Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Hamasha R, Gonzalez RS. Cholesterol polyp. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/gallbladdercholesterolpolyp.html. Accessed January 7th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign polypoid variant of cholesterolosis
Essential features
- Polypoid variant of cholesterolosis
- Cauliflower-like architecture with core of foamy lipid laden macrophages
- Benign
Epidemiology
- Cholesterol polyps are the most common type of gallbladder polyp, constituting 60 - 90% of all polyps (N Am J Med Sci 2012;4:203)
- Slightly more common in women (F:M = 2.2:1)
- Associated with metabolic syndrome, high BMI and young age (40 - 50 years) (N Am J Med Sci 2012;4:203, Lipids Health Dis 2021;20:26, Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:467)
Sites
- Almost always arises in gallbladder
- Possible in the common bile duct but very rare
Pathophysiology
- Lipids deposit inside macrophages, resulting in the formation of a distinct polyp
- Etiologic mechanism is not clear
- Suggested etiologies include dyslipidemia, high bile viscosity and increased expression of mucin genes (Lipids Health Dis 2021;20:26, Int J Biol Markers 2016;31:e73, BMC Gastroenterol 2020;20:268, Gut Liver 2016;10:851)
Clinical features
- Most are asymptomatic
- May detach and behave like gallstones, causing biliary colic, obstruction, nausea, vomiting and rarely pancreatitis (N Am J Med Sci 2012;4:203)
Diagnosis
- Incidental finding during abdominal ultrasound or on histopathologic examination following cholecystectomy
