Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Byrnes K. Follicular cholecystitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/gallbladderfollicularchol.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
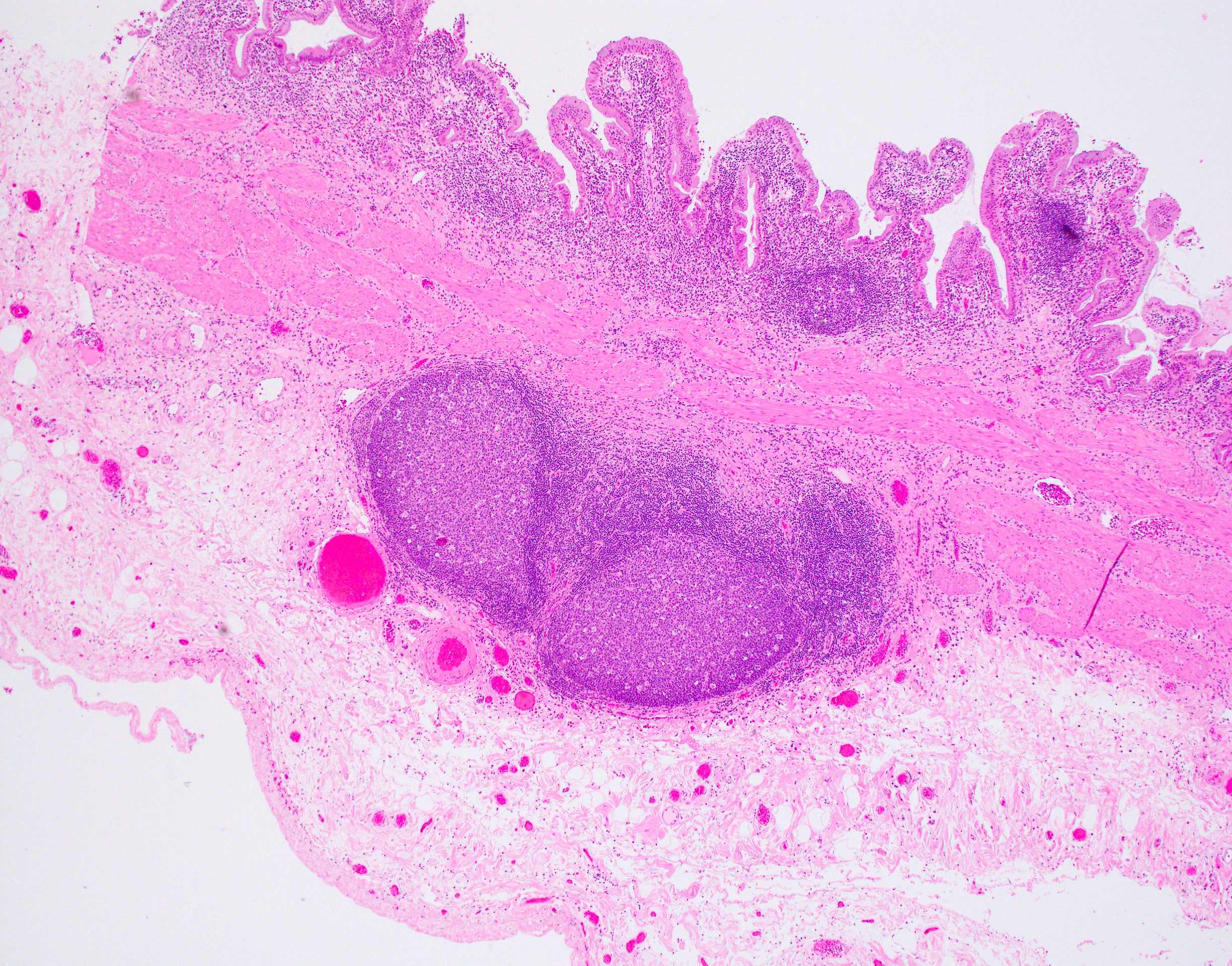
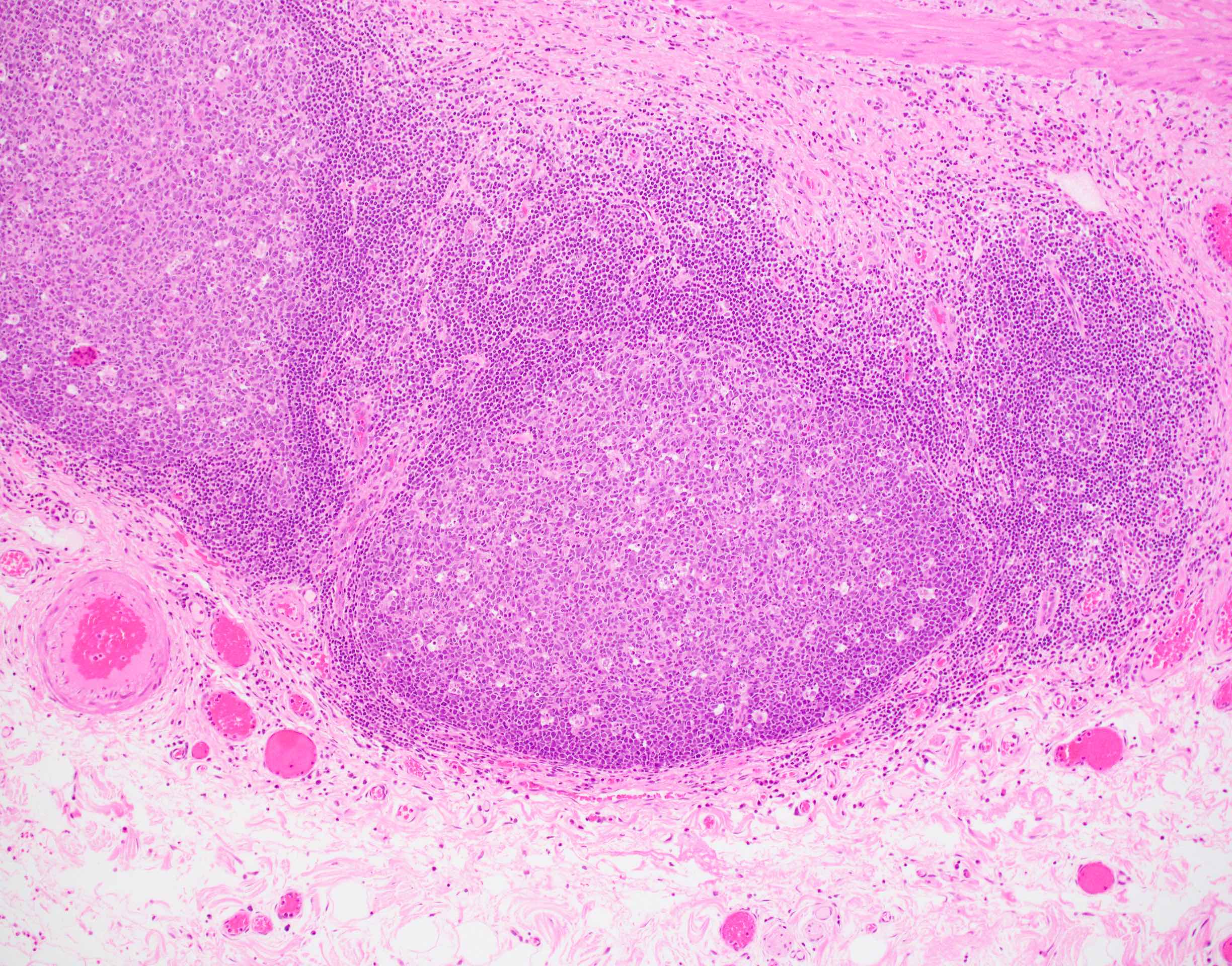
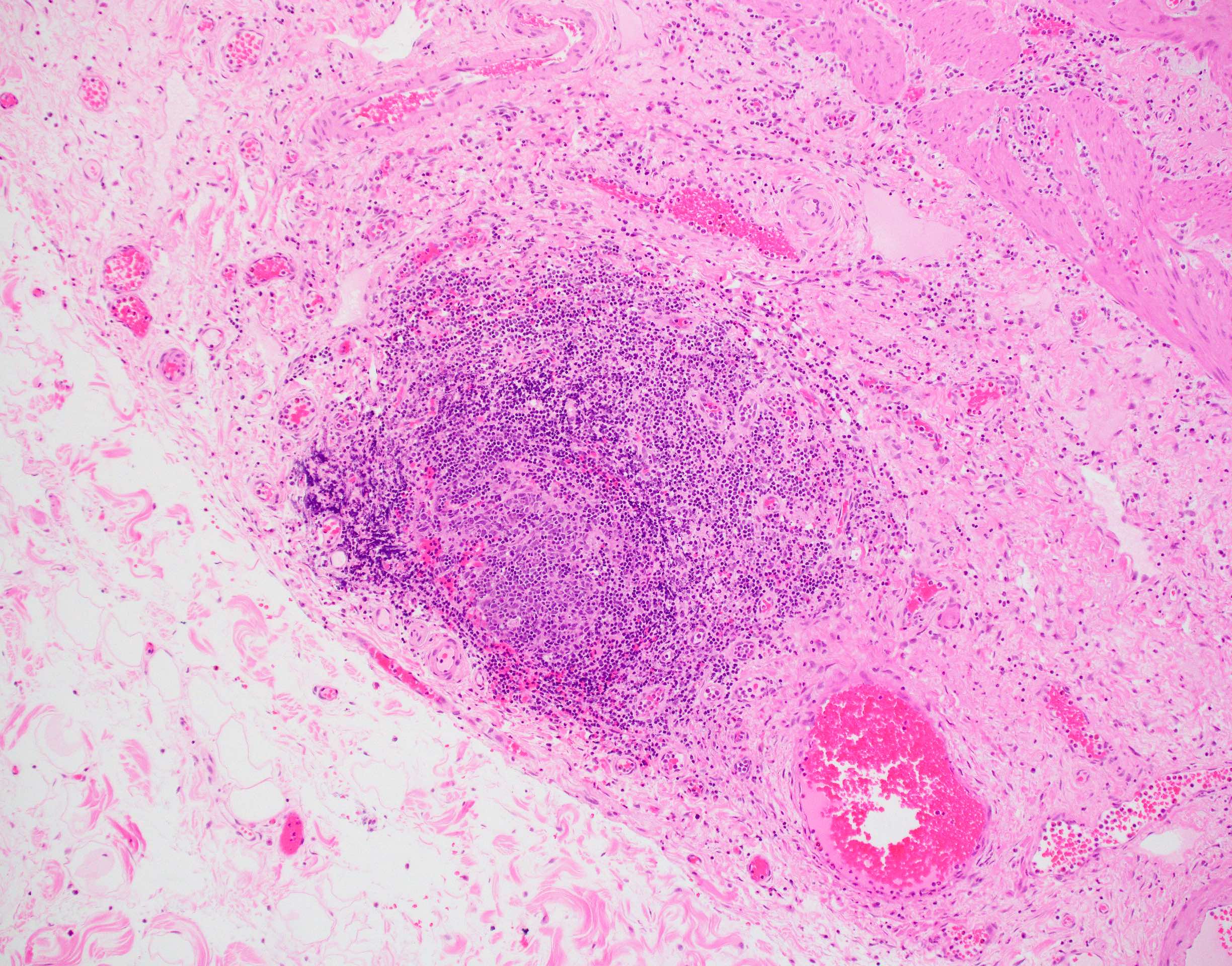
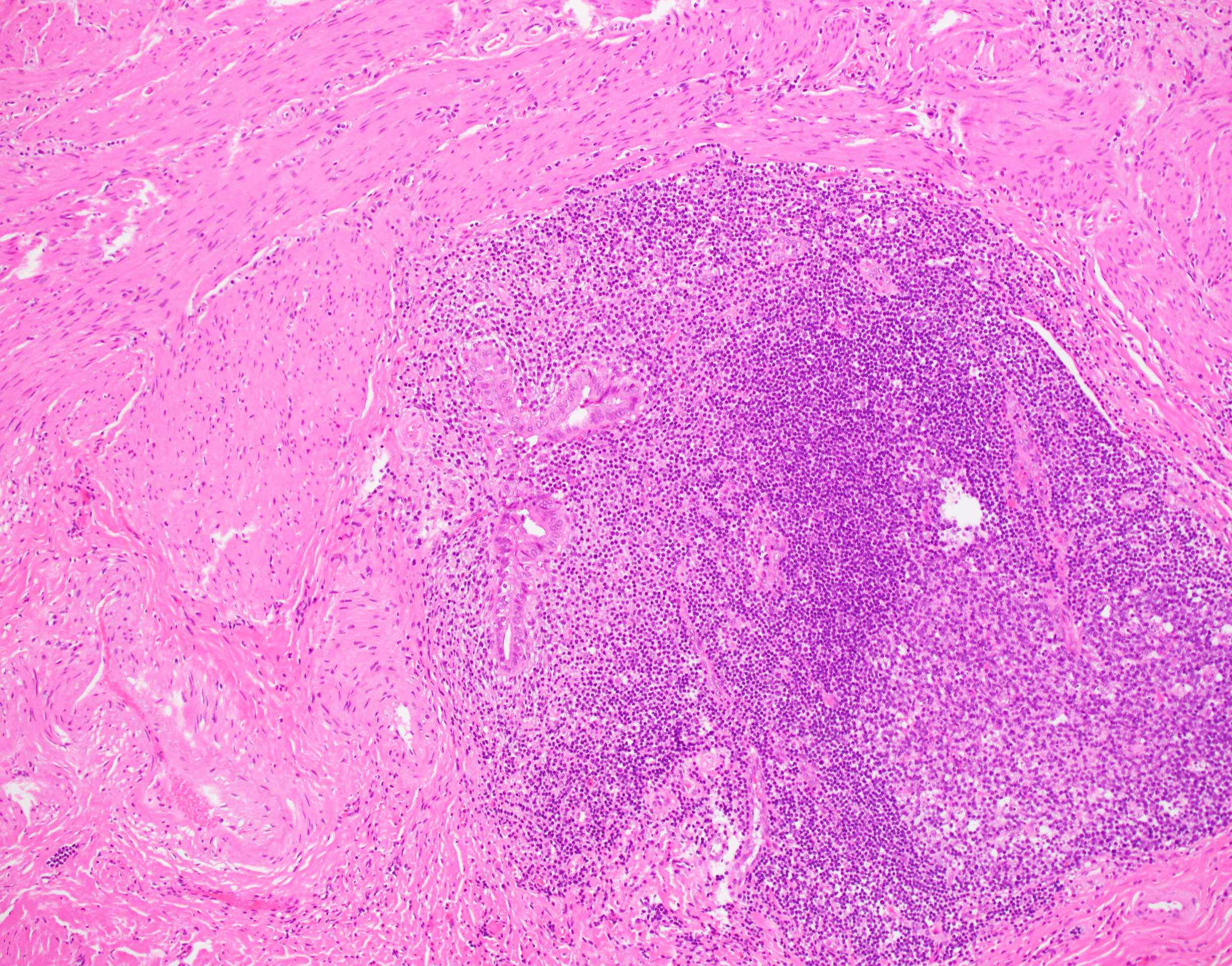
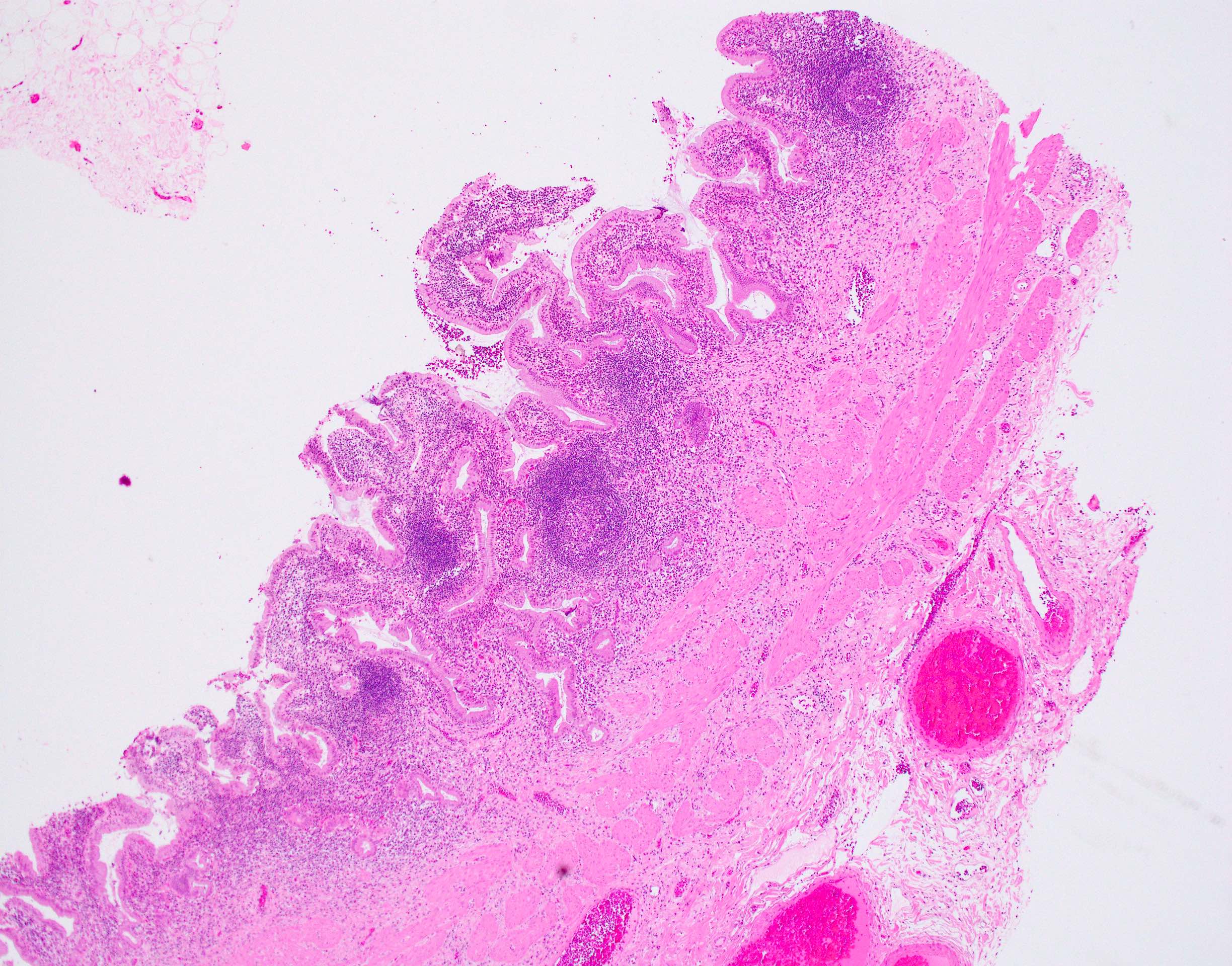
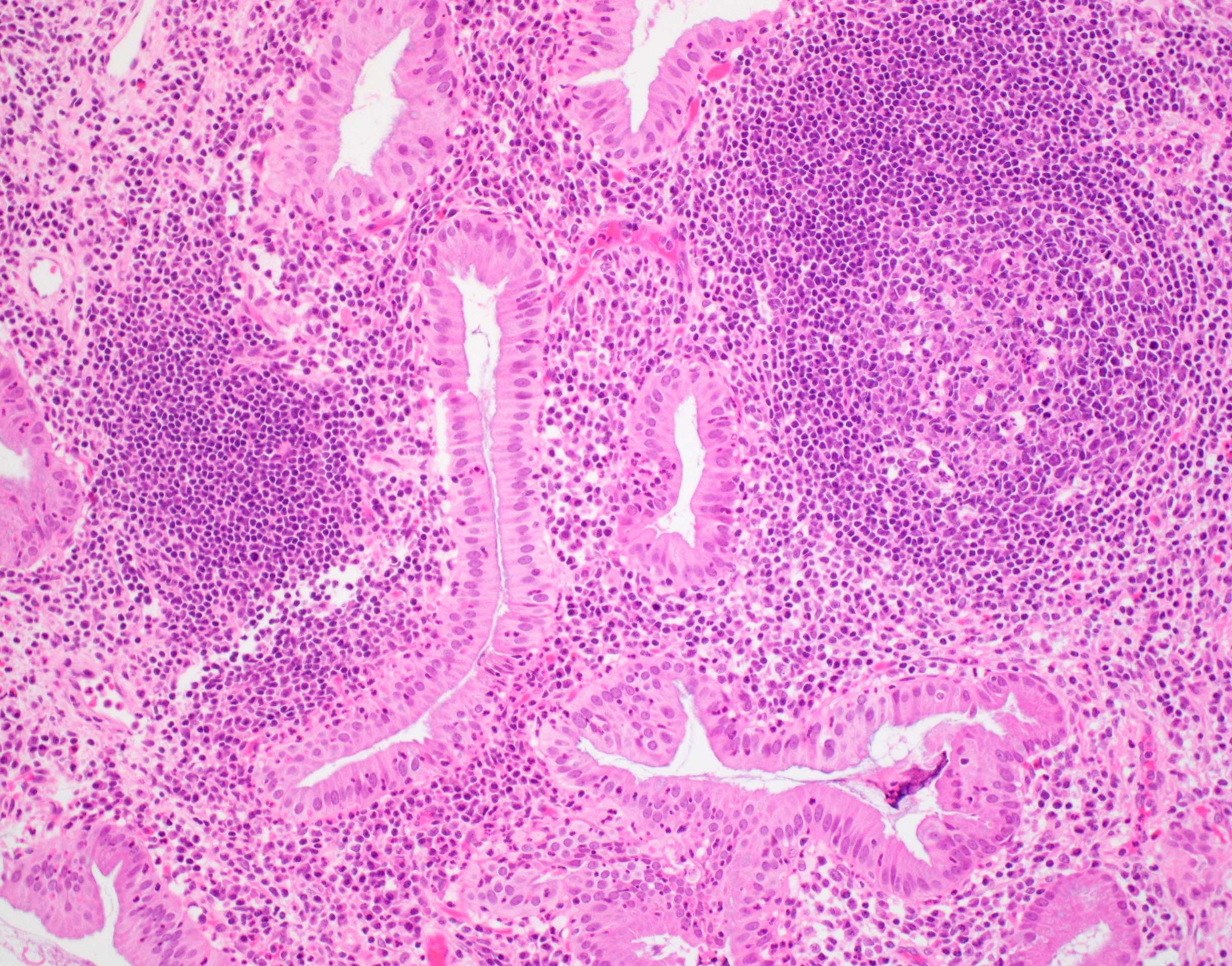
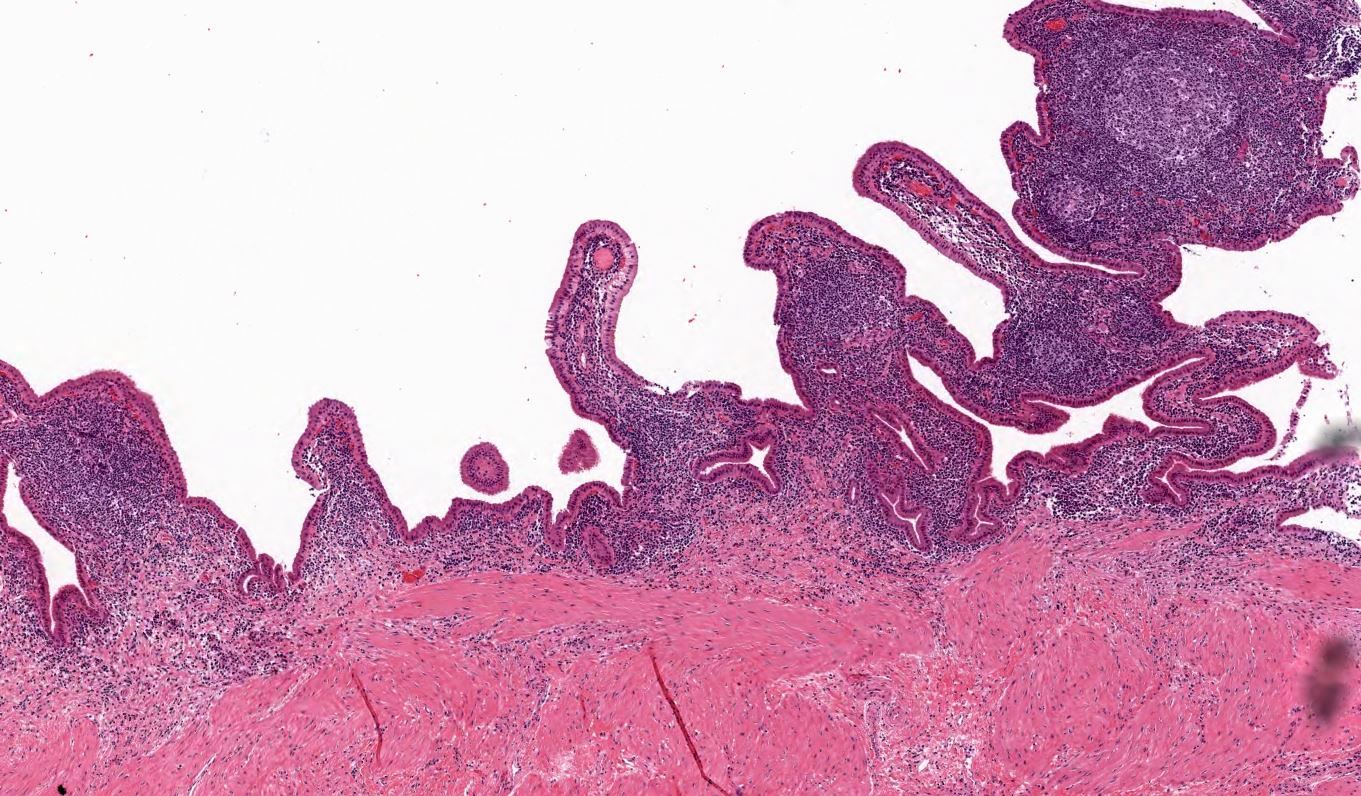
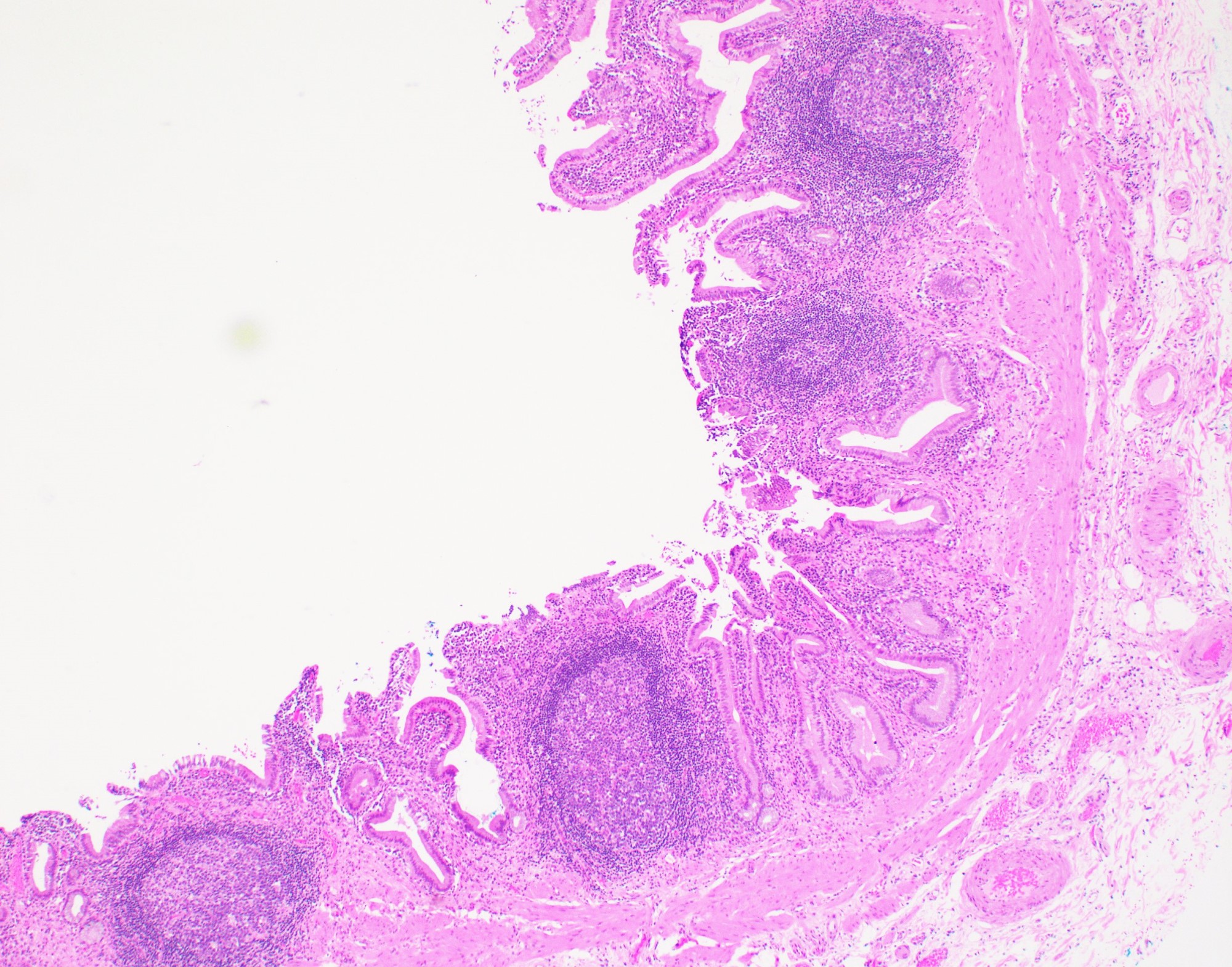
