Cite this page: Pernick N. Orbital inflammation. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/eyeorbitinflammatorypseudo.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Inflammatory pseudotumor
Definition / general
Case reports
Treatment
Gross description
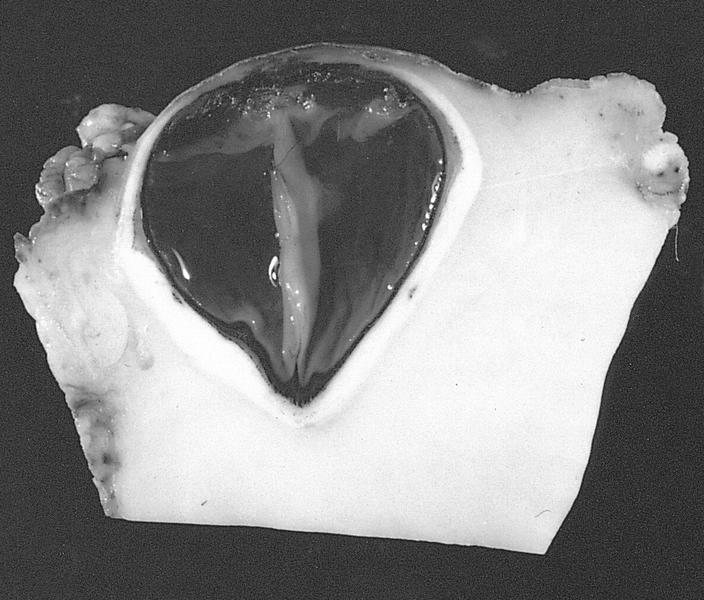
Gross images
AFIP images
Microscopic (histologic) description
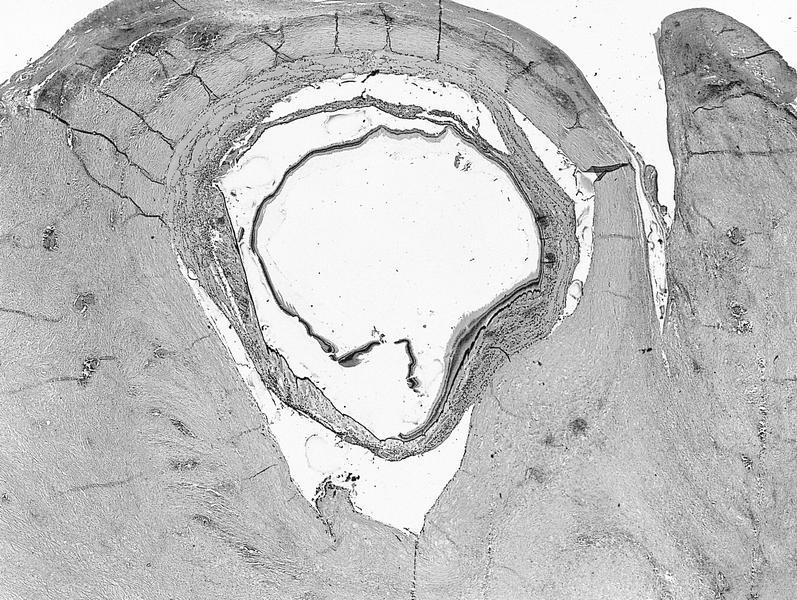
Whole mount images
AFIP images
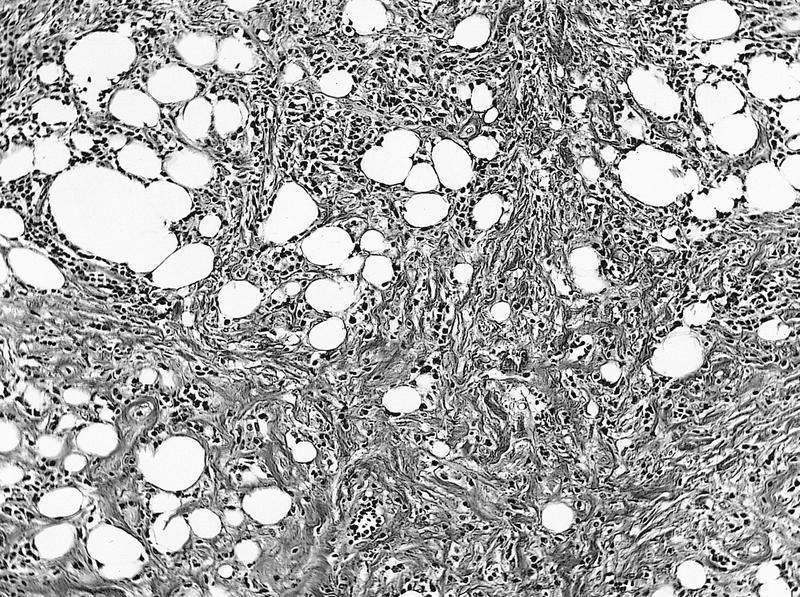
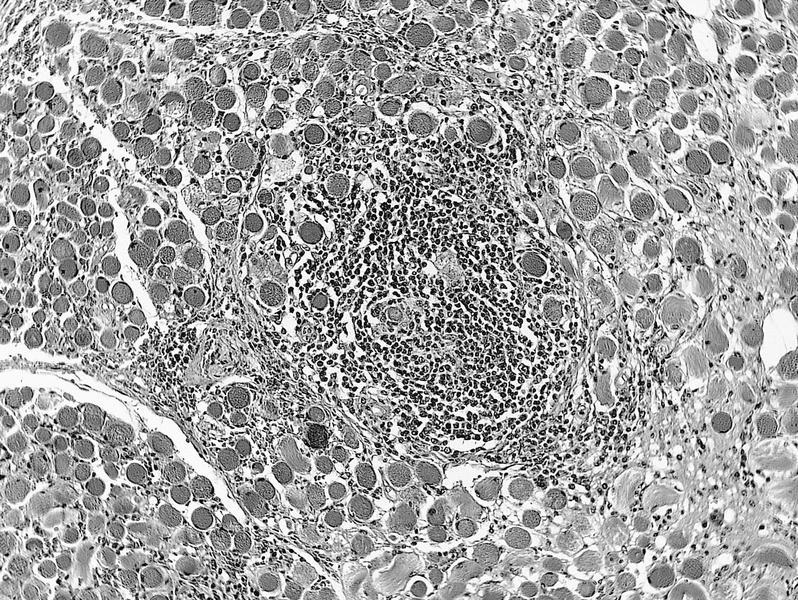
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images
Positive stains
Differential diagnosis
- May not be a specific disease process, but due to various causes (paranasal sinus tumors, Rosai-Dorfman disease, inflammatory fibrosclerosis, dysthyroid ophthalmopathy, cholesterol or keratin granulomas, traumatic fat necrosis, prior hemorrhage or abscess)
- More common than infectious granulomas
- Usually ages 20 - 49 years with good health and sudden onset of exophthalmos with variable lid or conjunctival edema
Case reports
- 50 year old man with intraocular inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor with ALK overexpression (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:e5)
Treatment
- Steroids (alleviate signs and symptoms)
- Excision
Gross description
- Indurated orbital mass, often surrounding optic nerve and enveloping extraocular muscles
Gross images
AFIP images
Microscopic (histologic) description
- General:
- Edematous tissue with excessive production of ground substance, chronic inflammatory cells, vascular proliferation and hyperplastic connective tissue
- May have periphlebitis with tissue eosinophilia
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor:
- Combinations of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in background of plasma cells and other inflammatory cells
- Rosai-Dorfman related:
- Large histiocytes, some with lymphocytophagocytosis, lymphocytes and plasma cells, often with prominent fibrosis
Whole mount images
AFIP images
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images
Positive stains
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: smooth muscle actin, variable ALK
Differential diagnosis
Idiopathic sclerosing inflammation
Definition / general
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Insidious, chronic and progressive fibrosing process
- Damages orbital structures by entrapment and mass effect
- May have cell mediated pathogenesis, similar to retroperitoneal fibrosis (Mod Pathol 1993;6:581)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Desmoplasia, sparse lymphocytes (usually T cells), histiocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils, eosinophils
Other
[Pending]