes heart block and sudden death
- Mean age 38 years, 75% female
- Should examine conduction system in all patients with sudden death, particularly if a history of arrhythmia or heart block
Case reports
- 7 year old boy with rare cause of sudden cardiac death (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2001;125:573)
- 24 year old woman with sudden cardiac death (Am J Forensic Med Pathol 2005;26:349)
- Patient with mesothelioma of the atrioventricular node (Am J Clin Pathol 1975;63:377)
- Patient with unusual site for the AV node tumor (Cardiovasc Pathol 1999;8:325)
- Patient with congenital cystic tumors of the atrioventricular node (Cardiovasc Pathol 1999;8:233)
- Patient with with atrioventricular nodal tumor associated with polyendocrine anomalies (Pathol Res Pract 1996;192:54)
Treatment
- Pacemaker implantation, anti-arrhythmic drugs, possibly surgical excision (Heart 2000;83:E6)
Gross description
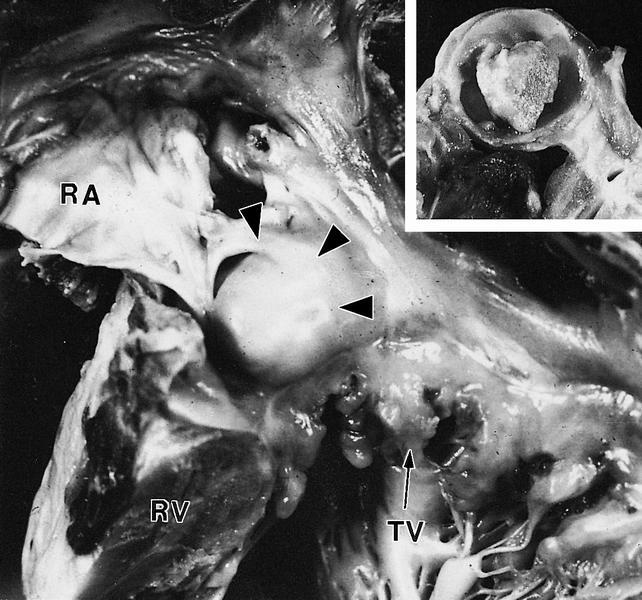
- May not be visible due to small size (2 to 20 mm)
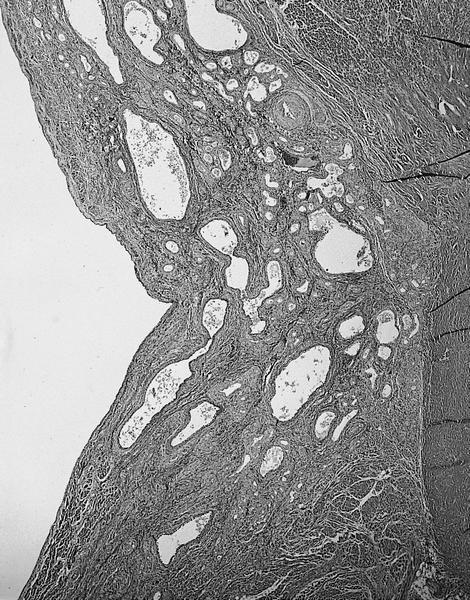
- Multicystic lesion in area of atrioventricular node and membranous septum
Gross images
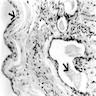
Microscopic (histologic) description
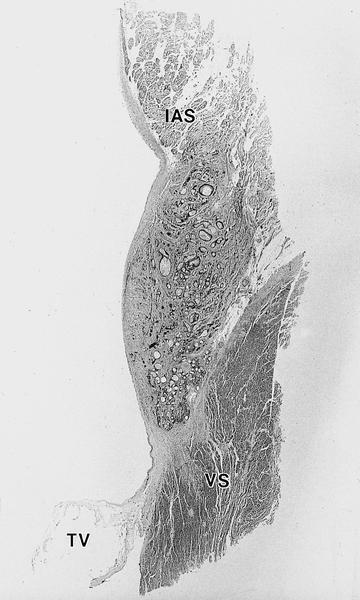
- Must sample conduction system
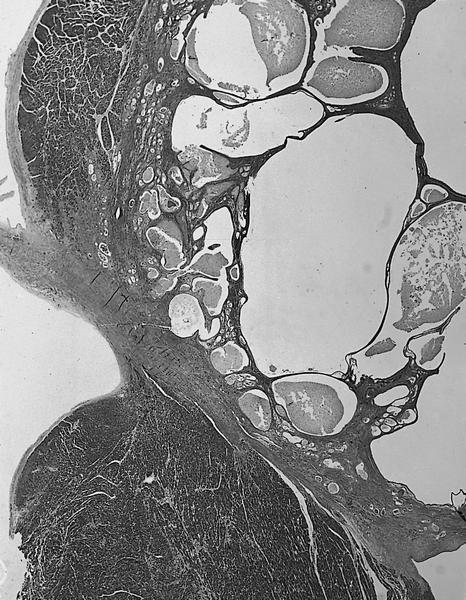
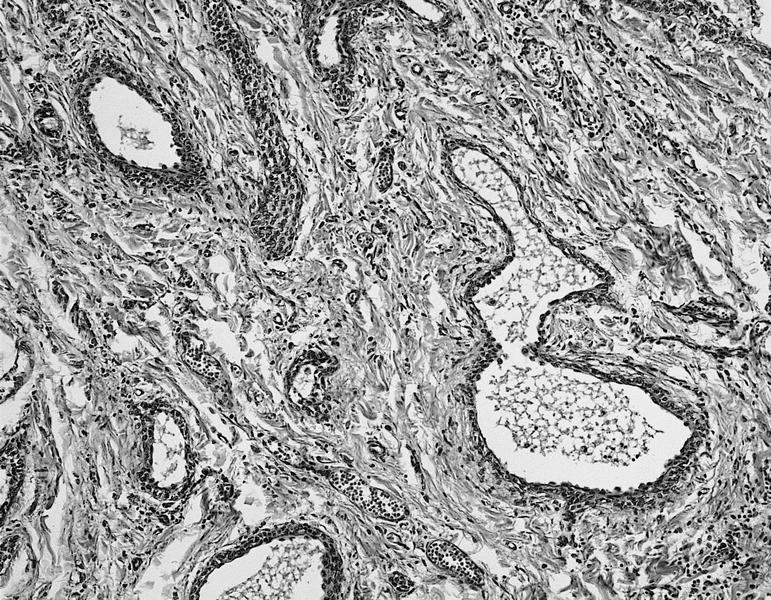
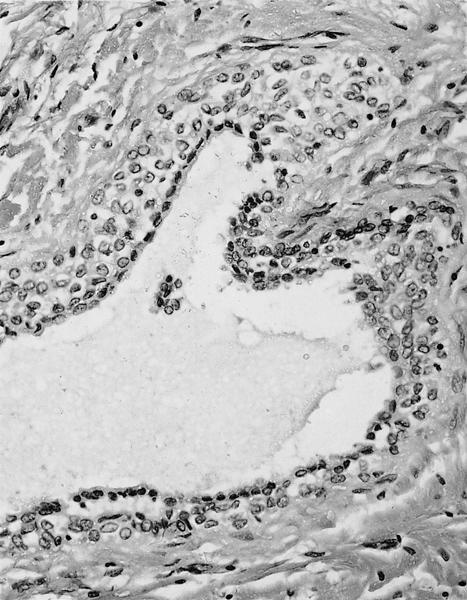
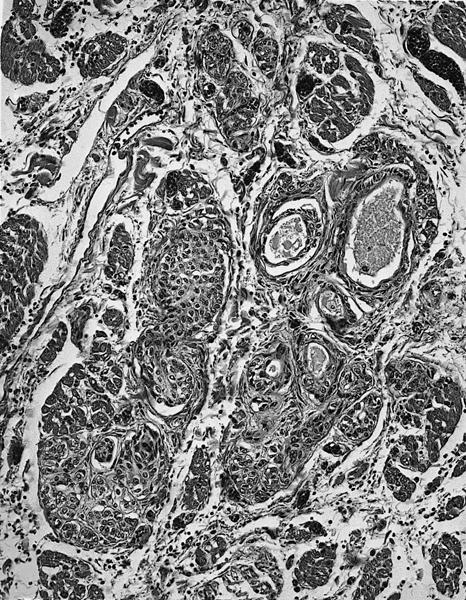
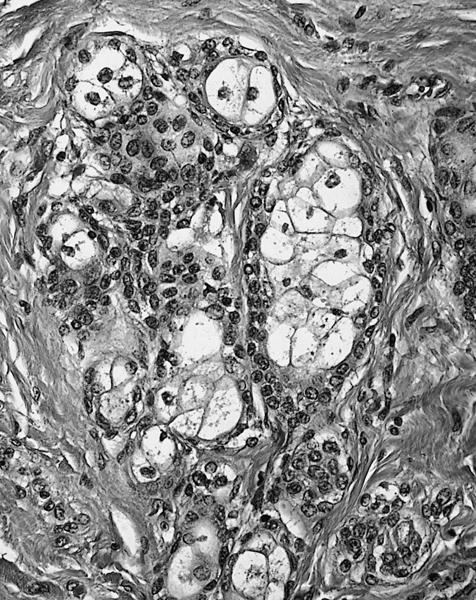
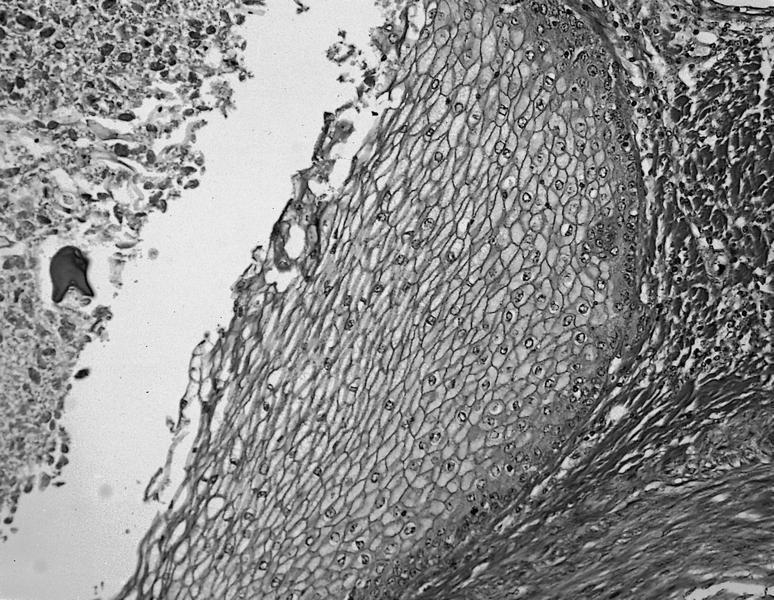
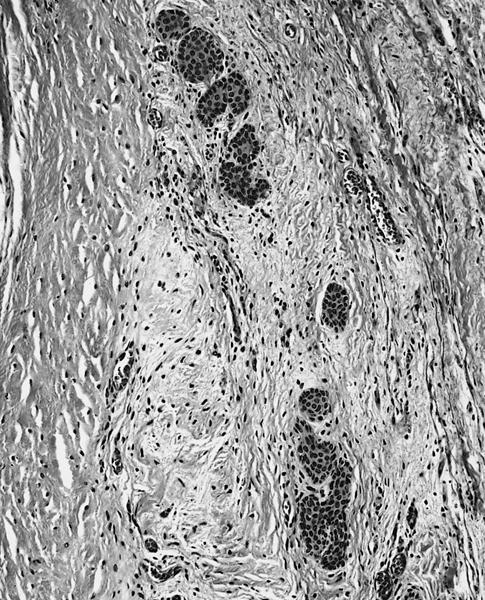
- Solid and cystic areas lined by nonciliated, epithelial appearing cuboidal cells (main cells), mixed with occasional clear cells (neuroendocrine or C cells)
- Lumina contains PAS+ diastase resistant material which may calcify
- May have inflammatory cells and fibrosis
- No smooth muscle, no mitotic figures, no atypia
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Cells form solid nests with well formed basement membranes, cytoplasmic tonofilaments and desmosomes or glandular structures with desmosomes, electron dense material and short microvilli
Differential diagnosis
- Bronchogenic cyst: solitary, grossly visible, on epicardial surface, smooth muscle present
- Mesothelial cyst: larger, unilocular, on surface of heart
- Teratoma: has neural or other ectodermal structures (Pediatr Pathol 1994;14:913)