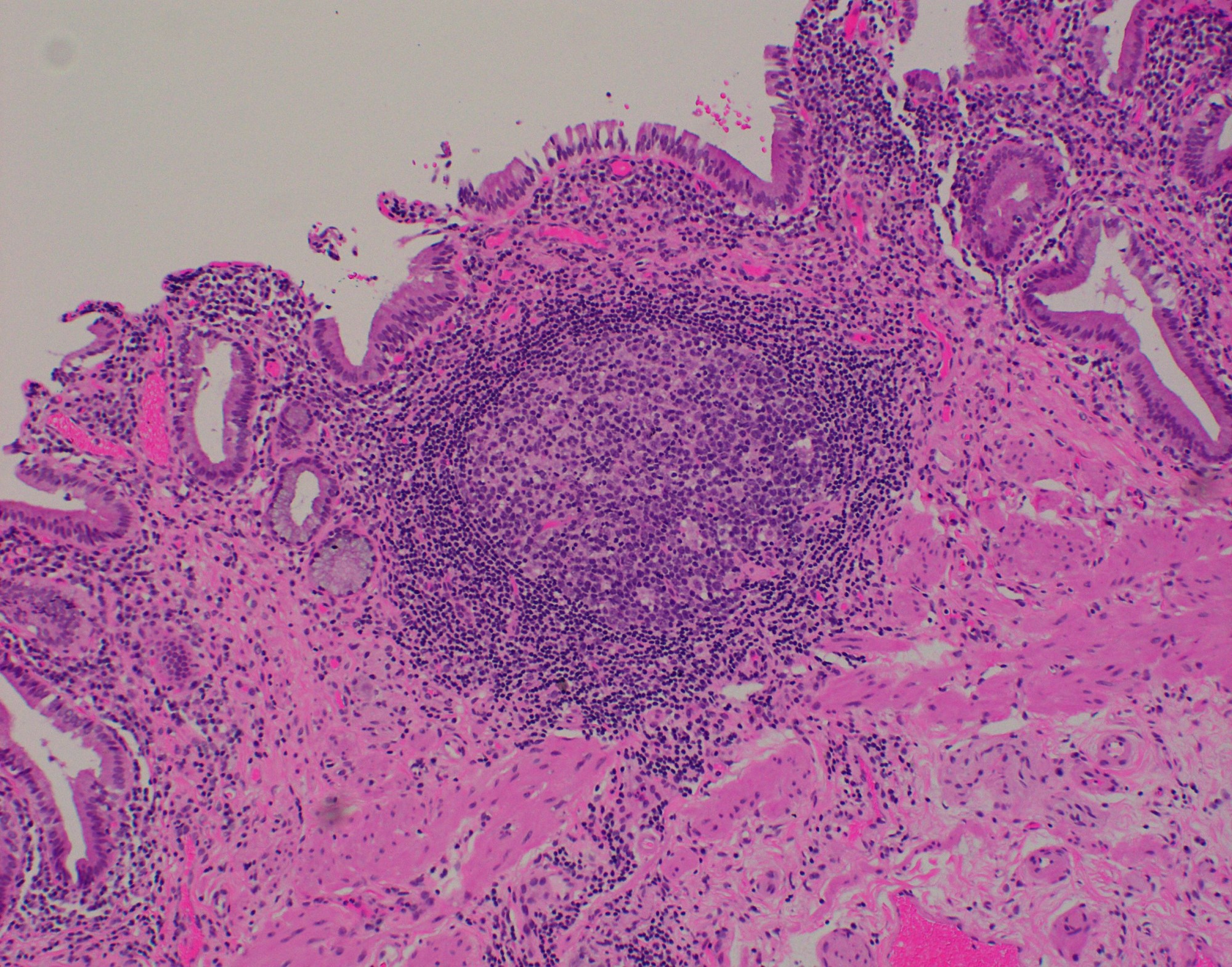
- Follicular cholecystitis is an inflammatory pattern of injury characterized by prominent reactive lymphoid follicles with germinal centers in the mucosa and wall of the gallbladder
Essential features
- Multiple reactive lymphoid follicles with germinal centers involving the mucosa and wall of the gallbladder
- Can be seen in the setting of infection and gastritis (Acta Pathol Jpn 1979;29:67, Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:826)
- Rare entity occurring in ~2% of gallbladders (Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:826)