- Definitive diagnosis requires microscopic examination (J Ultrasound 2021;24:131)
Laboratory
- Risk factors for cholesterol polyp formation are closely related to lipid metabolism (Lipids Health Dis 2021;20:26)
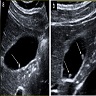
Radiology description
- Usually multiple, pedunculated, small (< 1 cm) (J Ultrasound 2021;24:131)
- Transabdominal ultrasound
- Homogeneous, slightly more hyperechoic than liver parenchyma
- Immobile / fixed despite positional change
- Posterior acoustic shadowing is absent
Prognostic factors
- Benign with no malignant potential (Lipids Health Dis 2021;20:26)
Case reports
- 39 year old man with acute cholecystitis (J Nippon Med Sch 2001;68:259)
- 53 year old woman with polyps in the distal common bile duct (Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e5374)
- 62 year old man with large cholesterol polyp clinically mimicking carcinoma (Abdom Imaging 2004;29:100)
Treatment
- Asymptomatic polyps diagnosed incidentally can be managed by clinical follow up
- If symptomatic, cholecystectomy
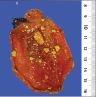
Gross description
- Yellow rounded polyps with smooth contours
- Up to 67% of cases are associated with cholesterolosis (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:467)
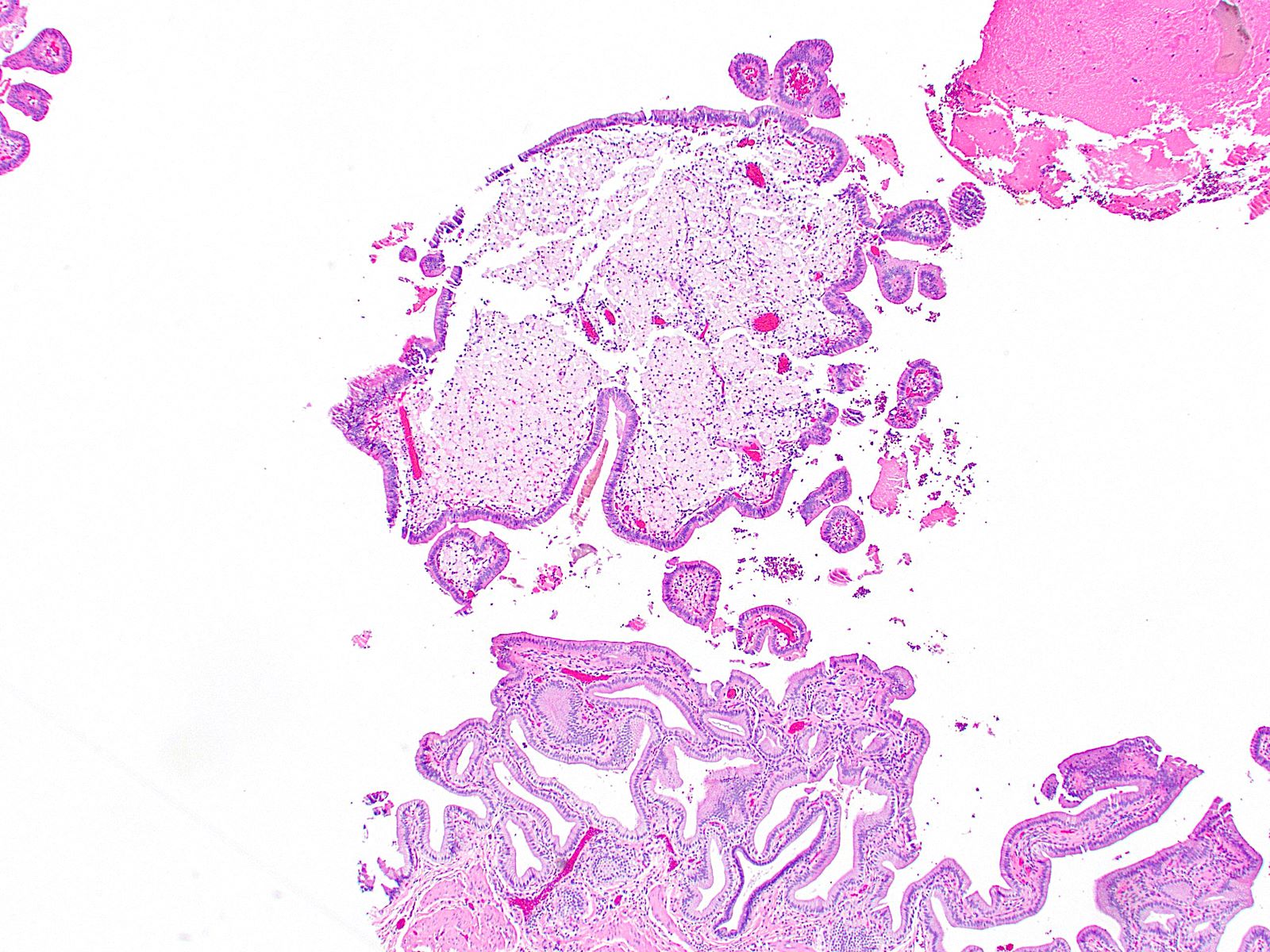
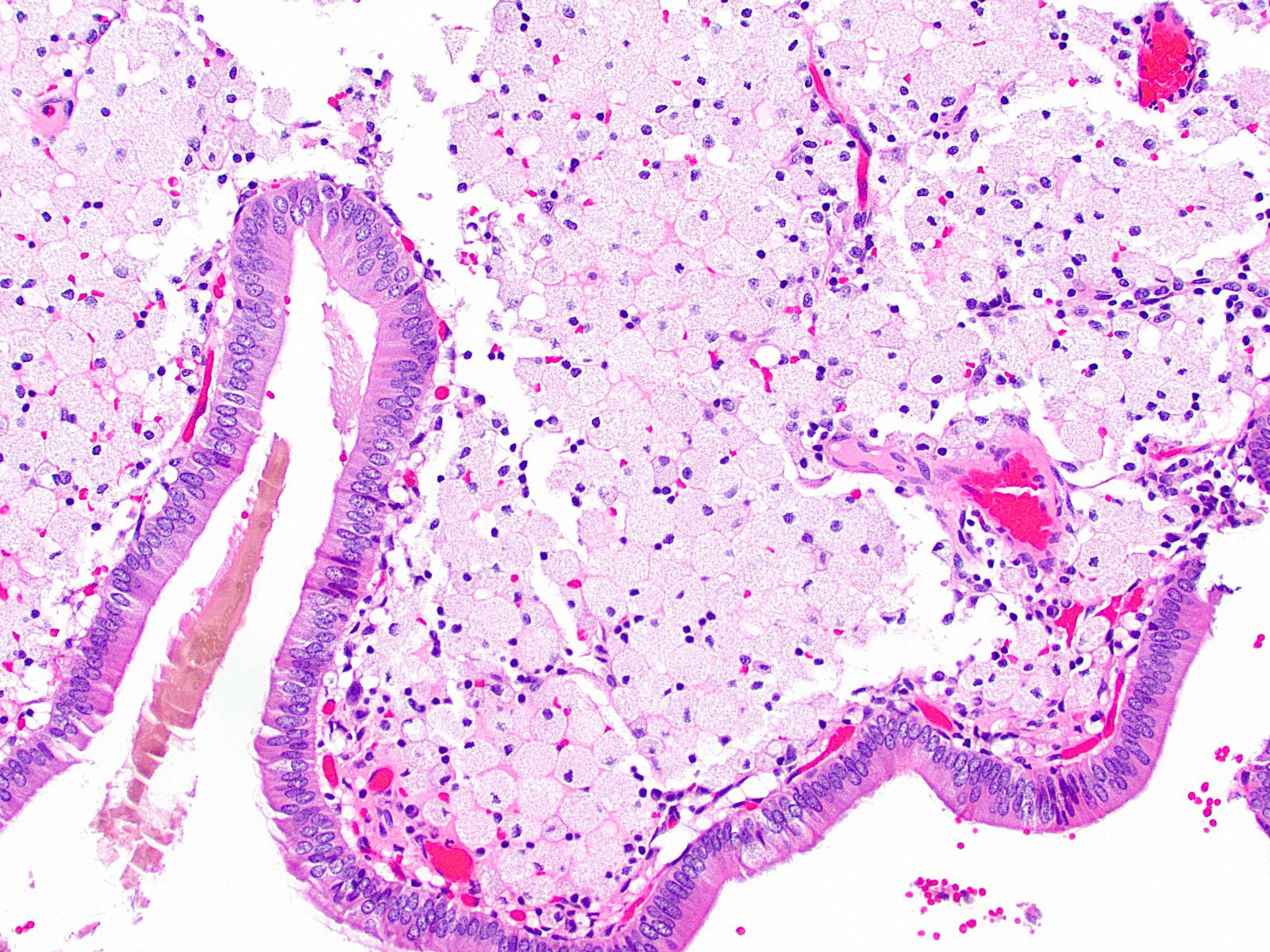
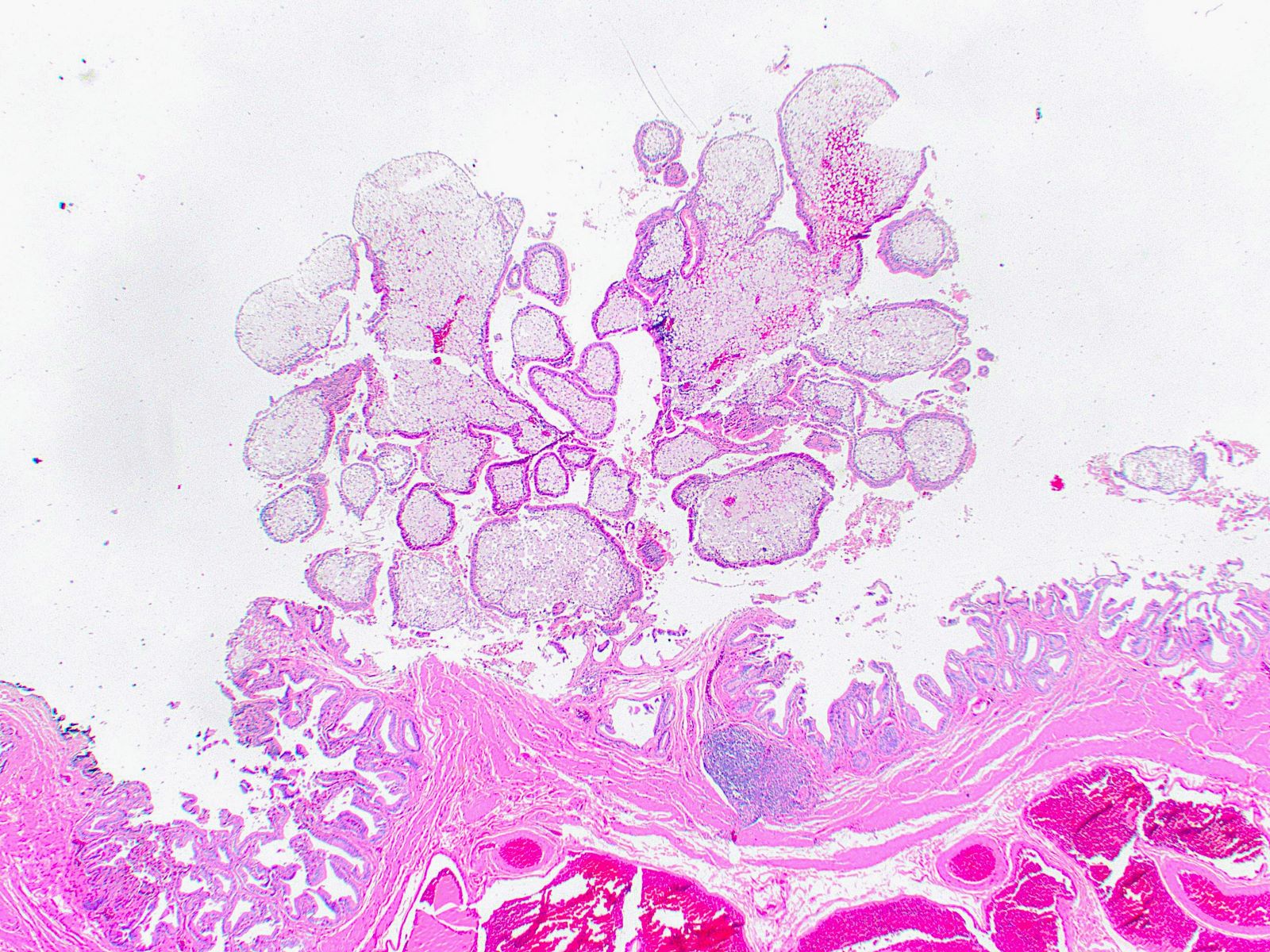
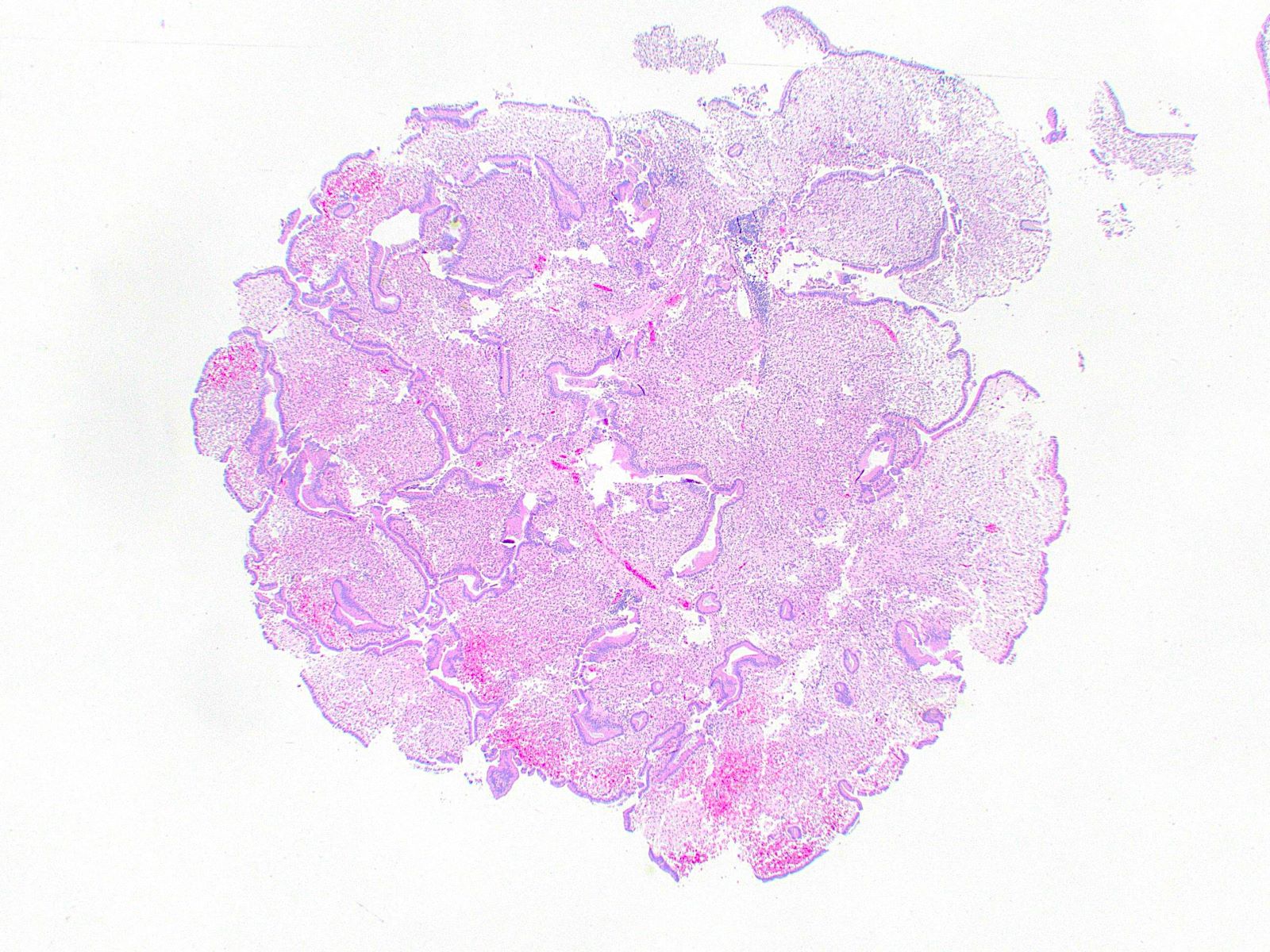
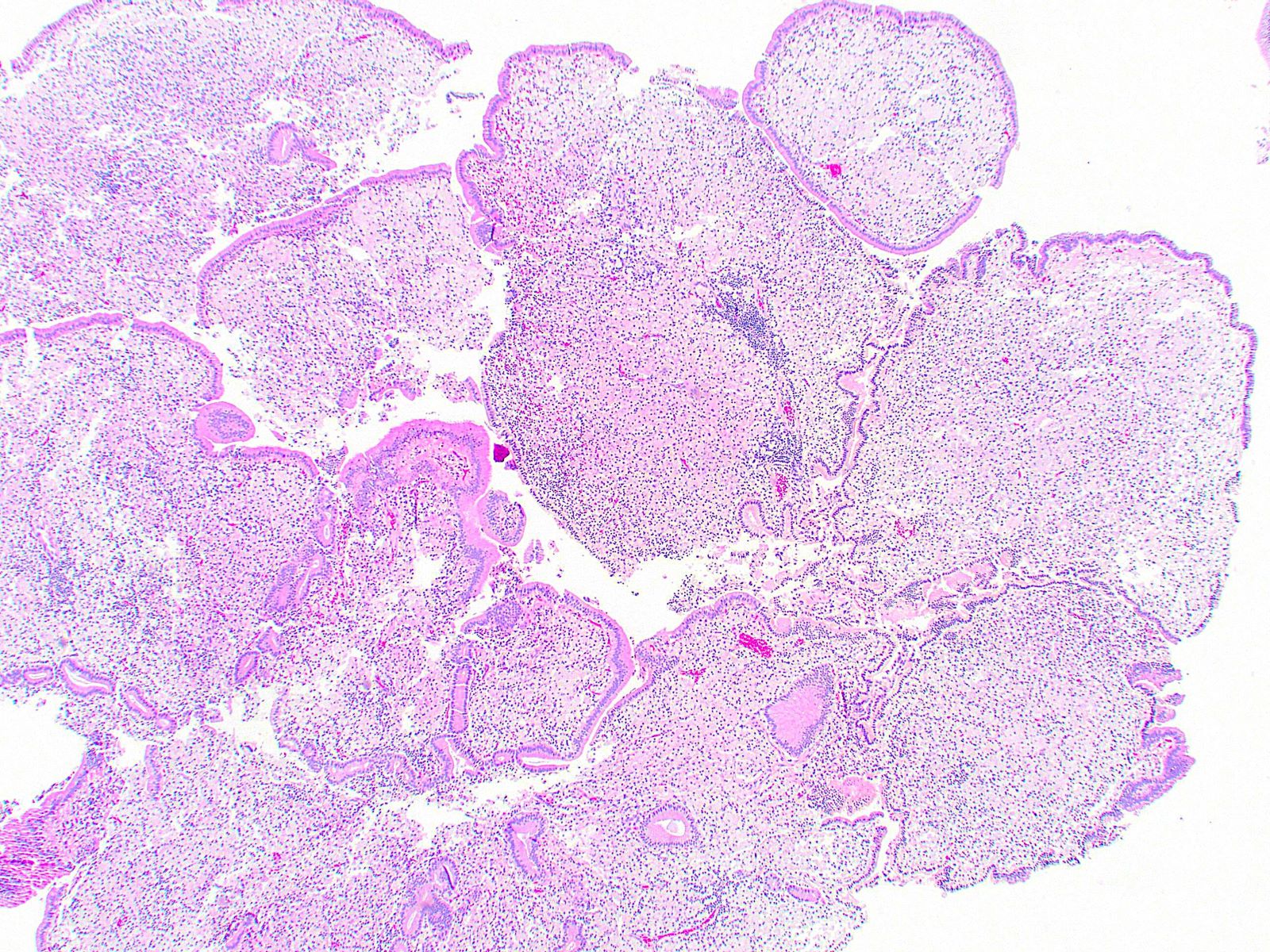
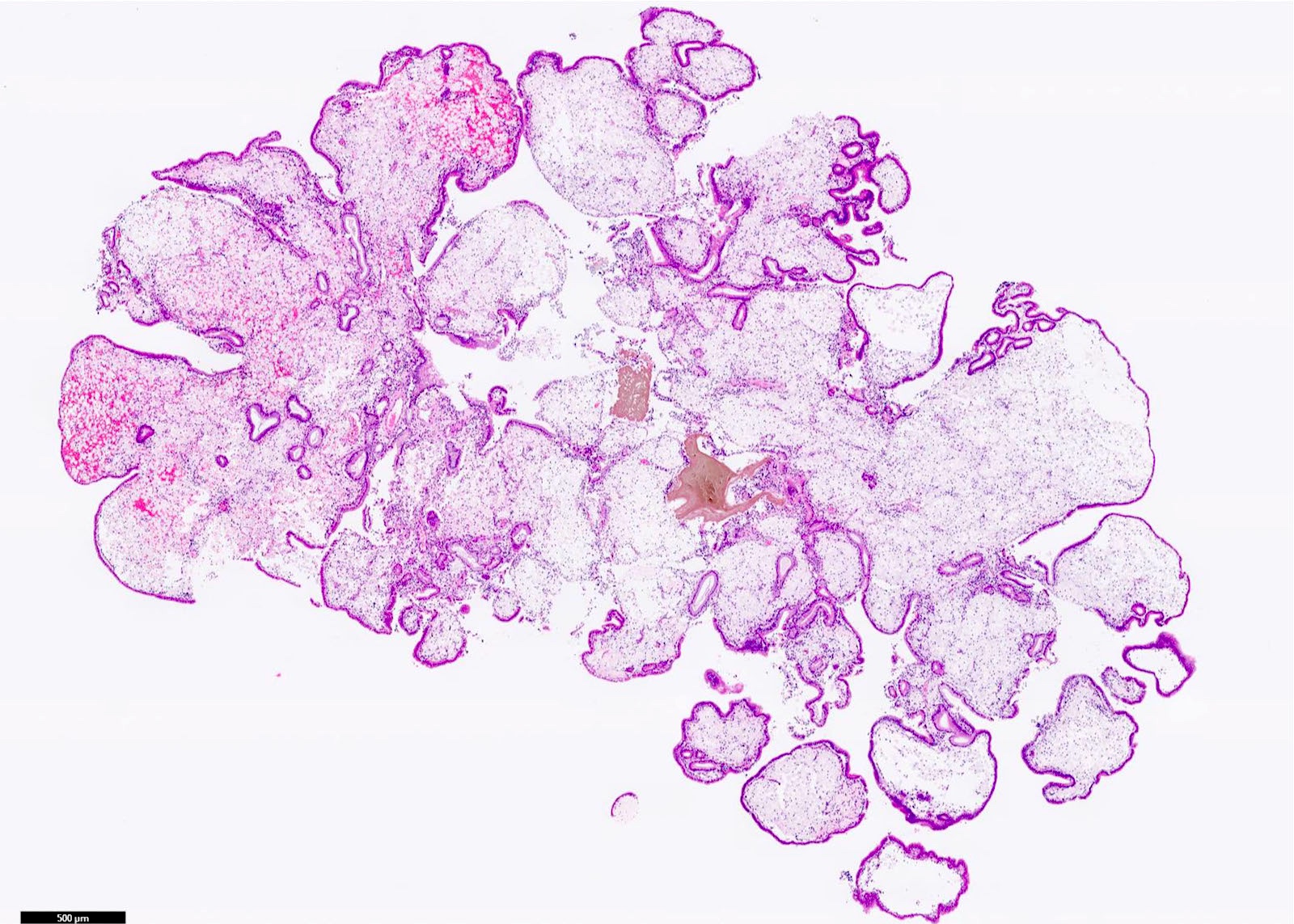
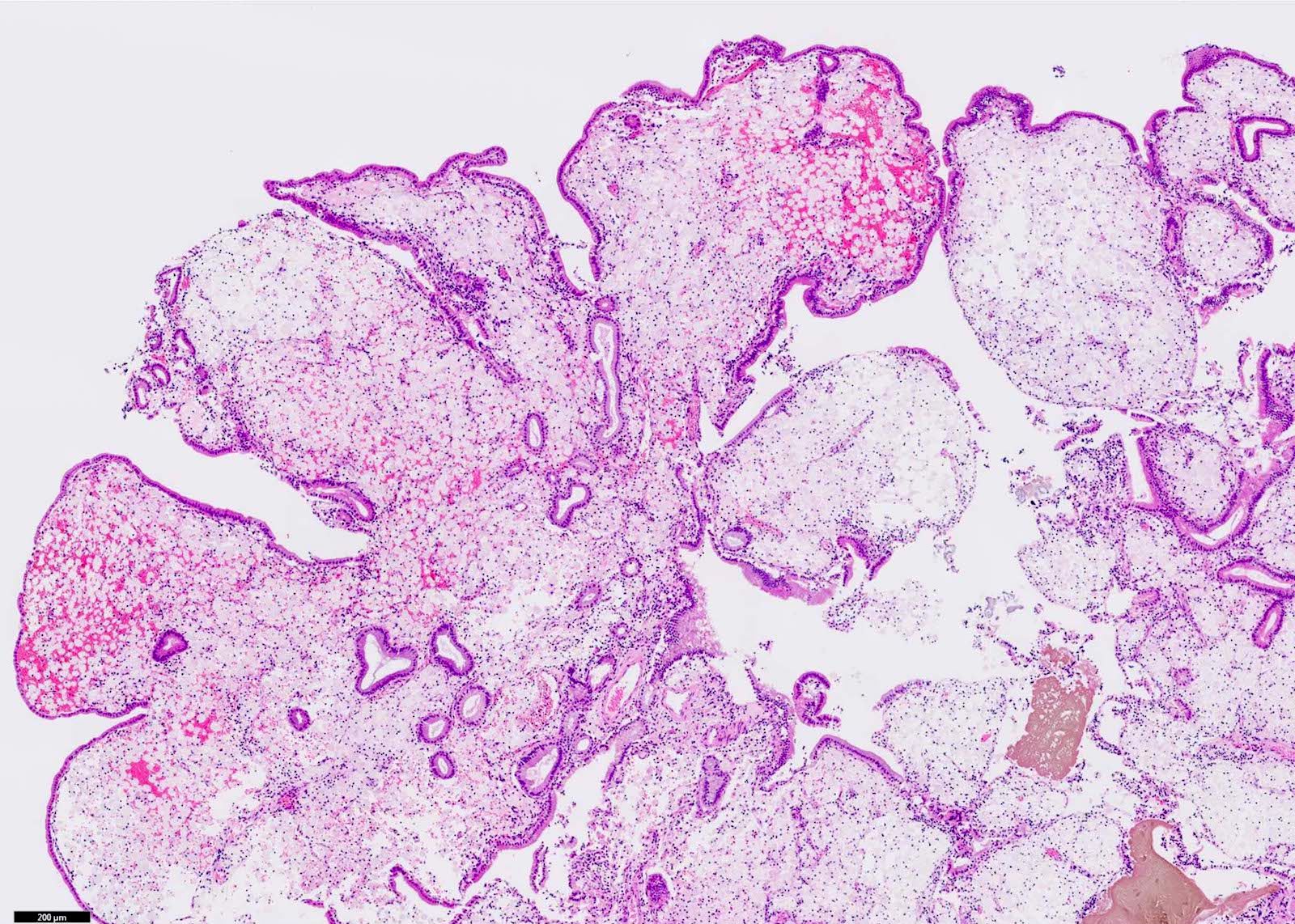
