Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Laboratory | Radiology description | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Gulwani H. Primary sclerosing cholangitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/gallbladderPSC.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Chronic cholestatic disorder of unknown origin (possibly autoimmune) involving entire biliary tract from ampulla of Vater to small intrahepatic bile ducts or gallbladder
- Much less common than secondary sclerosing cholangitis
Clinical features
- Rule of 70s: 70% men, 70% have chronic inflammatory bowel disease (particularly ulcerative colitis which is usually detected first; only 4% with ulcerative colitis have primary sclerosing cholangitis, which is unaffected by colectomy), 70% younger than age 45
- Also associated with chronic pancreatitis (15 - 25%), Riedel thyroiditis, retroperitoneal and mediastinal fibrosis, orbital pseudotumor, Sjögren syndrome, angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy
- End stage disease is associated with hyperplasia of glands of extrahepatic bile ducts, with low incidence of dysplasia and adenocarcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:349)
- Bile ducts in PSC show two distinct pathways of dysplasia-carcinoma, based on differences in cell morphology, growth patterns, immunophenotypes and grade of malignancy (Histopathology 2011;59:1100)
- Symptoms: fatigue, jaundice, pruritis
Complications:
- Biliary cirrhosis and liver failure in all cases with median survival 9 - 12 years
- Cholangiocarcinoma (10 - 43%), colon carcinoma
Staging:
- Inflammation without expansion of portal tracts or piecemeal necrosis
- Piecemeal necrosis or fibrosis without bridging
- Bridging necrosis or fibrosis
- Cirrhosis
Laboratory
- Elevated serum alkaline phosphatase, IgM, IgG
- Variable bilirubin
- May be pANCA positive
Radiology description
- Xray: beading of barium column in cholangiogram due to irregular strictures and dilations of affected bile ducts
Case reports
- 17 year old boy (Diagn Cytopathol 2012;40:337)
Treatment
- Liver transplant (Hum Pathol 2003;34:1127, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:907) since no effective medical therapy
Gross description
- Periductal portal tract fibrosis, segmental stenosis of extrahepatic and intrahepatic bile ducts
Microscopic (histologic) description
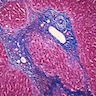
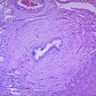
- Fibrosing cholangitis of intra and extrahepatic bile ducts with lymphocytic infiltration
- Progressive atrophy of bile duct epithelium and obliteration of the lumen, diffuse bile ductular proliferation
- "Onion skin" fibrosis around affected ducts, which later disappear, leaving cord-like fibrous scar
- Remaining ducts are ectatic and inflamed
- Mild to florid hyperplasia often noted
- Recurrence after transplant exhibits bile duct structuring and nonspecific autoimmune hepatitis with variable fibrosis
- Variable portal eosinophils
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Sclerosing, well differentiated adenocarcinoma