Terminology
- Chronic follicular cholecystitis
ICD coding
- ICD-10: K81 - cholecystitis
Epidemiology
- ~2% of all cholecystectomy specimens (Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:826)
- M = F, with some studies suggesting a slight F > M predominance (Hum Pathol 2019;88:1, Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:826)
- Mean age ~68, older than typical chronic cholecystitis (Hum Pathol 2019;88:1, Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:826)
Sites
- Gallbladder
Etiology
- Reported association with infection, specifically typhoid fever or Gram negative bacteria (e.g., E. coli and K. pneumonia) (Acta Pathol Jpn 1979;29:67)
Clinical features
- Described in association with chronic cholecystitis, infection and biliary obstruction (Hum Pathol 2019;88:1)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis of follicular cholecystitis is made on cholecystectomy specimens
Case reports
- 32 year old woman with follicular cholecystitis and focal periductal fibrosis in the liver (Int J Surg Case Rep 2022;98:107571)
- 58 year old man with follicular cholecystitis mimicking lymphoma (J Cancer Res Ther 2014;10:749)
- 66 year old man with follicular cholecystitis mimicking xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis (Indian J Radiol Imaging 2021;31:697)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Prominent lymphoid follicles with lymphoid hyperplasia and germinal centers present (Rev Invest Clin 1989;41:159)
- Usually seen in the mucosa of the gallbladder but can extend into the wall
- Lymphoid follicles may surround Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses