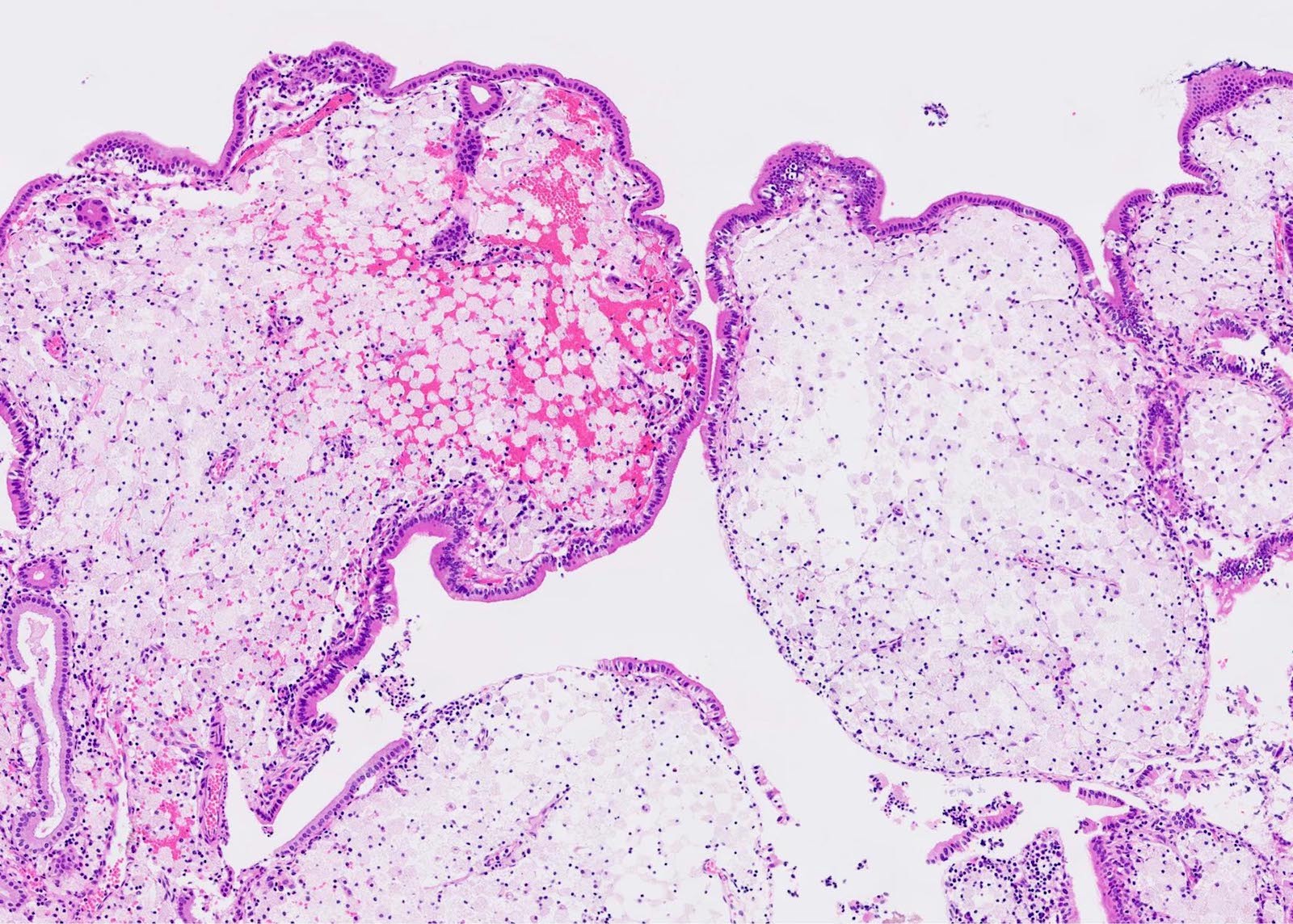
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Cauliflower-like architecture is a distinctive / pathognomonic feature present in all cases and is generally not seen in other polyps
- Connected to the gallbladder via very thin stalks; hence, they may detach from the surface
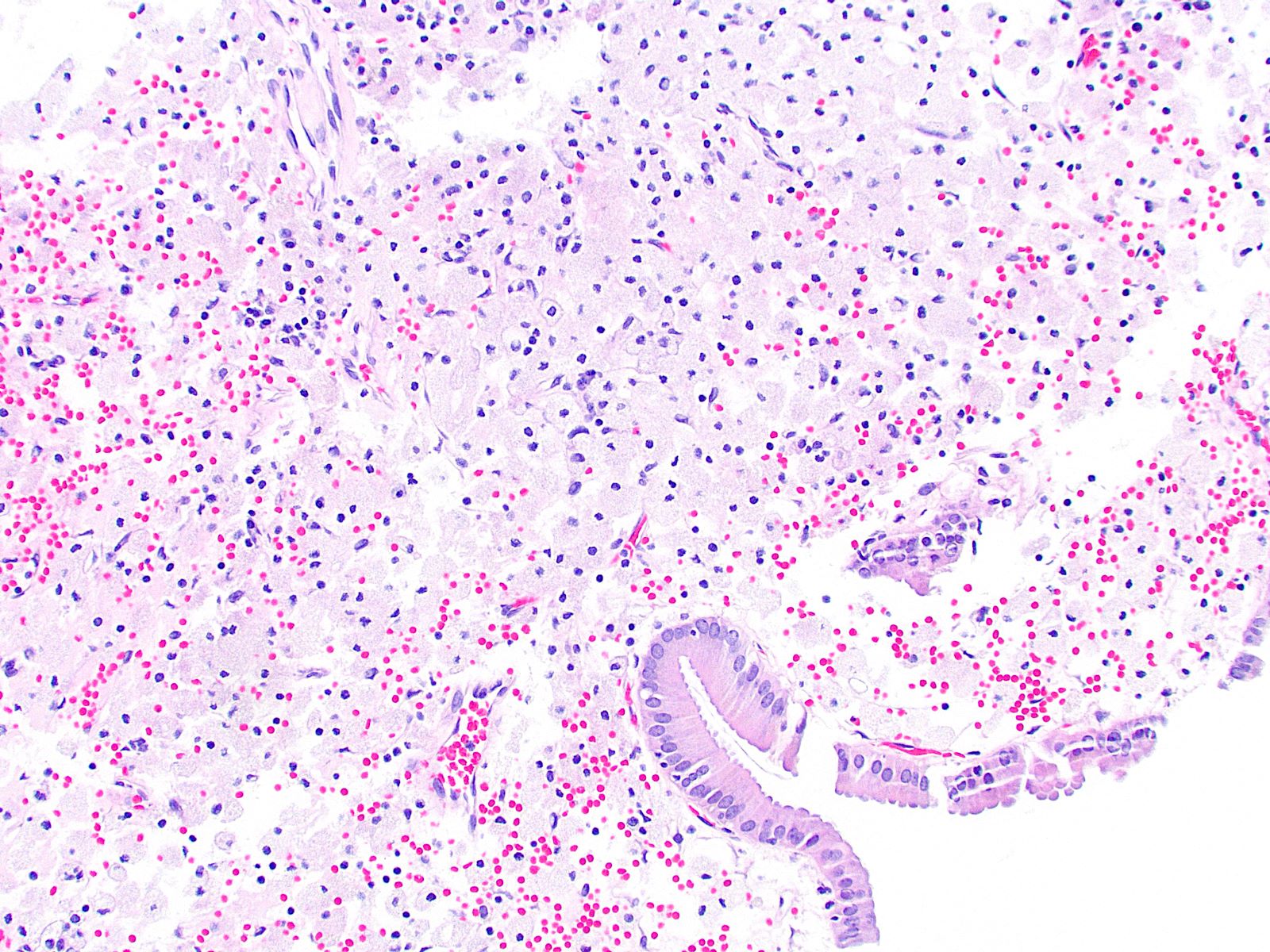
- Foamy lipid laden macrophages generally make up the wide and edematous core of the polyp
- 15% of cholesterol polyps may lack these lipid laden macrophages
- Lined by a single layer of normal gallbladder epithelium
- No epithelial elements in the core of the polyp and no dysplasia
- Cholesterol polyps can be found in gallbladders devoid of any significant chronic changes (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:467)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Gallbladder, cholecystectomy:
- Cholesterol polyps (see comment)
- Comment: Multiple yellowish round polyps are present in the body of the gallbladder, with the largest measuring 0.5 cm.
Differential diagnosis
- Cholesterolosis:
- Foamy lipid laden macrophages in the lamina propria and the villi (focal or diffuse)
- Affected areas do not have distinct polyp structures or cauliflower-like architecture
- Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis:
- Foamy lipid laden macrophages associated with inflammatory cells
- Intracholecystic papillary neoplasm:
- Resorption of the macrophages in a cholesterol polyp leaves behind edematous acellular stroma that might mimic neoplastic polyps (Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:467)
- True neoplastic polyps demonstrate dysplastic epithelium
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
B. Cholesterol polyp. Cholesterol polyps have cauliflower-like architecture and are made of foamy lipid laden macrophages (both features seen in the image provided above). Answer E is incorrect because the polyp lining epithelium is normal biliary epithelium unlike in intracholecystic papillary neoplasms. Answer D is incorrect because the body of the polyp does not show inflammatory cells as in inflammatory polyps. Answer A is incorrect because the body of the polyp does not show hyperplastic smooth muscle as in adenomyomatosis. Answer C is incorrect because the polyp does not show hyperplastic gallbladder epithelium with elongated villi as in hyperplastic polyps.
Comment Here
Reference: Cholesterol polyp
Comment Here
Reference: Cholesterol polyp
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is a gross feature of cholesterol polyps of the gallbladder?
- Most are > 1 cm
- Most are sessile
- The surface exhibits a gritty texture
- They are usually solitary
- They exhibit a yellowish color
Board review style answer #2
E. They exhibit a yellowish color. Answer C is incorrect because cholesterol polyps have a smooth yellowish surface. Answer B is incorrect because most are pedunculated. Answer A is incorrect because most are < 1 cm. Answer D is incorrect because multiple / multifocal cholesterol polyps often coexist.
Comment Here
Reference: Cholesterol polyp
Comment Here
Reference: Cholesterol polyp