- Defined by some studies as at least 3 lymphoid follicles per centimeter (Int J Surg Pathol 2020;28:826)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Gallbladder, cholecystectomy:
- Follicular cholecystitis
Differential diagnosis
- Chronic cholecystitis:
- Will not have numerous lymphoid follicles within the mucosa
- IgG4 related cholecystitis:
- Has prominent plasma cells, increased IgG4 positive plasma cells and can form a mass-like lesion
Board review style question #1
A 60 year old woman with cholecystitis underwent a cholecystectomy. Sections of the gallbladder show numerous lymphoid follicles involving the mucosa and wall of the gallbladder. Which of the following other disease processes does the patient likely have?
- Follicular lymphoma
- Gastric cancer
- IgG4 related disease
- Infection with E. coli
- Primary biliary cholangitis
Board review style answer #1
D. Infection with E. coli.
Follicular cholecystitis has been described in association with infection by Gram negative bacteria, external biliary obstruction and gastritis.
Answer C is incorrect because IgG4 related disease will have prominent plasma cells and is not associated with only lymphoid follicles.
Answer E is incorrect because primary biliary cholangitis does not involve the gallbladder.
Answer A is incorrect because follicular lymphoma is extremely rare in the gallbladder and will be characterized by large irregular follicles.
Answer B is incorrect because gastric cancer is not associated with follicular cholecystitis; instead, follicular cholecystitis has been reported in the setting of concurrent gastritis.
Comment Here
Reference: Follicular cholecystitis
Comment Here
Reference: Follicular cholecystitis